Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Series
9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Series
Uploaded by
Suhail Alam KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- COMPASS TEST by CADET PILOT - 2Document3 pagesCOMPASS TEST by CADET PILOT - 2Suhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- RIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsDocument15 pagesRIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsMarilyn CitadelNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report-Virtual Parent's OrientationnDocument3 pagesNarrative Report-Virtual Parent's OrientationnApril Ramos Dimayuga95% (21)
- Dimitra Fimi. Tolkien, Race and Cultural History From Fairies ToDocument4 pagesDimitra Fimi. Tolkien, Race and Cultural History From Fairies Tomadeehamaqbool736250% (4)
- Cambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/23Document8 pagesCambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/23Suhail Alam Khan100% (1)
- 50 Tapping Scripts Gene MonterastelliDocument27 pages50 Tapping Scripts Gene Monterastellilalek00100% (5)
- 0510 English As A Second Language: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument13 pages0510 English As A Second Language: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesChernYangEeNo ratings yet
- Sample Complaint For Sum of MoneyDocument4 pagesSample Complaint For Sum of MoneyRob Avenida100% (1)
- Network Security - 3.4) The Following Ciphertext Wa...Document3 pagesNetwork Security - 3.4) The Following Ciphertext Wa...Zeeshan Khan100% (1)
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperDocument8 pagesMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PapermarryNo ratings yet
- 0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument8 pages0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Series王涛No ratings yet
- 9701 iECRsDocument162 pages9701 iECRsnesrine boufadenNo ratings yet
- Computer Project Marking SchemeDocument4 pagesComputer Project Marking SchemeAlexander Njoroge100% (4)
- Cse2142 3 2011 1 PDFDocument7 pagesCse2142 3 2011 1 PDFmy pcNo ratings yet
- 0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument7 pages0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Series王涛No ratings yet
- DBMSFinal Jan15Document6 pagesDBMSFinal Jan15ComettNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced LevelDocument7 pagesCambridge International Advanced LevelTrynosNo ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesDocument7 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesYeNo ratings yet
- 0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesDocument8 pages0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 Series王涛No ratings yet
- Mnpict Ans 201Document12 pagesMnpict Ans 201arunodaya itNo ratings yet
- 2012 Nov P4 MarkschemeDocument5 pages2012 Nov P4 MarkschemeNana BakriNo ratings yet
- Academic Year: 2019-20: Blank White Paper or Loose Lined Sheets From Exercise BooksDocument5 pagesAcademic Year: 2019-20: Blank White Paper or Loose Lined Sheets From Exercise BooksGrasshopperNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 Hourslynn zigaraNo ratings yet
- Computing Yr10 Opt Ms 2022Document5 pagesComputing Yr10 Opt Ms 2022Sobia ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 Hourslynn zigaraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument15 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelAl-Sami MashrafeeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/11 October/November 2022Document11 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/11 October/November 2022Steven ShemdoeNo ratings yet
- June 2004 Paper 3Document4 pagesJune 2004 Paper 3api-3753397No ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersYeNo ratings yet
- 9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocument9 pages9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesefoneoNo ratings yet
- 9701 s16 Ms 22Document7 pages9701 s16 Ms 22Thaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- 9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocument13 pages9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesTrynosNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Bhubaneswar Region Session Ending Examination 2019-20 CLASS XI - Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Bhubaneswar Region Session Ending Examination 2019-20 CLASS XI - Computer Scienceiitiansrd2025No ratings yet
- 3.2.2 AnswersDocument15 pages3.2.2 AnswersTaha Khalid MianNo ratings yet
- 9608 November 2015 Paper 32 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages9608 November 2015 Paper 32 Mark SchemeShobhan KarthickNo ratings yet
- 9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument5 pages9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesShakila.D Raks PallikkoodamNo ratings yet
- Xii Infomatics PracticesDocument10 pagesXii Infomatics PracticesNitin PanchalNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument7 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelBilal Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 SeriesDocument44 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 Seriesaung aungNo ratings yet
- 4CP0 02 MSC 20190822Document30 pages4CP0 02 MSC 20190822Neily WimalasiriNo ratings yet
- 0417 w14 Ms 11Document8 pages0417 w14 Ms 11sarath dodampahalageNo ratings yet
- COPS Coursework 2021Document35 pagesCOPS Coursework 2021Sharon MasikiNo ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument17 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersannabellNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument6 pagesMARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsVandan NagdaNo ratings yet
- 0417 s09 Ms 1Document7 pages0417 s09 Ms 1Zanfalawy BashaNo ratings yet
- Database Design DBT1111C 5Document7 pagesDatabase Design DBT1111C 5Abhay Kumar Sharma BOODHOONo ratings yet
- 0452 s18 Ms 12Document14 pages0452 s18 Ms 12Seong Hun LeeNo ratings yet
- Cape Computer Science 2011 Unit 2 P2Document5 pagesCape Computer Science 2011 Unit 2 P2dnitehawk qNo ratings yet
- GCSE-Science Double Award-584-Summer2021-Higher Tier, Unit P2 - Physics-MSDocument6 pagesGCSE-Science Double Award-584-Summer2021-Higher Tier, Unit P2 - Physics-MSAoibhinn DeeyNo ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument11 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 Seriespyaaraasingh716No ratings yet
- Xii PB1 MS CS Set1Document9 pagesXii PB1 MS CS Set1Apeksha KumariNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: First Language English 0500/11 October/November 2020Document21 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: First Language English 0500/11 October/November 2020Prabhat DwivediNo ratings yet
- November 2015 (v2) MS - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument7 pagesNovember 2015 (v2) MS - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry IGCSEMariam BabarNo ratings yet
- 0625 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument5 pages0625 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 Seriesnishamani1128No ratings yet
- Paper 1 May 2005Document5 pagesPaper 1 May 2005MSHNo ratings yet
- Caie GR8 T1 Ict QP P1Document8 pagesCaie GR8 T1 Ict QP P1easedaeNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 AnswersDocument15 pages3.2.1 AnswersTaha Khalid MianNo ratings yet
- SQL Server 2019Document4 pagesSQL Server 2019rikor15464No ratings yet
- IECRs ASA Level Chemistry P22 Q2Document12 pagesIECRs ASA Level Chemistry P22 Q2Ahmad MubasharNo ratings yet
- 5070 - w18 - Ms - 21 CIE O Level ChemistryDocument11 pages5070 - w18 - Ms - 21 CIE O Level ChemistryRichard シNo ratings yet
- DWDM - 2021Document3 pagesDWDM - 2021rikor15464No ratings yet
- 2008 April Question PaperDocument5 pages2008 April Question PaperMukesh RegmiNo ratings yet
- 3248 Second Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument4 pages3248 Second Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 Seriesnmnmnmcxn mxNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The November 2005 Question PaperDocument2 pagesMARK SCHEME For The November 2005 Question PaperVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- 2020 Marking SchemeDocument31 pages2020 Marking SchemeamilacjNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Design and Programming with C++: Your Hands-On Guide to C++ Programming, with Special Emphasis on Design, Testing, and ReuseFrom EverandObject-Oriented Design and Programming with C++: Your Hands-On Guide to C++ Programming, with Special Emphasis on Design, Testing, and ReuseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Who DeservesDocument223 pagesWho DeservesSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Mass Spec WS2 PDFDocument8 pagesMass Spec WS2 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Item Weight MRP Item Weight MRP Item Weight MRP: List of Products at MRPDocument1 pageItem Weight MRP Item Weight MRP Item Weight MRP: List of Products at MRPSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Binary Tree Using A 2D ArrayDocument3 pagesBinary Tree Using A 2D ArraySuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Memory Management - Segmentation Paging and Virtual MemoryDocument6 pagesMemory Management - Segmentation Paging and Virtual MemorySuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Exercise 1 - Dot-Cross DiagramsDocument1 pageTopic 3 Exercise 1 - Dot-Cross DiagramsSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9618 Scheme of WorkDocument64 pages9618 Scheme of WorkSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- TAP 518-4: How A Magnetic Field Deflects An Electron BeamDocument2 pagesTAP 518-4: How A Magnetic Field Deflects An Electron BeamSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Figure of SpeechDocument3 pagesAnswer Key: Figure of SpeechSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 w18 QP 41 PDFDocument20 pages9701 w18 QP 41 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9691 s15 Ms 11 PDFDocument10 pages9691 s15 Ms 11 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Proofreading For Errors in Verb Tense: Correcting A Common Grammar MistakeDocument2 pagesProofreading For Errors in Verb Tense: Correcting A Common Grammar MistakeSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge Assessment International EducationSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Figure of Speech: AlliterationDocument5 pagesFigure of Speech: AlliterationSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Is Pollution An Insurmountable Challenge Faced by The World?Document8 pagesIs Pollution An Insurmountable Challenge Faced by The World?Suhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 s18 Ms 42 PDFDocument14 pages9701 s18 Ms 42 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Registration Form Nov 2020 - For Private Candidates OnlyDocument4 pagesRegistration Form Nov 2020 - For Private Candidates OnlySuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 w18 Ms 41 PDFDocument14 pages9701 w18 Ms 41 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced LevelDocument20 pagesCambridge International Advanced LevelSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument11 pages9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Emma J. Stafford - Greek Cults of Deified AbstractionsDocument269 pagesEmma J. Stafford - Greek Cults of Deified Abstractions21Tauri100% (1)
- Week 3 & 4Document12 pagesWeek 3 & 4elbaNo ratings yet
- Book Decade SDocument555 pagesBook Decade STrey MaklerNo ratings yet
- Annexure ADocument1 pageAnnexure Atoocool_sashi100% (2)
- Mas PrelimsDocument8 pagesMas PrelimsChristopher NogotNo ratings yet
- Hirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - LiDocument227 pagesHirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - Litrue dreamNo ratings yet
- BattleNight - Red HalidomsDocument47 pagesBattleNight - Red HalidomsWinner ElbertNo ratings yet
- Famous Letters of Mahatma GandhiDocument146 pagesFamous Letters of Mahatma Gandhivishalnaidu2010No ratings yet
- Chinchilla Cookie Recipe - LY ChinchillasDocument5 pagesChinchilla Cookie Recipe - LY ChinchillasSandy B GuzmánNo ratings yet
- TAX Calculation FY 22-23 AY23-24Document9 pagesTAX Calculation FY 22-23 AY23-24SamratNo ratings yet
- Consolations of PhilosophyDocument28 pagesConsolations of Philosophyrkrish67100% (2)
- Trail, G. T. (2018) - Theories of Consumer Behavior - Chapter 2. Seattle, WA: Sport Consumer Research Consultants LLCDocument35 pagesTrail, G. T. (2018) - Theories of Consumer Behavior - Chapter 2. Seattle, WA: Sport Consumer Research Consultants LLCMargoNo ratings yet
- The Subaltern and The Text: Reading Arundhati Roy's The God of Small ThingsDocument8 pagesThe Subaltern and The Text: Reading Arundhati Roy's The God of Small ThingsLaura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiZendy PradiktaNo ratings yet
- Reminiscences of Madame Sidney PrattenDocument121 pagesReminiscences of Madame Sidney PrattenjavisatrianiNo ratings yet
- IronbutterplyDocument3 pagesIronbutterplyCiliaNo ratings yet
- R18 B.tech I Year Syllabus of EEE CSE IT UpdatedDocument32 pagesR18 B.tech I Year Syllabus of EEE CSE IT UpdatedKrishna Teja NamuduriNo ratings yet
- Anang Yanuar Ramadhan - B1B015015 - Acara 2 (Prelab) - Identifikasi Karakter Taksonomi VertebrataDocument9 pagesAnang Yanuar Ramadhan - B1B015015 - Acara 2 (Prelab) - Identifikasi Karakter Taksonomi VertebrataAnang Yanuar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Wah Campus: Herzberg's Theory Alignment To The Case Study TESCODocument2 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Wah Campus: Herzberg's Theory Alignment To The Case Study TESCOiqra khanNo ratings yet
- Position Paper: Mexican Drug CartelsDocument6 pagesPosition Paper: Mexican Drug Cartels99problems56No ratings yet
- ABB SR MV Products - 72dpiDocument52 pagesABB SR MV Products - 72dpiSiddharth krishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- Einhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeDocument7 pagesEinhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeclawthebandNo ratings yet
- Uae Essential Network List July 2016Document75 pagesUae Essential Network List July 2016ubyisismayilNo ratings yet
9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Series
9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Series
Uploaded by
Suhail Alam KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Series
9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Series
Uploaded by
Suhail Alam KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
Cambridge International Advanced Level
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series
9691 COMPUTING
9691/33 Paper 3 (Written Paper), maximum raw mark 90
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of
the examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not
indicate the details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners’ meeting before marking began,
which would have considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner
Report for Teachers.
Cambridge will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge is publishing the mark schemes for the May/June 2015 series for most
Cambridge IGCSE®, Cambridge International A and AS Level components and some
Cambridge O Level components.
® IGCSE is the registered trademark of Cambridge International Examinations.
Page 2 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International A Level – May/June 2015 9691 33
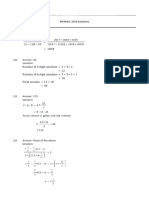
1 (a) (i) The table has a repeated (group of) attributes [1]
(ii) Title, Genre, ReleaseDate and ReviewDate are repeated for each reviewer [1]
(b) (i)
ReviewerID Location
510 London
808 New York
756 Dhaka
[1]
(ii)
Title Genre ReleaseDate ReviewDate ReviewerID
Hits 36 P 12/01/2015 01-15 510
Popular C 12/01/2015 02-15 808
Bach
The C 11/1/2014 11-14 756
Messiah
Or, any other row taken from the original table (ReviewID must be different) [2]
3 correct – 2 marks
2 correct – 1 mark
1 correct only – scores 0
(iii) 9 [1]
(iv) Many-to-one [1]
(v) Primary key/ReviewerID in the REVIEWER table [1]
Links to foreign key/ReviewerID in the REVIEW table [1]
(c) (i) Title [1]
(ii) There are non-key attributes which are dependent (may be stated as part of the attribute
description) (1)
ReviewerName is dependent on ReviewerID //
Fee is dependent on Genre (1) [2]
© Cambridge International Examinations 2015
Page 3 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International A Level – May/June 2015 9691 33
(iii) REVIEWER(ReviewerID, Location, ReviewerName)
REVIEW(Title, Genre, ReleaseDate,
ReviewDate, ReviewerID)
FEE(Genre, GenreFee)
Mark as follows:
new FEE table
containing Genre and GenreFee
Primary key for FEE correctly shown
REVIEW table has foreign key Genre
REVIEWER table contains ReviewerName [5]
[Total: 17]
2 (a) Syntax diagram [1]
(b) (i) The rule is defined in terms of itself / calls itself [1]
(ii) TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
CAO. [1]
(c) (i) D175N
Invalid (1)
5, 2 (1) [2]
(ii) W058M
Valid (1)
Rule 1 – 3 times
Rule 2 – once
Rule 3 – once
Rule 4 – once
Rule 5 – once (1) [2]
(iii) C86N
Invalid (1)
<producttype><digit><digit><location>
Rule 1 – 2/3 times
Rule 2 – once
Rule 4 – once
Rule 5 – once (1) [2]
[Total: 9]
© Cambridge International Examinations 2015
Page 4 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International A Level – May/June 2015 9691 33
3 (a) The class diagram includes:
Software + Network subclasses (1)
Bespoke + OffTheShelf subclasses of Software (1)
Note: Two marks – correct class names only
Recognised notation for inheritance (from Software and Network only) (1)
Project class StartDate : DATE
ProjectLeader : STRING (1)
Software class ProgrammingLanguage : STRING
AlphaTesting : STRING/CHAR (1)
For each of the following – at least two of the correct properties
Bespoke class CustomerName : STRING
AgreedCost : REAL/CURRENCY
AgreedDeliveryDate : DATE (1)
OffTheShelf class Title : STRING
BetaTesting : STRING/CHAR
RetailPrice : REAL/CURRENCY
SalesForecast : INTEGER (1)
Network class ClientName : STRING (1)
AgreedCost : INTEGER/CURRENCY [8]
(b) (i) Class…
The definition of an object // The ‘blueprint’ from which objects are created. [1]
(ii) Inheritance…
The ability of a subclass/child class to use properties and methods of a
parent/super/base class [1]
(c) (i) Instance …
– A specific object created from a class (1)
– Main program has created an instance of the Network class – referred to as
ThisNetworkProject (1) [2]
(ii) Method…
Something an object can do // Implemented with procedures/functions (1)
Project shows two methods – get_ProjectID() and set_ProjectID() (1) [2]
© Cambridge International Examinations 2015
Page 5 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International A Level – May/June 2015 9691 33
(iii) Encapsulation…
Technique which restricts the programmer’s access to the object’s data (1)
Data values can only be read/written using methods provided by the class (1)
– The ProjectID value can only be read/written using the two methods provided
// ProjectID is private to the class (1) [3]
[Total: 17]
4 (a) Last item in is the first item out // First item in is the last item out
R. LIFO [1]
(b) PROCEDURE InitialiseStack
FOR Index ← 0 to 99
Animal[Index] ← "" (1)
ENDFOR
StackPointer ← -1 (1)
ENDPROCEDURE [2]
(c) (i) "" //empty string (1)
1 (1) [2]
(ii) PROCEDURE Push
IF StackPointer = 99 (1)
THEN
OUTPUT "REFUSED – stack is full"
ELSE
INPUT NewAnimal (1)
StackPointer ← StackPointer + 1 (1)
Animal[StackPointer] ← NewAnimal (1)
ENDIF
ENDPROCEDURE [4]
(d) PROCEDURE Pop
IF StackPointer = -1
THEN
OUTPUT "Stack is empty"
ELSE
OUTPUT Animal[StackPointer]
StackPointer ← StackPointer – 1
ENDIF
ENDPROCEDURE
Mark as follows …
Test for empty with StackPointer = -1 [1]
OUTPUT ‘EMPTY’ message [1]
Animal[StackPointer] is value removed [1]
Decrement StackPointer [1]
[Total: 13]
© Cambridge International Examinations 2015
Page 6 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International A Level – May/June 2015 9691 33
5 (a) (i) –23 (1)
E9 (1) [2]
(ii) 107 (1)
6B (1) [2]
(iii) 127 [1]
(iv) Fewer digits used to represent any number // long string difficult to interpret (1)
Less likely to make a mistake when copying/converting a digit string (1)
Easy to convert from binary/denary to hex (vice versa) (than binary to denary) (1)
[Max 1]
(b)
99 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1
29 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 +
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
99 and 29 correct pattern (1)
Correct addition // ft (1)
Overflow has occurred // the expected answer is outside the possible range // the
answer is showing as –128 (1) [3]
(c) (i) 1578 [1]
(ii) 1101 is not a valid BCD digit string // 1101 represents ‘13’ [1]
[Total: 11]
6 (a) Systems flowchart [1]
(b) • 1 – Text editor
• 2 – on-screen errors
• 3 – Compiler
• 4 – Assembler
• 5 – Linker
• 6 – Program library code
• 7 – Executable code [7]
[Total: 8]
© Cambridge International Examinations 2015
Page 7 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International A Level – May/June 2015 9691 33
7 (a) Correct use of any of the following:
Single segment of wire (1)
Computers connected to the cable X 4 (1)
Terminators X 2 (1)
Computer C has attached printer (1)
File server (1)
Firewall / Proxy server + Indication of a connection to the Internet (1)
Router + Indication of a connection to the Internet (1)
Modem + Indication of a connection to the Internet (1)
[Max 5]
(b) Manage user accounts (1)
Authenticate all logons (1)
Manage the shared file storage (1)
Manage the installation and use of applications software (1)
[Max 3]
(c) Intranet …
Information system using Internet protocols (1)
Provides service of web pages (to client computers) (1)
Information system only available to staff within the organisation (1)
[Max 2]
[Total: 10]
8 (a) (i) ChangeString (1)
ThisString1, ThisString2 (only) (1) [2]
(ii) Ali J [1]
(iii) 7 // Error if LEFT("", 1) generates an error [1]
(iv) JONES 8 [1]
[Total: 5]
© Cambridge International Examinations 2015
You might also like
- COMPASS TEST by CADET PILOT - 2Document3 pagesCOMPASS TEST by CADET PILOT - 2Suhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- RIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsDocument15 pagesRIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsMarilyn CitadelNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report-Virtual Parent's OrientationnDocument3 pagesNarrative Report-Virtual Parent's OrientationnApril Ramos Dimayuga95% (21)
- Dimitra Fimi. Tolkien, Race and Cultural History From Fairies ToDocument4 pagesDimitra Fimi. Tolkien, Race and Cultural History From Fairies Tomadeehamaqbool736250% (4)
- Cambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/23Document8 pagesCambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/23Suhail Alam Khan100% (1)
- 50 Tapping Scripts Gene MonterastelliDocument27 pages50 Tapping Scripts Gene Monterastellilalek00100% (5)
- 0510 English As A Second Language: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument13 pages0510 English As A Second Language: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesChernYangEeNo ratings yet
- Sample Complaint For Sum of MoneyDocument4 pagesSample Complaint For Sum of MoneyRob Avenida100% (1)
- Network Security - 3.4) The Following Ciphertext Wa...Document3 pagesNetwork Security - 3.4) The Following Ciphertext Wa...Zeeshan Khan100% (1)
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperDocument8 pagesMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PapermarryNo ratings yet
- 0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument8 pages0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Series王涛No ratings yet
- 9701 iECRsDocument162 pages9701 iECRsnesrine boufadenNo ratings yet
- Computer Project Marking SchemeDocument4 pagesComputer Project Marking SchemeAlexander Njoroge100% (4)
- Cse2142 3 2011 1 PDFDocument7 pagesCse2142 3 2011 1 PDFmy pcNo ratings yet
- 0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument7 pages0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Series王涛No ratings yet
- DBMSFinal Jan15Document6 pagesDBMSFinal Jan15ComettNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced LevelDocument7 pagesCambridge International Advanced LevelTrynosNo ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesDocument7 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesYeNo ratings yet
- 0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesDocument8 pages0417 Information and Communication Technology: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 Series王涛No ratings yet
- Mnpict Ans 201Document12 pagesMnpict Ans 201arunodaya itNo ratings yet
- 2012 Nov P4 MarkschemeDocument5 pages2012 Nov P4 MarkschemeNana BakriNo ratings yet
- Academic Year: 2019-20: Blank White Paper or Loose Lined Sheets From Exercise BooksDocument5 pagesAcademic Year: 2019-20: Blank White Paper or Loose Lined Sheets From Exercise BooksGrasshopperNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 Hourslynn zigaraNo ratings yet
- Computing Yr10 Opt Ms 2022Document5 pagesComputing Yr10 Opt Ms 2022Sobia ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Time: 2 Hourslynn zigaraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument15 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelAl-Sami MashrafeeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/11 October/November 2022Document11 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/11 October/November 2022Steven ShemdoeNo ratings yet
- June 2004 Paper 3Document4 pagesJune 2004 Paper 3api-3753397No ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersYeNo ratings yet
- 9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocument9 pages9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesefoneoNo ratings yet
- 9701 s16 Ms 22Document7 pages9701 s16 Ms 22Thaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- 9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocument13 pages9608 Computer Science: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesTrynosNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Bhubaneswar Region Session Ending Examination 2019-20 CLASS XI - Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Bhubaneswar Region Session Ending Examination 2019-20 CLASS XI - Computer Scienceiitiansrd2025No ratings yet
- 3.2.2 AnswersDocument15 pages3.2.2 AnswersTaha Khalid MianNo ratings yet
- 9608 November 2015 Paper 32 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages9608 November 2015 Paper 32 Mark SchemeShobhan KarthickNo ratings yet
- 9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument5 pages9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesShakila.D Raks PallikkoodamNo ratings yet
- Xii Infomatics PracticesDocument10 pagesXii Infomatics PracticesNitin PanchalNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument7 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelBilal Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 SeriesDocument44 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 Seriesaung aungNo ratings yet
- 4CP0 02 MSC 20190822Document30 pages4CP0 02 MSC 20190822Neily WimalasiriNo ratings yet
- 0417 w14 Ms 11Document8 pages0417 w14 Ms 11sarath dodampahalageNo ratings yet
- COPS Coursework 2021Document35 pagesCOPS Coursework 2021Sharon MasikiNo ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument17 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersannabellNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument6 pagesMARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsVandan NagdaNo ratings yet
- 0417 s09 Ms 1Document7 pages0417 s09 Ms 1Zanfalawy BashaNo ratings yet
- Database Design DBT1111C 5Document7 pagesDatabase Design DBT1111C 5Abhay Kumar Sharma BOODHOONo ratings yet
- 0452 s18 Ms 12Document14 pages0452 s18 Ms 12Seong Hun LeeNo ratings yet
- Cape Computer Science 2011 Unit 2 P2Document5 pagesCape Computer Science 2011 Unit 2 P2dnitehawk qNo ratings yet
- GCSE-Science Double Award-584-Summer2021-Higher Tier, Unit P2 - Physics-MSDocument6 pagesGCSE-Science Double Award-584-Summer2021-Higher Tier, Unit P2 - Physics-MSAoibhinn DeeyNo ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument11 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 Seriespyaaraasingh716No ratings yet
- Xii PB1 MS CS Set1Document9 pagesXii PB1 MS CS Set1Apeksha KumariNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: First Language English 0500/11 October/November 2020Document21 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: First Language English 0500/11 October/November 2020Prabhat DwivediNo ratings yet
- November 2015 (v2) MS - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument7 pagesNovember 2015 (v2) MS - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry IGCSEMariam BabarNo ratings yet
- 0625 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument5 pages0625 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 Seriesnishamani1128No ratings yet
- Paper 1 May 2005Document5 pagesPaper 1 May 2005MSHNo ratings yet
- Caie GR8 T1 Ict QP P1Document8 pagesCaie GR8 T1 Ict QP P1easedaeNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 AnswersDocument15 pages3.2.1 AnswersTaha Khalid MianNo ratings yet
- SQL Server 2019Document4 pagesSQL Server 2019rikor15464No ratings yet
- IECRs ASA Level Chemistry P22 Q2Document12 pagesIECRs ASA Level Chemistry P22 Q2Ahmad MubasharNo ratings yet
- 5070 - w18 - Ms - 21 CIE O Level ChemistryDocument11 pages5070 - w18 - Ms - 21 CIE O Level ChemistryRichard シNo ratings yet
- DWDM - 2021Document3 pagesDWDM - 2021rikor15464No ratings yet
- 2008 April Question PaperDocument5 pages2008 April Question PaperMukesh RegmiNo ratings yet
- 3248 Second Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument4 pages3248 Second Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 Seriesnmnmnmcxn mxNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The November 2005 Question PaperDocument2 pagesMARK SCHEME For The November 2005 Question PaperVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- 2020 Marking SchemeDocument31 pages2020 Marking SchemeamilacjNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Design and Programming with C++: Your Hands-On Guide to C++ Programming, with Special Emphasis on Design, Testing, and ReuseFrom EverandObject-Oriented Design and Programming with C++: Your Hands-On Guide to C++ Programming, with Special Emphasis on Design, Testing, and ReuseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Who DeservesDocument223 pagesWho DeservesSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Mass Spec WS2 PDFDocument8 pagesMass Spec WS2 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Item Weight MRP Item Weight MRP Item Weight MRP: List of Products at MRPDocument1 pageItem Weight MRP Item Weight MRP Item Weight MRP: List of Products at MRPSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Binary Tree Using A 2D ArrayDocument3 pagesBinary Tree Using A 2D ArraySuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Memory Management - Segmentation Paging and Virtual MemoryDocument6 pagesMemory Management - Segmentation Paging and Virtual MemorySuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Exercise 1 - Dot-Cross DiagramsDocument1 pageTopic 3 Exercise 1 - Dot-Cross DiagramsSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9618 Scheme of WorkDocument64 pages9618 Scheme of WorkSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- TAP 518-4: How A Magnetic Field Deflects An Electron BeamDocument2 pagesTAP 518-4: How A Magnetic Field Deflects An Electron BeamSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Figure of SpeechDocument3 pagesAnswer Key: Figure of SpeechSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 w18 QP 41 PDFDocument20 pages9701 w18 QP 41 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9691 s15 Ms 11 PDFDocument10 pages9691 s15 Ms 11 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Proofreading For Errors in Verb Tense: Correcting A Common Grammar MistakeDocument2 pagesProofreading For Errors in Verb Tense: Correcting A Common Grammar MistakeSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge Assessment International EducationSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Figure of Speech: AlliterationDocument5 pagesFigure of Speech: AlliterationSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Is Pollution An Insurmountable Challenge Faced by The World?Document8 pagesIs Pollution An Insurmountable Challenge Faced by The World?Suhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 s18 Ms 42 PDFDocument14 pages9701 s18 Ms 42 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Registration Form Nov 2020 - For Private Candidates OnlyDocument4 pagesRegistration Form Nov 2020 - For Private Candidates OnlySuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 w18 Ms 41 PDFDocument14 pages9701 w18 Ms 41 PDFSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced LevelDocument20 pagesCambridge International Advanced LevelSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- 9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument11 pages9691 Computing: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesSuhail Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Emma J. Stafford - Greek Cults of Deified AbstractionsDocument269 pagesEmma J. Stafford - Greek Cults of Deified Abstractions21Tauri100% (1)
- Week 3 & 4Document12 pagesWeek 3 & 4elbaNo ratings yet
- Book Decade SDocument555 pagesBook Decade STrey MaklerNo ratings yet
- Annexure ADocument1 pageAnnexure Atoocool_sashi100% (2)
- Mas PrelimsDocument8 pagesMas PrelimsChristopher NogotNo ratings yet
- Hirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - LiDocument227 pagesHirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - Litrue dreamNo ratings yet
- BattleNight - Red HalidomsDocument47 pagesBattleNight - Red HalidomsWinner ElbertNo ratings yet
- Famous Letters of Mahatma GandhiDocument146 pagesFamous Letters of Mahatma Gandhivishalnaidu2010No ratings yet
- Chinchilla Cookie Recipe - LY ChinchillasDocument5 pagesChinchilla Cookie Recipe - LY ChinchillasSandy B GuzmánNo ratings yet
- TAX Calculation FY 22-23 AY23-24Document9 pagesTAX Calculation FY 22-23 AY23-24SamratNo ratings yet
- Consolations of PhilosophyDocument28 pagesConsolations of Philosophyrkrish67100% (2)
- Trail, G. T. (2018) - Theories of Consumer Behavior - Chapter 2. Seattle, WA: Sport Consumer Research Consultants LLCDocument35 pagesTrail, G. T. (2018) - Theories of Consumer Behavior - Chapter 2. Seattle, WA: Sport Consumer Research Consultants LLCMargoNo ratings yet
- The Subaltern and The Text: Reading Arundhati Roy's The God of Small ThingsDocument8 pagesThe Subaltern and The Text: Reading Arundhati Roy's The God of Small ThingsLaura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiZendy PradiktaNo ratings yet
- Reminiscences of Madame Sidney PrattenDocument121 pagesReminiscences of Madame Sidney PrattenjavisatrianiNo ratings yet
- IronbutterplyDocument3 pagesIronbutterplyCiliaNo ratings yet
- R18 B.tech I Year Syllabus of EEE CSE IT UpdatedDocument32 pagesR18 B.tech I Year Syllabus of EEE CSE IT UpdatedKrishna Teja NamuduriNo ratings yet
- Anang Yanuar Ramadhan - B1B015015 - Acara 2 (Prelab) - Identifikasi Karakter Taksonomi VertebrataDocument9 pagesAnang Yanuar Ramadhan - B1B015015 - Acara 2 (Prelab) - Identifikasi Karakter Taksonomi VertebrataAnang Yanuar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Wah Campus: Herzberg's Theory Alignment To The Case Study TESCODocument2 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Wah Campus: Herzberg's Theory Alignment To The Case Study TESCOiqra khanNo ratings yet
- Position Paper: Mexican Drug CartelsDocument6 pagesPosition Paper: Mexican Drug Cartels99problems56No ratings yet
- ABB SR MV Products - 72dpiDocument52 pagesABB SR MV Products - 72dpiSiddharth krishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- Einhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeDocument7 pagesEinhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeclawthebandNo ratings yet
- Uae Essential Network List July 2016Document75 pagesUae Essential Network List July 2016ubyisismayilNo ratings yet