Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Notes: Acidic / Basic Salts: Acid Anion From Base Cation From Solution Type
Chemistry Notes: Acidic / Basic Salts: Acid Anion From Base Cation From Solution Type
Uploaded by
Yash KapoorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Notes: Acidic / Basic Salts: Acid Anion From Base Cation From Solution Type
Chemistry Notes: Acidic / Basic Salts: Acid Anion From Base Cation From Solution Type
Uploaded by
Yash KapoorCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY NOTES: ACIDIC / BASIC SALTS
In neutralization reactions between acids and bases the two products are water and a “salt”.
HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → H2O(l) + KCl(aq)
+ −
The KCl in the above reaction is the “salt”. Notice that the K of the salt comes from the base and the Cl of the
salt comes from the acid. This will always hold true, the cation of the salt comes from the base and anion comes
from the acid in neutralization reactions. Another example:
HBr(aq) + NH4OH → H2O(l) + NH4Br
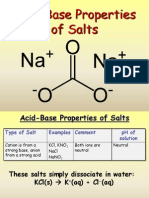
When the salt is dissolved in water, it is capable of producing an acidic, a basic, or a neutral solution. To
determine what type of solution the salt would form you need to determine what type of acid (strong or weak) the
anion could come from and what type of base (strong or weak) the cation could come from. The following table
can be used to determine the type of solution formed.
ACID ANION FROM BASE CATION FROM SOLUTION TYPE
strong strong neutral
strong weak acidic
weak strong basic
To do this you need to remember your strong acids and strong bases.
STRONG ACIDS STRONG BASES
HCl LiOH
HBr NaOH
HI KOH
HNO3 RbOH
HClO3 Ca(OH)2
HClO4 Sr(OH)2
H2SO4 Ba(OH)2
When determining the type of solution formed by a salt, simply consider the acid or base the two ions can come
from. Whichever comes from a strong acid/base, then the solution will be that unless both acid and base are
strong (then the solution is neutral).
Examples:
salt K2CO3 NH4NO3 LiBr
base for cation KOH (strong) NH4OH (weak) LiOH (strong)
acid for anion H2CO3 (weak) HNO3 (strong) HBr (strong)
Since the base is strong Since the acid is strong and Since both the acid and
solution type and the acid is weak, the the base is weak, the base are strong, the
solution will be BASIC. solution will be ACIDIC. solution will be NEUTRAL.
There are two other types of salts that should be considered:
o metallic oxides → form basic solutions
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq)
o nonmetallic oxides → form acidic solutions
SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)
CO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2CO3(aq)
SOME PRACTICE: See if you can figure out the type of solution formed by the salt without looking at the answers below.
1) Li2SO3
2) NH4ClO3
3) Ba(NO3)2
4) Rb2O
5) KC2H3O2
6) NO2
7) N2H5Br
8) Na2CO3
9) KNO3
ANSWERS:
+ 2−
1) basic (Li comes from strong base, SO3 from a weak acid)
+ −
2) acidic (NH4 comes from weak base, ClO3 from a strong acid)
2+ −
3) neutral (Ba comes from a strong base, NO3 from a strong acid)
4) basic (a metallic oxide)
+ −
5) basic (K comes from a strong base, C2H3O2 from a weak acid)
6) acidic (a nonmetallic oxide)
+ −
7) acidic (N2H5 comes from a weak base, Br from a strong acid)
+ 2−
8) basic (Na comes from a strong base, CO3 from a weak acid)
+ −
9) neutral (K comes from a strong base, NO3 from a strong acid)
You might also like
- Module 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptDocument10 pagesModule 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptYuan MasudaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Acids & Bases: Pauling'sDocument6 pagesInorganic Chemistry Acids & Bases: Pauling'sAlmasriJosephNo ratings yet
- Wax Additives and Surface Modifiers Product Guide - 20-63Document9 pagesWax Additives and Surface Modifiers Product Guide - 20-63chinmaydabkeNo ratings yet
- Acidic Basic SaltsDocument2 pagesAcidic Basic SaltsMuhit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument64 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionSoul Relaxation LabNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument83 pagesReactions in Aqueous Solutions張婷昀No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument90 pagesChapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous SolutionFABIO DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument48 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionDavid MaranzhyanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Neutralisation SaltsDocument5 pagesAcid Base Neutralisation SaltsGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Paper AnswersDocument1 pageScience 5 Paper AnswersMiles WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Properties of SaltsDocument7 pagesAcid-Base Properties of SaltsAbdelrhman AdelNo ratings yet
- NH + H O NH + Oh: (Aq) (L) (Aq) (Aq)Document23 pagesNH + H O NH + Oh: (Aq) (L) (Aq) (Aq)ZyreeneNicoleNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Part-2Document4 pagesCh-2 Part-2Kartik BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Chang Chap 4Document72 pagesChang Chap 4MR no oneNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Acids and Bases TheoryDocument31 pagesGR 12 Acids and Bases TheoryvitalismdriveNo ratings yet
- Edited - Acids Bases (Part 2) 6092 TeacherDocument27 pagesEdited - Acids Bases (Part 2) 6092 TeachersamrobbiesingcabarreraNo ratings yet
- Chem 102 Week 5Document65 pagesChem 102 Week 5CAILA CACHERONo ratings yet
- What Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesWhat Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterNishidh SinghNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Properties of SaltDocument2 pagesAcid Base Properties of SaltEvanNo ratings yet
- Sec 4.13 - Hydrolysis (Notes) : Group 1 (Alkali Metal Ions) Eg. Li Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Ions) Eg. BeDocument15 pagesSec 4.13 - Hydrolysis (Notes) : Group 1 (Alkali Metal Ions) Eg. Li Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Ions) Eg. BeDavid SobralNo ratings yet
- CBSE-X Science - Chap-2 (Acids, Bases and Salts)Document14 pagesCBSE-X Science - Chap-2 (Acids, Bases and Salts)aanwidivNo ratings yet
- Salt Hydrolysis: SRCL No Ba (Po) CusoDocument2 pagesSalt Hydrolysis: SRCL No Ba (Po) CusoDevon100% (1)
- 1 Notes - Acids and Bases Annotated 2Document87 pages1 Notes - Acids and Bases Annotated 2Jenny YoonNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases SummaryDocument8 pagesAcid Bases Summaryibraheemgamer786No ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical Report Nature of Bases Acid Salts SolutionDocument13 pagesChemistry Practical Report Nature of Bases Acid Salts SolutionSaffana Qolby MayanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis Hydrolysis: The Reaction of An ION With WATER To Produce An Acidic or Basic SolutionDocument11 pagesHydrolysis Hydrolysis: The Reaction of An ION With WATER To Produce An Acidic or Basic SolutionJenn ArdronNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument12 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsHVBCBMNZNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument12 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsJeevanshu SoniNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Acid N Base, Preparation and DilutionDocument59 pagesChapter 3-Acid N Base, Preparation and DilutionDn ZackNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Reactions and Solution StoichiometryDocument45 pagesAqueous Reactions and Solution StoichiometryThanh LanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Acids Bases & Salts - Part 2 NotesDocument10 pagesChemistry Acids Bases & Salts - Part 2 Notesancy45No ratings yet
- Acid-Base Properties of SaltsDocument7 pagesAcid-Base Properties of Saltsmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts 100l 1Document5 pagesAcids Bases and Salts 100l 1Michael EhondorNo ratings yet
- Acid Radicals and Basic RadicalsDocument4 pagesAcid Radicals and Basic Radicalstarak das50% (2)
- ( (Chapter 8&9 - Acids and Bases, Salts) )Document8 pages( (Chapter 8&9 - Acids and Bases, Salts) )bharadiadishitaNo ratings yet
- BasesDocument45 pagesBasesDinara DzhakishovaNo ratings yet
- Net Ionic EquationsDocument15 pagesNet Ionic EquationsAikaterine SmithNo ratings yet
- 4 Acid, Base and SaltDocument8 pages4 Acid, Base and Saltjosephmartinsogbu30No ratings yet
- Chap 05 - Ionic Equilibrium MindNotes by Arnav SirDocument10 pagesChap 05 - Ionic Equilibrium MindNotes by Arnav SirKhushi RoyNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Acids, Bases and Salts (Repaired) PDFDocument13 pagesFinal Revision Acids, Bases and Salts (Repaired) PDFRawan Abd ElaatyNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriaDocument10 pagesIonic EquilibriaShantanu KadamNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument6 pagesAcid Base and SaltRajnish kumarNo ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry Module 6 Notes 63858a418735dDocument13 pagesHSC Chemistry Module 6 Notes 63858a418735dnushrat.raya447No ratings yet
- Acid BasesDocument4 pagesAcid Basesundobrine.o1pNo ratings yet
- Notes On SaltsDocument4 pagesNotes On SaltsFelix S100% (1)
- Selina Solutions Concise Chemistry For Class 10 Chapter 4Document6 pagesSelina Solutions Concise Chemistry For Class 10 Chapter 4Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Qualitative Analysis of CationsDocument8 pagesExperiment 4 Qualitative Analysis of CationsUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise - 4Document9 pagesChapter - 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise - 4parijatbhattacharjee949No ratings yet
- DMS 1 - Reactions in Aqueous - SolutionDocument20 pagesDMS 1 - Reactions in Aqueous - Solutionsuhiermai3No ratings yet
- Topic 7Document16 pagesTopic 7nighat12No ratings yet
- Conjugate Acid of A and The Conjugate Base of A The Solution Will BeDocument1 pageConjugate Acid of A and The Conjugate Base of A The Solution Will BeQwrtyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Document22 pagesChemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Hayan LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Rxns Background Spring 2010Document5 pagesChemical Rxns Background Spring 2010Zikri ZamalulailNo ratings yet
- Acidsandbases 2Document37 pagesAcidsandbases 2Ram prabodhNo ratings yet
- Acidic, Basic, and Neutral Salts: Weak Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesAcidic, Basic, and Neutral Salts: Weak Acids and BasesSandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases (Hsab)Document5 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Bases (Hsab)nolimitsjustfashionNo ratings yet
- Split 3519884142096478998Document4 pagesSplit 3519884142096478998poetrobertfrost1No ratings yet
- 4.13 HydrolysisDocument15 pages4.13 HydrolysisDavid SobralNo ratings yet
- Handout - Acids and Bases - v2 - 101Document2 pagesHandout - Acids and Bases - v2 - 101maheenkhan1605No ratings yet
- Magnesium ChlorideDocument4 pagesMagnesium ChlorideParvani PatankarNo ratings yet
- Hard & Soft Acids and Bases: B.Sc. III YearDocument14 pagesHard & Soft Acids and Bases: B.Sc. III YearGaurav 016No ratings yet
- Certificado de Análisis de Resina Con 97.8% de CannabinoidesDocument2 pagesCertificado de Análisis de Resina Con 97.8% de CannabinoidesSativa Info PerúNo ratings yet
- DT-9 - Lesson 32Document7 pagesDT-9 - Lesson 32Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Report 2019Document32 pagesReport 2019knajikNo ratings yet
- Herbal WineDocument60 pagesHerbal Wineßhågyesh Jîrapure100% (1)
- Bioremediation Using Weeds: Deepak Pant Shashi Kant Bhatia Anil K. Patel Anand Giri EditorsDocument259 pagesBioremediation Using Weeds: Deepak Pant Shashi Kant Bhatia Anil K. Patel Anand Giri EditorsWladyslaw TorunskiNo ratings yet
- INVESTIGACIONDocument343 pagesINVESTIGACIONandres povedaNo ratings yet
- Tyre RecyclingDocument146 pagesTyre RecyclingErikNo ratings yet
- Final ProblemsDocument5 pagesFinal Problems王暐翔No ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 20 Asal Chem CBDocument3 pagesExam Style Answers 20 Asal Chem CBhxuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory Report PH Scale andDocument8 pagesChemistry Laboratory Report PH Scale andM.NASIRNo ratings yet
- Medications That Should Not Be CrushedDocument14 pagesMedications That Should Not Be CrushedAdelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Metabolism: DR S K BansalDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Metabolism: DR S K BansalSanjiv BansalNo ratings yet
- AVCL 2.1 Analysis of Unknown Carbohydrates Group 5Document4 pagesAVCL 2.1 Analysis of Unknown Carbohydrates Group 5Claire GUMAPACNo ratings yet
- Kurita Waste Water 04 15 en WebDocument2 pagesKurita Waste Water 04 15 en WebdanielNo ratings yet
- Characterization Studies Waste Plastic Oil and Its BlendsDocument12 pagesCharacterization Studies Waste Plastic Oil and Its BlendsPieyah ChomelNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Chemistry: Department of EducationDocument47 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry: Department of EducationJohnRenzoMolinarNo ratings yet
- Ch-Immobilization of Enzyme PDFDocument92 pagesCh-Immobilization of Enzyme PDFVNo ratings yet
- CMOS TechnologiesDocument27 pagesCMOS TechnologiesDebela TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Topic 18 Organic Chemistry: ArenesDocument4 pagesTopic 18 Organic Chemistry: ArenessalmaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Pipe Equipment Labeling Part III - RETA Breeze Jan FebDocument3 pagesAmmonia Pipe Equipment Labeling Part III - RETA Breeze Jan FebfivefourfiveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document9 pagesChapter 9mysthicriousNo ratings yet
- Bathsense CatalogueDocument56 pagesBathsense CatalogueGopinath SekarNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air System: by Raj PrabhakarDocument21 pagesCompressed Air System: by Raj PrabhakarNabilBouabanaNo ratings yet
- Inorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperDocument14 pagesInorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperRuan ReisNo ratings yet
- Industrial ReactorsDocument10 pagesIndustrial ReactorssarahNo ratings yet
- Chem 101 CH02 Ismail ANUDocument82 pagesChem 101 CH02 Ismail ANUameer jomaNo ratings yet
- mb502 P Assignments Solution by MeRRyDocument5 pagesmb502 P Assignments Solution by MeRRyaimenjavaid965No ratings yet