Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDF
Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamd barcaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Tutorial 4-SolutionDocument11 pagesTutorial 4-SolutionZaidi Mat ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) : Modulating (Analog) SignalDocument5 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM) : Modulating (Analog) SignalMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- PMM VFD Manual d11 03 010410Document100 pagesPMM VFD Manual d11 03 010410molanoavilaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications - H.AN PDFDocument12 pagesDigital Communications - H.AN PDFMohamd barca100% (1)
- Digital CommunicationsDocument39 pagesDigital Communicationsmakomdd100% (1)
- 416 Assignment 3Document3 pages416 Assignment 3mahmab70No ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractice Questionspratik shuklaNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument16 pagesDigital CommunicationAli Najim Al-AskariNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015Document3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015shreyas_stinsonNo ratings yet
- DCDocument8 pagesDCharshit420No ratings yet
- Digital Telecommunication (TN 320) Tutorial 2Document2 pagesDigital Telecommunication (TN 320) Tutorial 2Alango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Ee150hw04 2012Document2 pagesEe150hw04 2012thinkberry22No ratings yet
- Digital Communication Gate BitsDocument4 pagesDigital Communication Gate BitsVn LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Central College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiDocument8 pagesCentral College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiqweweNo ratings yet
- DCS Comprehension QuestionsDocument4 pagesDCS Comprehension QuestionsRameshkumar JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Chhhpppttteeerrr 55555Document12 pagesChhhpppttteeerrr 55555S Ahson ASNo ratings yet
- Digi Comm Model QP P1Document3 pagesDigi Comm Model QP P1bku14677No ratings yet
- PCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberDocument77 pagesPCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberTao Thích Màu ĐenNo ratings yet
- MimoDocument34 pagesMimoarun14089No ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) PDFDocument45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) PDFKunal KatariyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal Katariya100% (1)
- DCS SolnDocument6 pagesDCS SolnSandeep Kumar100% (1)
- Comm. Sys. Lect. 10Document21 pagesComm. Sys. Lect. 10sulllNo ratings yet
- DC Que BankDocument11 pagesDC Que BankGaurav Kumbharde0% (1)
- T) V. The Total SidebandDocument19 pagesT) V. The Total SidebandPramiti ParasharNo ratings yet
- Dcby Devils DukeDocument23 pagesDcby Devils DukeTummala JanakiramNo ratings yet
- DC Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesDC Tutorial Sheet 1Sabir SankhlaNo ratings yet
- EE370 Final 091Document6 pagesEE370 Final 091thinkberry22No ratings yet
- Kasraian ECET375 Week2Document42 pagesKasraian ECET375 Week2Raul PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Exp. PCMDocument9 pagesExp. PCMsairajdreamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Document4 pagesAssignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Sourav kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- QDocument4 pagesQSri NikethanNo ratings yet
- Baseband Questions StudentsDocument3 pagesBaseband Questions StudentsRishi JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ecm413 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Ecm413 PDFCaha yANo ratings yet
- PCM BahaaDocument50 pagesPCM BahaaNazar liveNo ratings yet
- Ec 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023Document24 pagesEc 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023223UTKARSH TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Design & Simulation of DSSSS Using MATLAB SIMULINKDocument16 pagesDesign & Simulation of DSSSS Using MATLAB SIMULINKNaman ChandNo ratings yet
- Comm Chptr4Document53 pagesComm Chptr4Muhamad Fuad100% (1)
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Digital Modulation and Forward Error CorrectionDocument74 pagesPresentation On Digital Modulation and Forward Error CorrectionJitendra Chuugh100% (1)
- Lecture Note8b Summer0203Document13 pagesLecture Note8b Summer0203Melaku DinkuNo ratings yet
- Voice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370Document7 pagesVoice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370saidur183No ratings yet
- Week 3 1 PDFDocument33 pagesWeek 3 1 PDFosmanriazNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument6 pagesQuestion Banksweetkhushboo786_592No ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesSignals and Systems Sample QuestionsSimon Deshte NderituNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument26 pagesPulse Code Modulationعبدالله سعد محمدصالحNo ratings yet
- Lec PU March05Document98 pagesLec PU March05Muhammad Awais AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Student TDM DPCM DM QDocument1 pageStudent TDM DPCM DM Qmoath farrajNo ratings yet
- Problemas Parte I Comunicaciones DigitalesDocument17 pagesProblemas Parte I Comunicaciones DigitalesNano GomeshNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument26 pagesPulse Code Modulationbree789No ratings yet
- 3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Document34 pages3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Brian Edward HarrisNo ratings yet
- Nemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1Document7 pagesNemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1pauliNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 21 Tutorial Sheet I Principles of Communication Engg IIDocument2 pages2020 - 21 Tutorial Sheet I Principles of Communication Engg IISHOBHIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- Peak-To-Average Power Ratio Reduction by CB-ACE and Adaptive Ace AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesPeak-To-Average Power Ratio Reduction by CB-ACE and Adaptive Ace AlgorithmsShankar GaneshNo ratings yet
- PCM Transmission Bandwidth: Digital CommunicationsDocument8 pagesPCM Transmission Bandwidth: Digital CommunicationsSarthak SouravNo ratings yet
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Convertor IIIDocument14 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertor IIIMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Data Comunication and Networking: Telecommunication, Which Includes Telephony, TelegraphyDocument12 pagesData Comunication and Networking: Telecommunication, Which Includes Telephony, TelegraphyMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter ADC: Lecturer Mohand LokmanDocument23 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter ADC: Lecturer Mohand LokmanMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Noise: Signal To Noise RatioDocument5 pagesNoise: Signal To Noise RatioMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Networks: Network CriteriaDocument6 pagesNetworks: Network CriteriaMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Physical Structures Before Discussing Networks, We Need To Define Some Network AttributesDocument23 pagesPhysical Structures Before Discussing Networks, We Need To Define Some Network AttributesMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Guided Transmission Media 1. Twisted PairDocument7 pagesGuided Transmission Media 1. Twisted PairMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter IIDocument8 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter IIMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Categories of Wireless Networks: System Interconnection Wireless Lans Wireless WansDocument15 pagesWireless Networks: Categories of Wireless Networks: System Interconnection Wireless Lans Wireless WansMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Write The Name of The Layer of The OSI Reference Model and Write Its TasksDocument1 pageWrite The Name of The Layer of The OSI Reference Model and Write Its TasksMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- مبادئ شبكات - حل أسئلة الكورسينDocument13 pagesمبادئ شبكات - حل أسئلة الكورسينMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Sheet (4) : ELE 466 Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesSheet (4) : ELE 466 Communication SystemsMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- The 3 Layer of The OSI Reference Model Is Network LayerDocument5 pagesThe 3 Layer of The OSI Reference Model Is Network LayerMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications - H.AN PDFDocument12 pagesDigital Communications - H.AN PDFMohamd barca100% (1)
- Real Time - Designs ProblemsDocument9 pagesReal Time - Designs ProblemsMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Position ModulationDocument3 pagesPulse Position ModulationMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Width Modulation: Modulating (Analog) Signal: Carrier (Pulse Train) SignalDocument3 pagesPulse Width Modulation: Modulating (Analog) Signal: Carrier (Pulse Train) SignalMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Part Exp 1Document2 pagesSimulation Part Exp 1Mohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Why The Parallel Port?Document11 pagesWhy The Parallel Port?Mohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm 215 Mobile PlatformDocument2 pagesQualcomm 215 Mobile PlatformMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm 205 Mobile Platform BriefDocument2 pagesQualcomm 205 Mobile Platform BriefMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression 4 UpdateDocument24 pagesImage Compression 4 UpdateMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression 3 UpdateDocument11 pagesImage Compression 3 UpdateMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression 2 UpdateDocument10 pagesImage Compression 2 UpdateMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 14Document4 pagesExperiment No 14Mohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Improved Direct Back EMF Detection For Sensorless Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor DrivesDocument6 pagesImproved Direct Back EMF Detection For Sensorless Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor DrivesBùi TuyếnNo ratings yet
- YLPS Quick Installation Guide (4S)Document25 pagesYLPS Quick Installation Guide (4S)remus popescuNo ratings yet
- PI Controlled Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter (BDDDC) and Highly Efficient Boost Converter For Electric VehiclesDocument5 pagesPI Controlled Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter (BDDDC) and Highly Efficient Boost Converter For Electric VehiclesOscar Olarte OrtizNo ratings yet
- BLHeli - 32 Manual ARM Rev32.x PDFDocument10 pagesBLHeli - 32 Manual ARM Rev32.x PDFaniket5941No ratings yet
- Rain Sensing Automatic Car Wiper Using 555 TimerDocument6 pagesRain Sensing Automatic Car Wiper Using 555 TimerSunil MoreNo ratings yet
- 04 M Engine Management SystemDocument56 pages04 M Engine Management SystemDupapipapapa100% (2)
- Philips Az1500 Az1505 SMDocument33 pagesPhilips Az1500 Az1505 SMJuan Carlos PerdomoNo ratings yet
- User Manual of 4th Control SystemDocument41 pagesUser Manual of 4th Control SystemMario ParodiNo ratings yet
- Viper 27Document31 pagesViper 27javierrincon800No ratings yet
- Electric Drives MyCoursesDocument37 pagesElectric Drives MyCoursesMochamad AldiNo ratings yet
- HM7000 Series Decoders Reference ManualDocument130 pagesHM7000 Series Decoders Reference ManualFernandoNo ratings yet
- Length and Speed Measurement Using High-Speed Counters (HSC)Document27 pagesLength and Speed Measurement Using High-Speed Counters (HSC)Admir HodzicNo ratings yet
- Current Source & Voltage Source InvertersDocument2 pagesCurrent Source & Voltage Source InvertersAhmed El SebaiiNo ratings yet
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFDocument27 pagesS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Model of The Elevator Controlled by ARDDocument6 pagesLaboratory Model of The Elevator Controlled by ARDFərid SəmədovNo ratings yet
- Control of Single-Phase Four-Quadrant PWM Rectifier For Traction SystemsDocument6 pagesControl of Single-Phase Four-Quadrant PWM Rectifier For Traction SystemsjaiminNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid-Switch-Based Soft-Switching Inverter For Ultrahigh-Efficiency Traction Motor DrivesDocument8 pagesA Hybrid-Switch-Based Soft-Switching Inverter For Ultrahigh-Efficiency Traction Motor DrivesraghuaadsNo ratings yet
- Kenwood Kdc-348u kdc-4751sd Kdc-Bt41u Kdc-Bt648u Kdc-U4549 Kdc-U4549s Kdc-U549bt kdc-x395 kdc-x695Document50 pagesKenwood Kdc-348u kdc-4751sd Kdc-Bt41u Kdc-Bt648u Kdc-U4549 Kdc-U4549s Kdc-U549bt kdc-x395 kdc-x695lucasNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement Using DVRDocument6 pagesPower Quality Improvement Using DVRNirav RanaNo ratings yet
- MSC Data Sheet ProStar PWM 161128 07 MM HIGHDocument2 pagesMSC Data Sheet ProStar PWM 161128 07 MM HIGHAndes PutraNo ratings yet
- KA5H0380R/KA5M0380R/KA5L0380R: Features DescriptionDocument14 pagesKA5H0380R/KA5M0380R/KA5L0380R: Features DescriptionVidal VelasquezNo ratings yet
- OPTOTRONIC Constant-Voltage LED Power Supplies and Controls (EN)Document29 pagesOPTOTRONIC Constant-Voltage LED Power Supplies and Controls (EN)Raphael LopesNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Chandkheda, Ahmedabad Affiliated HJD Institute of Technical Education & ResearchDocument33 pagesGujarat Technological University Chandkheda, Ahmedabad Affiliated HJD Institute of Technical Education & ResearchJaimin ChainaniNo ratings yet
- Atmega8 Uc: Timer1 - PWM !!!Document13 pagesAtmega8 Uc: Timer1 - PWM !!!malhiavtarsinghNo ratings yet
- IOT Practical File KOT 551Document46 pagesIOT Practical File KOT 551qz5jq94yh2No ratings yet
- Harmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierDocument112 pagesHarmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierGautam Umapathy0% (1)
- As Sine Wave Generation by UsingDocument51 pagesAs Sine Wave Generation by UsingAjay VarmaNo ratings yet
- BD Class D ModulationDocument18 pagesBD Class D ModulationDiego Cowes100% (1)
Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDF
Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamd barcaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDF
Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamd barcaCopyright:
Available Formats
|1|
Fig (1) Block Diagram of a Typical Digital Communication System.
Fig (2) 7-Bit American Standard Code for information Interchange
(ASCII).
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|2|
Q\ If you want to transmit the word (THINK) using an 8-ary, 32-ary system,
encode this word into a sequence of bits using 6-bits ASCII coding, how many
total bits (bit stream) are there in the message?
A\ For 8-ary system: each symbol = 3 bits ↔ K = log2 8 = log 8 / log 2 = 3
For 32-ary system: each symbol = 5 bits ↔ K = log2 32 = log 32 / log 2 = 5
Message (Text): “THINK”
8-ary waveforms: s1(t) s2(t) s0(t) s4(t) s4(t) s4(t) s3(t) s4(t) s6(t) s4(t)
32-ary waveforms: s5(t) s1(t) s4(t) s17(t) s25(t) s20(t)
Total Bits = 6-bits * Number of characters = 6 * 5 = 30 bits.
Q\ what are the advantages of PCM?
A\ (1) Effect of channel noise and interference reduced.
(2) PCM permits regeneration of pulses along the transmission path (this
reduces noise interference).
(3) The bandwidth and signal to noise ratio are related by exponential law.
(4) Multiplexing of various PCM signals is easily possible.
(5) Encryption or decryption can easily incorporated for security purpose.
Q\ what are the disadvantages (Limitation) of PCM?
A\ (1) PCM Systems are complex compared to Analog pulse nodulation
method.
(2) Increasing of channel bandwidth because of digital coding of analog
pulses.
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|3|
Q\ what are the possible modifications of PCM?
A\ PCM can be:
(1) modified to delta modulation [more simplified method of implementation].
(2) used in wideband communication channels to overcome bandwidth
problems.
(3) Reduces the data rate and remove the redundancy (with the help of data
comparison along with PCM).
Q\ How can you reconstruct the signal of DPCM?
A\ (1) the decoder reconstructs the quantized error signal as shown in Fig (3).
(2) The quantized error
signals are summing up
with predication filter
output to give the
quantized version of the
original signal.
Fig (3) DPCM Receiver (Reconstruction of PCM).
(3) The signal at
(Receiver) differs from actual signal by quantization error [q(nTs)].
Q\ what is the difference between present sample and next sample?
Draw the scheme of redundant information in PCM.
A\ any signal does not change fast
(the value from present sample to
next sample does not differs by
large amount), the adjacent
samples of the signal carry the
same information with little
difference as shown in figure (4).
Fig (4) Redundant information in PCM.
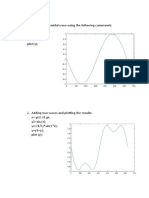
Q\ Draw:
(a) Transfer characteristic of quantizer.
(b) Variation of quantization error with input.
Answer\
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|4|
Fig (5B) Variation of quantization error with input.
Fig (5A) Transfer characteristic of quantizer.
Q\ Compare among PAM, PWM and PPM.
Sr. Pulse Amplitude Modulation Pulse Width (Duration) Pulse Position Modulation
No. (PAM) Modulation (PWM/PDM) (PPM)
Amplitude of pulse is Width of pulse is proportional The relative position of pulse
(1) proportional to amplitude of to amplitude of modulating is proportional to amplitude
modulating signal signal of modulating signal
Bandwidth of transmission Bandwidth of transmission Bandwidth of transmission
(2) channel depends on width of channel depends on rise time of channel depends on rising
the pulse the pulse time of the pulse
Instantaneous power of Instantaneous power of Instantaneous power of
(3) transmitter varies with transmitter varies with transmitter remains constant
amplitude of pulses (amplitude with width) of pulses with width of pulses
(4) High Noise interference Minimum Noise interference Minimum Noise interference
(5) Complex system Simple system Simple system
(6) Similar to (AM) Similar to (FM) Similar to (PM)
(7)
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|5|
Q\ what is the relationship between pulse duration and frequency spectrum?
A\ Pulse duration (T) varies inversely with frequency spectrum shape
according to the equation:
𝟏
T= [increasing of (T) will decreases (f) and vice versa).
𝐟
Example (1): Calculate the bandwidth required to transmit (5) signals having
a maximum frequency of (2 kHz) using TDM system.
Solution: BT = N * W= (5) (2 kHz) = 10 kHz
Example (2): For the analog signal: s (t) = 2 cos(100πt) + 18 cos(2000πt)
determine the allowable sampling rate and sampling interval.
Solution: take the highest [18 cos(2000πt)]
2πf t = 2000πt → fm = 2000/2 = 1000 Hz = 1kHz
fs ≥ 2fm ≥ 2 (1kHz) ≥ 2kHz → Ts = 1/fs = 1/2kHz = 0.5 msec
Example (3): A binary channel with bit rate of (36 kbps) is available for PCM
voice transmission (W=3.4kHz); evaluate the Nyquist sampling rate,
recommended sampling rate, the number of quantization levels, the
transmission bandwidth, and the number of binary digits in PCM encoder.
Solution:
fs ≥ 2fm ≥ 2W ≥ 2 (3.4kHz) ≥ 6.8kHz [N.Q sampling rate = recommended]
𝟏
BT = r = 36kbps /2 = 18kHz [Transmission bandwidth]
𝟐
r = v * fs → v = r/fs = 36kbps/6.8kHz ≈ 5 bits/sample [No. of binary digits]
q = 2v = 25 = 32 [No. of quantized levels]
Example (4): Audio signals having bandwidth up to (15kHz) are recorded
digitally using PCM. If the audio signal is sampled at a rate (20%) more than
the Nyquist rate for practical considerations and the samples are quantized
into (65536 levels), determine the minimum bandwidth required to transmit
the PCM signal.
Solution:
fs ≥ 2fm ≥ 2W ≥ 2 (15kHz) ≥ 30kHz [At 100% sampling rate]
fs (120%) = (120/100) fs = 1.2 (30kHz) = 36kHz [(20%) more than the N.Q rate]
q = 2v → v = log (q) / log (2) = log (65536) / log (2) = 16 bits/sample
𝟏 𝟏 𝟏
BT = r= [v * fs (120%)] = [16 * 36kHz] = 288kHz
𝟐 𝟐 𝟐
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|6|
Example (5): The information in analog signal having maximum frequency of
(3kHz) is required to be transmitted using (16) quantization levels in PCM
system. Find the number of bits per sample and minimum sampling rate
required for PCM transmission.
Solution:
q = 2v → v = log (q) / log (2) = log (16) / log (2) = 4 bits/sample
fs (min) ≥ 2fm ≥ 2W ≥ 2 (3kHz) ≥ 6kHz [Minimum sampling rate required]
Example (6): A (6-bit) single-channel PCM system gives an output
transmission data rate of (60 kbps), what could be the maximum possible
analog frequency for this system?
Solution: r = v * fs → fs = r/v = 60kbps/6 = 10kHz
fs ≥ 2fm → fmax = fs/2 = 10kHz/2 = 5kHz [maximum possible analog frequency]
Example (7): Consider the maximum frequency of an analog information
signal is (3.2 kHz). A binary channel of bit rate (36kbps) is available for PCM
voice transmission. Compute the minimum sampling frequency, number of
bits required per sample, and number of quantized levels.
Solution: fs ≥ 2fm ≥ 2W ≥ 2 (3.2kHz) ≥ 6.4kHz [minimum sampling frequency]
r = v * fs → v = r/fs = 36kbps/6.4kHz ≈ 5 bits/sample [No. of binary digits]
q = 2v = 25 = 32 [No. of quantized levels]
Example (8): Consider an analog signal: x(t) = 3 cos(500πt).
Evaluate the signal-to-noise power ratio using (10-bit) PCM system.
𝐒
Solution: ( )dB = (1.8 + 6v)dB = 1.8 + (6)(10) = 1.8 + 60 = 61.8 dB
𝐍
Example (9): Determine the step size for a quantized PAM signal whose peak
voltages are (+16.8V) & (-22.4V), assuming 16-bit PCM code for each sample.
Solution: q = 2v = 216 = 65536 , 𝜺max = |𝜹/2|
vp-p = 2|xmax| = [16.8 - (-22.4)]V = 39.2V
𝜺max = 2|xmax| / q = 39.2V/65536 = 0.6mV (maximum quantization error)
∴ Step size: 𝜹 = 2 * 𝜺max = 2 (0.6mV) = 1.2 mV
Example (10): 24 telephone channels, each band limited to (3.4kHz), are to be
time division multiplexed by using PCM. Calculate the bandwidth of the
PCM system for (128) quantization levels and an (8kHz) sampling frequency.
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|7|
Solution: q = 2v → v = log (q) / log (2) = log (128) / log (2) = 7 bits/sample
BT = N * r = N * v * fs = (24) (7) (8kHz) = 1344kHz = 1.344MHz
)q( ) وعدد المستوياتfs( ) وتردد النمذجةN( عندما يتوفر في السؤال قنوات متعددة للنقل:مالحظة
𝟏
.)BT = r( ) بدالً من القانونBT = N * r = N * v * fs( فيجب أن نستخدم قانون عرض الحزمة
𝟐
Example (11): The analog signal has a bandwidth of (1kHz) and an
amplitude range of [(-10) to (+10)]V is to be transmitted over 16-levels PCM
system. If the average power is (20mW), determine the:
(a) number of bits per symbol. (b) bit rate and bandwidth. (c) S/N.
(d) maximum quantization error and percentage of accuracy.
Solution: (a) q = 2v → v = log (q) / log (2) = log (16) / log (2) = 4 bits/symbol
(b) fs ≥ 2W ≥ 2 (1kHz) ≥ 2kHz ; r = v * fs = 4 * (2kHz) = 8kHz
𝐒
(c) ( )dB = (4.8 + 6v)dB = 4.8 + (6)(4) = 4.8 + 24 = 28.8 dB
𝐍
(d) 𝜺max = 2|xmax| / q = 2(10)V/16 = 20/16 = 1.25V = Accuracy
∴ Percentage of accuracy = 𝜺max * 100% = (1.25) (100)% = 125%
Q\ Choose the correct branch:
Q1: Identify which process of sampling in pulse code modulation is known as
(A) Analog modulation (B) Impulse modulation
(C) Digital modulation (D) Quadrature amplitude modulation.
Q2: Choose the sampling rate at which the amplitude of the analog speech
signal is sampled in standard digital voice communication systems
(A) 1600 Samples/sec (B) 3200 Samples/sec
(C) 6400 Samples/sec (D) 8000 Samples/sec
Q3: Select the appropriate Nyquist sampling rate when an analog signal
having highest frequency of (1630Hz) and lowest frequency of (250Hz)
(A) 1630 Hz (B) 1880 Hz (C) 2760 Hz (D) 3260 Hz
Q4: A continuous time signal is represented by [s(t) = 8 cos(200πt)].
The minimum sampling rate to avoid aliasing should be
(A) 100 Hz (B) 200 Hz (C) 400 Hz (D) 800 Hz
Q5: Statement I: In uniform quantizers, step size remains same throughout
the amplitude range of the input analog signal. Statement II: The process of
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
|8|
companding allows binary codes to be compressed, thereby reducing
transmission time and bandwidth requirements
(A) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect.
(B) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect.
(C) Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct.
(D) Both statements are correct.
Q6: In ___________________, the code used for each sample is based on the
difference between successive samples rather than samples themselves
(A) Differential pulse code modulation. (B) Delta modulation.
(C) Delta-sigma modulation. (D) Adaptive delta modulation.
Q7: To avoid slope overload distortion in delta modulation, which one of the
following relationship between the sampling rate (fs), the maximum
frequency (fm), the maximum amplitude of the input sinusoidal signal (Vm),
and the step-size (𝜹) is correct
𝟐𝛑𝐟𝐦 𝛅 𝟐𝛑𝐟𝐦 𝐕𝐦 𝟐𝛑𝐕𝐦 𝟐𝛑𝐟𝐦
(A) fs ≥ ( ) (B) fs ≥ ( ) (C) fs ≥ ( ) (D) fs ≥ ( )
𝐕𝐦 𝛅 𝐟𝐦 𝛅 𝐕𝐦 𝛅
Q8: Statement I: The (S/N) performance of DM is better than PCM by more
than (3dB). Statement II: For same quality of transmission, the bit rate
needed for DM is much higher than by PCM
(A) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect.
(B) Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct.
(C) Both statements are correct.
(D) Both statements are incorrect.
Q9: Slope overload is a large difference between the original and replicated
delta modulation signals. It can be avoided by using
(A) Uniform step size. (B) Non-uniform step size.
(C) Adaptive step size. (D) Non-adaptive step size.
Q10: PCM using at the standard transmission bit rate of (64kbps) requires
(A) (4kHz) channel bandwidth for transmission of digitized voice signals.
(B) (8kHz) channel bandwidth for transmission of digitized voice signals.
(C) (32kHz) channel bandwidth for transmission of digitized voice signals.
(D) (64kHz) channel bandwidth for transmission of digitized voice signals.
College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Techniques 2016
You might also like
- Tutorial 4-SolutionDocument11 pagesTutorial 4-SolutionZaidi Mat ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) : Modulating (Analog) SignalDocument5 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM) : Modulating (Analog) SignalMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- PMM VFD Manual d11 03 010410Document100 pagesPMM VFD Manual d11 03 010410molanoavilaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications - H.AN PDFDocument12 pagesDigital Communications - H.AN PDFMohamd barca100% (1)
- Digital CommunicationsDocument39 pagesDigital Communicationsmakomdd100% (1)
- 416 Assignment 3Document3 pages416 Assignment 3mahmab70No ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractice Questionspratik shuklaNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument16 pagesDigital CommunicationAli Najim Al-AskariNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015Document3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015shreyas_stinsonNo ratings yet
- DCDocument8 pagesDCharshit420No ratings yet
- Digital Telecommunication (TN 320) Tutorial 2Document2 pagesDigital Telecommunication (TN 320) Tutorial 2Alango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Ee150hw04 2012Document2 pagesEe150hw04 2012thinkberry22No ratings yet
- Digital Communication Gate BitsDocument4 pagesDigital Communication Gate BitsVn LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Central College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiDocument8 pagesCentral College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiqweweNo ratings yet
- DCS Comprehension QuestionsDocument4 pagesDCS Comprehension QuestionsRameshkumar JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Chhhpppttteeerrr 55555Document12 pagesChhhpppttteeerrr 55555S Ahson ASNo ratings yet
- Digi Comm Model QP P1Document3 pagesDigi Comm Model QP P1bku14677No ratings yet
- PCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberDocument77 pagesPCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberTao Thích Màu ĐenNo ratings yet
- MimoDocument34 pagesMimoarun14089No ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) PDFDocument45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) PDFKunal KatariyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal Katariya100% (1)
- DCS SolnDocument6 pagesDCS SolnSandeep Kumar100% (1)
- Comm. Sys. Lect. 10Document21 pagesComm. Sys. Lect. 10sulllNo ratings yet
- DC Que BankDocument11 pagesDC Que BankGaurav Kumbharde0% (1)
- T) V. The Total SidebandDocument19 pagesT) V. The Total SidebandPramiti ParasharNo ratings yet
- Dcby Devils DukeDocument23 pagesDcby Devils DukeTummala JanakiramNo ratings yet
- DC Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesDC Tutorial Sheet 1Sabir SankhlaNo ratings yet
- EE370 Final 091Document6 pagesEE370 Final 091thinkberry22No ratings yet
- Kasraian ECET375 Week2Document42 pagesKasraian ECET375 Week2Raul PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Exp. PCMDocument9 pagesExp. PCMsairajdreamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Document4 pagesAssignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Sourav kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- QDocument4 pagesQSri NikethanNo ratings yet
- Baseband Questions StudentsDocument3 pagesBaseband Questions StudentsRishi JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ecm413 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Ecm413 PDFCaha yANo ratings yet
- PCM BahaaDocument50 pagesPCM BahaaNazar liveNo ratings yet
- Ec 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023Document24 pagesEc 2004 (PDC) - CS - End - May - 2023223UTKARSH TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Design & Simulation of DSSSS Using MATLAB SIMULINKDocument16 pagesDesign & Simulation of DSSSS Using MATLAB SIMULINKNaman ChandNo ratings yet
- Comm Chptr4Document53 pagesComm Chptr4Muhamad Fuad100% (1)
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Digital Modulation and Forward Error CorrectionDocument74 pagesPresentation On Digital Modulation and Forward Error CorrectionJitendra Chuugh100% (1)
- Lecture Note8b Summer0203Document13 pagesLecture Note8b Summer0203Melaku DinkuNo ratings yet
- Voice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370Document7 pagesVoice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370saidur183No ratings yet
- Week 3 1 PDFDocument33 pagesWeek 3 1 PDFosmanriazNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument6 pagesQuestion Banksweetkhushboo786_592No ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesSignals and Systems Sample QuestionsSimon Deshte NderituNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument26 pagesPulse Code Modulationعبدالله سعد محمدصالحNo ratings yet
- Lec PU March05Document98 pagesLec PU March05Muhammad Awais AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Student TDM DPCM DM QDocument1 pageStudent TDM DPCM DM Qmoath farrajNo ratings yet
- Problemas Parte I Comunicaciones DigitalesDocument17 pagesProblemas Parte I Comunicaciones DigitalesNano GomeshNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument26 pagesPulse Code Modulationbree789No ratings yet
- 3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Document34 pages3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Brian Edward HarrisNo ratings yet
- Nemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1Document7 pagesNemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1pauliNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 21 Tutorial Sheet I Principles of Communication Engg IIDocument2 pages2020 - 21 Tutorial Sheet I Principles of Communication Engg IISHOBHIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- Peak-To-Average Power Ratio Reduction by CB-ACE and Adaptive Ace AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesPeak-To-Average Power Ratio Reduction by CB-ACE and Adaptive Ace AlgorithmsShankar GaneshNo ratings yet
- PCM Transmission Bandwidth: Digital CommunicationsDocument8 pagesPCM Transmission Bandwidth: Digital CommunicationsSarthak SouravNo ratings yet
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Convertor IIIDocument14 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertor IIIMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Data Comunication and Networking: Telecommunication, Which Includes Telephony, TelegraphyDocument12 pagesData Comunication and Networking: Telecommunication, Which Includes Telephony, TelegraphyMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter ADC: Lecturer Mohand LokmanDocument23 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter ADC: Lecturer Mohand LokmanMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Noise: Signal To Noise RatioDocument5 pagesNoise: Signal To Noise RatioMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Networks: Network CriteriaDocument6 pagesNetworks: Network CriteriaMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Physical Structures Before Discussing Networks, We Need To Define Some Network AttributesDocument23 pagesPhysical Structures Before Discussing Networks, We Need To Define Some Network AttributesMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Guided Transmission Media 1. Twisted PairDocument7 pagesGuided Transmission Media 1. Twisted PairMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter IIDocument8 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter IIMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Categories of Wireless Networks: System Interconnection Wireless Lans Wireless WansDocument15 pagesWireless Networks: Categories of Wireless Networks: System Interconnection Wireless Lans Wireless WansMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Write The Name of The Layer of The OSI Reference Model and Write Its TasksDocument1 pageWrite The Name of The Layer of The OSI Reference Model and Write Its TasksMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- مبادئ شبكات - حل أسئلة الكورسينDocument13 pagesمبادئ شبكات - حل أسئلة الكورسينMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Sheet (4) : ELE 466 Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesSheet (4) : ELE 466 Communication SystemsMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- The 3 Layer of The OSI Reference Model Is Network LayerDocument5 pagesThe 3 Layer of The OSI Reference Model Is Network LayerMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications - H.AN PDFDocument12 pagesDigital Communications - H.AN PDFMohamd barca100% (1)
- Real Time - Designs ProblemsDocument9 pagesReal Time - Designs ProblemsMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Position ModulationDocument3 pagesPulse Position ModulationMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Width Modulation: Modulating (Analog) Signal: Carrier (Pulse Train) SignalDocument3 pagesPulse Width Modulation: Modulating (Analog) Signal: Carrier (Pulse Train) SignalMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Part Exp 1Document2 pagesSimulation Part Exp 1Mohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Why The Parallel Port?Document11 pagesWhy The Parallel Port?Mohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm 215 Mobile PlatformDocument2 pagesQualcomm 215 Mobile PlatformMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm 205 Mobile Platform BriefDocument2 pagesQualcomm 205 Mobile Platform BriefMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression 4 UpdateDocument24 pagesImage Compression 4 UpdateMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression 3 UpdateDocument11 pagesImage Compression 3 UpdateMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression 2 UpdateDocument10 pagesImage Compression 2 UpdateMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 14Document4 pagesExperiment No 14Mohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Improved Direct Back EMF Detection For Sensorless Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor DrivesDocument6 pagesImproved Direct Back EMF Detection For Sensorless Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor DrivesBùi TuyếnNo ratings yet
- YLPS Quick Installation Guide (4S)Document25 pagesYLPS Quick Installation Guide (4S)remus popescuNo ratings yet
- PI Controlled Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter (BDDDC) and Highly Efficient Boost Converter For Electric VehiclesDocument5 pagesPI Controlled Bi-Directional DC-DC Converter (BDDDC) and Highly Efficient Boost Converter For Electric VehiclesOscar Olarte OrtizNo ratings yet
- BLHeli - 32 Manual ARM Rev32.x PDFDocument10 pagesBLHeli - 32 Manual ARM Rev32.x PDFaniket5941No ratings yet
- Rain Sensing Automatic Car Wiper Using 555 TimerDocument6 pagesRain Sensing Automatic Car Wiper Using 555 TimerSunil MoreNo ratings yet
- 04 M Engine Management SystemDocument56 pages04 M Engine Management SystemDupapipapapa100% (2)
- Philips Az1500 Az1505 SMDocument33 pagesPhilips Az1500 Az1505 SMJuan Carlos PerdomoNo ratings yet
- User Manual of 4th Control SystemDocument41 pagesUser Manual of 4th Control SystemMario ParodiNo ratings yet
- Viper 27Document31 pagesViper 27javierrincon800No ratings yet
- Electric Drives MyCoursesDocument37 pagesElectric Drives MyCoursesMochamad AldiNo ratings yet
- HM7000 Series Decoders Reference ManualDocument130 pagesHM7000 Series Decoders Reference ManualFernandoNo ratings yet
- Length and Speed Measurement Using High-Speed Counters (HSC)Document27 pagesLength and Speed Measurement Using High-Speed Counters (HSC)Admir HodzicNo ratings yet
- Current Source & Voltage Source InvertersDocument2 pagesCurrent Source & Voltage Source InvertersAhmed El SebaiiNo ratings yet
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFDocument27 pagesS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Model of The Elevator Controlled by ARDDocument6 pagesLaboratory Model of The Elevator Controlled by ARDFərid SəmədovNo ratings yet
- Control of Single-Phase Four-Quadrant PWM Rectifier For Traction SystemsDocument6 pagesControl of Single-Phase Four-Quadrant PWM Rectifier For Traction SystemsjaiminNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid-Switch-Based Soft-Switching Inverter For Ultrahigh-Efficiency Traction Motor DrivesDocument8 pagesA Hybrid-Switch-Based Soft-Switching Inverter For Ultrahigh-Efficiency Traction Motor DrivesraghuaadsNo ratings yet
- Kenwood Kdc-348u kdc-4751sd Kdc-Bt41u Kdc-Bt648u Kdc-U4549 Kdc-U4549s Kdc-U549bt kdc-x395 kdc-x695Document50 pagesKenwood Kdc-348u kdc-4751sd Kdc-Bt41u Kdc-Bt648u Kdc-U4549 Kdc-U4549s Kdc-U549bt kdc-x395 kdc-x695lucasNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement Using DVRDocument6 pagesPower Quality Improvement Using DVRNirav RanaNo ratings yet
- MSC Data Sheet ProStar PWM 161128 07 MM HIGHDocument2 pagesMSC Data Sheet ProStar PWM 161128 07 MM HIGHAndes PutraNo ratings yet
- KA5H0380R/KA5M0380R/KA5L0380R: Features DescriptionDocument14 pagesKA5H0380R/KA5M0380R/KA5L0380R: Features DescriptionVidal VelasquezNo ratings yet
- OPTOTRONIC Constant-Voltage LED Power Supplies and Controls (EN)Document29 pagesOPTOTRONIC Constant-Voltage LED Power Supplies and Controls (EN)Raphael LopesNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Chandkheda, Ahmedabad Affiliated HJD Institute of Technical Education & ResearchDocument33 pagesGujarat Technological University Chandkheda, Ahmedabad Affiliated HJD Institute of Technical Education & ResearchJaimin ChainaniNo ratings yet
- Atmega8 Uc: Timer1 - PWM !!!Document13 pagesAtmega8 Uc: Timer1 - PWM !!!malhiavtarsinghNo ratings yet
- IOT Practical File KOT 551Document46 pagesIOT Practical File KOT 551qz5jq94yh2No ratings yet
- Harmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierDocument112 pagesHarmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierGautam Umapathy0% (1)
- As Sine Wave Generation by UsingDocument51 pagesAs Sine Wave Generation by UsingAjay VarmaNo ratings yet
- BD Class D ModulationDocument18 pagesBD Class D ModulationDiego Cowes100% (1)