Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toxic Shock Syndrome PDF
Toxic Shock Syndrome PDF
Uploaded by
mariam ibrahim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageStreptococcal toxic shock syndrome involves isolation of group A streptococcus, hypotension, and two other symptoms such as renal impairment. Treatment involves intravenous benzylpenicillin and either clindamycin or lincomycin. For penicillin-allergic patients, cephalothin or cephazolin can be substituted. Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome resembles streptococcal toxic shock and is toxin-mediated; treatment involves intravenous flucloxacillin or cephalosporins for penicillin-allergic patients. Intravenous immunoglobulin may be considered for toxic shock syndrome with expert advice.
Original Description:
Original Title
Toxic Shock Syndrome.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStreptococcal toxic shock syndrome involves isolation of group A streptococcus, hypotension, and two other symptoms such as renal impairment. Treatment involves intravenous benzylpenicillin and either clindamycin or lincomycin. For penicillin-allergic patients, cephalothin or cephazolin can be substituted. Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome resembles streptococcal toxic shock and is toxin-mediated; treatment involves intravenous flucloxacillin or cephalosporins for penicillin-allergic patients. Intravenous immunoglobulin may be considered for toxic shock syndrome with expert advice.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageToxic Shock Syndrome PDF
Toxic Shock Syndrome PDF
Uploaded by
mariam ibrahimStreptococcal toxic shock syndrome involves isolation of group A streptococcus, hypotension, and two other symptoms such as renal impairment. Treatment involves intravenous benzylpenicillin and either clindamycin or lincomycin. For penicillin-allergic patients, cephalothin or cephazolin can be substituted. Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome resembles streptococcal toxic shock and is toxin-mediated; treatment involves intravenous flucloxacillin or cephalosporins for penicillin-allergic patients. Intravenous immunoglobulin may be considered for toxic shock syndrome with expert advice.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
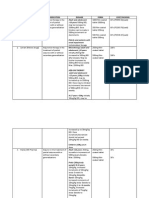
- Streptococcal toxic shock is the isolation of a group A streptococcus (Streptococcus
pyogenes), hypotension and 2 of the following: renal impairment, coagulopathy, liver
involvement, adult respiratory distress syndrome, generalised rash or soft tissue necrosis.
- Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome is a toxin-mediated disease which
Use:
may appear from an apparently minor infection. It resembles streptococcal
- benzylpenicillin 1.8 g (child: 45 mg/kg up to 1.8 g) IV, 4-hourly
toxic shock syndrome. Aggressive resuscitation and treatment of the source
PLUS EITHER
are important aspects of therapy. Use:
clindamycin 600 mg (child: 15 mg/kg up to 600 mg) IV, 8-hourly streptococcal staphylococcal
toxic di/flucloxacillin 2 g (child: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV, 6-hourly.
OR
lincomycin 600 mg (child: 15 mg/kg up to 600 mg) IV, 8-hourly. toxic shock toxic shock - The addition of clindamycin may stop toxin production although there is no
syndrome shock syndrome clinical evidence to support this
For patients hypersensitive to penicillin (excluding immediate hypersensitivity), substitute
syndrome - For patients hypersensitive to penicillin (excluding immediate hypersensitivity), use:
for benzylpenicillin:
cephalothin 2 g (child: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV, 6-hourly
cephalothin 2 g (child: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV, 6-hourly
OR
OR
cephazolin 2 g (child: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV, 8-hourly.
cephazolin 2 g (child: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV, 8-hourly.
- In toxic shock syndrome, consider the use of IV immunoglobulin after expert advice:
normal immunoglobulin 0.4 to 2 g/kg IV, for 1 or 2 doses during the first 72 hours.
You might also like
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFHuang Hasjim33% (9)
- Paediatric Dosage of Some DrugsDocument46 pagesPaediatric Dosage of Some DrugsS S LNo ratings yet
- YOUNG MIN LEE CASE STUDY Update 2Document7 pagesYOUNG MIN LEE CASE STUDY Update 2E.R.ONo ratings yet
- Paediatric Dosage of Some Drugs-1Document45 pagesPaediatric Dosage of Some Drugs-1JaneNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Finished 2Document6 pagesConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- Antimicrobial Drugs FormularyDocument95 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs FormularymahamoudNo ratings yet
- D-6-12 Sanaani, Mohammad Khaisar H. August 9, 2020: Bacterial VaginosisDocument4 pagesD-6-12 Sanaani, Mohammad Khaisar H. August 9, 2020: Bacterial VaginosisKenMNo ratings yet
- Measles PHIDSPILDocument5 pagesMeasles PHIDSPILriczen mae vilaNo ratings yet
- Theraputic Agent in NeonateDocument7 pagesTheraputic Agent in Neonateد. محمد فريد الغنامNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument13 pagesAntibioticsJOrgeNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial PDFDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial PDFvhonNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Antibiotic DosingDocument7 pagesPediatric Antibiotic DosingAnonymous mm1yTelKNo ratings yet
- Homeo Drug CompenDocument6 pagesHomeo Drug CompenSittie Nadia MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument15 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsAnonymous elSqPhzKNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Beta Laktam: Apt. Ika Mustikaningtias, M.SCDocument26 pagesAntibiotik Beta Laktam: Apt. Ika Mustikaningtias, M.SCdita novia maharaniNo ratings yet
- Oxaciline PDFDocument7 pagesOxaciline PDFamatoryfictionliteraNo ratings yet
- Modul PneumoniaDocument16 pagesModul Pneumoniaandamar0290No ratings yet
- Degracia, John Noeh D. Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDegracia, John Noeh D. Drug StudyLenie DegraciaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Fever Cough Breathlessnes S DR J Pap/ich/ GMC Kottayam/19723Document4 pagesPneumonia: Fever Cough Breathlessnes S DR J Pap/ich/ GMC Kottayam/19723Firdouse ShajiNo ratings yet
- Terapi AnakDocument10 pagesTerapi AnakIka KrastanayaNo ratings yet
- Route/Dosage: Concentration: Not To Exceed 10 Mg/ml. Do NotDocument2 pagesRoute/Dosage: Concentration: Not To Exceed 10 Mg/ml. Do NotMaria MargaritaNo ratings yet
- Common Goat Medications and "Easy To Understand" Dosages: WormersDocument2 pagesCommon Goat Medications and "Easy To Understand" Dosages: WormersCrosley NasmNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Regimens For The Treatment of Streptococcus Anginosus GDocument2 pagesAntimicrobial Regimens For The Treatment of Streptococcus Anginosus GKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Quick Ref Guide MNGT Antivenom Reactions SGB2021 Ver. 2Document3 pages6.1 Quick Ref Guide MNGT Antivenom Reactions SGB2021 Ver. 2anju sulishaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Daftar ObatDocument6 pagesKumpulan Daftar ObatZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- SPC IntratectDocument9 pagesSPC IntratectprincezettaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For PediatricsDocument33 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For PediatricsVarshini Tamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- NICU ABX ChartDocument11 pagesNICU ABX ChartdrchiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Treatment of Infection Due To Vibrio Vulnificus - UpToDateDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Treatment of Infection Due To Vibrio Vulnificus - UpToDateKevo VillagranNo ratings yet
- FlucloxacillinDocument4 pagesFlucloxacillinSergeNo ratings yet
- Moderately HighLY Protein Bound DrugsDocument10 pagesModerately HighLY Protein Bound DrugsArah MomoNo ratings yet
- Nidua's Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNidua's Drug ChartSarah Michelle NiduaNo ratings yet
- Finasteride: Analgesics (Non-Opioid) & AntipyreticsDocument5 pagesFinasteride: Analgesics (Non-Opioid) & AntipyreticsSarah Michelle NiduaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic RegimetotreatpneumoniaDocument1 pageAntibiotic RegimetotreatpneumoniaNousheen ThakurNo ratings yet
- Guide Paed Bone JNTDocument11 pagesGuide Paed Bone JNTDorica GiurcaNo ratings yet
- Drug of Treatment For Meningitis: Penicillin Cefotaxime ResistantDocument5 pagesDrug of Treatment For Meningitis: Penicillin Cefotaxime ResistantNama BestNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudybaniniycsebNo ratings yet
- Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument7 pagesName of The Medicinal ProductSyifa Dina Az-ZahraNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Immune SystemDocument6 pagesDrugs Acting On Immune SystemSORENI SORENINo ratings yet
- Rle Neonate DrugsDocument13 pagesRle Neonate DrugsLhara Vhaneza CuetoNo ratings yet
- Analgesik/Pire Tik Dosis Sediaan Obat DOA OOA Drug Interaction Paracetamol IVDocument9 pagesAnalgesik/Pire Tik Dosis Sediaan Obat DOA OOA Drug Interaction Paracetamol IVNicole NgoNo ratings yet
- S Aureus TableDocument1 pageS Aureus TableCherylNo ratings yet
- EPIGENTDocument3 pagesEPIGENTmahgad100% (1)
- Ampicillin PDFDocument3 pagesAmpicillin PDFandriNo ratings yet
- Ac IphinDocument5 pagesAc IphinAdittya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Classification of PenicillinDocument3 pagesClassification of PenicillinNurfarzana NadhirahNo ratings yet
- MPC Antidote ChartDocument1 pageMPC Antidote Chartogodothomas51No ratings yet
- Levetiracetam PDFDocument3 pagesLevetiracetam PDFShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Tamiflu Epar Product Information - enDocument118 pagesTamiflu Epar Product Information - enUmar AliNo ratings yet
- 4 SeizuresDocument11 pages4 SeizuresApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument4 pagesGeneric NamePharmacist Amy CharlieNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ConversionDocument9 pagesAntibiotic ConversionfabianNo ratings yet
- Medications: Medication Name Generic/Trade Classification Pregnancy CategoryDocument8 pagesMedications: Medication Name Generic/Trade Classification Pregnancy CategoryapalestiNo ratings yet
- Levetiracetam Brand Indication Dosage Form Cost/Packing: Adult and Adolescent 16 Years 500mg BIDDocument4 pagesLevetiracetam Brand Indication Dosage Form Cost/Packing: Adult and Adolescent 16 Years 500mg BIDMark PradsNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease DrugsDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease DrugsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Meningitis ReviewDocument2 pagesMeningitis ReviewBolbol hayranNo ratings yet
- Obat AnestesiDocument9 pagesObat AnestesiNatanael SusantoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Pain Management For PediatricDocument2 pages2015 Pain Management For Pediatricdiany astutiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Drug UsageDocument13 pagesPaediatric Drug UsageasmaNo ratings yet
- AntibiocardDocument25 pagesAntibiocardchildicuNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Linezolid PDFDocument1 pageLinezolid PDFmariam ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Systemic Toxicity of Local AnaestheticsDocument1 pageSystemic Toxicity of Local Anaestheticsmariam ibrahimNo ratings yet
- AminoglycosidesDocument1 pageAminoglycosidesmariam ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolones PDFDocument1 pageFluoroquinolones PDFmariam ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Linezolid PDFDocument1 pageLinezolid PDFmariam ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pasien Neurologi Rabu, 17 FEBRUARI 2021: Lontara 3 Saraf Kamar 1Document4 pagesDaftar Pasien Neurologi Rabu, 17 FEBRUARI 2021: Lontara 3 Saraf Kamar 1Louis MailuhuNo ratings yet
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesRamsay Hunt Syndrome: Infectious DiseasesAldy BimaNo ratings yet
- US Biological Symbols 05AU17Document11 pagesUS Biological Symbols 05AU17Reid KirbyNo ratings yet
- Types of Disability and Disorders-1&2Document44 pagesTypes of Disability and Disorders-1&2Digambar SahooNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia: (Primary & Secondary)Document16 pagesPolycythemia: (Primary & Secondary)Vanessa Camille DomingoNo ratings yet
- Endomaterial Cancer-1Document28 pagesEndomaterial Cancer-1A.H.ANo ratings yet
- Psikiatri: Nonfarmako: CBT Farmako: SsriDocument4 pagesPsikiatri: Nonfarmako: CBT Farmako: SsriRekapriantiNo ratings yet
- Cholera in NepalDocument57 pagesCholera in NepalBinayaNo ratings yet
- Fat-And Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument9 pagesFat-And Water-Soluble VitaminsJessa Mae OhaoNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory EssayDocument1 pageInflammatory EssayJenny BaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesLesson PlanAisa B. TaerNo ratings yet
- CalamineDocument4 pagesCalamineFaye FelicesNo ratings yet
- MIO SheetDocument1 pageMIO SheetjnetNo ratings yet
- Urticaria, Angioedema, and Anaphylaxis AGO 2020Document12 pagesUrticaria, Angioedema, and Anaphylaxis AGO 2020Elizabeth HendersonNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Anna Schwartz, M.D. and Adriana Feder, M.D.: EtiologyDocument4 pagesAnxiety Anna Schwartz, M.D. and Adriana Feder, M.D.: EtiologyIrish_Tolentin_6195No ratings yet
- Ophthalmology: NEET PG 2020 QuestionsDocument17 pagesOphthalmology: NEET PG 2020 QuestionsAnmol KudalNo ratings yet
- ANT Handbook 2023Document84 pagesANT Handbook 2023latibaleni02No ratings yet
- Gall StoneDocument38 pagesGall Stoneumay83% (6)
- Gastrointestinal Stromal TumoursDocument22 pagesGastrointestinal Stromal TumoursThomas KlebNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Oncology NursingDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Oncology NursingDesh Deepak100% (1)
- Lapkas Marasmus JadiDocument48 pagesLapkas Marasmus JadiRivhan FauzanNo ratings yet
- Disease Diagnosis System: Software Requirement Specification (SRS)Document11 pagesDisease Diagnosis System: Software Requirement Specification (SRS)Shubham BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- Moh - Fahri (Dermatitis Venenata)Document5 pagesMoh - Fahri (Dermatitis Venenata)fahriitoNo ratings yet
- AbViser IAP Monitoring Device BrochureDocument2 pagesAbViser IAP Monitoring Device BrochuremasmblinkNo ratings yet
- F&E ExamDocument3 pagesF&E ExamDino PringNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeKM67% (3)
- Granuloma AnnulareDocument6 pagesGranuloma AnnulareGitarefinaNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis and Acute LeukemiaDocument6 pagesThrombosis and Acute Leukemiaannisa edwarNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Pakar Anemia in Pregnancy Dr. Ima IndirayaniDocument74 pagesKuliah Pakar Anemia in Pregnancy Dr. Ima IndirayaniHamba AllahNo ratings yet