Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment # 2 Submitted To: Sir Tahir Mehmmood Submitted By: Class - Section: BBA (3) - B
Assignment # 2 Submitted To: Sir Tahir Mehmmood Submitted By: Class - Section: BBA (3) - B
Uploaded by
Ahmadshabir ShabirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment # 2 Submitted To: Sir Tahir Mehmmood Submitted By: Class - Section: BBA (3) - B
Assignment # 2 Submitted To: Sir Tahir Mehmmood Submitted By: Class - Section: BBA (3) - B
Uploaded by
Ahmadshabir ShabirCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT # 2
Submitted to: Sir Tahir Mehmmood
Submitted by: Ahmad Shabbir
ROLLNO#LCM-3576
Class – Section: BBA (3)-B
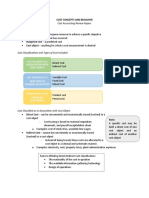
Cost behavior is an indicator of how a cost will change in total when there is a change in some
activity. In cost accounting and managerial accounting, three types of cost behavior are
usually discussed:
Fixed Costs
Fixed cost are those which do not change with the level of activity
within the relevant range. These costs will be incurred even if no units
are produced. For example rent expense, straight-line depreciation
expense, etc.
FIXED COST PER UNIT decreases with increase in production.
Following example explains this fact:
Total Fixed Cost $30,000 $30,000 $30,000
÷ Units Produced 5,000 10,000 15,000
Fixed Cost per
$6.00 $3.00 $2.00
Unit
Variable Costs
Variable costs change in direct proportion to the level of production.
This means that total variable cost increase when more units are
produced and decreases when less units are produced. Average
variable cost i.e. variable cost per unit is constant . For example
Total Variable Cost $10,000 $20,000 $30,000
÷ Units Produced 5,000 10,000 15,000
Variable Cost per
$2.00 $2.00 $2.00
Unit
Mixed Costs
Mixed costs or semi-variable costs have properties of both fixed and
variable costs due to the presence of both variable and fixed
components in them. An example of mixed cost is telephone expense
because it usually consists of a fixed component such as line rent and
fixed subscription charges as well as variable cost charged per minute
cost. Another mixed cost example is delivery cost which has a fixed
component of depreciation cost of trucks and a variable component of
fuel expense.
Since mixed cost figures are not useful in their raw form, therefore
they are split into their fixed and variable components by using cost
behavior analysis techniques such as High-Low Method, Scatter Graph
Method and Regression Analysis.
The following table shows a comparison of different costs
classifications based on behavior:
Category Fixed Costs Variable Costs Mixed Costs
Total cost Constant Changes Change with output
proportionately but not
with output proportionately
Decreases with
Decreases
Cost per increase in output but
with increase Constant
unit less than the decrease
in output
in fixed cost per unit
Plant Telecommunication
Fuel expense,
depreciation, costs, senior
Examples wages, raw
property management salaries,
materials
taxes transportation cost
You might also like
- Kwazimu Guest House AccountsDocument11 pagesKwazimu Guest House AccountsThoboloMaun100% (1)
- M ASIF LCM 3710 SCMDocument3 pagesM ASIF LCM 3710 SCMAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis Coles GroupDocument5 pagesFinancial Analysis Coles GroupAmmar HassanNo ratings yet
- MR. Rosiak PerpetualDocument13 pagesMR. Rosiak PerpetualSelfi Riani100% (2)
- Cattle Fattening Business Plan ContentsDocument3 pagesCattle Fattening Business Plan ContentsKhalid Firoz94% (17)
- Financial Management Syllabus - Madras University - B.com CA - 2019Document2 pagesFinancial Management Syllabus - Madras University - B.com CA - 2019jeganrajrajNo ratings yet
- FCFF Vs FCFE Reconciliation TemplateDocument2 pagesFCFF Vs FCFE Reconciliation TemplateLalit KheskwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cost Volume and Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Cost Volume and Cost Volume Profit AnalysisGabai AsaiNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter20Document40 pages4 Chapter20154 ahmed ehabNo ratings yet
- 1b - Cost Concepts and Terminology - 14sept06Document31 pages1b - Cost Concepts and Terminology - 14sept06Zaid AnsariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document5 pagesLecture 01Yen RozarioNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document48 pagesCH 2Sadia MunawarNo ratings yet
- How Costs Vary With Output in The Short Run and in The Long RunDocument69 pagesHow Costs Vary With Output in The Short Run and in The Long RunKavisha RatraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ReviewDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Reviewណយ សុវណ្ណNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior:Analysis and UseDocument4 pagesCost Behavior:Analysis and UseFerial FerniawanNo ratings yet
- END3972 Week2 v2Document27 pagesEND3972 Week2 v2Enes TürksalNo ratings yet
- 02-Cost-Terms-Concepts-and-Behavior - Managerial AccountingDocument58 pages02-Cost-Terms-Concepts-and-Behavior - Managerial Accountingsabrina jane falconNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument63 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisJunaid KhalidNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing and Absorption CostingDocument10 pagesMarginal Costing and Absorption Costingferos100% (12)
- Lecture 7 Theory of CostDocument32 pagesLecture 7 Theory of CostMd. Didarul AlamNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing of Larsen ToubroDocument31 pagesMarginal Costing of Larsen ToubroShubashPoojariNo ratings yet
- Section CDocument86 pagesSection CaspirantuscmaNo ratings yet
- Most Common Frameworks - ProfitabilityDocument13 pagesMost Common Frameworks - Profitabilitynaresh veesam1No ratings yet
- Marginal CostingDocument33 pagesMarginal CostingYaminiDevpuraSomaniNo ratings yet
- ACC202 SU6 Jan2020Document31 pagesACC202 SU6 Jan2020hashtagjxNo ratings yet
- Cost Terms, Concepts, and ClassificationDocument27 pagesCost Terms, Concepts, and ClassificationParadise VillageNo ratings yet
- Cost in EconomicsDocument11 pagesCost in EconomicsRail FanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cost Concepts and BehaviorsDocument4 pages2 - Cost Concepts and BehaviorsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 8 Marginal CostingDocument50 pages8 Marginal CostingBhagaban DasNo ratings yet
- types of costsDocument56 pagestypes of costsvamsibuNo ratings yet
- 边际成本Marginal costDocument9 pages边际成本Marginal costepicpinnNo ratings yet
- Slide Chapter 2Document65 pagesSlide Chapter 2daoviethung29No ratings yet
- CVPDocument75 pagesCVPAina Syazwana ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- MALec Batch 2Document105 pagesMALec Batch 2duong duongNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document21 pagesCH 5hohrmpm2No ratings yet
- BMT1009 Production and Operations Management BMT1009 Production and Operations ManagementDocument37 pagesBMT1009 Production and Operations Management BMT1009 Production and Operations ManagementYash PathakNo ratings yet
- 2MATypes of CostDocument44 pages2MATypes of CostAARUSHI NARANG-DMNo ratings yet
- 10-CVP AnalysisDocument77 pages10-CVP AnalysissurangauorNo ratings yet
- CMA CH 1 - Cost Concept, Behavior and Estimations March 2019-2Document58 pagesCMA CH 1 - Cost Concept, Behavior and Estimations March 2019-2Henok FikaduNo ratings yet
- Session Topic 1: Production & Cost Analysis Learning OutcomesDocument11 pagesSession Topic 1: Production & Cost Analysis Learning OutcomesMeian De JesusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior: Analysis and UseDocument66 pagesCost Behavior: Analysis and UseJayson ReyesNo ratings yet
- Marginal CostDocument3 pagesMarginal CostUdhaya SangariNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cost Terms and PurposesDocument33 pagesAn Introduction To Cost Terms and PurposesCarrie ChanNo ratings yet
- Cost - Volume - ProfitDocument52 pagesCost - Volume - ProfitsueernNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and Analysis: Management Advisory ServicesDocument7 pagesCost Concepts and Analysis: Management Advisory ServicesAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- BMT1009 Production and Operations Management: Unit-IIDocument37 pagesBMT1009 Production and Operations Management: Unit-IIKartik ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing and Absorption CostingDocument12 pagesMarginal Costing and Absorption CostingStili MwasileNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing IntroductionDocument5 pagesMarginal Costing IntroductionPavan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Be601 Lecture7 (Module6 CVP) 03nov21 ClassDocument36 pagesBe601 Lecture7 (Module6 CVP) 03nov21 ClassMohammad Musa AbidNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document25 pagesModule 6prabodhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2Ngọc Minh Đỗ ChâuNo ratings yet
- CostDocument46 pagesCostsatya narayana100% (1)
- New MicrosoftDocument16 pagesNew MicrosoftarpanavsNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument28 pagesCVP AnalysisSurender SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Aklil TeganewNo ratings yet
- Act 202. Chap002Document18 pagesAct 202. Chap002Mahmudulhasan PallabNo ratings yet
- Final AssignmentDocument19 pagesFinal AssignmentManoj JainNo ratings yet
- Classification of CostDocument2 pagesClassification of CostRizve AhmedNo ratings yet
- MS03 - Cost Behavior and Cost Classification PDFDocument12 pagesMS03 - Cost Behavior and Cost Classification PDFTina PascualNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume ProvitDocument57 pagesCost Volume ProvitannisaNo ratings yet
- Design CostDocument21 pagesDesign CostDr. Ashish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Classification of CostDocument33 pagesClassification of CostGeet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cost Behavior - Scatter & High-LowDocument37 pagesModule 2 Cost Behavior - Scatter & High-LowColeng RiveraNo ratings yet
- CA&C 02 - Handout - 1 PDFDocument10 pagesCA&C 02 - Handout - 1 PDFMelchie RepospoloNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Culture and Its Differences - PPTDocument33 pagesCulture and Its Differences - PPTAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- National University of Modern Languages Department of Management SciencesDocument12 pagesNational University of Modern Languages Department of Management SciencesAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Nature of Negotiable Instruments: Meaning & DefinitionDocument9 pagesNature of Negotiable Instruments: Meaning & DefinitionAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsDocument9 pagesHofstede's Cultural DimensionsAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Bba OutlinesDocument195 pagesBba OutlinesAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Understanding Groups and TeamsDocument40 pagesUnderstanding Groups and TeamsAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instrument ACT 1881: PriyankaDocument12 pagesNegotiable Instrument ACT 1881: PriyankaAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document19 pagesCH 2Ahmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Strategic Customer Relationship ManagementDocument17 pagesStrategic Customer Relationship ManagementAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan of Pepsi & Failure of Pepsi TwistDocument21 pagesMarketing Plan of Pepsi & Failure of Pepsi TwistAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Asma ShahidDocument9 pagesAsma ShahidAhmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Bba (Hons. Section B' Semester V 19 - March-2021Document11 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Bba (Hons. Section B' Semester V 19 - March-2021Ahmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Kotler Pom16e Inppt 20-1Document46 pagesKotler Pom16e Inppt 20-1Ahmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Bba (Hons. Section B' Semester V 19 - March-2021Document11 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Bba (Hons. Section B' Semester V 19 - March-2021Ahmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Assignment #5: Ahmad Shabbir ROLLNO#LCM-3576Document7 pagesAssignment #5: Ahmad Shabbir ROLLNO#LCM-3576Ahmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Asma Shahid (Supply Chain Management) Lcm-3756Document6 pagesAsma Shahid (Supply Chain Management) Lcm-3756Ahmadshabir ShabirNo ratings yet
- Quant QuestionsDocument11 pagesQuant Questionspriyanka goenkaNo ratings yet
- Phi27106 ch03 094 145 Revised1Document52 pagesPhi27106 ch03 094 145 Revised1xxmbetaNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Revision 1Document4 pagesCH 10 Revision 1Deeb. DeebNo ratings yet
- Errors: Objectives: Define and Identify Types of Errors. Give Examples of ErrorsDocument31 pagesErrors: Objectives: Define and Identify Types of Errors. Give Examples of ErrorsPang SiulienNo ratings yet
- Far410 Lesson Plan Oct 2023 - Feb 2024Document2 pagesFar410 Lesson Plan Oct 2023 - Feb 2024syamimiazmiNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - PPT TemplateDocument2 pagesTask 3 - PPT TemplateYASHASVI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Project Report On Grocery Shop: Mrs Atsü PhomDocument5 pagesProject Report On Grocery Shop: Mrs Atsü PhomShyamal DuttaNo ratings yet
- RMASDocument6 pagesRMASSVTKhsiaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting I: Debarati@xlri - Ac.inDocument22 pagesManagement Accounting I: Debarati@xlri - Ac.inSimran JainNo ratings yet
- Enterprise ValuationDocument3 pagesEnterprise ValuationParth MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 007Document16 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 007Farhan Khan NiaZiNo ratings yet
- Kiosk Financial Study v1.0Document18 pagesKiosk Financial Study v1.0Elie AtikNo ratings yet
- Acca SBR LSBFDocument230 pagesAcca SBR LSBFLucky DoraNo ratings yet
- Acctg 102 - Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesAcctg 102 - Cost AccountingLenyBarrogaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Problems: Name SectionDocument1 pageFinancial Statement Analysis Problems: Name SectionrakeshblrNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptDocument25 pagesCost ConceptMadli SiregarNo ratings yet
- Slide AKT 405 Teori Akuntansi 9 GodfreyDocument30 pagesSlide AKT 405 Teori Akuntansi 9 Godfreyfarisa25No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Adjustments and The WorksheetDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Adjustments and The WorksheetReynaleen Agta100% (1)
- Book of Accounts Practice SetDocument60 pagesBook of Accounts Practice SetMylene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- DagohoyDocument6 pagesDagohoylinkin soyNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting Canadian 5Th Edition by Harrison Isbn 0132979276 9780132979276 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Accounting Canadian 5Th Edition by Harrison Isbn 0132979276 9780132979276 Full Chapter PDFcarmen.hall969100% (12)
- SdsasacsacsacsacsacDocument4 pagesSdsasacsacsacsacsacIden PratamaNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument11 pagesCVP AnalysisNicolaus Copernicus67% (3)
- Suggested Answers Final Examination - Winter 2014: Management AccounitngDocument5 pagesSuggested Answers Final Examination - Winter 2014: Management AccounitngAbdulAzeemNo ratings yet