Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Sci Rev PDF
Gen Sci Rev PDF
Uploaded by
Maddie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pages- The scientific method involves making observations, stating a problem, forming a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and drawing a conclusion.
- There are two main types of reasoning used in science: inductive reasoning which makes conclusions based on repeated observations, and deductive reasoning which makes conclusions based on established principles.
- Key steps in the scientific method include developing a controlled experimental setup with independent, dependent, and controlled variables to test hypotheses.
Original Description:
Original Title
GEN SCI REV.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document- The scientific method involves making observations, stating a problem, forming a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and drawing a conclusion.
- There are two main types of reasoning used in science: inductive reasoning which makes conclusions based on repeated observations, and deductive reasoning which makes conclusions based on established principles.
- Key steps in the scientific method include developing a controlled experimental setup with independent, dependent, and controlled variables to test hypotheses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesGen Sci Rev PDF
Gen Sci Rev PDF
Uploaded by
Maddie- The scientific method involves making observations, stating a problem, forming a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and drawing a conclusion.
- There are two main types of reasoning used in science: inductive reasoning which makes conclusions based on repeated observations, and deductive reasoning which makes conclusions based on established principles.
- Key steps in the scientific method include developing a controlled experimental setup with independent, dependent, and controlled variables to test hypotheses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
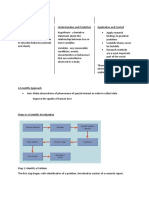
- control and experimental set ups
GEN SCIENCE must be used for comparison of
results
BRANCHES OF SCIENCE - independent varirables - factors
that are not affected by other
a. Physical Sciences variables; usually predetermined
- study of nature and properties of - dependent variables - factors that
the universe and all its contents are affected by other variables
Astronomy - controlled variables - factors that
Chemistry are kept the same for all set ups
Geology - manipulated variables - factor that
Meteorology is different in each set up; usually
Physics the variable under study
b. Biological Sciences 5. Conclusion
- study of living organisms and life - results may be analyzed for validity
itself - final answer to the problem
Botany - should always be true based on
Sociology analysis
c. Social Sciences
- study of humans as individuals, the KINDS OF REASONING
human society and human a. Inductive Reasoning - a
interactions conclusion is made based on
Psychology repeated observations ; basis of
Sociology most research conclusions
b. Deductive Reasoning - a
SCIENTIFIC METHOD conclusion is made based on
established principles and
1. Making Observations concepts; basis of most research
- make an observatio using one’s conclusions
senses
2. Stating the problem MEASUREMENTS AND QUANTITIES
- must be clear and specific
- must be measurable and have an Scientific Notation
atainable solution - a shorthand representation of
- usually stated in question form numbers using powers of 10
3. Forming the hypothesis STANDARD TO SCIENTIFIC
- Hypothesis is a tentative solution or
a prediction of the outcome FUNDAMENTAL QUANTITIES
- must be a clear and specific - physical quantities that can be
statement determined using measuring
4. Testing the Hypothesis devices
- implement the hypothesis under Length - distance between two points
carefully considered conditions
Mass - amount of matter present in a
substance
Time - temporal duration between two
events
Temperature - degree of heat present
in a substance or object
Amount of substance - measure the
size of an ensemble of entities
Electric current - the rate at
whichcharge flows through a surface
Luminous Intensity - rate of flow of
light
Measurement - standard unit to
express the size, amount, or degree of
something
Systems of Measurement:
a. English System - evolved from
medieval systems of measurement
b. Metric System - based on
multiples of 10, except for time
GIGA 9
MEGA 6
KILO 3
HECTO 2
DEKA 1
DECI -1
CENTI -2
MILLI -3
MICRO -6
NANO -9
^10 raise to ano haahhaha
You might also like
- MicroStation Training Manual 2D Level 1Document296 pagesMicroStation Training Manual 2D Level 1Tarunbir Singh50% (2)
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 2nd Grade Ccss Math Rubric FinalDocument10 pages2nd Grade Ccss Math Rubric Finalapi-321011860100% (1)
- Nat Sci 1Document16 pagesNat Sci 1Angel ZairNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry NotesAngelo Kyle AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Biology 1.1the Study of BiologyDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Biology 1.1the Study of BiologyCikguAgnesNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemistry?: Chemistry Form 4 Chapter One: Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesWhat Is Chemistry?: Chemistry Form 4 Chapter One: Introduction To ChemistryThilaga LaxmyNo ratings yet
- Rma Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesRma Midterm ReviewerKryzza MaeNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (4551) : Paper 1 (50 Objectives) - 50 MDocument24 pagesBIOLOGY (4551) : Paper 1 (50 Objectives) - 50 Mwienna1987No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Practical Research 2Document3 pagesReviewer in Practical Research 2Elmo Vincent Bernardo MurosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ResearchDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Basic ResearchG19 Domino, MarionNo ratings yet
- TreatmentDocument4 pagesTreatmentJaspher CarpioNo ratings yet
- By: Jelord B. RosalitaDocument16 pagesBy: Jelord B. Rosalitajusten camingawanNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument7 pagesResearch ReviewerETHAN SIGARILIONo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument2 pagesResearch ReviewerJoseline SisonNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Characteristics of ResearchDocument20 pagesMeaning and Characteristics of ResearchHANSEL HOPE A PEREZNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and Research 1Document39 pagesNature of Inquiry and Research 1Euro Anthony SayonNo ratings yet
- STS READINGS No. 2Document4 pagesSTS READINGS No. 2Maria Desiree AgustinNo ratings yet
- PR & Fabm2Document2 pagesPR & Fabm27xnc4st2g8No ratings yet
- Bio 181 NotesDocument34 pagesBio 181 NotesGale AustriaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewerIsabella Sofia AgitoNo ratings yet
- Cahpter 2 OpsommingsDocument20 pagesCahpter 2 OpsommingsAnke PrinslooNo ratings yet
- Research Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Research Notes Summarized For MidtermsDocument5 pagesResearch Notes Summarized For Midterms김나연No ratings yet
- Carried Out When We Wish To UnderstandDocument1 pageCarried Out When We Wish To UnderstandClark Vince Caezar AfableNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodsDocument4 pagesScientific MethodsmisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- PR2 HeDocument12 pagesPR2 HeJay-r MatibagNo ratings yet
- GST - 108 - Scientific - Methodology - Man-And - Energy - Effects of Air Pollution - 16 - 09 - 202bDocument21 pagesGST - 108 - Scientific - Methodology - Man-And - Energy - Effects of Air Pollution - 16 - 09 - 202bcjstyles456No ratings yet
- KDocument8 pagesKSophia Shannon D. DeiparineNo ratings yet
- PR ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR ReviewerVictoria Lourdes Mesias LoquinteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer RRRRRRRR RawrDocument7 pagesReviewer RRRRRRRR RawrClarisse FranciscoNo ratings yet
- SHS - Research in Daily Life 2 - Review - G12 PDFDocument5 pagesSHS - Research in Daily Life 2 - Review - G12 PDFJair Valdez - ICT Programming 12No ratings yet
- Module 1 Doing Scientific InvestigationDocument4 pagesModule 1 Doing Scientific InvestigationLJ Valdez91% (11)
- Introduction To Educational Research (Res 1)Document21 pagesIntroduction To Educational Research (Res 1)Cherry Lynn RoloyanNo ratings yet
- Research 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchAbie Joyce RemoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1wienna1987No ratings yet
- Scientific Method On ResearchDocument2 pagesScientific Method On Researchsophia chuaNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument5 pagesZoologyrjdc972No ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 2Document5 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2Mike Reyes (XxMKExX)No ratings yet
- Week 2 - MechanicsDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- IOP Pratical 1 - in INTRODUCTION TO EXPERIMENTAL PSYCHOLOGYDocument3 pagesIOP Pratical 1 - in INTRODUCTION TO EXPERIMENTAL PSYCHOLOGYdevyanipant340No ratings yet
- Research: Scientific Methods of Research Importance of ResearchDocument4 pagesResearch: Scientific Methods of Research Importance of ResearchSai RillNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument50 pagesScience ReviewerDon KeyNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Vivekananda 2015 Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Document32 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Vivekananda 2015 Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Nurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionB.simhachalamNo ratings yet
- Overview of "General Biology"Document9 pagesOverview of "General Biology"B.simhachalamNo ratings yet
- Educators Curriculum: 1. Prognostic ResearchDocument8 pagesEducators Curriculum: 1. Prognostic ResearchJamela RoweNo ratings yet
- Science 20 Process SkillsDocument11 pagesScience 20 Process SkillsticoninxNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 Methods of Enquiry in Psychology Notes For Class XIDocument11 pagesCh. 2 Methods of Enquiry in Psychology Notes For Class XISaachee SamaddarNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Document33 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Abdullah Yusof AzzamNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH ReviewerDocument4 pagesRESEARCH ReviewerCARDO SegumaNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument3 pagesResearch ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Raja Perempuan, Ipoh Scheme of Work Science (Form 4) 2010Document33 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Raja Perempuan, Ipoh Scheme of Work Science (Form 4) 2010magisperanNo ratings yet
- 8Document8 pages8Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Research Comes From A Two Syllables "Re" and "Search". "Re" Is A PrefixDocument31 pagesResearch Comes From A Two Syllables "Re" and "Search". "Re" Is A PrefixMiggy PascualNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Definition of Terms: NameDocument12 pagesAssignment: Definition of Terms: NameACATALEPSYEPIPHANY WanderlustNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY f4 Chapter1Document21 pagesBIOLOGY f4 Chapter1Kar KuanNo ratings yet
- Science For Grade 7 (1ST Quarter Module)Document90 pagesScience For Grade 7 (1ST Quarter Module)Norigen Itang100% (2)
- ResearchDocument15 pagesResearchGee Banao BungotNo ratings yet
- 2023 Scientific Method - Skills BookletDocument18 pages2023 Scientific Method - Skills BookletenochscribdNo ratings yet
- Caridad, Thrizha Veronica M. - RESEARCH METHODS 1.1 WORKSHEET BEEDDocument7 pagesCaridad, Thrizha Veronica M. - RESEARCH METHODS 1.1 WORKSHEET BEEDThrizha Veron NicaNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Engineering: Introduction To Engineering CalculationsDocument38 pagesBioprocess Engineering: Introduction To Engineering CalculationssaveenaNo ratings yet
- Measuring LengthDocument64 pagesMeasuring Lengthramilyn canoneoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment: in Physics 1Document9 pagesLaboratory Experiment: in Physics 1Charles ContridasNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument33 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryELVIS BoradNo ratings yet
- Unitratesandconversions Skills Practice CL SeDocument7 pagesUnitratesandconversions Skills Practice CL Seapi-2618943550% (1)
- f1 Chapter 1 Introduction To Scientific InvestigationDocument20 pagesf1 Chapter 1 Introduction To Scientific InvestigationNur dini FauziNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Statik Dan DinamikDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 1 Statik Dan DinamikLogarithemNo ratings yet
- D1422-D1422M 13 (Reapproved 2020)Document5 pagesD1422-D1422M 13 (Reapproved 2020)Doulat Ram100% (1)
- Additional Tutorial 1Document3 pagesAdditional Tutorial 1lllNo ratings yet
- Jurong Junior College Physics Department Tutorial: Measurements (Solutions)Document4 pagesJurong Junior College Physics Department Tutorial: Measurements (Solutions)Shaikh Mohammed EhsenNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mechanical EngineeringDocument150 pagesFundamental Mechanical Engineeringmariza razuri cordovaNo ratings yet
- RIO HONDO DUPA FORM Revised 3Document110 pagesRIO HONDO DUPA FORM Revised 3Bert EngNo ratings yet
- Physics Summary Class9Document18 pagesPhysics Summary Class9Ivan dragoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory ActivityDocument6 pagesChemistry Laboratory ActivityRowel AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- DA PAM 415 28 Guide To Army Real Property Category CodesDocument483 pagesDA PAM 415 28 Guide To Army Real Property Category CodesAntonio C. Keith100% (1)
- Module 01 Solutions ChemistryDocument29 pagesModule 01 Solutions ChemistryLuisa Jane De LunaNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Conversion of Units of MeasurementDocument28 pagesMeasurement: Conversion of Units of MeasurementRichel Borres MangmangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Fluid Properties: Second, 2010Document48 pagesChapter 1: Basic Concepts and Fluid Properties: Second, 2010beam84No ratings yet
- Module 6A Process Costing WeightedDocument3 pagesModule 6A Process Costing WeightedSky SoronoiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1Document32 pagesFluid Mechanics 1essum belaNo ratings yet
- HBSC4103 Topic 1Document41 pagesHBSC4103 Topic 1atun28No ratings yet
- Physical Science: Tables & Formulas: SI Base UnitsDocument8 pagesPhysical Science: Tables & Formulas: SI Base UnitsNiño AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lesson 1 PDFDocument30 pagesThermodynamics Lesson 1 PDFJerico CruelNo ratings yet
- NUST Fluid Mechanics Module1Document41 pagesNUST Fluid Mechanics Module1Insta TecchNo ratings yet
- Planck Units: Natural Units and The Key Equations in PhysicsDocument38 pagesPlanck Units: Natural Units and The Key Equations in PhysicsJagjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Bitsat ProvideDocument22 pagesBitsat ProvideRajesh DheliaNo ratings yet
- TLE - HE (Dressmaking) 78 - Q1 - CLAS3 - Performing Simple Calculations - RHEA ROMERODocument10 pagesTLE - HE (Dressmaking) 78 - Q1 - CLAS3 - Performing Simple Calculations - RHEA ROMEROMelady TurlaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AssignmentDocument7 pagesInstrumentation AssignmentBereket Bersha OrkaidoNo ratings yet