Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equation of A Line
Equation of A Line
Uploaded by
Binu Kumar SOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equation of A Line
Equation of A Line
Uploaded by
Binu Kumar SCopyright:
Available Formats
Equation of a Line
Important Concepts
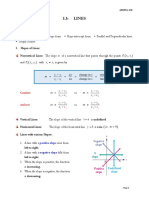
1. The angle which a straight line makes with the positive direction of x-axis measured in the
anticlockwise direction is called the inclination (or angle of inclination) of the line. The inclination is
usually denoted by θ.
2. If θ is the inclination of a line l, then tan θ is called the slope or gradient of the line l.
3. The slope of a line whose inclination is 90° is not defined.
4. The slope of x-axis is zero and slope of y-axis is not defined.
5. Three points A, B and C are collinear if Slope of AB = slope of BC.
6. Let AB be a line cutting x-axis and the y-axis at A(a, 0) and B(0, b) respectively. Then the intercepts
made on the axes are a and b respectively. That is, x-intercept = a and y-intercept = b.
7. The equation of line parallel to x-axis at a distance a in the positive direction of y-axis is y = a and in
negative direction of y-axis is y = -a.
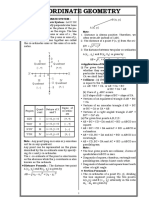
Slope of a line
y 2 y1
The slope m of the line through the points x1,y1 and x2 ,y2 is given by m .
x 2 x1
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
1. Two non-vertical lines l and m are parallel if and only if their slopes are equal.
That is m1 m2
2. Two non-vertical lines are perpendicular to each other if and only if their slopes are negative
reciprocals of each other.
1
That is m2 m1 m2 1
m1
Condition for Collinearity of Points
Three points A, B and C are collinear if Slope of AB = slope of BC
Equation of coordinate axes
1. The equation of x-axis is y = 0
2. The equation of y-axis is x = 0
Various Forms of the Equations of Straight Lines
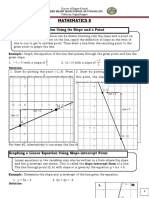
Slope-intercept form: The equation of a line having slope m and y-intercept c is given by y = mx + c.
Point-Slope form: The equation of a line passing through (x1, y1) and having slope m is given by
y y1 m(x x1) .
Two-point form: The equation of line passing through two points A x1, y1 and B x2 , y2 is given by
y y1 y 2 y1
x x1 x 2 x1
You might also like
- Advanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedDocument299 pagesAdvanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedShikhar Gupta92% (36)
- 07 Straight Line - Sheet - by MC SirDocument44 pages07 Straight Line - Sheet - by MC SirPiyush Agarwal100% (1)
- Straight LinesDocument1 pageStraight LinesLexicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Points To RememberDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Points To RememberMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- 111 NarayanaDocument40 pages111 Narayanaumesh100% (3)
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1ghlafhlyNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths - Chapter 10 - STRAIGHTLINESDocument47 pagesXI - Maths - Chapter 10 - STRAIGHTLINESStephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument23 pagesDefinitionashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Practice Booklet 1Document7 pagesStraight Line Practice Booklet 1jeevan gowdaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations: Section 1.1 p1Document42 pagesLinear Equations: Section 1.1 p1陳育禾100% (1)
- لقطة شاشة 2024-04-22 في 9.24.24 مDocument126 pagesلقطة شاشة 2024-04-22 في 9.24.24 مsalmf6580No ratings yet
- Straight Line: AIEEE SyllabusDocument27 pagesStraight Line: AIEEE SyllabusDeepali KotaryNo ratings yet
- 02-Straight Line (Theory)Document15 pages02-Straight Line (Theory)sadhithyaa7No ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument5 pagesStraight LinesNutan MishraNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Notes 10 Straight LinesDocument7 pages11 Maths Notes 10 Straight LinesAdiNo ratings yet
- 11self Theory-Straight LineDocument5 pages11self Theory-Straight Lineرافت باصهيNo ratings yet
- 11 TH Two Dimensional GeometryDocument20 pages11 TH Two Dimensional GeometryUmakant AvateNo ratings yet
- Maths For Business Recombiled by FADocument140 pagesMaths For Business Recombiled by FAEphrem GetachewNo ratings yet
- The Rate of Change of A Function: Chapter - OneDocument6 pagesThe Rate of Change of A Function: Chapter - OneabasNo ratings yet
- Key Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Document21 pagesKey Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Ayah100% (1)
- 1 Post NotesDocument7 pages1 Post Notesraw.junkNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Demonstration Dharmendra MeenaDocument28 pagesStraight Line Demonstration Dharmendra MeenaRahul JatNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper On MathDocument151 pagesA Research Paper On MathFafa AgbakpeNo ratings yet
- A Pair of ST - LinesDocument28 pagesA Pair of ST - LinesRajesh PurohitNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument6 pagesStraight LinesSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Notes 10 Straight Lines PDFDocument7 pages11 Maths Notes 10 Straight Lines PDFArpit MalikNo ratings yet
- 1.3: Lines: Pxy Pxy X XDocument3 pages1.3: Lines: Pxy Pxy X XAHMED ALSHAMMARINo ratings yet
- MATH I - Analytic Geometry (REVIEWER)Document9 pagesMATH I - Analytic Geometry (REVIEWER)Roberto Del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Iitjee Notes by Dipesh Sir Straight LineDocument6 pagesIitjee Notes by Dipesh Sir Straight LineKakakaunNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 ArDocument25 pagesChapter - 1 Arrandompupil2008No ratings yet
- Straight Lines PDFDocument6 pagesStraight Lines PDFCoc LegendNo ratings yet
- Gradeup Short Notes On Point and Straight Line - pdf-21Document5 pagesGradeup Short Notes On Point and Straight Line - pdf-21Tafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- Best Approach Straight Lines Answer Key - CopyDocument82 pagesBest Approach Straight Lines Answer Key - Copynamangoyal1024No ratings yet
- Best Approach Straight Lines Answer Key - CopyDocument82 pagesBest Approach Straight Lines Answer Key - Copynamangoyal1024No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Qee Review 2015Document45 pagesAnalytic Geometry: Qee Review 2015kangkongNo ratings yet
- MPM1D - Check in Quiz - Eqtns of Lines - SolutionsDocument2 pagesMPM1D - Check in Quiz - Eqtns of Lines - SolutionsMelisa AcarNo ratings yet
- 18 Mathematics Straight LineDocument17 pages18 Mathematics Straight LineArunava BasuNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Session PDF RemovedDocument124 pagesStraight Line Session PDF Removedashmt.ofblNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts:) y y X X (Document5 pagesKey Concepts:) y y X X (virat gandhiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointDocument5 pagesMathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointRoella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Session PDFDocument201 pagesStraight Line Session PDF8rg48v4zgfNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Straight LinesDocument15 pagesSheet - 01 - Straight LinesNoob Game PlayNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Straight Line - A0ba0e0e 1abf 466c Bb96 1ab599fdb5b6Document32 pagesUNIT 2 Straight Line - A0ba0e0e 1abf 466c Bb96 1ab599fdb5b6dande3359No ratings yet
- Xi-Quarterly Time TableDocument31 pagesXi-Quarterly Time TableInbloodNo ratings yet
- Definition of Perpendicular LinesDocument7 pagesDefinition of Perpendicular Linesapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Define Perpendicular LinesDocument7 pagesDefine Perpendicular Linesapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Slope and Intercept Form ReviewerDocument3 pagesSlope and Intercept Form Reviewerzh4hft6pnzNo ratings yet
- Fi Eu Vs VOb Ew 9 PFZZ AeyxDocument16 pagesFi Eu Vs VOb Ew 9 PFZZ AeyxRangeNo ratings yet
- Straight Line1Document12 pagesStraight Line1Rißhith Patel100% (1)
- Linear FunctionsDocument19 pagesLinear FunctionsTheresa Grace Balansag-Calimpusan AlsongNo ratings yet
- Yyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy YyyDocument4 pagesYyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy YyycambreayaNo ratings yet
- If You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanDocument16 pagesIf You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanSanaka LogesNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Document11 pagesCo-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Aarti Sharma100% (1)
- StraightLine Sheet3Document79 pagesStraightLine Sheet3Harsh100% (1)
- M102 Lines HandoutDocument1 pageM102 Lines HandoutLorenzo TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document11 pagesLecture 4Haider AliNo ratings yet
- 01 02 Linear Functions Straight LinesDocument47 pages01 02 Linear Functions Straight Linespop.korn7No ratings yet
- An Introduction to Differential Geometry - With the Use of Tensor CalculusFrom EverandAn Introduction to Differential Geometry - With the Use of Tensor CalculusRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- JudgementDocument282 pagesJudgementBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- SL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDDocument10 pagesSL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- SL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDDocument3 pagesSL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- SL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDDocument8 pagesSL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- SL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDDocument5 pagesSL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- SL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDDocument3 pagesSL No Ticket No Customer Name Circuit IDBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- E BGP MultihopDocument2 pagesE BGP MultihopBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21. The United Nations Principal OrgansDocument10 pagesChapter 21. The United Nations Principal OrgansBinu Kumar S100% (1)
- ConstructorDocument1 pageConstructorBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12. Physical Health and Hygiene: Short QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 12. Physical Health and Hygiene: Short QuestionsBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22. The United Nations (Major Agencies-Their Functions)Document8 pagesChapter 22. The United Nations (Major Agencies-Their Functions)Binu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Properties of Alkali Metals and HalogensDocument1 pageComparison of Properties of Alkali Metals and HalogensBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Geography 1Document4 pagesGeography 1Binu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23. Universal Declaration of Human Rights: Very Short QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 23. Universal Declaration of Human Rights: Very Short QuestionsBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13. Pollution: Short QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 13. Pollution: Short QuestionsBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Circles Tangents and Intersecting ChordsDocument3 pagesCircles Tangents and Intersecting ChordsBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Circles Arc and Cyclic PropertiesDocument3 pagesCircles Arc and Cyclic PropertiesBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Heights and DistancesDocument2 pagesHeights and DistancesBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression: Important TermsDocument2 pagesArithmetic Progression: Important TermsBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- 1ADocument3 pages1ABinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Geo 4 PDFDocument9 pagesGeo 4 PDFBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- ICSE Solutions For Class 8 Geography Voyage - Natural and Man-Made Disasters With Case Studies - A Plus Topper PDFDocument17 pagesICSE Solutions For Class 8 Geography Voyage - Natural and Man-Made Disasters With Case Studies - A Plus Topper PDFBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet