Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food & Disease
Food & Disease
Uploaded by
Prince Nickson Ngwira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesOriginal Title
FOOD & DISEASE (2).doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesFood & Disease
Food & Disease
Uploaded by
Prince Nickson NgwiraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
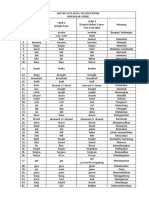
TABLE 1 : Specimens to obtain from patients in food
borne disease investigation.
Suspect Agent Specimen
Bacillus cereus Stool
Brucella Blood taken at several intervation
Chemical (gastrointestinal symptoms) Vomitus, stomach contents, urine
Chemical (neurological symptoms) Blood, urine
Clostridium botulinum Blood, feces
Clostridium perfringens Stool or rectal swab*
Infection hepatitis virus Urine, blood
Salmonella, Shigella, other enteric
Stool or rectal swab; occasionally blood
bacteria
Salmonella typhi (typhoid fever) Stool, urine, blood
Staphylococcus aureus Vomitus, stool
Trichinella Blood, biopsy tissue
Other parasites Stool, sometimes blood
Vibrio parahaemolyticus Stool
Useful only if serotyping is done
TABLE 2 : Sources and Modes of Transmission of Food Borne
pathogens by infected workers.
Source Mode of Transmission Example Diseases
Feces Intestinal carriers who are Typhoid fever
excreting organisms, touch Paratyphoid fever
feces or contaminated skin Salmonellosis
with hands, fail to wash hand Shigellosis
adequately, and then handle Infectious hepatitis
food before the organisms C. perfringens foodborne
succumb to drying or the pH illness
reaction of the skin. Enterococcal foodborne illness
Enteropathogenic
E. coli infections
ECHO and Coxsackie
viral infections
Amebiasis
Balantidiasis
Raw food of Workers touch raw food or Salmonellosis
animal origin equipment that previously C. perfringens foodborne
contacted raw foods and then illness
handle other foods. V. parahaemolyticus infection
Enterococcal foodborne illness.
Nose or throat Workers touch nose or mouth Staphylococcal intoxication
with hands and then handle Beta hemolytic streptococcal
foods; coughing; sneezing infection.
Infected lesions Worker touch food with Staphylococcal intoxication
infected lesion or they touch Beta hemolytic streptococcal
lesion with hands and then infection.
handle foods.
Table 3 : Specimens to obtain from food workers when a
particular disease is suspected.
Suspected Disease Specimen from Food Worker
Staphylocaccal intoxication Anterior nasal
Nasopharyngeal
Septic lesion or pus
Skin surface swab
Hand swab or rinse
Salmonellosis Stool or rectal swab Blood (on rare
occasions)
Stool or rectal swab
C. perfringens foodborne illness
Typhoid fever Stool
Blood
Urine
Stool or rectal swab
Shigellosis
Stool
Parasitic infections
Beta hemolytic streptococcal infections Throat
Anterior nasal
Nasopharyngeal
Septic lesions or pus
Stool or rectal swab
Enterrococcal infections
Stool or rectal swab
Enteropathogenic E. coli
Stool or rectal swab
ECHO or Coxsackie viral infection
You might also like
- Skittles Fractions Math Target Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesSkittles Fractions Math Target Lesson Planapi-396384317No ratings yet
- Sylvia Gregorio Case StudyDocument10 pagesSylvia Gregorio Case StudyJoyleen Cervantes100% (2)
- Tonka FinalDocument16 pagesTonka Finalআন নাফি100% (1)
- Gram Negative BacilliDocument108 pagesGram Negative Bacilliblue_blooded23100% (1)
- Digestive System InfectionsDocument30 pagesDigestive System InfectionsGoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2selambante shiferawNo ratings yet
- Pathologic and NonDocument11 pagesPathologic and NonAisha DoreenNo ratings yet
- Icd11 Mms enDocument2,513 pagesIcd11 Mms enJASVANT PARMARNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diarrhea: Charles S. Bryan, M.DDocument62 pagesInfectious Diarrhea: Charles S. Bryan, M.DLuis BrennanNo ratings yet
- Environmentally Transmitted Pathogens CH 22 - 2018Document24 pagesEnvironmentally Transmitted Pathogens CH 22 - 2018reprano PNo ratings yet
- Gastro Intestinal Infections NotesDocument9 pagesGastro Intestinal Infections NotesBayan AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- Environmental SurveillanceDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Surveillancedr rajoreNo ratings yet
- Waterborne Diseases: Group 2Document21 pagesWaterborne Diseases: Group 2Jay RickNo ratings yet
- MicroparasitologyDocument28 pagesMicroparasitologyMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Module 25 - Hospital Hygiene Infection Control and Health Care Waste ManagementDocument38 pagesModule 25 - Hospital Hygiene Infection Control and Health Care Waste ManagementHao Le HoangNo ratings yet
- Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Entamoeba Histolytica. ShigellaDocument19 pagesShigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Entamoeba Histolytica. ShigellaAlmas TNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative RodsDocument8 pagesGram Negative RodsRuel Maddawin100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2አድሜ ልስልሱNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea UpdatedDocument66 pagesDiarrhea UpdatedAna KarlaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Infeksi Saluran PencernaanDocument22 pagesJurnal Infeksi Saluran PencernaanDini Okta PutriNo ratings yet
- Enteric BacteriaDocument14 pagesEnteric BacteriaShubham Pareshkumar KadiwalaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: Escherichia ColiDocument4 pagesGastroenteritis: Escherichia ColiFanny BudimanNo ratings yet
- GI Tract InfectionsDocument29 pagesGI Tract InfectionsMahrukh SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument65 pagesInfectious DiseasesFathimah UswahNo ratings yet
- UTI SeminarDocument3 pagesUTI SeminarAmbi KNo ratings yet
- Peran Mikroorganisme Dalam Kehidupan-2Document51 pagesPeran Mikroorganisme Dalam Kehidupan-2Safhira Nur HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Enterobacter With Mucoid Colonies) : Clinical BacteriologyDocument29 pagesEnterobacter With Mucoid Colonies) : Clinical BacteriologyIra ElizagaNo ratings yet
- Week 10 WsDocument33 pagesWeek 10 Wsapi-262089947No ratings yet
- Salmonella LectureDocument21 pagesSalmonella Lectureghosson01006228961No ratings yet
- Dirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningDocument17 pagesDirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningAbcdefg HijklNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument5 pagesLumbar PunctureJennifer JaneNo ratings yet
- Enteric Gram-Negative Rods (Enterobacteriaceae) : Prepared by Assistant Professor Dr. Khawaja Shakeel AhmedDocument26 pagesEnteric Gram-Negative Rods (Enterobacteriaceae) : Prepared by Assistant Professor Dr. Khawaja Shakeel AhmedZheemo ArshavinNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal and Intrabadominal Infection PharmacotherapyDocument50 pagesGastrointestinal and Intrabadominal Infection Pharmacotherapylibentadesse57No ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument107 pagesEnterobacteriaceaeClaire Gonzales100% (1)
- Microbial AspectsDocument29 pagesMicrobial AspectsLolit PopNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The GITDocument31 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The GITNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Disease Transmitted Through MilkDocument12 pagesDisease Transmitted Through MilkSUTHAN100% (9)
- List of Causative AgentDocument26 pagesList of Causative AgentMe2 ModhNo ratings yet
- Daren G. Linatoc, RN, RM, LPT, Man, MaedDocument36 pagesDaren G. Linatoc, RN, RM, LPT, Man, MaedMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- Week2 Biological Hazards 2023 PDFDocument45 pagesWeek2 Biological Hazards 2023 PDFgris valeryNo ratings yet
- ICD11 - MMS en 01Document116 pagesICD11 - MMS en 01komangallan wpNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis in Children Acute Gastroenteritis in ChildrenDocument28 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis in Children Acute Gastroenteritis in ChildrenFernando AnibanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - VMICRO 4th TopicDocument8 pagesReviewer - VMICRO 4th TopicAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Which of These Are Normal Intestinal Microbiota?: Correct AnswerDocument1 pageWhich of These Are Normal Intestinal Microbiota?: Correct AnswerAmberShanty TalerNo ratings yet
- E ColiDocument12 pagesE ColiMedox007No ratings yet
- Human Health and Disease-1Document12 pagesHuman Health and Disease-1Ananya MoniNo ratings yet
- Quizlet BacteDocument18 pagesQuizlet BacteMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument49 pagesMicrobiologyinnyNo ratings yet
- GIT 24 AnanDocument135 pagesGIT 24 AnanjjjkkNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiarrheaDocument64 pagesInfectious DiarrheanathanielNo ratings yet
- Final - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsDocument5 pagesFinal - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsVijay JadhavNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument52 pagesTyphoid Fevertummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (5)
- Enteric Pathogens Part One: DR A.Aziz Djamal MSC - DTM&H.SPMK (KDocument20 pagesEnteric Pathogens Part One: DR A.Aziz Djamal MSC - DTM&H.SPMK (KikaawiratamaNo ratings yet
- Icrobiology: Pathogenic Gram-Negative Bacilli (Enterobacteriaceae)Document67 pagesIcrobiology: Pathogenic Gram-Negative Bacilli (Enterobacteriaceae)Drashua AshuaNo ratings yet
- 17-06 - DiarrheaDocument11 pages17-06 - DiarrheaRodrigo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nosocomial InfectionDocument4 pagesNosocomial InfectionPabinaNo ratings yet
- 4 Stool Culture PDFDocument35 pages4 Stool Culture PDFVenny PatriciaNo ratings yet
- Practical No:1 Title: Zoonotic Disease of Poultry and Their Control MeasureDocument3 pagesPractical No:1 Title: Zoonotic Disease of Poultry and Their Control MeasureShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases 2Document2 pagesInfectious Diseases 2thedarkwingNo ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AAVV, Future Husserlian PhenomenologyDocument175 pagesAAVV, Future Husserlian Phenomenologybrevi1100% (1)
- Tort I Vicarious LiabilityDocument6 pagesTort I Vicarious LiabilityMoureen MosotiNo ratings yet
- Onsite-Brochure May2017Document5 pagesOnsite-Brochure May2017zeeshanrahman714No ratings yet
- Protected Banking Verification by Figure Pixel Comparison and Bit Coin Transaction Using Block Chain and Image ProcessingDocument18 pagesProtected Banking Verification by Figure Pixel Comparison and Bit Coin Transaction Using Block Chain and Image ProcessingBalamurugan SMNo ratings yet
- English 10Document1 pageEnglish 10Dolorfey SumileNo ratings yet
- Design of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersDocument10 pagesDesign of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersJake OkuyeNo ratings yet
- Political Dynasty: A Political InequalityDocument11 pagesPolitical Dynasty: A Political InequalityAngelNo ratings yet
- Caneda vs. CADocument3 pagesCaneda vs. CAAnnalie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Isik Doll Body and OutfitDocument34 pagesIsik Doll Body and Outfitdeniselopdi100% (1)
- Good Quotes VenkatDocument10 pagesGood Quotes Venkatbhappy4ever100% (2)
- Rutherford County BallotsDocument8 pagesRutherford County BallotsUSA TODAY NetworkNo ratings yet
- Authentication of Instruments and Documents Without The Philippine IslandsDocument19 pagesAuthentication of Instruments and Documents Without The Philippine Islandswakadu095068No ratings yet
- 5G Certification OverviewDocument14 pages5G Certification Overviewluis100% (1)
- JournalsDocument9 pagesJournalsapi-302089675No ratings yet
- York - 2001 - New Age Commodification and Appropriation of SpiritualityDocument14 pagesYork - 2001 - New Age Commodification and Appropriation of SpiritualityAnkur GargNo ratings yet
- Letter MIX 02Document76 pagesLetter MIX 02Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- North Jersey Jewish Standard, April 17, 2015Document64 pagesNorth Jersey Jewish Standard, April 17, 2015New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- 19/05/2021 Visit Date 39Y/Male Age & Gender Med110222452 Customerid MR.L Venkatachalam CustomernameDocument5 pages19/05/2021 Visit Date 39Y/Male Age & Gender Med110222452 Customerid MR.L Venkatachalam Customernamesyed imranNo ratings yet
- Core, Care, Cure ModelDocument33 pagesCore, Care, Cure ModelThushara Krishnas50% (2)
- Irregular Siap PrintDocument3 pagesIrregular Siap PrintGerald TeufNo ratings yet
- ISIELT Lecture 9.2:: Rules of Statutory Interpretation: The Golden RuleDocument12 pagesISIELT Lecture 9.2:: Rules of Statutory Interpretation: The Golden RuleManjare Hassin RaadNo ratings yet
- Book 3 SuccessionDocument189 pagesBook 3 SuccessiontatatalaNo ratings yet
- Dental Act 2018Document110 pagesDental Act 2018copyourpairNo ratings yet
- BMC Control-M Control Your FutureDocument18 pagesBMC Control-M Control Your Futureemily emmaNo ratings yet
- Management of Eclampsia by Nursing StaffDocument42 pagesManagement of Eclampsia by Nursing Staffمالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Successful New Design For The Fog HarpDocument2 pagesSuccessful New Design For The Fog HarpJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- PEE - Alice in WonderlandDocument5 pagesPEE - Alice in Wonderlandmary lauNo ratings yet