Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pranam Internship
Pranam Internship
Uploaded by
PrathapgowdaPm PrathapCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nails Making GuideDocument61 pagesNails Making GuideDj Backspin254100% (1)
- KOLee Tool Grinder Owners ManualDocument139 pagesKOLee Tool Grinder Owners ManualJason Bowman100% (4)
- Workshop Practice Series 38 - Tool Cutter SharpeningDocument68 pagesWorkshop Practice Series 38 - Tool Cutter SharpeningWillian Maza100% (6)
- Quality in Construction ProjectsDocument179 pagesQuality in Construction ProjectsJaydeepDas100% (2)
- QM Week 2 Role of Q in OrganisationDocument20 pagesQM Week 2 Role of Q in OrganisationnadzirnasirNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management (TQM) - 3328 Words - Report ExampleDocument7 pagesTotal Quality Management (TQM) - 3328 Words - Report ExampleMuhammad Talha FayyazNo ratings yet
- Supply Management (CUSCM208) : Quality in PurchasingDocument30 pagesSupply Management (CUSCM208) : Quality in PurchasingSIMBARASHE MABHEKANo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of QualityDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts of QualityrohitcshettyNo ratings yet
- Systems and Quality Day2Document86 pagesSystems and Quality Day2Prof Daniel KitawNo ratings yet
- Quality PLNG Control Imp, Benchmarking SDDocument95 pagesQuality PLNG Control Imp, Benchmarking SDANKIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- TQM in Msil (Amit & Pranav)Document41 pagesTQM in Msil (Amit & Pranav)Amit AnandNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1api-723710078100% (1)
- Systems and Quality ElectromechanicalRDocument69 pagesSystems and Quality ElectromechanicalRProf Daniel KitawNo ratings yet
- Module-V Customer FocusDocument11 pagesModule-V Customer FocusPrashant JhaNo ratings yet
- Goods and Service Design: By: Weezie Kay O. Manucan and Bernie Joseph A. JiaoDocument50 pagesGoods and Service Design: By: Weezie Kay O. Manucan and Bernie Joseph A. JiaoJosef JiaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document66 pagesLecture 1Samriddhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument45 pagesUnit - INihal KocheNo ratings yet
- Marketing Quality Management (MRK 7010) Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesMarketing Quality Management (MRK 7010) Final Exam SolutionsGürkan SağlamNo ratings yet
- TQM QA Unit1Document9 pagesTQM QA Unit1akhshayamNo ratings yet
- Management of Quality The Quest For QualityDocument12 pagesManagement of Quality The Quest For QualityKelvin mwai100% (1)
- Apparel Quality Management: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyDocument13 pagesApparel Quality Management: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyBhaswati PandaNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Practices by TVS Group IndiaDocument19 pagesQuality Management Practices by TVS Group Indiasnata92No ratings yet
- Customer Focus AND SatisfacationDocument18 pagesCustomer Focus AND SatisfacationArslan SaleemNo ratings yet
- QM 0013Document7 pagesQM 0013Bhupendra KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Taguchi Loss FunctionDocument9 pagesTaguchi Loss FunctionSang PhanNo ratings yet
- Customer SatisfactionDocument28 pagesCustomer SatisfactionLeUqar Bico-Enriquez GabiaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management (TQM)Document9 pagesTotal Quality Management (TQM)grace1217No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document41 pagesChapter 1CALIPDAN, Roselyn D. (Lyn)No ratings yet
- Goods and Service DesignDocument16 pagesGoods and Service DesignJayvee Joble BigataNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlDocument25 pagesLecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlKayode Samuel80% (5)
- IIMB Project Final ReportDocument36 pagesIIMB Project Final ReportSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- TQM Unit 1 SBDocument21 pagesTQM Unit 1 SBViji LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1: SalamDocument12 pagesAssignment No. 1: Salamzia uddin khattakNo ratings yet
- Joseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality TrilogyDocument7 pagesJoseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality Trilogy07081988No ratings yet
- Joseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality TrilogyDocument7 pagesJoseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality TrilogyMadhuri HusrajNo ratings yet
- Otal Uality AnagementDocument143 pagesOtal Uality AnagementJohn Rex PanestanteNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting OmDocument18 pagesFactors Affecting Omerielle mejicoNo ratings yet
- World Class OperationDocument11 pagesWorld Class OperationAvisekh KumarNo ratings yet
- Software QualityDocument33 pagesSoftware QualityDevendra RaneNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument27 pagesQuality ManagementLloyd Allison QuintoNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 101 SG 1Document9 pagesCbmec 101 SG 1Heesung LeeNo ratings yet
- TQM AssignmentDocument15 pagesTQM Assignmentbryan cabarles100% (1)
- Sqa LecturesDocument21 pagesSqa LecturesVanessa SarahNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesTotal Quality Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Kaizen: /watch?v 0dZYC2XBF2UDocument13 pagesKaizen: /watch?v 0dZYC2XBF2UNoel NantesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 TQM ReportsDocument18 pagesTopic 1 TQM ReportsAida Ganituen100% (1)
- Lecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlDocument25 pagesLecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesQuality ManagementMahajan ShashankNo ratings yet
- Reduce Cost of Poor Quality at Austin Engineering Company LTDDocument33 pagesReduce Cost of Poor Quality at Austin Engineering Company LTDpatel2431No ratings yet
- Importance of Quality in BusinessDocument3 pagesImportance of Quality in BusinessJennifer Andrea Pardo100% (1)
- QFD As A Tool For Business Excellence Through TQMDocument9 pagesQFD As A Tool For Business Excellence Through TQMseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- How The Kaizen and PokaDocument15 pagesHow The Kaizen and Pokashaista naazNo ratings yet
- MT 14 - Total Quality ManagementDocument43 pagesMT 14 - Total Quality ManagementRuíz Figueroa, Jean E.No ratings yet
- MGT311 Assignment 1Document7 pagesMGT311 Assignment 1Hut MutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document3 pagesChapter 7Cathy MamigoNo ratings yet
- TQM Module 1Document20 pagesTQM Module 1Jhan Reach EnagoNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa Kualitas Rekayasa Kualitas Pertemuan 4: Teknik IndustriDocument15 pagesRekayasa Kualitas Rekayasa Kualitas Pertemuan 4: Teknik IndustriDeni Deri SetianaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cost of QualityDocument44 pages2 Cost of QualityCASTRO, HANNAH CAMILLE E.No ratings yet
- CODE: DIM 1010 Production and Operation Management: AssignmentDocument16 pagesCODE: DIM 1010 Production and Operation Management: AssignmentChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Quality Control and Materials ManagementDocument39 pagesUnit-Iii: Quality Control and Materials ManagementLAKKANABOINA LAKSHMANARAONo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagemantDocument23 pagesTotal Quality ManagemantnajieyuyaNo ratings yet
- Grinding MachinesDocument11 pagesGrinding MachinesVikash Kumar Vimal100% (1)
- MX7 Brochure 2010Document8 pagesMX7 Brochure 2010Clement JohnNo ratings yet
- Materials Forming, Machining and Tribology Viktor P. AstakhovDocument200 pagesMaterials Forming, Machining and Tribology Viktor P. AstakhovZerina ČustovićNo ratings yet
- CNC Workshop Projects - CNCCookbook - Be A Better CNC'ErDocument24 pagesCNC Workshop Projects - CNCCookbook - Be A Better CNC'ErJondaNo ratings yet
- Drill Grinding With The PP-U3 Grinder Copy of The Deckel SO GrinderDocument14 pagesDrill Grinding With The PP-U3 Grinder Copy of The Deckel SO GrinderAndy L100% (1)
- AEC KumbakonamDocument29 pagesAEC KumbakonamArun DharmarajNo ratings yet
- ANCA FXLinear Brochure 2021Document20 pagesANCA FXLinear Brochure 2021Rodrigo Frasseto MicheliniNo ratings yet
- WTP-I - Module 5 Study MaterialDocument63 pagesWTP-I - Module 5 Study MaterialBea Daniella CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Auto Punch Die Tooling Grinder F6Document4 pagesAuto Punch Die Tooling Grinder F6AFAB Machinery and Tools LtdNo ratings yet
- Technology of Machine Tools: Universal Cutter and Tool GrinderDocument64 pagesTechnology of Machine Tools: Universal Cutter and Tool GrinderAnibal Daza100% (1)
- Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument13 pagesTool and Cutter GrinderUmair MypusakaNo ratings yet
- Tool & Cutter GrinderDocument64 pagesTool & Cutter GrinderAFIFAHZABIDI ZABIDINo ratings yet
- "©HAND Rapids" Grinders .: & Livomsstron CODocument42 pages"©HAND Rapids" Grinders .: & Livomsstron CONew100% (1)
- Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument6 pagesTool and Cutter GrinderNav Srinath100% (1)
- DrillDocument18 pagesDrillvivekNo ratings yet
- MT2 University Question PaperDocument4 pagesMT2 University Question PaperKrishnan VelavanNo ratings yet
- 00 CINCINNATI No 2 Radius Grinding AttachmentDocument4 pages00 CINCINNATI No 2 Radius Grinding AttachmentGilberto GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Cost-Effective CNC Grinding MachineDocument5 pagesThe Cost-Effective CNC Grinding MachineRodrigo Frasseto MicheliniNo ratings yet
- Model Engineers' Workshop 11.2021Document68 pagesModel Engineers' Workshop 11.2021Leapfrog100% (2)
- Nil Report EP LabDocument6 pagesNil Report EP LabCHANDRAPRAKASHNo ratings yet
- McTools ToolCutGrdDocument2 pagesMcTools ToolCutGrdabyzenNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Abrasive Processes and Gear Cutting: 4.1 GrindingDocument30 pagesUnit Iv Abrasive Processes and Gear Cutting: 4.1 Grindingrkscad11No ratings yet
- Practical 7Document2 pagesPractical 7AARSHNo ratings yet
- Rudrali Hitech - IM - 2020 - Unlocked - 1Document47 pagesRudrali Hitech - IM - 2020 - Unlocked - 1Rudrali HitechNo ratings yet
- Machine ShopDocument13 pagesMachine ShopAmin MalikNo ratings yet
- Machinist: 2 Year (Volume - I of II)Document146 pagesMachinist: 2 Year (Volume - I of II)irshadNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument276 pagesCompleteIonuts Sorin100% (1)
Pranam Internship
Pranam Internship
Uploaded by
PrathapgowdaPm PrathapOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pranam Internship
Pranam Internship
Uploaded by
PrathapgowdaPm PrathapCopyright:
Available Formats
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 1
COMPANY PROFILE
1.1 Vision
Our vision is to be recognized as the solutions leader in the print industry.
1.2 Mission
Convertible Solutions mission is to provide pre-converted substrates to the digital print industry,
and to provide solutions for our customers to help promote their success through our innovative
products and services.
Our commitment is to act in the highest ethical manner with our customers and
associates.
To keep uppermost the goal of customer satisfaction.
To be receptive to our customers needs and partner with them with honesty and
integrity.
To be the industry leader providing pre-converted substrates which save time, and
provide labor and waste reduction.
To continually educate ourselves on the latest trends and technologies.
1.3 Quality Policy
Convertible Solutions Quality Policy is to continually improve the quality of our customer
interaction, and our products and services. I will do this by
Clearly understanding customer needs and meeting those needs.
On-time delivery of product manufactured to specification at agreeable pricing.
Establish an alliance with suppliers and partners to achieve customer expectations.
Accelerate revenue growth through a progressive quality-focused environment.
Comply with the relevant regulatory requirements.
1.4 Objectives of PMTC
Conversion of enquiries into order.
On time delivery.
Reduce rejection.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 1
Manufacturing Process
Improve workplace safely.
Improve customer service.
Improve internal operating efficiencies and reduce expenses.
Increase flexibility.
Improve supply chain efficiency.
Increase sustainability.
Fig. 1.1 Quality Policy
1.5 Inspection Facilities
Digital Vernier 0-200mm
(Mitutoyo) Vernier 0-150mm, 0-300mm
(Mitutoyo) Micrometer 0-25mm, 25-50mm
Digital Micrometer 0-25mm
Digital Height Guage 0-300mm
Height guage, Depth guage 0-300, Feeler guage, Try square, Meter scales, Surface table,
Angle plate, “Coating Thickness guage” Bevel Protractor, Tap guage. Basic measuring
instruments like profile projector (10X to 50X), Special purpose guages, jigs and fixtures to
control critical dimensions/parameters.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 2
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 2
ABOUT THE COMPANY
P M Tools & Components are manufacturing concern established in 18 th January 2010. PMTC is
professionally managed, young innovative company promoted by a group of technicians who
have put up decades of service in the manufacturing industry with sufficient engineering
qualifications, working knowledge, exposure to the international standards and ‘Quality’
standards with expertise in the field of design, development and manufacturing of press
components, wire formed components, flat springs, multi-side components with sound
knowledge of these products. To know the activities of organization it is very much essential to
understand the functioning of the entire functional departments of the organization which helps
to know how the theoretical knowledge is implemented in the functioning of the organization. In
this organization study. I have studied different department in an organization and relationship
between different departments, duties and responsibilities, problems, conclusions, suggestions,
recommendation etc., and also type of organization structure. Finally, it was a nice experience
during my entire training period in PMTC. I felt, it was a great opportunity for me to work with
this company as if being a part of the company.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 3
Manufacturing Process
2.1 Infrastructure Facilities
In-House Tool Manufacturing
Basic tool room machines like Milling, surface grinding, shaping, drilling, pedestal grinding,
universal tool & cutter grinding, lathe etc.
Component Manufacturing
CNC wire bending machine
Spot welding
Projection welding
Grinding machine
CNC Wire EDM
Profile projector
Our quality policy is formulated with a conscious commitment for customer satisfaction through
continual improvement processes and cost effectiveness. The main objective of this venture is to
pioneer in carrying press tool components and maintaining high level of “customer satisfaction”.
Manufacturing to customers specification and measuring the pressed parts needs measuring
instruments, we have accommodated the same by strengthening our quality assurance
department, by providing almost all ranges in Micrometers, vernier caliper and gauges. The
employees are highly skilled and carryout intricate setting in virtually no time.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 4
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 3
INTRODUCTION TO QUALITY AND CUSTOMER
SATISFACTION
3.1 Quality
Quality control in its simplest term is the control of quality during manufacturing. Both quality
control and inspection are used to assure quality. Inspection is a determining function which
determines raw materials, supplies, parts or finished products etc. as acceptable or unacceptable.
As control becomes effective, the need for inspection decreases. Quality control determines the
cause for variations in the characteristics of products and gives solutions by which these
variations can be controlled. It is economic in its purpose, objective in its procedure, dynamic in
its operation and helpful in its treatment. Since variations in raw materials have large effects on
the quality of in-process materials, quality control includes statistical sampling and testing before
acceptance. It also includes the examination of quality characteristics in finished products so as
to assure satisfactory outgoing quality. Every organization has customers. Some have only
internal customers, some have only external customers, and some have both. When you are
working to determine what you need to accomplish to satisfy or even delight your customers,
quality function deployment is an essential tool.
Background
QFD is a focused methodology for carefully listening to the voice of the customer and then
effectively responding to those needs and expectations. First developed in Japan in the late 1960s
as a form of cause-and-effect analysis, QFD was brought to the United States in the early 1980s.
It gained its early popularity as a result of numerous successes in the automotive industry.
Methodology
Methodology is a structured method that uses the seven management and planning tools to
identify and prioritize customers’ expectations quickly and effectively. Beginning with the initial
matrix, commonly termed the House of Quality (Figure 1), the QFD methodology focuses on the
most important product or service attributes or qualities.
These are composed of customer wows, wants, and musts. (See the Kano model of customer
perception versus customer reality.) Once you have prioritized the attributes and qualities, QFD
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 5
Manufacturing Process
deploys them to the appropriate organizational function for action, as shown in Figure. Thus,
QFD is the deployment of customer-driven qualities to the responsible functions of an
organization.
3.2 Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is defined as a measurement that determines how happy customers are
with a company’s products, services, and capabilities. Customer satisfaction information,
including surveys and ratings, can help a company determine how to best improve or changes its
products and services. An organization’s main focus must be to satisfy its customers. This
applies to industrial firms, retail and wholesale businesses, government bodies, service
companies, nonprofit organizations, and every subgroup within an organization.
3.2.1 Measure to take customer satisfaction
Organizations should not assume they know what the customer wants. Instead, it is important to
understand the voice of the customer, using tools such as customer surveys, focus groups, and
polling. Using these tools, organizations can gain detailed insights as to what their customers
want and better tailor their services or products to meet or exceed customer expectations.
3.2.2 Customer satisfaction resources
By following the same steps for every issue and performing full root cause analysis for 100% of
issues, Polk increased operational excellence and improved customer satisfaction.
Move from Product to Customer Centric (Quality Progress) "Customer centricity" is about
listening to your customers, with a focus on collecting, understanding, and acting on customer
feedback and providing tools for easy access to this information.
Don’t measure customer satisfaction customer perceived value is a better alternative to
traditional customer satisfaction measurements.
Linking customer satisfaction to product design a key to success for volvo a framework for
bridging the quality satisfaction gap at Volvo integrates quality function deployment and
customer-satisfaction modeling.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 6
Manufacturing Process
3.3 Quality Assurance (QA)
The terms "quality assurance" and "quality control" are often used interchangeably to refer to
ways of ensuring the quality of a service or product. For instance, the term "assurance" is often
used as follows Implementation of inspection and structured testing as a measure of quality
assurance in a television set software project at philips semiconductors is described.
Quality assurance includes two principles "Fit for purpose" (the product should be suitable for
the intended purpose) and "right first time" (mistakes should be eliminated). QA includes
management of the quality of raw materials, assemblies, products and components, services
related to production, and management, production and inspection processes. The two principles
also manifest before the background of developing (engineering) a novel technical product. The
task of engineering is to make it work once, while the task of quality assurance is to make it
work all the time.
3.3.1 Quality Assurance Best Pratices
1. Integration of a Robust ERP with QA Capabilities Delivers the Highest Quality Products
Integrate the quality inspection activities in production processes.
Use inspection plans for quality inspection.
Use the reports and charts for valuation of inspection characteristics.
Detect nonconformities during production to avoid cost-intensive reprocessing or
unnecessary waste.
2. Quality Assurance Yields Higher Customer Satisfaction
Capture defects and nonconformities for documentation and for further processing.
Execute quality tasks to mitigate or resolve defects.
Capture status of quality tasks.
Define and execute additional manual quality inspections.
3. Improved Workflows Mean Reduced Expenses and Better Decision-making
Integrate quality inspection activities in the stock handling process, be it inbound, in
process or outbound stock.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 7
Manufacturing Process
Detect nonconformities and necessary follow-up actions as soon as possible to avoid
inappropriate usage and waste.
Eliminate inconsistencies, when creating an inspection plan.
4. Quality Products Breed Loyal Customers
Ingrate quality inspection activities in the product development process.
Use inspection plans foe quality inspections with dynamic modification, sampling
scheme and material release.
Record nonconformities at the right point in time to avoid cost-intensive reprocessing or
unnecessary waste.
5. Compliance
Capture problem details, related defects, causes and activities in one place.
Manage various activity types.
Assign a person responsible to each action item and track action statuses and outcomes.
3.4 Marketing Department (Commercial Process)
Objective
To ensure that customer needs are clearly identified, understood and documented for
proper co-ordination of the contract or order, submission of tender / proposal.
Enquiries and contract reviews are carried out without any contradiction from the
accepted terms.
To ensure resolving of customer complaints.
To ensure customer satisfaction.
Scope
All verbal enquiries, telephonic enquiries and orders, written enquiries, tenders. Contracts
& orders.
Review of all contracts or orders and amendments.
Responsibilities
Get Clarification and other necessary documentation from customer based on
requirement from Purchase, Quality and Production.
Discuss and finalize Quotation with MD for new enquires.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 8
Manufacturing Process
Prepare and send quotation and get feedback from new customers.
Get Purchase Order and delivery schedule from customer.
Get customer approval in the case of sample submission.
Give delivery schedule to customer in consultation with operations head.
Identify and get New Customer Enquires.
Get Purchase Order and delivery schedule from customer.
Communicate with customer in the case of any delay in delivery schedule.
Authorities
Review and decide on taking up a new customer enquiry based on customer profile, P M
TOOLS capability etc. in consultation with MD.
Decide on the Product Price in consultation with MD.
Decide and give priority on the production schedule for the customer products handled.
Decide on giving clearance to any deviation to products in consultation with customer.
3.5 Production Department (Product Realization)
Objectives
To have planned production process, ensuring availability of items to enable production
process and achieve production target.
To reduce rejection, rework and scrap while manufacturing.
To provide suitable working environment for quality production.
To ensure proper identification and traceability of items.
Responsibilities
Plan Production as per Production plan schedules released by CEO/MD.
Allocate man power as per production plan.
Plan on manpower requirements for new products and workout the stages required for the
same.
Carrying out preventive and breakdown maintenance.
Processes validation and Monitoring Process control parameters.
Interacting with subcontractors for out sourced products.
Prepare work instruction and standard operating procedures for various stages.
Identify and inform top management for any additional requirements for resources.
Monitor daily productivity and sent report to top management.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 9
Manufacturing Process
Maintain housekeeping, planning and conducting self-internal quality audits.
Managing production activities and labor.
Maintaining identification and traceability of processed and finished material.
Maintaining records to ensure continued adherence to documented requirements.
Authorities
Release of finished product to final quality after inspection.
Plan additional production hour requirements based on production demand.
Change processes flow as required either to improve Quality or Productivity on
consultation with Quality and Operation head.
To approve permission/leave requirement of operators based on the policy.
3.6 Quality Department
Objectives
Conversion of enquiries into order.
On time delivery.
Reduce rejection.
Scope
Application to monitoring and measurement of purchased and products of PMTC.
Application to all measurement / test equipment, instruments and gauges used at PMTC.
Improvement process is applicable in all areas of operation of PMTC.
Responsibilities
Update, document and release any processes or product changes due to customer input or
internal input, through PCN-Processes change note and ECN-Engineering change note.
Maintain and update master list PCN, ECN and drawing released.
Plan and conduct new product introduction meeting and record the proceedings and
circulate it to all concerned.
Responsible for preparing quality plans for incoming quality and final quality.
Responsible for carrying out incoming and final inspections.
Receive customer inputs such as drawing etc from marketing and verify and release it to
concerned departments.
Monitor in processes and collect rejection data.
Authorities
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 10
Manufacturing Process
Authorized to release Final finished product for dispatch.
Give disposition to Non-Conforming Part/Product n consultation with MD, CEO and
Customer on case by case basis.
Approve Corrective and Preventive Action proposed by production.
Authorized to plan and conduct Internal Quality Audits.
Approve and give disposition on processes rejection part sand products in consultation
with MD and CEO on case by case basis.
To generate Non-Conformity report on any processes or product deviation.
3.7 Store Department (Store Process)
Objectives
To establish a procedure for storage of items at PMTC with a view to prevent damage &
deterioration.
To have procedure for issue from stores against authorized requisition and controlling the
product surpluses returned to the stores.
To ensure the availability of components to facilitate production.
Scope
All the activities involved in the stores process which are performed at PMTC.
Responsibilities
Generate a product wise Shortage Report based on the production schedule and give it to
Purchase for releasing Purchase Order.
To Receive Material from supplier and verify against Purchase order and check quality.
To inform Incoming Quality for verification and approval.
Maintaining store records and stock register.
Update and issues store stock to Top management at the end of every month.
3.8 Purchase Department (Procedure for purchase process)
Objectives
To establish a procedure to ensure that the purchased products conform to the specified
requirements.
To ensure that quality components / raw material are procured and are cost effective.
To ensure that materials are purchased as per minimum stock level/indents/ Specification.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 11
Manufacturing Process
Scope
This procedure is applicable to all the direct materials purchased to be used in
components.
This procedure not applicable to capitals goods procurement and for consumables.
Responsibilities
To receive Customer order requirement from marketing and production departments.
To get material availability and shortage report from stores / production.
Plan and release Purchase Orders on Suppliers for shortage items.
Get delivery schedule from Suppliers and give material receipt schedule to operation
along with the Shortage report.
Authorities
Authorized to release Purchase Orders based on the shortage report for the products
which are planned for production in co-ordination with CEO.
Can black list a supplier based on Quality and Delivery performance.
Recommending payments to suppliers.
3.9 Operating Department
Operator’s responsibilities
Following the instruction of production in charge.
Giving feedback to production in charge regarding in process and final product quality.
Machining and storing of products as per work instructions.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 12
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 4
INTRODUCTION CNC WIRE BENDING MACHINE
4.1 Numerical control machines
The numerical control machines mold comprises a bracket, working table and a clamping plate,
when used by wire to the coil is energized, electricity gravitation to the pressing plate is
generated, thus realizing the plate and the base plate clamp.
Fig. 4.1 CNC Wire Bending Machine
CNC Wire Bending machines, which are generally automatic, can be made to have a single or
double head, and can be made fully electric. They can also be equipped with integrated load and
unload capabilities. They accept many types of wire, such as aluminum and stainless steel, to fit
the needs of the consumer. Bends can be set to custom angles. They may come with one or more
reversible bending heads. They have clockwise or counterclockwise rotation and variable
radius.This helps for the wire bend cut to the desired shape.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 13
Manufacturing Process
Double-headed bending machines are well-suited to performing machining operations on a
medium and long workpieces with many bends. Symmetrical and/or closed workpieces also
work well. These are generally used in automotive, appliances, internal and external furnishing,
shop and supermarket equipment and military sectors.
All CNC Wire Bending machines save money through efficiency increase, by easily recreating
the programmed design on a robust and continuous basis. It also decreases the number of
workers needed to complete a function. The CNC Wire Bending machine produces highly
accurate parts and it is more functional than a 3D printer.
4.2 Applications and uses
Wire forming is used to create wire products of all shapes, sizes and dimensions, including both
2D and 3D. Vital to numerous applications, wire forms serve an extensive range of industries
such as Commercial and retail, medicine and healthcare, energy storage, maintenance, undustrial
washing, lighting, automotive, aerospace , construction, hardware and storage.
4.3 Overview
Here’s the working principle of this 3D wire bending machine. So first, the wire goes through a
series rollers, or straighteners. Using a stepper motor the wire is precisely fed to the wire bending
mechanism which also uses a stepper motor as well as a small servo for the bending process.
Arduino 3D Wire Bending Machine Working Principle, There’s also another stepper motor,
called the Z-axis, which actually enables the machine to create three dimensional forms. Of
course, the brain of the machine is an Arduino board which along with the other electronics
components is attached on a custom designed PCB. As for the program, I made few custom
functions for making various shapes, like a star, a cube and a simple stand, as well as a manual
mode where we can make the wire forms by entering commands through the serial monitor.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 14
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 5
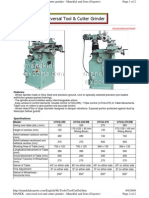
INTRODUCTION TO GRINDING MACHINE
Fig. 5.1 Grinding machine
5.1 Working and uses
A tool and cutter grinder is used to sharpen milling cutters and tool bits along with a host of
other cutting tools. It is an extremely versatile machine used to perform a variety of grinding
operations surface, cylindrical, or complex shapes.
A tool and cutter grinder is used to sharpen milling cutters and tool bits along with a host of
other cutting tools. It is an extremely versatile machine used to perform a variety of grinding
operations surface, cylindrical, or complex shapes. The image shows a manually operated setup,
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 15
Manufacturing Process
however highly automated Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are becoming
increasingly common due to the complexities involved in the process.
The operation of this machine requires a high level of skill. The two main skills needed are
understanding of the relationship between the grinding wheel and the metal being cut and
knowledge of tool geometry. The illustrated set-up is only one of many combinations available.
The huge variety in shapes and types of machining cutters requires flexibility in usage. A variety
of dedicated fixtures are included that allow cylindrical grinding operations or complex angles to
be ground. The vise shown can swivel in three planes. The table moves longitudinally and
laterally, the head can swivel as well as being adjustable in the horizontal plane, as visible in the
first image. This flexibility in the head allows the critical clearance angles required by the
various cutters to be achieved.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 16
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 6
INTRODUCTION TO SPOT WELDING
Fig. 6.1 Spot welding
6.1 Welding Procedure
The weld sheet metal is cleaned together and that are free from dirt, oxide, grease and
oxides.
The electrode tip will be cleaned it should be conduct current otherwise the electric
resistance is generated between work piece and electrode.
Both side of plate, the electrode are stick. When the pressures is created to the electrodes
and maintain a particular time period is known as sequence of time for before starting of
weld.
Now, the current is passed through electrode. The weld time is, time of application of
time taken. At the weld time during the process pressure to be maintained and weld
current range of 3000 A to 100000 A, it passed to electrode at time of 0.1 to 0.5 sec. The
step down transformer controls the magnitude of high current possible.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 17
Manufacturing Process
The current is passed one electrode to another electrode through the work piece, a small
area contact between the work pieces. This spot is known as resistance spot. The spot
generate the temperature and increase above 900⁰
After weld time completed, the current is shout down and pressure will be maintain a
particular brief of time is called as hold time. So the heat metal solidified and form of
weld hugest.
After brief time the pressure released, then work piece is removed.
Now water is supplied to the electrode because of avoid overheating of electrode. In this
welding process, set proper welding current and time before welding.
The size and shape of weld gradually limited by size and contour of electrode. It welding
configuration can be relatively simple and inexpensive.
Foot operated spot welding machine consist of as shown in figure. That should be having two
jaws. One jaw is stationary and another jaw is movable. In between the two jaws, the sheet
metals are placed and force is applied to per jaw through foot pedal and livers. The motion and
pressure are provided from hydraulic or pneumatic operation.
6.2 Application of resistance spot welding
It mostly used in automobile industry and to weld sheet metal for mostly.
In orthodontist`s clinic, small spot weld equipment used to resizing the metal “molar
bands”.
The different metal and alloys alloy steel, medium carbon and high carbon steels, low
carbon steel can be welded.
Products of spot welding
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 18
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 7
INTRODUCTION TO PROJECTION WELDING
Fig. 7.1 Projection welding
In the projection welding, as per the name, different projections are formed for effective welding.
Projection Welding is one of the types of resistance welding and its working principle is quite the
same as the resistance welding. The only difference here is that projection or embossed joints
are used for the welding purpose.
7.1 Working Principle
As per the definition, different projections are formed in this welding technique. Here, the metal
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 19
Manufacturing Process
pieces that are to be joined are kept in between the two electrodes. A larger pressure force is
applied to the electrodes. As current is passed through the system, the heat formation takes place
due to the internal resistance of the metal workpieces. One point that you must note down here,
is that the heat generation takes place due to the internal resistance of the metal workpieces
rather than an electric arc. Those projections concentrate the heat. As the pressure applied to the
electrodes increases, this projection collapses and the formation of the fused weld nugget takes
place. Thus, a quality weld is formed.
Advantages
Now, it is the time to know about the advantages. So, let’s discuss some of the most important
benefits of this welding technique
As the above stated, this welding requires a very small supply of current and thus, it saves
the electricity usage. So, less electricity requirement and a longer electrode life are the
two most prominent benefits of this welding process.
While doing spot welding there is a limitation on the thickness of the metal that has to be
welded. But in this welding, almost metals of all thickness are welded.
It can be used effectively for welding of the joints which are on the complicate locations.
Disadvantages
This welding process is not applicable for some types of the coppers and brasses.
Projection formation is a quite complicated process and it takes time to form the
projections. It is very difficult to form the spherical projection and a skilled person is
required to form such projections. While making those projections, a height of the
projection has to be maintained properly.
7.2 Application
As Projection welding is mostly used for the mass production. It has many applications such as:
Automobile industry uses projection welding to a very large extent.
This welding process is also used for the fan covers and hollow metal doors.
It is also used for producing the compressor parts and for the semi-conductors.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 20
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 8
INTRODUCTION TO CNC WIRE EDM
Fig. 8.1 CNC Wire cut electrical discharge machine
8.1 Working principle of EDM
In WEDM, an electrical spark is created between an electrode and a work piece. The spark is
visible evidence of the flow of electricity. This electric spark produces intense heat with
temperatures reaching 8000 to 12000 degrees Celsius, melting almost anything. The spark is
very carefully controlled and localized so that it only affects the surface of the material. The
EDM process usually does not affect the heat treat below the surface. With wire EDM the spark
always takes place in the dielectric of de-ionized water. The conductivity of the water is carefully
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 21
Manufacturing Process
controlled making an excellent environment for the EDM process. The water acts as a coolant
and flushes away the eroded metal particles.
EDM wire cutting uses a metallic wire to cut a programmed contour in a work piece. Extrusion
dies and blanking punches are very often machined by wire cutting. Cutting is always through
the entire work piece. To start machining it is first necessary to drill a hole in the work piece or
start from the edge. On the machining area, each discharge creates a crater in the work piece and
an impact on the tool. The wire can be inclined, thus making it possible to make parts with taper
or with different profiles at the top and bottom. There is never any mechanical contact between
the electrode and work piece. The wire is usually made of brass or stratified copper, and is
between 0.1 and 0.3 mm diameter.
8.2 Influence of process parameters on the wire cut EDM process
The main goal of WEDM manufacturers and users is to achieve a better stability of the process
and higher productivity. As newer, more exotic materials are developed and more complex
shapes are presented, conventional machining operations reach their limitations; hence the
increased use of WEDM in manufacturing continues to grow at an accelerated rate. Wire
electrical discharge machining manufacturers and user emphasize on achievement of higher
machining productivity with a desired accuracy and surface finish. However, due to a large
number of variables even a highly skilled operator with a state-of the art WEDM is rarely able to
achieve the optimal performance. The optimum utilization of the capacity of WEDM process
requires proper selection of machining parameters. This part of literature review aims to
investigate the effect of various process parameters on desirable output. WEDM is complex in
nature and is controlled by large number of parameter.
8.3 Application of wire cut EDM machining
Wire cut EDM machining is mainly used to process various punch tie, plastic mold, Powder
metallurgy mold and etc, which have 2D and 3D faces combined, or components. It can also cut
various sample plate, magnetic steel, Silicon Steel Sheet, semi-conductive material or precious
metal. Furthermore, it is able to do tiny machining, abnormal shape groove or machining of
standard defect of sample parts, widely used in electrics, precious machine tools, light industry,
army industry and so on.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 22
Manufacturing Process
1. Mold machining
Wire cut EDM is widely used to machine various molds, such as punch die, squeezing die,
powder metallurgy mold, bend mold, plastic mold. Among these different kind molds, cutting
punch die take a great share, to precious punch die machining, wire cut EDM machining is a
indispensable technology. By adjusting different compensation value while programming, wire
cut EDM can cut terrace die, punch plate, stripper plate and etc, it is easy to meet the
requirement of mold fitting clearance and machining accuracy.
Advanced punch dies have characteristics of complicated structure, big producing difficult, high
accuracy, long life, high efficiency and low consumption ratio of material. These new advanced
technology of mold also bring continuous development of wire cut EDM technology.
2. Mechanical parts machining
To mechanical parts machining, wire cut EDM is suitable to machine parts with large varieties
and small quantity, special material which is not easy to processed by conventional machines,
special gear, forming cutting tools, various shape holes, please check figure 1-2.
When try to make new product, use wire cut EDM machine to cut parts out of workpiece, there is
no need to make molds, producing time is shortened obviously, at the same time, cost is reduced.
Besides, as it is easy to adjust electrical parameters of wire cut EDM, so it is possible to overlap
thin plate and cut together to increase machining efficiency. And wire cut EDM machine can
also machine parts with tiny gap, narrow slit and complex shape.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 23
Manufacturing Process
Chapter 9
INTRODUCTION TO PROFILE PROJECTOR
Fig. 9.1 Profile projector
9.1 Working principle
Also known as an optical comparator, or even called a shadowgraph, a profile projector is an
optical instrument that can be used for measuring. It is a useful item in a small parts machine
shop or production line for the quality control inspection team. The projector magnifies the
profile of the specimen, and displays this on the built-in projection screen. On this screen there is
typically a grid that can be rotated 360 degrees so the X-Y axis of the screen can be aligned with
a straight edge of the machined part to examine or measure. This projection screen displays the
profile of the specimen and is magnified for better ease of calculating linear measurements. An
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 24
Manufacturing Process
edge of the specimen to examine may be lined up with the grid on the screen. From there, simple
measurements may be taken for distances to other points. This is being done on a magnified
profile of the specimen. It can be simpler as well as reduce errors by measuring on the magnified
projection screen of a profile projector.
The typical method for lighting is by diascopic illumination, which is lighting from behind. This
type of lighting is also called transmitted illumination when the specimen is translucent and light
can pass through it. If the specimen is opaque, then the light will not go through it, but will form
a profile of the specimen. Measuring of the sample can be done on the projection screen. A
profile projector may also have episcopic illumination which is light shining from above. This
useful in displaying bores or internal areas that may need to be measured.
9.2 Usage/Applications
Profile projector is widely used for complex shape stampings, gears, cams, threads and
comparing the measured contour model. It’s easy to use and high efficient. It is a commonly used
measurement of optical instruments. Thus, profile projector is widely used in major machinery
manufacturing including aviation, aerospace industry, watches and clocks, electronics,
instrumentation industry, research institutes and detection metering stations at all levels and etc.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 25
Manufacturing Process
CONCLUSION
The duration of internship went for 4 weeks of training on manufacturing process. It was a new
experience for me and all the interns present over there and i was very keen to have hands on
production process for the first time. The thing is i studied about the machines only in text books,
but this internship helped me to learn lot of things about production process in practically. It was
over all new experiences for me and also enjoyed learning new things and new subjects. The
most enjoyable part of this internship course was practical sessions. The practical sessions
include hands on experience on machines and also they let me practice and how to handle and
working of the machines, it was just amazing work and finally it was a four week internship
which helped me lot to learn about the production process and how to use them.
Dept. of Mechanical Engg., RIT, Hassan 26
You might also like
- Nails Making GuideDocument61 pagesNails Making GuideDj Backspin254100% (1)
- KOLee Tool Grinder Owners ManualDocument139 pagesKOLee Tool Grinder Owners ManualJason Bowman100% (4)
- Workshop Practice Series 38 - Tool Cutter SharpeningDocument68 pagesWorkshop Practice Series 38 - Tool Cutter SharpeningWillian Maza100% (6)
- Quality in Construction ProjectsDocument179 pagesQuality in Construction ProjectsJaydeepDas100% (2)
- QM Week 2 Role of Q in OrganisationDocument20 pagesQM Week 2 Role of Q in OrganisationnadzirnasirNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management (TQM) - 3328 Words - Report ExampleDocument7 pagesTotal Quality Management (TQM) - 3328 Words - Report ExampleMuhammad Talha FayyazNo ratings yet
- Supply Management (CUSCM208) : Quality in PurchasingDocument30 pagesSupply Management (CUSCM208) : Quality in PurchasingSIMBARASHE MABHEKANo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of QualityDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts of QualityrohitcshettyNo ratings yet
- Systems and Quality Day2Document86 pagesSystems and Quality Day2Prof Daniel KitawNo ratings yet
- Quality PLNG Control Imp, Benchmarking SDDocument95 pagesQuality PLNG Control Imp, Benchmarking SDANKIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- TQM in Msil (Amit & Pranav)Document41 pagesTQM in Msil (Amit & Pranav)Amit AnandNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1api-723710078100% (1)
- Systems and Quality ElectromechanicalRDocument69 pagesSystems and Quality ElectromechanicalRProf Daniel KitawNo ratings yet
- Module-V Customer FocusDocument11 pagesModule-V Customer FocusPrashant JhaNo ratings yet
- Goods and Service Design: By: Weezie Kay O. Manucan and Bernie Joseph A. JiaoDocument50 pagesGoods and Service Design: By: Weezie Kay O. Manucan and Bernie Joseph A. JiaoJosef JiaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document66 pagesLecture 1Samriddhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument45 pagesUnit - INihal KocheNo ratings yet
- Marketing Quality Management (MRK 7010) Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesMarketing Quality Management (MRK 7010) Final Exam SolutionsGürkan SağlamNo ratings yet
- TQM QA Unit1Document9 pagesTQM QA Unit1akhshayamNo ratings yet
- Management of Quality The Quest For QualityDocument12 pagesManagement of Quality The Quest For QualityKelvin mwai100% (1)
- Apparel Quality Management: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyDocument13 pagesApparel Quality Management: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyBhaswati PandaNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Practices by TVS Group IndiaDocument19 pagesQuality Management Practices by TVS Group Indiasnata92No ratings yet
- Customer Focus AND SatisfacationDocument18 pagesCustomer Focus AND SatisfacationArslan SaleemNo ratings yet
- QM 0013Document7 pagesQM 0013Bhupendra KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Taguchi Loss FunctionDocument9 pagesTaguchi Loss FunctionSang PhanNo ratings yet
- Customer SatisfactionDocument28 pagesCustomer SatisfactionLeUqar Bico-Enriquez GabiaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management (TQM)Document9 pagesTotal Quality Management (TQM)grace1217No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document41 pagesChapter 1CALIPDAN, Roselyn D. (Lyn)No ratings yet
- Goods and Service DesignDocument16 pagesGoods and Service DesignJayvee Joble BigataNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlDocument25 pagesLecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlKayode Samuel80% (5)
- IIMB Project Final ReportDocument36 pagesIIMB Project Final ReportSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- TQM Unit 1 SBDocument21 pagesTQM Unit 1 SBViji LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1: SalamDocument12 pagesAssignment No. 1: Salamzia uddin khattakNo ratings yet
- Joseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality TrilogyDocument7 pagesJoseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality Trilogy07081988No ratings yet
- Joseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality TrilogyDocument7 pagesJoseph Juran: Happen by Accident" Gave Rise To The Quality TrilogyMadhuri HusrajNo ratings yet
- Otal Uality AnagementDocument143 pagesOtal Uality AnagementJohn Rex PanestanteNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting OmDocument18 pagesFactors Affecting Omerielle mejicoNo ratings yet
- World Class OperationDocument11 pagesWorld Class OperationAvisekh KumarNo ratings yet
- Software QualityDocument33 pagesSoftware QualityDevendra RaneNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument27 pagesQuality ManagementLloyd Allison QuintoNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 101 SG 1Document9 pagesCbmec 101 SG 1Heesung LeeNo ratings yet
- TQM AssignmentDocument15 pagesTQM Assignmentbryan cabarles100% (1)
- Sqa LecturesDocument21 pagesSqa LecturesVanessa SarahNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesTotal Quality Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Kaizen: /watch?v 0dZYC2XBF2UDocument13 pagesKaizen: /watch?v 0dZYC2XBF2UNoel NantesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 TQM ReportsDocument18 pagesTopic 1 TQM ReportsAida Ganituen100% (1)
- Lecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlDocument25 pagesLecture Note On Statistical Quality ControlGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesQuality ManagementMahajan ShashankNo ratings yet
- Reduce Cost of Poor Quality at Austin Engineering Company LTDDocument33 pagesReduce Cost of Poor Quality at Austin Engineering Company LTDpatel2431No ratings yet
- Importance of Quality in BusinessDocument3 pagesImportance of Quality in BusinessJennifer Andrea Pardo100% (1)
- QFD As A Tool For Business Excellence Through TQMDocument9 pagesQFD As A Tool For Business Excellence Through TQMseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- How The Kaizen and PokaDocument15 pagesHow The Kaizen and Pokashaista naazNo ratings yet
- MT 14 - Total Quality ManagementDocument43 pagesMT 14 - Total Quality ManagementRuíz Figueroa, Jean E.No ratings yet
- MGT311 Assignment 1Document7 pagesMGT311 Assignment 1Hut MutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document3 pagesChapter 7Cathy MamigoNo ratings yet
- TQM Module 1Document20 pagesTQM Module 1Jhan Reach EnagoNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa Kualitas Rekayasa Kualitas Pertemuan 4: Teknik IndustriDocument15 pagesRekayasa Kualitas Rekayasa Kualitas Pertemuan 4: Teknik IndustriDeni Deri SetianaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cost of QualityDocument44 pages2 Cost of QualityCASTRO, HANNAH CAMILLE E.No ratings yet
- CODE: DIM 1010 Production and Operation Management: AssignmentDocument16 pagesCODE: DIM 1010 Production and Operation Management: AssignmentChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Quality Control and Materials ManagementDocument39 pagesUnit-Iii: Quality Control and Materials ManagementLAKKANABOINA LAKSHMANARAONo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagemantDocument23 pagesTotal Quality ManagemantnajieyuyaNo ratings yet
- Grinding MachinesDocument11 pagesGrinding MachinesVikash Kumar Vimal100% (1)
- MX7 Brochure 2010Document8 pagesMX7 Brochure 2010Clement JohnNo ratings yet
- Materials Forming, Machining and Tribology Viktor P. AstakhovDocument200 pagesMaterials Forming, Machining and Tribology Viktor P. AstakhovZerina ČustovićNo ratings yet
- CNC Workshop Projects - CNCCookbook - Be A Better CNC'ErDocument24 pagesCNC Workshop Projects - CNCCookbook - Be A Better CNC'ErJondaNo ratings yet
- Drill Grinding With The PP-U3 Grinder Copy of The Deckel SO GrinderDocument14 pagesDrill Grinding With The PP-U3 Grinder Copy of The Deckel SO GrinderAndy L100% (1)
- AEC KumbakonamDocument29 pagesAEC KumbakonamArun DharmarajNo ratings yet
- ANCA FXLinear Brochure 2021Document20 pagesANCA FXLinear Brochure 2021Rodrigo Frasseto MicheliniNo ratings yet
- WTP-I - Module 5 Study MaterialDocument63 pagesWTP-I - Module 5 Study MaterialBea Daniella CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Auto Punch Die Tooling Grinder F6Document4 pagesAuto Punch Die Tooling Grinder F6AFAB Machinery and Tools LtdNo ratings yet
- Technology of Machine Tools: Universal Cutter and Tool GrinderDocument64 pagesTechnology of Machine Tools: Universal Cutter and Tool GrinderAnibal Daza100% (1)
- Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument13 pagesTool and Cutter GrinderUmair MypusakaNo ratings yet
- Tool & Cutter GrinderDocument64 pagesTool & Cutter GrinderAFIFAHZABIDI ZABIDINo ratings yet
- "©HAND Rapids" Grinders .: & Livomsstron CODocument42 pages"©HAND Rapids" Grinders .: & Livomsstron CONew100% (1)
- Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument6 pagesTool and Cutter GrinderNav Srinath100% (1)
- DrillDocument18 pagesDrillvivekNo ratings yet
- MT2 University Question PaperDocument4 pagesMT2 University Question PaperKrishnan VelavanNo ratings yet
- 00 CINCINNATI No 2 Radius Grinding AttachmentDocument4 pages00 CINCINNATI No 2 Radius Grinding AttachmentGilberto GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Cost-Effective CNC Grinding MachineDocument5 pagesThe Cost-Effective CNC Grinding MachineRodrigo Frasseto MicheliniNo ratings yet
- Model Engineers' Workshop 11.2021Document68 pagesModel Engineers' Workshop 11.2021Leapfrog100% (2)
- Nil Report EP LabDocument6 pagesNil Report EP LabCHANDRAPRAKASHNo ratings yet
- McTools ToolCutGrdDocument2 pagesMcTools ToolCutGrdabyzenNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Abrasive Processes and Gear Cutting: 4.1 GrindingDocument30 pagesUnit Iv Abrasive Processes and Gear Cutting: 4.1 Grindingrkscad11No ratings yet
- Practical 7Document2 pagesPractical 7AARSHNo ratings yet
- Rudrali Hitech - IM - 2020 - Unlocked - 1Document47 pagesRudrali Hitech - IM - 2020 - Unlocked - 1Rudrali HitechNo ratings yet
- Machine ShopDocument13 pagesMachine ShopAmin MalikNo ratings yet
- Machinist: 2 Year (Volume - I of II)Document146 pagesMachinist: 2 Year (Volume - I of II)irshadNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument276 pagesCompleteIonuts Sorin100% (1)