Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Also Known As Pelvic Inflammatory Disorder (PID), Is
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Also Known As Pelvic Inflammatory Disorder (PID), Is
Uploaded by
hiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Candida VulvovaginitisDocument20 pagesCandida VulvovaginitisVicobeingoNo ratings yet
- Bacteسيبليسليسl genital tract infectionsDocument60 pagesBacteسيبليسليسl genital tract infectionsDr.Issam JumaaNo ratings yet
- 4 Prevention of Pregnancy and STDDocument50 pages4 Prevention of Pregnancy and STDJEHAN HADJIUSMANNo ratings yet
- Pid XureDocument8 pagesPid XureMary Karen Rose BorjaNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases OverviewDocument45 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases OverviewJean De Vera MelendezNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - 1Document8 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease - 1fatqur28No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionDocument13 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionnathanNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument9 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseChika JonesNo ratings yet
- Information About AidsDocument2 pagesInformation About AidsanonymousNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument71 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesAkwu AkwuNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Document3 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)munirbonaya325No ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Cause Infertility: A Condition Requiring Closer AttentionDocument60 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease Cause Infertility: A Condition Requiring Closer AttentionVergina ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPathophysiologyJessyl GirayNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument3 pagesAidsMargie Ballesteros ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - EditedDocument7 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease - EditedDanNo ratings yet
- PID and ChancroidDocument2 pagesPID and ChancroidRoy MutahiNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument8 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseAndyan Adlu Prasetyaji0% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsPowerzNo ratings yet
- Diseasesanddisorders 160407092222 PDFDocument33 pagesDiseasesanddisorders 160407092222 PDFNicole LamNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Tract Infections: An Introductory Overview: Types of InfectionDocument30 pagesReproductive Tract Infections: An Introductory Overview: Types of InfectionSherlocknovNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Infection in Adults and Adolescents - UpToDateDocument18 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Infection in Adults and Adolescents - UpToDateLeón RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument7 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseMephisto D. LeffertlarkNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infection - WikipediaDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted Infection - WikipediaAre Pee EtcNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment-Iiii Elaborate Your Knowledge On Various Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument11 pagesDigital Assignment-Iiii Elaborate Your Knowledge On Various Sexually Transmitted Diseasesamrita padmakumarNo ratings yet
- Pid PDFDocument4 pagesPid PDFNilakshi Barik MandalNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument40 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseJoaquín PeñaNo ratings yet
- About Us: Who We AreDocument11 pagesAbout Us: Who We AreIman Taufik UsmanNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Detection and Treatment of STD - Science 10Document17 pagesPrevention, Detection and Treatment of STD - Science 10JuliusNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument1 pageSexually Transmitted DiseasesGabrielle StewartNo ratings yet
- Occurrence of Hypertension in Nueva Ecija, A Documentary AnalysisDocument63 pagesOccurrence of Hypertension in Nueva Ecija, A Documentary AnalysisZypherson CastilloNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C Is An Infectious Disease Caused by TheDocument29 pagesHepatitis C: Hepatitis C Is An Infectious Disease Caused by Theteam engineerNo ratings yet
- GYN 讀書報告Document67 pagesGYN 讀書報告Chia-Yuan ChenNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Blood-Borne PathogenDocument4 pagesExposure To Blood-Borne PathogenHesti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Study Notes For Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument4 pagesStudy Notes For Sexually Transmitted DiseasesPrince K. TaileyNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument8 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionsEmilio Antang JrNo ratings yet
- Boushra Rahman Postpartum InfectionDocument1 pageBoushra Rahman Postpartum InfectionClinica GinecologicaNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento EpiDocument13 pagesTratamiento EpiFrankRodríguezLuisNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeDocument1 pageHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromemsofyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction STIDocument7 pagesIntroduction STIAishaibrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia InfectionDocument5 pagesChlamydia InfectionYogesh PhadtareNo ratings yet
- (000043) PDFDocument30 pages(000043) PDFedi_wsNo ratings yet
- AIDS & Clinical: Symptoms of AIDS Related Opportunistic Infections and Their Effects On Human BodyDocument5 pagesAIDS & Clinical: Symptoms of AIDS Related Opportunistic Infections and Their Effects On Human BodyMarviane ThenNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Document2 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Budd DeviceNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectKarishma TiwariNo ratings yet
- STIsDocument4 pagesSTIsKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- What Is Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesRevathi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis InfectionsDocument28 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis InfectionsAmbarNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument14 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasetesleemmayjuneNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea: SymptomsDocument9 pagesGonorrhea: Symptomspragna novaNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis (TV) Is Likely The Most Common Non-Viral Sexually TransmittedDocument8 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis (TV) Is Likely The Most Common Non-Viral Sexually TransmittedHarmilaNo ratings yet
- CervicitisDocument7 pagesCervicitisElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- 1995 Congenital Cytomegalovirus InfectionDocument10 pages1995 Congenital Cytomegalovirus InfectionIndra T BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument3 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseokaciaNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases NotesDocument2 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases NotesIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- Final Chlamydia PaperDocument32 pagesFinal Chlamydia Paperapi-284978286No ratings yet
- Symptoms: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsDocument7 pagesSymptoms: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsAdalbert Carl CabritoNo ratings yet
- Malaria - WikipediaDocument75 pagesMalaria - Wikipediaadandiba06No ratings yet
- Ensayo Ingles FinalDocument7 pagesEnsayo Ingles FinalANDREITHAOSORIONo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- Healing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficenceDocument1 pageHealing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficencehiNo ratings yet
- Oath Ethics Physicians Healing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficenceDocument1 pageOath Ethics Physicians Healing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficencehiNo ratings yet
- Anaerobes Facultative MicroorganismsDocument1 pageAnaerobes Facultative MicroorganismshiNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Bladder Disease/Stones: Hippocratic OathDocument1 pageTreatment of Bladder Disease/Stones: Hippocratic OathhiNo ratings yet
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Also Known As Pelvic Inflammatory Disorder (PID), Is
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Also Known As Pelvic Inflammatory Disorder (PID), Is
Uploaded by
hiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Also Known As Pelvic Inflammatory Disorder (PID), Is
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Also Known As Pelvic Inflammatory Disorder (PID), Is
Uploaded by
hiCopyright:
Available Formats
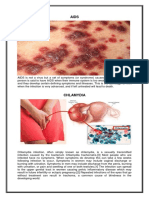
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is
an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes,
and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis.[5][2] Often, there may be no symptoms.[1] Signs and symptoms,
when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with
urination, pain with sex, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation.[1] Untreated PID can result in
long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer.[2][3][4]
The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. [5] Infections by Neisseria
gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases.[2] Often, multiple
different bacteria are involved.[2] Without treatment, about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial
infection and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection will develop PID.[2][9] Risk factors are
generally similar to those of sexually transmitted infections and include a high number of sexual
partners and drug use.[2] Vaginal douching may also increase the risk.[2] The diagnosis is typically
based on the presenting signs and symptoms.[2] It is recommended that the disease be considered in
all women of childbearing age who have lower abdominal pain. [2] A definitive diagnosis of PID is
made by finding pus involving the fallopian tubes during surgery.[2] Ultrasound may also be useful in
diagnosis.[2]
You might also like
- Candida VulvovaginitisDocument20 pagesCandida VulvovaginitisVicobeingoNo ratings yet
- Bacteسيبليسليسl genital tract infectionsDocument60 pagesBacteسيبليسليسl genital tract infectionsDr.Issam JumaaNo ratings yet
- 4 Prevention of Pregnancy and STDDocument50 pages4 Prevention of Pregnancy and STDJEHAN HADJIUSMANNo ratings yet
- Pid XureDocument8 pagesPid XureMary Karen Rose BorjaNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases OverviewDocument45 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases OverviewJean De Vera MelendezNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - 1Document8 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease - 1fatqur28No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionDocument13 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionnathanNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument9 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseChika JonesNo ratings yet
- Information About AidsDocument2 pagesInformation About AidsanonymousNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument71 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesAkwu AkwuNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Document3 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)munirbonaya325No ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Cause Infertility: A Condition Requiring Closer AttentionDocument60 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease Cause Infertility: A Condition Requiring Closer AttentionVergina ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPathophysiologyJessyl GirayNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument3 pagesAidsMargie Ballesteros ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - EditedDocument7 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease - EditedDanNo ratings yet
- PID and ChancroidDocument2 pagesPID and ChancroidRoy MutahiNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument8 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseAndyan Adlu Prasetyaji0% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsPowerzNo ratings yet
- Diseasesanddisorders 160407092222 PDFDocument33 pagesDiseasesanddisorders 160407092222 PDFNicole LamNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Tract Infections: An Introductory Overview: Types of InfectionDocument30 pagesReproductive Tract Infections: An Introductory Overview: Types of InfectionSherlocknovNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Infection in Adults and Adolescents - UpToDateDocument18 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Infection in Adults and Adolescents - UpToDateLeón RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument7 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseMephisto D. LeffertlarkNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infection - WikipediaDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted Infection - WikipediaAre Pee EtcNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment-Iiii Elaborate Your Knowledge On Various Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument11 pagesDigital Assignment-Iiii Elaborate Your Knowledge On Various Sexually Transmitted Diseasesamrita padmakumarNo ratings yet
- Pid PDFDocument4 pagesPid PDFNilakshi Barik MandalNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument40 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseJoaquín PeñaNo ratings yet
- About Us: Who We AreDocument11 pagesAbout Us: Who We AreIman Taufik UsmanNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Detection and Treatment of STD - Science 10Document17 pagesPrevention, Detection and Treatment of STD - Science 10JuliusNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument1 pageSexually Transmitted DiseasesGabrielle StewartNo ratings yet
- Occurrence of Hypertension in Nueva Ecija, A Documentary AnalysisDocument63 pagesOccurrence of Hypertension in Nueva Ecija, A Documentary AnalysisZypherson CastilloNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C Is An Infectious Disease Caused by TheDocument29 pagesHepatitis C: Hepatitis C Is An Infectious Disease Caused by Theteam engineerNo ratings yet
- GYN 讀書報告Document67 pagesGYN 讀書報告Chia-Yuan ChenNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Blood-Borne PathogenDocument4 pagesExposure To Blood-Borne PathogenHesti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Study Notes For Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument4 pagesStudy Notes For Sexually Transmitted DiseasesPrince K. TaileyNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument8 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionsEmilio Antang JrNo ratings yet
- Boushra Rahman Postpartum InfectionDocument1 pageBoushra Rahman Postpartum InfectionClinica GinecologicaNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento EpiDocument13 pagesTratamiento EpiFrankRodríguezLuisNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeDocument1 pageHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromemsofyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction STIDocument7 pagesIntroduction STIAishaibrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia InfectionDocument5 pagesChlamydia InfectionYogesh PhadtareNo ratings yet
- (000043) PDFDocument30 pages(000043) PDFedi_wsNo ratings yet
- AIDS & Clinical: Symptoms of AIDS Related Opportunistic Infections and Their Effects On Human BodyDocument5 pagesAIDS & Clinical: Symptoms of AIDS Related Opportunistic Infections and Their Effects On Human BodyMarviane ThenNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Document2 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Budd DeviceNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectKarishma TiwariNo ratings yet
- STIsDocument4 pagesSTIsKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- What Is Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesRevathi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis InfectionsDocument28 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis InfectionsAmbarNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument14 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasetesleemmayjuneNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea: SymptomsDocument9 pagesGonorrhea: Symptomspragna novaNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis (TV) Is Likely The Most Common Non-Viral Sexually TransmittedDocument8 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis (TV) Is Likely The Most Common Non-Viral Sexually TransmittedHarmilaNo ratings yet
- CervicitisDocument7 pagesCervicitisElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- 1995 Congenital Cytomegalovirus InfectionDocument10 pages1995 Congenital Cytomegalovirus InfectionIndra T BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument3 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseokaciaNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases NotesDocument2 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases NotesIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- Final Chlamydia PaperDocument32 pagesFinal Chlamydia Paperapi-284978286No ratings yet
- Symptoms: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsDocument7 pagesSymptoms: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsAdalbert Carl CabritoNo ratings yet
- Malaria - WikipediaDocument75 pagesMalaria - Wikipediaadandiba06No ratings yet
- Ensayo Ingles FinalDocument7 pagesEnsayo Ingles FinalANDREITHAOSORIONo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- Healing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficenceDocument1 pageHealing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficencehiNo ratings yet
- Oath Ethics Physicians Healing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficenceDocument1 pageOath Ethics Physicians Healing Gods Medical Ethics Medical Confidentiality Non-MaleficencehiNo ratings yet
- Anaerobes Facultative MicroorganismsDocument1 pageAnaerobes Facultative MicroorganismshiNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Bladder Disease/Stones: Hippocratic OathDocument1 pageTreatment of Bladder Disease/Stones: Hippocratic OathhiNo ratings yet