Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsAdventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean Stem
Adventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean Stem
Uploaded by
Aprille CastroThe document discusses different types of modifications to roots and stems in plants. It describes modifications like corms, tubers, bulbs and rhizomes that occur in underground storage stems. It also lists different stem types based on habitat, such as aerial herbaceous stems, woody stems, and underground stems like corms and tubers. Additionally, it defines various stem modifications and habits including boloes, caudex, stolons, scapes and different types of projections like prickles, spines, thorns and bristles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapAstha Agrawal90% (10)
- Botany Plant MorphologyDocument42 pagesBotany Plant MorphologyNigel Nicholls100% (7)
- 64f05e275bb8d20018edfdf5 - ## - Morphology of Flowering Plants - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Document4 pages64f05e275bb8d20018edfdf5 - ## - Morphology of Flowering Plants - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Sakshi MakkarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- Ustet ReviewerDocument16 pagesUstet ReviewerVinzynt Isler Carmona100% (19)
- Table FinalDocument3 pagesTable Finallegendsac2000No ratings yet
- LKM 3b Morfologi Batang - Id.enDocument10 pagesLKM 3b Morfologi Batang - Id.enaura albiziaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2B Agr3101Document52 pagesTopic 2B Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology 2020Document10 pagesPlant Morphology 2020Dipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Botany Lecture Finals Stems: © Kamilah Lasco BS Biology 1-3Document47 pagesBotany Lecture Finals Stems: © Kamilah Lasco BS Biology 1-3Paula LibaoNo ratings yet
- AM Morphology FamiliesDocument11 pagesAM Morphology Familiestechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Bot - New FamiliesDocument3 pagesBot - New Familiesatiyabegum282No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- VegetationDocument14 pagesVegetationChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- NCERT Filtrate 12 PAGESDocument11 pagesNCERT Filtrate 12 PAGESKabir ThakurNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument40 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantschdhrysudeepNo ratings yet
- BOT LEC CHAPTER 23 AngiospermsDocument6 pagesBOT LEC CHAPTER 23 AngiospermsAUBREY JOY SALENo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Botany PPT 1Document60 pagesBotany PPT 1SidNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument23 pagesMorphologysittimunisaasaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument13 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsTanishq AroraNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument10 pagesMorphologyaaradhyadevsharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Organs MarmolejoDocument8 pagesPlant Organs Marmolejojoelmarmolejo38No ratings yet
- The Stem and LeavesDocument2 pagesThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNo ratings yet
- Different Tissue Types and Organ Systems in PlantsDocument6 pagesDifferent Tissue Types and Organ Systems in Plantsashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Morphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesMorphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAyako HayashidaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of Flowering PlantsNeil SNo ratings yet
- Study of Habit Diversity in AngiospermsDocument5 pagesStudy of Habit Diversity in Angiospermsrs5939900No ratings yet
- L4-Stem MorphologyDocument57 pagesL4-Stem MorphologySleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantDocument41 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Family SystematicsDocument5 pagesFamily SystematicsJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Botlec The Stems 4Document10 pagesBotlec The Stems 4Jeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Botany: Stems ReviewerDocument2 pagesBotany: Stems Reviewera yellow flowerNo ratings yet
- MorfhologyDocument60 pagesMorfhologyMohd. FarhanNo ratings yet
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocument18 pagesTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- 1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryDocument38 pages1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryManjunath K JNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Organismal Body of PlantsDocument20 pagesLesson1 Organismal Body of PlantsKyle MantoNo ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS (CONTENT)Document37 pagesCHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS (CONTENT)kevenliamwilliam.exampointNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Plants MorphologyDocument3 pagesPlants MorphologyNovilyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Leaves and StemsDocument77 pagesWeek 8 - Leaves and StemsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument5 pagesMorphologyPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- Bagi 'StemsDocument54 pagesBagi 'StemsAlif tiyyah.rNo ratings yet
- TALLODocument2 pagesTALLOvictoria lopez quesquenNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument4 pagesMorphologytarunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Forestry - Module 3Document31 pagesIntroduction To Forestry - Module 3almoiteofelia18No ratings yet
- Dizon - Module 5Document9 pagesDizon - Module 5Penelopy DizonNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plantsaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Roots and StemsDocument14 pagesRoots and StemsSN - 11CC 678197 Meadowvale SSNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and WhiteDocument96 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and Whiterivera hutchNo ratings yet
- Flora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeFrom EverandFlora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeNo ratings yet
- Mosses and Liverworts of Rainforest in Tasmania and South-eastern AustraliaFrom EverandMosses and Liverworts of Rainforest in Tasmania and South-eastern AustraliaNo ratings yet
- Invasive Flora of the West Coast: British Columbia and the Pacific NorthwestFrom EverandInvasive Flora of the West Coast: British Columbia and the Pacific NorthwestNo ratings yet
Adventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean Stem
Adventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean Stem
Uploaded by
Aprille Castro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesThe document discusses different types of modifications to roots and stems in plants. It describes modifications like corms, tubers, bulbs and rhizomes that occur in underground storage stems. It also lists different stem types based on habitat, such as aerial herbaceous stems, woody stems, and underground stems like corms and tubers. Additionally, it defines various stem modifications and habits including boloes, caudex, stolons, scapes and different types of projections like prickles, spines, thorns and bristles.
Original Description:
Original Title
ADVENTITIOUS ROOTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of modifications to roots and stems in plants. It describes modifications like corms, tubers, bulbs and rhizomes that occur in underground storage stems. It also lists different stem types based on habitat, such as aerial herbaceous stems, woody stems, and underground stems like corms and tubers. Additionally, it defines various stem modifications and habits including boloes, caudex, stolons, scapes and different types of projections like prickles, spines, thorns and bristles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesAdventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean Stem
Adventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean Stem
Uploaded by
Aprille CastroThe document discusses different types of modifications to roots and stems in plants. It describes modifications like corms, tubers, bulbs and rhizomes that occur in underground storage stems. It also lists different stem types based on habitat, such as aerial herbaceous stems, woody stems, and underground stems like corms and tubers. Additionally, it defines various stem modifications and habits including boloes, caudex, stolons, scapes and different types of projections like prickles, spines, thorns and bristles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
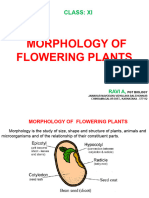
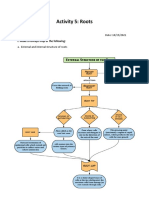
ADVENTITIOUS ROOTS
MODIFICATIONS OF TAP ROOT (FOOD
STORAGE)
MODIFICATION OF FIBROUS ROOT
MODIFICATION OF THE ADVENTITIOUS
(STORAGE)
STEM
TYPES ACCORDING TO PLACE OF GROWTH
1) UNDERGROUND/ SUBTERRANEAN STEM
- Food storage
Corm – papery layer ex. garlic
Tuber – the eyes/nodes give rise to roots
ex. potato
Bulb – onion
Rhizome – adventitious ex. ginger
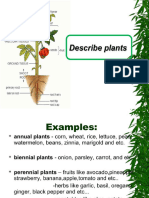
2) AERIAL STEMS
- Herbaceous
- Woody – secondary growth
- Suffrutescent – combination of wood and
herbaceous
TYPES ACCORDING TO HABIT
BOLES – dicot stems become unbranched, erect
CAUDEX – monocot, unbranched, erect, ex. palm
STOLONs/runners – for propagation,
reproduction, ex. strawberry
CLADOPHYLL – opuntia (cactus), leaf-like stem,
for water storage
CULM – hollow space inside the stem (internodes),
1) Erect capacity to store water, ex. Bamboo
2) Ascending/Assurgent
3) Climbing/Twining SCAPE – can carry compound flowers like dandelion, tulip
4) Procumbent - - Erect, unbranched, leafless stem, are usually long like
5) Decumbent spring onions
6) Repent
PRICKLES – roses, epidermal in origin, easily detachable
SPINES – associated with leaves, petiolar, citrus
THORNS – associated with stem, extension or vascular part
BRISTLES – occur multiply, epidermal
You might also like
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapAstha Agrawal90% (10)
- Botany Plant MorphologyDocument42 pagesBotany Plant MorphologyNigel Nicholls100% (7)
- 64f05e275bb8d20018edfdf5 - ## - Morphology of Flowering Plants - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Document4 pages64f05e275bb8d20018edfdf5 - ## - Morphology of Flowering Plants - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Sakshi MakkarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- Ustet ReviewerDocument16 pagesUstet ReviewerVinzynt Isler Carmona100% (19)
- Table FinalDocument3 pagesTable Finallegendsac2000No ratings yet
- LKM 3b Morfologi Batang - Id.enDocument10 pagesLKM 3b Morfologi Batang - Id.enaura albiziaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2B Agr3101Document52 pagesTopic 2B Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology 2020Document10 pagesPlant Morphology 2020Dipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Botany Lecture Finals Stems: © Kamilah Lasco BS Biology 1-3Document47 pagesBotany Lecture Finals Stems: © Kamilah Lasco BS Biology 1-3Paula LibaoNo ratings yet
- AM Morphology FamiliesDocument11 pagesAM Morphology Familiestechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Bot - New FamiliesDocument3 pagesBot - New Familiesatiyabegum282No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- VegetationDocument14 pagesVegetationChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- NCERT Filtrate 12 PAGESDocument11 pagesNCERT Filtrate 12 PAGESKabir ThakurNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument40 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantschdhrysudeepNo ratings yet
- BOT LEC CHAPTER 23 AngiospermsDocument6 pagesBOT LEC CHAPTER 23 AngiospermsAUBREY JOY SALENo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Botany PPT 1Document60 pagesBotany PPT 1SidNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument23 pagesMorphologysittimunisaasaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument13 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsTanishq AroraNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument10 pagesMorphologyaaradhyadevsharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Organs MarmolejoDocument8 pagesPlant Organs Marmolejojoelmarmolejo38No ratings yet
- The Stem and LeavesDocument2 pagesThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNo ratings yet
- Different Tissue Types and Organ Systems in PlantsDocument6 pagesDifferent Tissue Types and Organ Systems in Plantsashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Morphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesMorphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAyako HayashidaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of Flowering PlantsNeil SNo ratings yet
- Study of Habit Diversity in AngiospermsDocument5 pagesStudy of Habit Diversity in Angiospermsrs5939900No ratings yet
- L4-Stem MorphologyDocument57 pagesL4-Stem MorphologySleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantDocument41 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Family SystematicsDocument5 pagesFamily SystematicsJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Botlec The Stems 4Document10 pagesBotlec The Stems 4Jeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Botany: Stems ReviewerDocument2 pagesBotany: Stems Reviewera yellow flowerNo ratings yet
- MorfhologyDocument60 pagesMorfhologyMohd. FarhanNo ratings yet
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocument18 pagesTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- 1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryDocument38 pages1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryManjunath K JNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Organismal Body of PlantsDocument20 pagesLesson1 Organismal Body of PlantsKyle MantoNo ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS (CONTENT)Document37 pagesCHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS (CONTENT)kevenliamwilliam.exampointNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Plants MorphologyDocument3 pagesPlants MorphologyNovilyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Leaves and StemsDocument77 pagesWeek 8 - Leaves and StemsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument5 pagesMorphologyPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- Bagi 'StemsDocument54 pagesBagi 'StemsAlif tiyyah.rNo ratings yet
- TALLODocument2 pagesTALLOvictoria lopez quesquenNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument4 pagesMorphologytarunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Forestry - Module 3Document31 pagesIntroduction To Forestry - Module 3almoiteofelia18No ratings yet
- Dizon - Module 5Document9 pagesDizon - Module 5Penelopy DizonNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plantsaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Roots and StemsDocument14 pagesRoots and StemsSN - 11CC 678197 Meadowvale SSNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and WhiteDocument96 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and Whiterivera hutchNo ratings yet
- Flora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeFrom EverandFlora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeNo ratings yet
- Mosses and Liverworts of Rainforest in Tasmania and South-eastern AustraliaFrom EverandMosses and Liverworts of Rainforest in Tasmania and South-eastern AustraliaNo ratings yet
- Invasive Flora of the West Coast: British Columbia and the Pacific NorthwestFrom EverandInvasive Flora of the West Coast: British Columbia and the Pacific NorthwestNo ratings yet