Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Discrete Math Intro of Algo
Discrete Math Intro of Algo
Uploaded by
sumon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views12 pagesThe linear search algorithm takes as input a list of numbers and a target number. It iterates through the numbers, comparing each to the target. If a match is found, it returns the current position. If no match is found after iterating through all numbers, it returns that the number was not in the list.
Original Description:
Original Title
discrete_math_intro_of_algo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe linear search algorithm takes as input a list of numbers and a target number. It iterates through the numbers, comparing each to the target. If a match is found, it returns the current position. If no match is found after iterating through all numbers, it returns that the number was not in the list.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views12 pagesDiscrete Math Intro of Algo
Discrete Math Intro of Algo
Uploaded by
sumonThe linear search algorithm takes as input a list of numbers and a target number. It iterates through the numbers, comparing each to the target. If a match is found, it returns the current position. If no match is found after iterating through all numbers, it returns that the number was not in the list.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Algorithms: An Introduction
Computer Science is About Problem Solving
• A Problem is specified by
1. The givens (a formulation)
• A set of objects
• Relations between them
2. The query
• The information one is trying to extract from the formulation, the question to
answer
• An algorithm is a method or procedure that solves instances of a problem
• ‘Algorithm’ is a distortion of Al-Khawarizmi, a Persian mathematician
Real World Computing World
Objects represented by… data Structures, ADTs, Classes
Relations implemented with… relations & functions (e.g., predicates)
Actions Implemented with… algorithms: a sequence of instructions
Algorithms: Formal Definition
• Definition: An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous
instructions for solving a problem.
• Properties of an algorithm
– Finite: the algorithm must eventually terminate
– Complete: Always give a solution when one exists
– Correct (sound): Always give a correct solution
• For an algorithm to be an acceptable solution to a problem, it
must also be effective. That is, it must give a solution in a
‘reasonable’ amount of time
• Efficient= runs in polynomial time. Thus, effective efficient
• There can be many algorithms to solve the same problem
Algorithms: General Techniques
• There are many broad categories of algorithms
– Deterministic versus Randomized (e.g., Monte-Carlo)
– Exact versus Approximation
– Sequential/serial versus Parallel, etc.
• Some general styles of algorithms include
– Brute force (enumerative techniques, exhaustive search)
– Divide & Conquer
– Transform & Conquer (reformulation)
– Greedy Techniques
– Dynamic programming and so on..
Good Pseudo-Code: Example
Intersection
Input: Two finite sets A, B
Output: A finite set C such that C = A B
1. C0
2. If |A|>|B|
3. Then Swap(A,B)
4. End
5. For every x A Do
6. If x B
7. Then C C {x} Union(C,{x})
8. End
9. End
10. Return C
Algorithms: Pseudo-Code
• Algorithms are usually presented using pseudo-code
• Bad pseudo-code
– gives too many details or
– is too implementation specific (i.e., actual C++ or Java code or giving
every step of a sub-process such as set union)
• Good pseudo-code
– Is a balance between clarity and detail
– Abstracts the algorithm
– Makes good use of mathematical notation
– Is easy to read and
– Facilitates implementation (reproducible, does not hide away
important information)
Writing Pseudo-Code: Advice
• Input/output must properly defined
• All your variables must be properly initialized, introduced
• Variables are instantiated, assigned using
• All `commands' (while, if, repeat, begin, end) bold face \bf
For i 1 to n Do
• All functions in small caps Union(s,t) \sc
• All constants in courier: pi 3.14 \tt
• All variables in italic: temperature 78 (\it, \em)
• LaTeX: Several algorithm formatting packages exist on WWW
Designing an Algorithm
• A general approach to designing algorithms is as follows
– Understanding the problem, assess its difficulty
– Choose an approach (e.g., exact/approximate, deterministic/
probabilistic)
– (Choose appropriate data structures)
– Choose a strategy
– Prove
1. Termination
2. Completeness
3. Correctness/soundness
– Evaluate complexity
– Implement and test it
– Compare to other known approach and algorithms
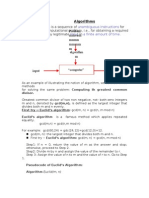
Algorithm Example: Max
• When designing an algorithm, we usually give a
formal statement about the problem to solve
• Problem
– Given: a set A={a1,a2,…,an} of integers
– Question: find the index i of the maximum integer ai
• A straightforward idea is
– Simply store an initial maximum, say a1
– Compare the stored maximum to every other integer in A
– Update the stored maximum if a new maximum is ever
encountered
Pseudo-code of Max
Max
Input: A finite set A={a1,a2,…,an} of integers
Output: An index i such that ai = max{a1,a2,…,an}
1. index 1
2. For i =2 to n Do
3. If ai > aindex
4. Then index i
5. End
6. End
7. Return aindex
Flow chart
• A diagram of the sequence of movements or
actions of people or things involved in a
complex system or activity or solving a
particular problem.
• A graphical representation of a computer
program/algorithm in relation to its sequence
of functions (as distinct from the data it
processes).
Simple algorithm for practices
Assignment#1
• Write an algorithm and draw a corresponding
flowchart to find the maximum element in a
finite sequence of input.
• Write an algorithm and draw a corresponding
flowchart to search a number in the given list
of numbers and also display its position by
linear search.
You might also like
- ThesisDocument18 pagesThesisapi-29776055293% (15)
- DDAL-ELW11 - Secrets BelowDocument26 pagesDDAL-ELW11 - Secrets BelowUniewielNo ratings yet
- Marwari Wedding For DummiesDocument8 pagesMarwari Wedding For DummieslokeshtodiNo ratings yet
- 1 AlgorithmAnalysis-2 PDFDocument39 pages1 AlgorithmAnalysis-2 PDFSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chap 9 Algorithms IntroductionDocument22 pagesChap 9 Algorithms IntroductionAnh ViệtNo ratings yet
- Cos 431 Algorithms HandbookDocument97 pagesCos 431 Algorithms HandbookEzeuko EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 1 Alg Lecture1 (1) (7 Files Merged)Document185 pages1 Alg Lecture1 (1) (7 Files Merged)Harshit RoyNo ratings yet
- Algorithms: An Introduction: Algorithm' Is A Distortion of Al-KhawarizmiDocument88 pagesAlgorithms: An Introduction: Algorithm' Is A Distortion of Al-KhawarizmiNgọc HùngNo ratings yet
- Algorithm: - DefinitionsDocument17 pagesAlgorithm: - Definitionsaamir ali100% (1)
- Algorithm CH 1 BestDocument49 pagesAlgorithm CH 1 BestDawit BeyeneNo ratings yet
- Objectives: A Problem Example 1Document5 pagesObjectives: A Problem Example 1iam_wilberNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DaaDocument126 pagesIntroduction To DaaMalajebamaniraj MalaNo ratings yet
- CSCI20 Prelim: Instructor: Priyanka SDocument37 pagesCSCI20 Prelim: Instructor: Priyanka SRonald CordovaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Analysis and Design - LectureDocument94 pagesAlgorithm Analysis and Design - LectureSuleiman GargaareNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Algorithms DSDocument27 pagesAnalysis of Algorithms DSAviral SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit-1Document19 pagesDAA Unit-1Vengat VengatesanNo ratings yet
- CSC 305 VTL Lecture 01Document8 pagesCSC 305 VTL Lecture 01Bello TaiwoNo ratings yet
- AdvD&AoA - Lecture1Document36 pagesAdvD&AoA - Lecture1shahabNo ratings yet
- Daa 3Document127 pagesDaa 3abhiNo ratings yet
- Iiyr It - Cs8451 Daa - 5 Units NotesDocument117 pagesIiyr It - Cs8451 Daa - 5 Units Notes5054 - Monish SNo ratings yet
- A Computer Algorithm: - Is A Step-By-Step Method of Solving Some ProblemDocument13 pagesA Computer Algorithm: - Is A Step-By-Step Method of Solving Some Problemabood jalladNo ratings yet
- Data Structure and Algorithms PDFDocument151 pagesData Structure and Algorithms PDFmitiku tolasaNo ratings yet
- L03-04 - 08.02.2021&10.02.2021 - Introduction To Analysis of AlgorithmDocument45 pagesL03-04 - 08.02.2021&10.02.2021 - Introduction To Analysis of AlgorithmSamia RahmanNo ratings yet
- HCS 111 Handout 1Document11 pagesHCS 111 Handout 1Gerald KapinguraNo ratings yet
- Daa1ppt2024 240408040827 55e92202Document174 pagesDaa1ppt2024 240408040827 55e92202pratushk484No ratings yet
- Week1 IntroductionDocument28 pagesWeek1 Introductionlama alessaNo ratings yet
- DaaDocument39 pagesDaaVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- DaaDocument113 pagesDaajayanthikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Analysis of Algorithms: Lecture # 1 MS (Computer Science) Semester 1Document21 pagesAdvanced Analysis of Algorithms: Lecture # 1 MS (Computer Science) Semester 1Demo accountNo ratings yet
- Ds-Unit 1Document114 pagesDs-Unit 1cocayushwar30No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument36 pagesIntroductionDiya GuptaNo ratings yet
- 01Chapter-One Introduction To Analysis of AlgorithmDocument39 pages01Chapter-One Introduction To Analysis of AlgorithmtasheebedaneNo ratings yet
- EEB 435 Python LECTURE 3Document34 pagesEEB 435 Python LECTURE 3oswardNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Algorithm Lecture NotesDocument337 pagesAnalysis and Design of Algorithm Lecture NotesEfrain Sanjay AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- To See Comments Click On Review and and Click On Show CommentsDocument107 pagesTo See Comments Click On Review and and Click On Show CommentsNuredin AbdumalikNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit 1Document39 pagesDAA Unit 1Loganayagi PNo ratings yet
- 1 - Design and Analysis of Algorithms by Karamagi, RobertDocument346 pages1 - Design and Analysis of Algorithms by Karamagi, RobertK TiếnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Algorithms: Unit 1Document42 pagesIntroduction To Algorithms: Unit 1rushanandNo ratings yet
- Advanced Analysis of Algorithms: Lecture # 1Document19 pagesAdvanced Analysis of Algorithms: Lecture # 1feelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Data Structures and Algorithms AnalysisDocument44 pagesChapter-2-Data Structures and Algorithms Analysisbini100% (1)
- Jim DSA QuestionsDocument26 pagesJim DSA QuestionsTudor CiotloșNo ratings yet
- Daa UnitiDocument41 pagesDaa UnitiRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Algorithm (2 Hrs and Contains 3 Marks)Document6 pagesUnit 2: Algorithm (2 Hrs and Contains 3 Marks)Sarwesh MaharzanNo ratings yet
- Unit1 DaaDocument21 pagesUnit1 DaaArunachalam SelvaNo ratings yet
- CH-1 AdaDocument14 pagesCH-1 AdaMustafiz KhanNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit - IDocument32 pagesDAA Unit - ISubathra Devi MourouganeNo ratings yet
- MIT 6.00 Notes From Lessons 1,2 and 3.Document8 pagesMIT 6.00 Notes From Lessons 1,2 and 3.Nikola Nino IvankovićNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmDocument35 pagesData Structures and Algorithmdan hernandoNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction OldDocument62 pages01 Introduction OldAnushka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic AlgoritmDocument15 pagesBasic AlgoritmIvania PandaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Lec1 DR MMEDocument46 pagesAlgorithm Lec1 DR MMEmalkmoh781.mmNo ratings yet
- As An Example of Illustrating The Notion of AlgorithmDocument7 pagesAs An Example of Illustrating The Notion of AlgorithmKiran Kumar0% (1)
- Formal Verification of Programs With Arrays: Vu An Hoa Assoc. Prof. Chin Wei NganDocument25 pagesFormal Verification of Programs With Arrays: Vu An Hoa Assoc. Prof. Chin Wei Ngananhoa1No ratings yet
- DAA-Lecture Notes-Unit I-2Document30 pagesDAA-Lecture Notes-Unit I-2Manu KushaalNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Analysis Design Lecture1 PowerPoint PresentationDocument9 pagesAlgorithm Analysis Design Lecture1 PowerPoint PresentationPedro PedNo ratings yet
- DSA Notes by Inam Unit 4Document6 pagesDSA Notes by Inam Unit 4freeeducationpksNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument133 pagesDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmsKenneth Carl RabulanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Data Structure and AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesIntro To Data Structure and AlgorithmsjeoNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Algorithm (c-14) AnswerDocument15 pages6th Sem Algorithm (c-14) Answerrituprajna2004No ratings yet
- Dsa Basic Data StructureDocument72 pagesDsa Basic Data StructureVamsi PradeepNo ratings yet
- LECTURE1-OVERVIEW OF DATA STRUCTURE Week1Document28 pagesLECTURE1-OVERVIEW OF DATA STRUCTURE Week1Oboza Angel RoseNo ratings yet
- Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDDocument11 pagesAcute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDbanu kuhanNo ratings yet
- 2 SimplePendulumDocument12 pages2 SimplePendulumSs SsrNo ratings yet
- Quiz English Week 2015 Year 1 NameDocument7 pagesQuiz English Week 2015 Year 1 NameSiti Zunairah Abd AzizNo ratings yet
- 12MM Calculus SAC Part 1 Solutions 2022Document10 pages12MM Calculus SAC Part 1 Solutions 2022cp cpNo ratings yet
- Darwishs Allegorical Critique of OsloDocument13 pagesDarwishs Allegorical Critique of OslorenatairiartefilleaudeauNo ratings yet
- State Sovereign Immunity and The False Claims ActDocument38 pagesState Sovereign Immunity and The False Claims ActDex DexNo ratings yet
- Ra 10627Document41 pagesRa 10627Nvpmfc Ppo100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms PDFDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms PDFDesire FrkNo ratings yet
- GTU Comprehensive ProjectDocument13 pagesGTU Comprehensive ProjectMohammed GheewalaNo ratings yet
- Embassy of DeathDocument3 pagesEmbassy of DeathZigzaGODNo ratings yet
- Spark 3 INT Game 4Document1 pageSpark 3 INT Game 4Biljana NestorovskaNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence and Its ValueDocument2 pagesJurisprudence and Its ValueAnant ThakkarNo ratings yet
- FIDH Annual Report 2021 ENDocument58 pagesFIDH Annual Report 2021 ENFIDHNo ratings yet
- Why Should We Hire You? Learn How To Answer This Job Interview QuestionDocument24 pagesWhy Should We Hire You? Learn How To Answer This Job Interview QuestionDeniz SasalNo ratings yet
- Managing Conflict, Politics, and Negotiation: Chapter QuizDocument3 pagesManaging Conflict, Politics, and Negotiation: Chapter QuizJudson PastranoNo ratings yet
- Eco Project-Ms Esl EflDocument6 pagesEco Project-Ms Esl Eflapi-524845185No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentJunko CaytonNo ratings yet
- Program - NCS 10th ConConDocument8 pagesProgram - NCS 10th ConConJim HoftNo ratings yet
- O Come All Ye Faithful Planetshakers Christmas Vol 2 FDocument3 pagesO Come All Ye Faithful Planetshakers Christmas Vol 2 FBA GomNo ratings yet
- A Test of English ComprehensionDocument19 pagesA Test of English ComprehensionGreg CalhounNo ratings yet
- TH STDocument27 pagesTH STDaniel NyagechiNo ratings yet
- MI6 Chief Alex Younger Full SpeechDocument13 pagesMI6 Chief Alex Younger Full SpeechLatika M BourkeNo ratings yet
- Python VS KotlinDocument4 pagesPython VS KotlinAravind Naveen gamesNo ratings yet
- Brief Reports of CPCS's Advocacy (2010-11)Document10 pagesBrief Reports of CPCS's Advocacy (2010-11)sikandermarriNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On EidsDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Eidszewdie.nataniaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Final Revision 2023Document16 pagesSampling Final Revision 2023Bbb AaNo ratings yet
- 12.course OutlineDocument3 pages12.course OutlineMD. ANWAR UL HAQUENo ratings yet