Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 viewsAnimal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printout
Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printout
Uploaded by
jallie niepesThis document provides information about the structures and organelles found within animal cells. It defines key cellular components such as the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosomes, ribosomes, centrosomes, cytoplasm, vacuoles, and nucleolus. The glossary entries describe the form and function of each organelle within the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- RomeoAndJuliet PlainText 2Document10 pagesRomeoAndJuliet PlainText 2Indah L Lestari0% (3)
- 1968 Northport High School Yearbook, Northport New YorkDocument225 pages1968 Northport High School Yearbook, Northport New YorkJoseph ReinckensNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell PDFPerry Sin67% (3)
- Junior Amuse Journey PDFDocument24 pagesJunior Amuse Journey PDFChristina BrandNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocument5 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- Cells Vocabulary PDFDocument2 pagesCells Vocabulary PDFMoody SaiiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Animal CellDocument4 pagesAnatomy of An Animal CellYukiNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell and Its FunctionsDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell and Its FunctionsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Voice of The GenomeDocument6 pagesThe Voice of The GenomeSeaCarrotNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusDocument32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesCell Structure and Functionapi-217439283No ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport MechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport Mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- cls9 cp5Document4 pagescls9 cp5Pankaj PathakNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Virly CellstructureDocument23 pagesVirly CellstructureVirly vcNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- 2 Anatomy 2021 Cells and TissuesDocument87 pages2 Anatomy 2021 Cells and TissuesMJ Jomoc ArejolaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSDocument38 pagesUNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeDocument33 pagesCell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeKristine JoyNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNADocument8 pagesCell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNAQadirNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Biology FSC Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology FSC Chapter 1Diana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell StructurePRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellDaryl De LeonNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Science Bio (Cell) Short NotesDocument4 pagesScience Bio (Cell) Short NotesdominodframeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Types of Sexual ReproductionDocument7 pagesTypes of Sexual Reproductionjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Electric Current: Electrolysis, Process by WhichDocument12 pagesElectric Current: Electrolysis, Process by Whichjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Food Labelling: Types and RationalesDocument8 pagesFood Labelling: Types and Rationalesjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: I. Objectivesjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP Symbols of ElementsDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed LP Symbols of Elementsjallie niepes100% (3)
- Metals Vs Non-Metals: ElementsDocument3 pagesMetals Vs Non-Metals: Elementsjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Electrolysis: Division of BatangasDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Electrolysis: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Acid and BaseDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Acid and Basejallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP in Periodic Table OrigDocument7 pagesDetailed LP in Periodic Table Origjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP Symbols of ElementsDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed LP Symbols of Elementsjallie niepes100% (3)
- Lesson Plan Ecological RelationshipDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Ecological Relationshipjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Ecological Relationships Describe The Interactions Between and Among Organisms Within Their EnvironmentDocument39 pagesEcological Relationships Describe The Interactions Between and Among Organisms Within Their Environmentjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- A Man Walks 7 KM in 2 Hours and 2 KM in 1 Hour in The Same DirectionDocument2 pagesA Man Walks 7 KM in 2 Hours and 2 KM in 1 Hour in The Same Directionjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- POM - Chapter 02-FinaleDocument29 pagesPOM - Chapter 02-FinaleMohsana IqbalNo ratings yet
- RaridadesDocument22 pagesRaridadesInvasorNo ratings yet
- Monthly Meal Planner TemplateDocument11 pagesMonthly Meal Planner TemplateMUHAMMAD UMAIR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TestDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect TestAldanaVerónicaSpinozzi33% (3)
- Musical Rubrics For The Schola at The Extraordinary Form of The MassDocument1 pageMusical Rubrics For The Schola at The Extraordinary Form of The MassChurch Music Association of AmericaNo ratings yet
- Visual Impairment PresentationDocument47 pagesVisual Impairment PresentationPrayogi Dwina AnggaNo ratings yet
- Eternal Eyes WalktroughDocument159 pagesEternal Eyes WalktroughPriyadi AdiluhungNo ratings yet
- 1 STDocument47 pages1 STMuppana NikhilaNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing - Unit II Part 2 - 1st Sem. S.Y. 2022-2023Document5 pagesCreative Writing - Unit II Part 2 - 1st Sem. S.Y. 2022-2023Rosemarie Linggato BulsaoNo ratings yet
- Epson WorkForce M105 Business Inkjet Tank System PrinterDocument2 pagesEpson WorkForce M105 Business Inkjet Tank System PrinterWebAntics.com Online Shopping StoreNo ratings yet
- Nokia c2-03 c2-06 c2-08 Rm-702 Service Schematics v1.0Document9 pagesNokia c2-03 c2-06 c2-08 Rm-702 Service Schematics v1.0AWR OprekerNo ratings yet
- DP1200 1500 SM PDFDocument110 pagesDP1200 1500 SM PDFЯница ХристоваNo ratings yet
- Poeticsofaristot 00 ArisuoftDocument152 pagesPoeticsofaristot 00 Arisuoftfinder08No ratings yet
- The New Age of Russia. Occult and Esoteric Dimensions 05 - Mannherz - T6e - 048y051Document4 pagesThe New Age of Russia. Occult and Esoteric Dimensions 05 - Mannherz - T6e - 048y051BrianNo ratings yet
- Eduqas GCSE Music 9-1 Practice PaperDocument34 pagesEduqas GCSE Music 9-1 Practice PaperBruce HygateNo ratings yet
- Chicken EnchiladasDocument1 pageChicken EnchiladasLantern02No ratings yet
- Class Prophecy 2023Document2 pagesClass Prophecy 2023CRISTAN ALONZONo ratings yet
- Rebecca Horn, Moveable Shoulder Extensions 1971 - TateDocument4 pagesRebecca Horn, Moveable Shoulder Extensions 1971 - TateJuliana CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Douglas Teixeira Monteiro Professor - Fundamental - IfbDocument128 pagesDouglas Teixeira Monteiro Professor - Fundamental - Ifbnatalia alvesNo ratings yet
- Baofeng Uv 5rDocument9 pagesBaofeng Uv 5rljnjombangNo ratings yet
- Kiichiro Itsumi Pindaric Metre The Other Half PDFDocument485 pagesKiichiro Itsumi Pindaric Metre The Other Half PDFMladen Toković100% (1)
- English Language Written Exercise - Year 5Document4 pagesEnglish Language Written Exercise - Year 5Suzanawati OmarNo ratings yet
- Prospex SumoDocument3 pagesProspex Sumoflorenciamaribelfernandez2000No ratings yet
- Spanish 3 El Aire Libre TareaDocument2 pagesSpanish 3 El Aire Libre Tareaapi-263267469No ratings yet
- Box and Whisker PlotsDocument8 pagesBox and Whisker PlotsVasilios BairdNo ratings yet
- Plot The Railway ChildrenDocument4 pagesPlot The Railway ChildrenAing YaNo ratings yet
- Love Is Blue: Moderatеly SlowDocument2 pagesLove Is Blue: Moderatеly Slowhuong trinh67% (3)
Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printout
Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printout
Uploaded by
jallie niepes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 views3 pagesThis document provides information about the structures and organelles found within animal cells. It defines key cellular components such as the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosomes, ribosomes, centrosomes, cytoplasm, vacuoles, and nucleolus. The glossary entries describe the form and function of each organelle within the cell.
Original Description:
TOPIC 7
Original Title
Animal Cell Anatomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about the structures and organelles found within animal cells. It defines key cellular components such as the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosomes, ribosomes, centrosomes, cytoplasm, vacuoles, and nucleolus. The glossary entries describe the form and function of each organelle within the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 views3 pagesAnimal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printout
Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printout
Uploaded by
jallie niepesThis document provides information about the structures and organelles found within animal cells. It defines key cellular components such as the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosomes, ribosomes, centrosomes, cytoplasm, vacuoles, and nucleolus. The glossary entries describe the form and function of each organelle within the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Plant Cell Printout
Animal Cell Anatomy
Bacterium Cell Printout
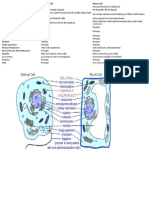
The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of
cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small;
most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered
by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. The
contents of a cell are called the protoplasm.
The following is a glossary of animal cell terms:
cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds
the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some
substances to pass into the cell and blocking others.
centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a
small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and
radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are
made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and
the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The
centriole is the dense center of the centrosome.
cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in
which the organelles are located.
Golgi body - (also called the Golgi apparatus or golgi complex)
a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of
pancakes and is located near the nucleus. It produces the
membranes that surround the lysosomes. The Golgi body
packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound
vesicles for "export" from the cell.
lysosome - (also called cell vesicles) round organelles
surrounded by a membrane and containing digestive enzymes.
This is where the digestion of cell nutrients takes place.
mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a
double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times,
forming a series of projections (called cristae). The
mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) for the cell.
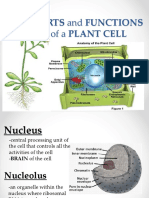
nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where
ribosomal RNA is produced. Some cells have more than one
nucleolus.
nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including
the nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the
cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in
chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear
membrane.
ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich
cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of
interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that
are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the
outer nuclear membrane). Rough ER is covered with ribosomes
that give it a rough appearance. Rough ER transports materials
through the cell and produces proteins in sacks called cisternae
(which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell
membrane).
smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of
interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that
are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the
outer nuclear membrane). The space within the ER is called the
ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It
contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and
membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER,
moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body,
lysosomes, and membranes.
vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a
cell. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste
material that is on its way out of the cell.
You might also like
- RomeoAndJuliet PlainText 2Document10 pagesRomeoAndJuliet PlainText 2Indah L Lestari0% (3)
- 1968 Northport High School Yearbook, Northport New YorkDocument225 pages1968 Northport High School Yearbook, Northport New YorkJoseph ReinckensNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell PDFPerry Sin67% (3)
- Junior Amuse Journey PDFDocument24 pagesJunior Amuse Journey PDFChristina BrandNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocument5 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- Cells Vocabulary PDFDocument2 pagesCells Vocabulary PDFMoody SaiiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Animal CellDocument4 pagesAnatomy of An Animal CellYukiNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell and Its FunctionsDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell and Its FunctionsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Voice of The GenomeDocument6 pagesThe Voice of The GenomeSeaCarrotNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusDocument32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesCell Structure and Functionapi-217439283No ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport MechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport Mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- cls9 cp5Document4 pagescls9 cp5Pankaj PathakNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Virly CellstructureDocument23 pagesVirly CellstructureVirly vcNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- 2 Anatomy 2021 Cells and TissuesDocument87 pages2 Anatomy 2021 Cells and TissuesMJ Jomoc ArejolaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSDocument38 pagesUNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeDocument33 pagesCell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeKristine JoyNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNADocument8 pagesCell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNAQadirNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Biology FSC Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology FSC Chapter 1Diana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell StructurePRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellDaryl De LeonNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Science Bio (Cell) Short NotesDocument4 pagesScience Bio (Cell) Short NotesdominodframeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Types of Sexual ReproductionDocument7 pagesTypes of Sexual Reproductionjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Electric Current: Electrolysis, Process by WhichDocument12 pagesElectric Current: Electrolysis, Process by Whichjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Food Labelling: Types and RationalesDocument8 pagesFood Labelling: Types and Rationalesjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: I. Objectivesjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP Symbols of ElementsDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed LP Symbols of Elementsjallie niepes100% (3)
- Metals Vs Non-Metals: ElementsDocument3 pagesMetals Vs Non-Metals: Elementsjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Electrolysis: Division of BatangasDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Electrolysis: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Acid and BaseDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Acid and Basejallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP in Periodic Table OrigDocument7 pagesDetailed LP in Periodic Table Origjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP Symbols of ElementsDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed LP Symbols of Elementsjallie niepes100% (3)
- Lesson Plan Ecological RelationshipDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Ecological Relationshipjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Ecological Relationships Describe The Interactions Between and Among Organisms Within Their EnvironmentDocument39 pagesEcological Relationships Describe The Interactions Between and Among Organisms Within Their Environmentjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of BatangasDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Division of Batangasjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- A Man Walks 7 KM in 2 Hours and 2 KM in 1 Hour in The Same DirectionDocument2 pagesA Man Walks 7 KM in 2 Hours and 2 KM in 1 Hour in The Same Directionjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- POM - Chapter 02-FinaleDocument29 pagesPOM - Chapter 02-FinaleMohsana IqbalNo ratings yet
- RaridadesDocument22 pagesRaridadesInvasorNo ratings yet
- Monthly Meal Planner TemplateDocument11 pagesMonthly Meal Planner TemplateMUHAMMAD UMAIR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TestDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect TestAldanaVerónicaSpinozzi33% (3)
- Musical Rubrics For The Schola at The Extraordinary Form of The MassDocument1 pageMusical Rubrics For The Schola at The Extraordinary Form of The MassChurch Music Association of AmericaNo ratings yet
- Visual Impairment PresentationDocument47 pagesVisual Impairment PresentationPrayogi Dwina AnggaNo ratings yet
- Eternal Eyes WalktroughDocument159 pagesEternal Eyes WalktroughPriyadi AdiluhungNo ratings yet
- 1 STDocument47 pages1 STMuppana NikhilaNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing - Unit II Part 2 - 1st Sem. S.Y. 2022-2023Document5 pagesCreative Writing - Unit II Part 2 - 1st Sem. S.Y. 2022-2023Rosemarie Linggato BulsaoNo ratings yet
- Epson WorkForce M105 Business Inkjet Tank System PrinterDocument2 pagesEpson WorkForce M105 Business Inkjet Tank System PrinterWebAntics.com Online Shopping StoreNo ratings yet
- Nokia c2-03 c2-06 c2-08 Rm-702 Service Schematics v1.0Document9 pagesNokia c2-03 c2-06 c2-08 Rm-702 Service Schematics v1.0AWR OprekerNo ratings yet
- DP1200 1500 SM PDFDocument110 pagesDP1200 1500 SM PDFЯница ХристоваNo ratings yet
- Poeticsofaristot 00 ArisuoftDocument152 pagesPoeticsofaristot 00 Arisuoftfinder08No ratings yet
- The New Age of Russia. Occult and Esoteric Dimensions 05 - Mannherz - T6e - 048y051Document4 pagesThe New Age of Russia. Occult and Esoteric Dimensions 05 - Mannherz - T6e - 048y051BrianNo ratings yet
- Eduqas GCSE Music 9-1 Practice PaperDocument34 pagesEduqas GCSE Music 9-1 Practice PaperBruce HygateNo ratings yet
- Chicken EnchiladasDocument1 pageChicken EnchiladasLantern02No ratings yet
- Class Prophecy 2023Document2 pagesClass Prophecy 2023CRISTAN ALONZONo ratings yet
- Rebecca Horn, Moveable Shoulder Extensions 1971 - TateDocument4 pagesRebecca Horn, Moveable Shoulder Extensions 1971 - TateJuliana CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Douglas Teixeira Monteiro Professor - Fundamental - IfbDocument128 pagesDouglas Teixeira Monteiro Professor - Fundamental - Ifbnatalia alvesNo ratings yet
- Baofeng Uv 5rDocument9 pagesBaofeng Uv 5rljnjombangNo ratings yet
- Kiichiro Itsumi Pindaric Metre The Other Half PDFDocument485 pagesKiichiro Itsumi Pindaric Metre The Other Half PDFMladen Toković100% (1)
- English Language Written Exercise - Year 5Document4 pagesEnglish Language Written Exercise - Year 5Suzanawati OmarNo ratings yet
- Prospex SumoDocument3 pagesProspex Sumoflorenciamaribelfernandez2000No ratings yet
- Spanish 3 El Aire Libre TareaDocument2 pagesSpanish 3 El Aire Libre Tareaapi-263267469No ratings yet
- Box and Whisker PlotsDocument8 pagesBox and Whisker PlotsVasilios BairdNo ratings yet
- Plot The Railway ChildrenDocument4 pagesPlot The Railway ChildrenAing YaNo ratings yet
- Love Is Blue: Moderatеly SlowDocument2 pagesLove Is Blue: Moderatеly Slowhuong trinh67% (3)