Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A Differentiation Strategy?
What Is A Differentiation Strategy?
Uploaded by
Antonio Marroquin looking uOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is A Differentiation Strategy?
What Is A Differentiation Strategy?
Uploaded by
Antonio Marroquin looking uCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a differentiation strategy?
A differentiation strategy is the opposite of a cost strategy. Rather
than providing customers with the same product as the competition
but at a lower cost, the company provides a different product.
This approach involves either a more sophisticated product or a
simpler product. To successfully use a differentiation strategy, your
customers must feel the difference in price is acceptable whether
value has been added to or taken away from the product. The
problem is working out what that difference should be.
What is a differentiation strategy?
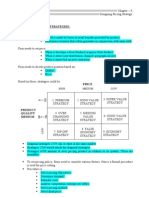
Determining the leading product
• For a given category of products, the leading product is the product consumers implicitly expect to see for
a given market at a given moment.
So the leading product for wine is generally a 750 ml bottle with a cork; and the leading product for breakfast
cereal is generally a 375 g packet.
• Two main factors determine a leading product:
-- its price
-- the value the customer attributes to it.
Differentiation strategies
With a leading product in mind, companies can obtain their competitive advantage in two ways.
• By designing a product of identical value to the leading product, but with a lower sale price—the cost strategy.
• Or by providing customers with a product which differs in both value and price from the leading product—the
differentiation strategy.
A differentiation strategy can be profitable only if it is accepted by the market. A true differentiation strategy is one
for which the product has differences other than pricing when compared with the leading product. The differences
must be perceived as such by a significant proportion of the market.
Differentiation: how and why?
Going upmarket
This is when you produce a higher-value product than the leading product, at a higher price.
Here is what makes a differentiation strategy successful:
• Increasing prices more than costs. An increase in value generally causes costs to rise. The increase must be offset
by an increase in price or higher volumes.
• The characteristics of the product or service (quality, performance and design) must be perceived as superior
to those of competing products or services. Customers must accept this implicitly by agreeing to pay a premium
to obtain those characteristics. Because of its superiority, an upmarket product also gives the buyer a feeling of
prestige: it becomes a status symbol.
The contents of this page are the property of CrossKnowledge.
1/
Any reproduction or representation for non-private use is strictly forbidden. 2
A higher-value product
Value at a higher price.
“Upmarket” strategy
Value
Price Price
Going downmarket
This involves selling a product for which the perceived value is lower than that of competing products.
A downmarket strategy is essentially aimed at customers who cannot or will not buy a higher-value product.
To succeed, a downmarket strategy should:
• Involve products with a sufficiently lower price so as to justify the lower value. As an example, prices in hard-
discount retail outlets are seen by customers as being low enough to justify restricted choice and no service.
• Reduce costs more than prices. Cost differentials generated by a differentiation strategy should be beneficial to
the company.
There is a difference between a cost strategy and a downmarket strategy.
• A cost strategy maintains the level of value perceived by the customer, but reduces prices via a reduction in
costs.
• A downmarket strategy is founded on the simultaneous but non-symmetrical reduction of price and value.
Value
Cost
strategy
“Downmarket”
strategy
Value
Price Price
The alternative: low price/high value
• There is an alternative to sophistication and simplification: providing a value premium at a lower price.
• If done well, this alternative strategy can lead to a competitive advantage that competitors will find extremely
difficult to match.
The contents of this page are the property of CrossKnowledge.
2/
Any reproduction or representation for non-private use is strictly forbidden. 2
You might also like
- Test Bank For Foundations and Adult Health Nursing 7th Edition by Kim Cooper Kelly GosnellDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Foundations and Adult Health Nursing 7th Edition by Kim Cooper Kelly Gosnellgomeerrorist.g9vfq698% (51)
- Edexcel GCSE Business Practice Exam Paper 2aDocument20 pagesEdexcel GCSE Business Practice Exam Paper 2aMohamedNo ratings yet
- Volvo Global Deviation FormDocument3 pagesVolvo Global Deviation FormAnonymous oxdF07Ot0ENo ratings yet
- Ch-9 (Designing Pricing Strategies)Document17 pagesCh-9 (Designing Pricing Strategies)api-19958143No ratings yet
- 4.5 The Seven Ps of The Marketing Mix PriceDocument15 pages4.5 The Seven Ps of The Marketing Mix PriceAlexia Pachan CollNo ratings yet
- Marketing Finance 101 For Brand ManagersDocument23 pagesMarketing Finance 101 For Brand ManagersPramod Surya MakkenaNo ratings yet
- STRM 05Document44 pagesSTRM 05Professor Dr. Md. Atiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument64 pagesPricing Strategybertjohnvillavert14No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Marketing Mix PriceDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Marketing Mix Pricenewempir11No ratings yet
- Pricing Decisions (Objectives, Price Determinants, Pricing Methods)Document32 pagesPricing Decisions (Objectives, Price Determinants, Pricing Methods)ravi anandNo ratings yet
- CH 13 - The Marketing Mix - PriceDocument22 pagesCH 13 - The Marketing Mix - PriceBlack arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- Pricing For Competetive Advantage Rahul SahaiDocument36 pagesPricing For Competetive Advantage Rahul Sahaish00nyaNo ratings yet
- Pricing Decisions & StrategiesDocument23 pagesPricing Decisions & StrategiesdeepakrelhanNo ratings yet
- Pricing: PriceDocument1 pagePricing: Priceruby.shipseyNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategyDocument12 pagesMarketing StrategySajuti RumnazNo ratings yet
- 2021-22 1st Price Strategy General Pricing StrategiesDocument16 pages2021-22 1st Price Strategy General Pricing StrategiesglennNo ratings yet
- 2021-22 1st Price Strategy General Pricing StrategiesDocument16 pages2021-22 1st Price Strategy General Pricing StrategiesglennNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pricing Strategy What Is Price ?Document8 pagesIntroduction To Pricing Strategy What Is Price ?Marvin Rabanal IgnacioNo ratings yet
- PRICEDocument57 pagesPRICEJames BuslonNo ratings yet
- Strategic Pricing Final PresentationDocument27 pagesStrategic Pricing Final PresentationBMS MAHARASHTRA COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Manajemen PemasaranDocument33 pagesChapter 16 Manajemen PemasaranTimotius SurantoNo ratings yet
- 4 - PricingDocument11 pages4 - PricingAaron GuoNo ratings yet
- Session 5Document6 pagesSession 5Andrea Nicole CachoNo ratings yet
- Pricing in Persian LanguageDocument72 pagesPricing in Persian LanguageAlireza FarjamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Strategic ChoiceDocument39 pagesChapter 5 Strategic Choiceprasad guthiNo ratings yet
- Marketing 8Document31 pagesMarketing 8AliNo ratings yet
- Business Chapter 12 Section 3.3 Marketing Mix - Product and PriceDocument16 pagesBusiness Chapter 12 Section 3.3 Marketing Mix - Product and PriceJuné MaraisNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument14 pagesPricing StrategyMaddu VelangiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 SDocument24 pagesLecture 1 SMarie SarangayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Marketing ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 6 Marketing ManagementhidayahrosidiNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategy Worksheet: PurposeDocument8 pagesPricing Strategy Worksheet: PurposeN. AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Price and Price StrategiesDocument18 pagesPrice and Price Strategiesrufaro senpaiNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategiesDocument29 pagesPricing Strategiesjawahar babu0% (1)
- Business Studies Notes 4.3.4 PRICE MIX NAME: - DATE: - The Second P - PriceDocument8 pagesBusiness Studies Notes 4.3.4 PRICE MIX NAME: - DATE: - The Second P - Priceabdulrahman alalawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 The Marketing Mix - Pricing StrategiesDocument14 pagesChapter 19 The Marketing Mix - Pricing StrategiesKoshla RentonNo ratings yet
- Developing Pricing StrategyDocument44 pagesDeveloping Pricing StrategyFaria Aktar TonnyNo ratings yet
- SM 11 PDFDocument45 pagesSM 11 PDFSamridh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Managing PriceDocument56 pagesChapter 6 - Managing PriceShafayet JamilNo ratings yet
- Institute of Management & Sciences Pakaims: Presentation of Strategic Marketing byDocument27 pagesInstitute of Management & Sciences Pakaims: Presentation of Strategic Marketing bymanisha maniNo ratings yet
- Saksham PricingDocument28 pagesSaksham PricingTemp MailNo ratings yet
- 77 Bowman's ClockDocument12 pages77 Bowman's ClockGeorge ButlerNo ratings yet
- Designing Pricing Strategies and ProgramsDocument17 pagesDesigning Pricing Strategies and ProgramsRiazel OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategiesDocument58 pagesPricing StrategiesMark K. Eapen100% (2)
- Class 7 - New - Part 1Document47 pagesClass 7 - New - Part 1daniel neyraNo ratings yet
- IBP S7 Market AnalysisDocument36 pagesIBP S7 Market Analysisjose vergarayNo ratings yet
- Marketing I CHAPTERS 10, 11 & 12Document8 pagesMarketing I CHAPTERS 10, 11 & 12Alejandra Oliver RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MKTG 2001 LECTURE 8-PricingDocument23 pagesMKTG 2001 LECTURE 8-PricingSilke HerbertNo ratings yet
- Tết - Vietnamese Lunar New Year by SlidesgoDocument61 pagesTết - Vietnamese Lunar New Year by Slidesgotn969926No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Slide 8 - Lecture 7Document38 pagesUnit 2 - Slide 8 - Lecture 7Quân TrầnNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument22 pagesPriceNicolasNo ratings yet
- Business Level StrategyDocument28 pagesBusiness Level Strategydjayaram144No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 MKTDocument4 pagesChapter 7 MKTbouchahdamajd7No ratings yet
- Marketing Management Chapter 9Document22 pagesMarketing Management Chapter 9Jean AlbaciteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Business-Level StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 5: Business-Level StrategyNadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- BUS 311 Chapter 10 and 11 NewDocument45 pagesBUS 311 Chapter 10 and 11 Newosmanincekara2002No ratings yet
- Chap 5 MCQDocument8 pagesChap 5 MCQethanvampireNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Document21 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?RajatNo ratings yet
- SM-4 - Generic StrategiesDocument34 pagesSM-4 - Generic StrategiesMedha WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Management of Marketing Mix: Pricing Strategies & Distribution Strategies and ChannelsDocument18 pagesManagement of Marketing Mix: Pricing Strategies & Distribution Strategies and ChannelsMd. Nafis KhanNo ratings yet
- Saceda - Lipayon Chapter 10 PricingDocument26 pagesSaceda - Lipayon Chapter 10 PricingBebe Recah SacedaNo ratings yet
- STM ch5Document18 pagesSTM ch5muhammad atifNo ratings yet
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1From EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1No ratings yet
- 2016.05.03+Revenue+Trifecta 30+Profit+Multipliers+ChecklistDocument22 pages2016.05.03+Revenue+Trifecta 30+Profit+Multipliers+ChecklistHayiath QureshiNo ratings yet
- Case 08 16e, Oct 20th, 2023Document4 pagesCase 08 16e, Oct 20th, 2023Itzel OvalleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - 4Ps in EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - 4Ps in EntrepreneurshipAldrin VerganoNo ratings yet
- Vinamilk's Supply Chain and The Small Farmers' Involvement: Luc Thi Thu HuongDocument9 pagesVinamilk's Supply Chain and The Small Farmers' Involvement: Luc Thi Thu HuongĐức MinhNo ratings yet
- PTCL ReportDocument199 pagesPTCL ReportSalman SaeedNo ratings yet
- Bizmanualz Human Resources Policies and Procedures SampleDocument11 pagesBizmanualz Human Resources Policies and Procedures SampleIzatul AzmaNo ratings yet
- Radio MirchiDocument15 pagesRadio MirchiManmeet SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Dy - Supdt .AccountsDocument9 pagesDy - Supdt .AccountsKhushi BhadraNo ratings yet
- TikTok Response To Sen Blackburn Et Al June 30Document8 pagesTikTok Response To Sen Blackburn Et Al June 30TechCrunchNo ratings yet
- Ivana Telečki: Unit 1 Careeres / Exercise 1Document4 pagesIvana Telečki: Unit 1 Careeres / Exercise 1benjaminsaraNo ratings yet
- Internship PresentationDocument11 pagesInternship Presentationrimsha zahidNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Recuriting and Selection in ParleDocument78 pagesProject Report On Recuriting and Selection in ParleRoyal Projects67% (12)
- BACLIAT - Business AdaptaitonDocument32 pagesBACLIAT - Business Adaptaitonclimateready.org.ukNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting Spring 2022 Bba 1-A & B Worksheet No 1: Basic Accounting Equation - Identification of AccountsDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Accounting Spring 2022 Bba 1-A & B Worksheet No 1: Basic Accounting Equation - Identification of AccountsYumna TauqeerNo ratings yet
- Shoji DesignDocument12 pagesShoji DesignNuraini JafarNo ratings yet
- Adaptability of SHRM in The Context of PakistanDocument6 pagesAdaptability of SHRM in The Context of PakistanMuhammad Salman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Notes in Other Percentage TaxDocument2 pagesNotes in Other Percentage TaxNovie Marie Balbin AnitNo ratings yet
- Staff StructureDocument3 pagesStaff StructuresaleenaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Toyota Strategy SPIDocument12 pagesAssignment On Toyota Strategy SPImjaiqbal100% (1)
- Internet Banking History and StrategiesDocument129 pagesInternet Banking History and StrategiesSuny PaswanNo ratings yet
- Oracle ERP Cloud Service Integrations OverviewDocument12 pagesOracle ERP Cloud Service Integrations OverviewSergeyNo ratings yet
- What Is Reverse Logistics?: Supply Chain ManagementDocument9 pagesWhat Is Reverse Logistics?: Supply Chain ManagementAnush RaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment PSC OsheDocument7 pagesAssignment PSC OsheSiti sNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation (Company Update)Document46 pagesInvestor Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Exponent Thesis by AhkDocument2 pagesExponent Thesis by Ahkkotharik52No ratings yet
- Comparative Vs Competitive AdvantageDocument19 pagesComparative Vs Competitive AdvantageSuntari CakSoenNo ratings yet
- Insurance TermsDocument6 pagesInsurance TermsJoseph WilliamsNo ratings yet