Professional Documents
Culture Documents
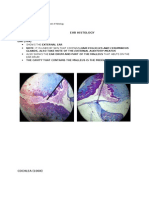
Chapter 9&10: Microscopic Examination of Urinary Sediment: Casts
Chapter 9&10: Microscopic Examination of Urinary Sediment: Casts
Uploaded by
Allexandra CameliaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9&10: Microscopic Examination of Urinary Sediment: Casts
Chapter 9&10: Microscopic Examination of Urinary Sediment: Casts
Uploaded by
Allexandra CameliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9&10:
Microscopic Examination
of Urinary Sediment: Casts
Graff’s Textbook of Urinalysis and Body Fluids,
Third Edition
Mundt, L. & Shanahan K.
Copyright © 2011 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Chapters Outline: Casts
• Overview of Urinary Cast Formation
• Hyaline Casts
• Cellular Casts
• Granular Casts
• Waxy Casts
• Pseudo Casts
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Formation
• Formed in lumen of the kidney distal convoluted tubules
and Loop of Henle.
• Molded in the shape of the tubules
• Tamm–Horsfall mucoprotein comprises the matrix
• May contain cells that are present in the tubules at the
time of cast formation.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Formation (cont.)
• Factors of cast formation:
– urinary stasis
– Acid pH
– high solute concentration
– abnormal ionic or protein constituents
• May be indicated by the presence of urinary protein.
– However, casts can be present in the absence of
protein.
– Microscopic examination is important.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Identification of Casts
• Casts:
– have parallel sides with rounded or blunted ends
– vary in size and shape according to the tubules in
which they were formed
– convoluted, straight, or curved
– are cylindrical in shape with no dark edges
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Significance of Casts
• The width of the cast indicates the diameter of the
tubule in which it was formed
• Broad casts
– formed in pathologically dilated or atrophied
tubules or in collecting tubules
– indicate renal failure
• Cast are always renal in origin and indicate pathologies:
– glomerular damage
– tubular damage
– renal inflammation
– renal infection
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Broad and Narrow
Fine granular casts and WBCs
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Classification
• Based on appearance and contents:
– hyaline
– red cell
– white cell
– epithelial cell
– granular (coarse and fine)
– waxy
– fatty
– mixed
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Sequence of Degeneration
Sequence of urinary cast degeneration
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Cast: Enumeration
• Counted on low-power (100x)
– More frequently seen along the edges of coverslip
• Reported according to type and range seen
– 0-2, 2-5, 5-10, 10-20
• Example:
– Hyaline casts 5-10/LPF
– Granular casts 2-5/LPF
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Hyaline Casts
Hyaline cast and red blood cells.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Hyaline Casts (cont.)
• Can be seen in even the mildest kind of renal disease.
• Not associated with any one disease in particular.
• A few hyaline casts may be found in the normal urine.
• Frequently present:
– following physical exercise
– physiologic dehydration
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Hyaline Casts (cont.)
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Hyaline Casts (cont.)
Hyaline casts. Viewed with an 80A filter
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Hyaline Casts (cont.)
• Hyaline casts using phase contrast microscopy
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Red Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
Red cell cast and RBCs
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Red Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
• Always pathologic
• Hematuria is present
• Conditions include:
– acute glomerulonephritis
– lupus nephritis
– Goodpasture syndrome
– subacute bacterial endocarditis
– renal trauma
– renal infarction
– severe pyelonephritis
– right-sided congestive heart failure
– renal vein thrombosis
– periarteritis nodosa
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Red Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
Convoluted red blood cell cast
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Red Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: White Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
White cell cast and WBCs
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: White Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
• Can be present during renal infection and inflammation.
– acute pyelonephritis
– interstitial nephritis
– lupus nephritis
– glomerular disease
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: White Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: White Blood Cell Casts
(cont.)
SM-stained WBC cast
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Epithelial Cell Casts
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Epithelial Cell Casts
(cont.)
• May be present after exposure to:
– nephrotoxic agents
– viruses (e.g., cytomegalovirus, hepatitis virus)
• Due to damage that accompanies glomerular injury
• Also present in the rejection of a kidney allograft
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Epithelial Cell Casts
(cont.)
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Mixed Cell Casts
Mixed cell cast, WBCs, and RBCs.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Mixed Cell Casts (cont.)
SM-stained mixed cellular cast.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Mixed Cell Casts (cont.)
SM-stained hyaline cast, granular cast, mixed
cellular cast, and partially degenerated renal
tubule epithelial cells
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Granular Casts
Broad coarsely granular
Finely granular casts
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Granular Casts (cont.)
• Usually indicate renal disease.
• But may be briefly present after strenuous exercise.
• These casts have remained in the tubule for enough
time to allow for the degeneration of cellular
components.
• May be confused with casts containing bacteria or
crystals.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Granular Casts (cont.)
Coarse granular cast
Coarse granular cast
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Granular Casts (cont.)
Bilirubin-stained granular cast
SM-stained granular cast
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Waxy Casts
• Waxy cast and WBCs
Waxy cast, WBCs, and
bacteria
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Waxy Casts (cont.)
• Found in urine from patients with:
– severe chronic renal failure
– malignant hypertension
– renal amyloidosis
– and diabetic nephropathy
– acute renal disease
– tubular inflammation and degeneration
– and during renal allograft rejection.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Waxy Casts (cont.)
• Waxy cast and amorphous urates.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Granular to Waxy
transformation
Fine granular cast becoming a waxy cast.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Waxy Casts
Convoluted waxy cast.
SM-stained waxy granular cast.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Fatty Casts
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Fatty Casts (cont.)
• Present during fatty degeneration of the RTE cells
– degenerative tubular disease
– nephrotic syndrome
– diabetic glomerulosclerosis
– lipoid nephrosischronic
– Glomerulonephritis
– Kimmelstiel–Wilson syndrome
– Systemic Lupus Erythematosis
– toxic renal poisoning
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Other Casts
• Mixed cast.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Pseudo Casts
Cylindroid.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Confusing Artefacts-
Mucous Threads
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Confusing Artefacts-Fibers
Fibers
Debris from a diaper
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Confusing Artefacts-Hair
Hair and a coarsely granular cast
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Confusing Sediment - Yeast
SM-stained yeast with pseudohyphae and WBCs
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Urinary Casts: Confusing Comparison
A. Fine granular cast B. Fiber.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Summary
• Casts, comprised of a Tamm–Horsfall mucoprotein
matrix are formed in lumen of distal tubules.
• Casts are classified by their contents.
• Several artifacts may be misidentified as casts.
• Reagent strip tests for protein may or may not be
positive when casts are present.
• Casts may be present in physiologically normal
conditions.
• Casts usually accompany renal disorders.
Copyright © 2016 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Pranab Dey - Basic and Advanced Laboratory Techniques in Histopathology and Cytology-Springer (2023)Document350 pagesPranab Dey - Basic and Advanced Laboratory Techniques in Histopathology and Cytology-Springer (2023)Senthil MuruganNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To Cardiopulmonary Care 4th EditionDocument185 pagesQuick Guide To Cardiopulmonary Care 4th EditionLorenzo Romero AlbarranNo ratings yet
- 3 Decalcification and DehydrationDocument5 pages3 Decalcification and DehydrationAngel RamosNo ratings yet
- Staining TechniquesDocument19 pagesStaining TechniquesSwayamprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- 2670 Chapter 14Document24 pages2670 Chapter 14Abdallah Essam Al-Zireeni100% (5)
- Reticulocyte Count StainDocument4 pagesReticulocyte Count StainGopikonda Leela RaniNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells MorphologyDocument20 pagesBlood Cells Morphologymoonfire2009No ratings yet
- Hematology 1 Lab - The Reticulocyte CountDocument17 pagesHematology 1 Lab - The Reticulocyte CountCIRILO MABBORANGNo ratings yet
- Oncology Revision: Paul BaillieDocument299 pagesOncology Revision: Paul BaillieMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Haematology SAQDocument16 pagesHaematology SAQPowell KitagwaNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell TestDocument14 pagesSickle Cell TestkayNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Inflammation ThyroidDocument55 pagesGranulomatous Inflammation ThyroidKamlesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 18 - Flow Cytometry and Introduction To Molecular PathologyDocument11 pages18 - Flow Cytometry and Introduction To Molecular Pathologyhamadadodo7No ratings yet
- Pap Smear: Dr. Monika NemaDocument114 pagesPap Smear: Dr. Monika NemafadoNo ratings yet
- Aubf Prelim 1Document59 pagesAubf Prelim 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Haemolytic AnaemiaDocument44 pagesHaemolytic AnaemiaMark DemNo ratings yet
- 2 Medicine HematologyDocument78 pages2 Medicine HematologyAmitNo ratings yet
- Microanatomy pt1Document27 pagesMicroanatomy pt1poopziNo ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument77 pagesMicrowaveDineshprakash GovindhrajNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Platelet CountDocument40 pages2.5 Platelet Count西矢椛No ratings yet
- Bleeding Time, Clotting Time, PT, Aptt, Platelet IndicesDocument59 pagesBleeding Time, Clotting Time, PT, Aptt, Platelet Indicespriya madhooliNo ratings yet
- EDs Basic Histology PDFDocument208 pagesEDs Basic Histology PDFTemesgen Endalew0% (1)
- Presented By, N. Swetha M.SC Medical BiochemistryDocument47 pagesPresented By, N. Swetha M.SC Medical BiochemistryKuzhandai Velu100% (1)
- Defining The Practice of Medical Technology or Clinical Laboratory Science ProfessionDocument27 pagesDefining The Practice of Medical Technology or Clinical Laboratory Science ProfessionKianna TicsayNo ratings yet
- Ear HistologyDocument3 pagesEar HistologyGrace Shan Bernus100% (1)
- Biological Hazard: Presented by Group 7 Cayamdas, Aimee Castillo, Marie Galleon, Cearlene Santos, KevinDocument31 pagesBiological Hazard: Presented by Group 7 Cayamdas, Aimee Castillo, Marie Galleon, Cearlene Santos, KevinCearlene GalleonNo ratings yet
- Tissue Processing Part 2Document120 pagesTissue Processing Part 2Aliah Anne MagnoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Examination of UrineDocument13 pagesChemical Examination of UrinePam Fajardo100% (1)
- Routine UrinalysisDocument4 pagesRoutine UrinalysisDanica Joy Christelle L. PilarNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument12 pagesCytologyEsther HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesDocument57 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and Qualitative Disorders of WBCsDocument9 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative Disorders of WBCsOliver BarnyakNo ratings yet
- NullDocument16 pagesNullapi-15026641100% (2)
- Urine AnalysisDocument63 pagesUrine AnalysisVench DemicaisNo ratings yet
- Orientation To Blood Bank 2Document24 pagesOrientation To Blood Bank 2Darshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mounting Media: An Overview: January 2014Document9 pagesMounting Media: An Overview: January 2014Niketa SharmaNo ratings yet
- AUBF - Chapter 2Document5 pagesAUBF - Chapter 2Kristin SoquilloNo ratings yet
- Hema Ii Laboratory Week 7 - PT & PTT MethodsDocument37 pagesHema Ii Laboratory Week 7 - PT & PTT MethodsAl-hadad AndromacheNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative Cytology PDFDocument2 pagesExfoliative Cytology PDFStaceyNo ratings yet
- Haem. Notes (MBCHB) ProperDocument162 pagesHaem. Notes (MBCHB) ProperKelvinTMaikanaNo ratings yet
- Sources of Errors in Clinical ChemistryDocument9 pagesSources of Errors in Clinical Chemistrykalantan23No ratings yet
- Haematological MalignanciesDocument63 pagesHaematological MalignanciesIsaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- Clearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSDocument25 pagesClearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSChandan SahNo ratings yet
- Clinical MicrosDocument14 pagesClinical MicrosKRISTINE JOY PANGAHINNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument6 pagesBloodFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Platelet Function Tests - DR Makboul 2018 PDFDocument50 pagesPlatelet Function Tests - DR Makboul 2018 PDFmagendi indra muktiNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid Cell Counts by Automated MethodsDocument11 pagesBody Fluid Cell Counts by Automated MethodsntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To HematologyDocument30 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Hematologyimam100% (1)
- Hematology Written SummariesDocument6 pagesHematology Written SummariesDrexler Ray EukanNo ratings yet
- Lipids and LipoproteinsDocument47 pagesLipids and LipoproteinsUzair MansoorNo ratings yet
- Hematology Week 1 CBCDocument4 pagesHematology Week 1 CBCMICHELLE RAPELONo ratings yet
- Urine Sediment Particles PDFDocument119 pagesUrine Sediment Particles PDFambadepravinNo ratings yet
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument105 pages3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue.: Dr. Zahid Mehmood DPT, MS-NMPTDocument25 pagesNervous Tissue.: Dr. Zahid Mehmood DPT, MS-NMPTZahid Mehmood100% (1)
- Hematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFDocument10 pagesHematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFJohn Rhel DenqueNo ratings yet
- Amoeba ChartDocument4 pagesAmoeba ChartRafael CastilloNo ratings yet
- Section 13 - Hematology (Updated)Document34 pagesSection 13 - Hematology (Updated)Lorelie CarlosNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Special Histopath TechniquesDocument21 pagesMtap - Special Histopath TechniquesK-idol LiveNo ratings yet
- BM Procedure and ProcessingDocument28 pagesBM Procedure and ProcessingNidhi JaisNo ratings yet
- Clinical EnzymologyDocument84 pagesClinical EnzymologyYeyeh SantosNo ratings yet
- Membranes for Life SciencesFrom EverandMembranes for Life SciencesKlaus-Viktor PeinemannNo ratings yet
- Dialogue Physical AssessmentDocument4 pagesDialogue Physical AssessmentSuryani67% (3)
- Presentation Facilitated by Madam: Saima Mateen: Group Members: Shahzad Raza Saba KaleemDocument54 pagesPresentation Facilitated by Madam: Saima Mateen: Group Members: Shahzad Raza Saba KaleemParas MauriceNo ratings yet
- Thali - Virtopsy, A New Imaging Horizon in Forensic Pathology, Virtual Autopsy by Postmortem MSCT and MRI, A Feasibility Study - 2003 - J Forensic Sci PDFDocument18 pagesThali - Virtopsy, A New Imaging Horizon in Forensic Pathology, Virtual Autopsy by Postmortem MSCT and MRI, A Feasibility Study - 2003 - J Forensic Sci PDFChristianWicaksonoNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Golf For Your HealthDocument2 pagesThe Benefits of Golf For Your Healthlifemaantra comNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument52 pagesAnatomy and Cardiovascular AssessmentNaomi Anne AsuntoNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument17 pagesBlood ComponentsJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- Management of Intra-Abdominal InfectionDocument65 pagesManagement of Intra-Abdominal InfectionKamran SherazNo ratings yet
- Anemia PresentationDocument11 pagesAnemia Presentationcecan 06No ratings yet
- Synopsis - Chronic-kidney-disease-prediction-usingMLDocument7 pagesSynopsis - Chronic-kidney-disease-prediction-usingMLKamran AnasNo ratings yet
- Arni PPT 2 PDFDocument19 pagesArni PPT 2 PDFKumarsai Durusoju100% (1)
- Cytokine Levels Correlate With A Radiologic ScoreDocument6 pagesCytokine Levels Correlate With A Radiologic ScoresuryoNo ratings yet
- Attention Deficit-Hyperactive DisorderDocument3 pagesAttention Deficit-Hyperactive Disorderadan oladiveNo ratings yet
- SJAIT Broj 4 CeoDocument155 pagesSJAIT Broj 4 CeoNatalija StamenkovicNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone (RX) : Dosing & UsesDocument4 pagesDexamethasone (RX) : Dosing & UsesFauzi GanihNo ratings yet
- BOBATHDocument10 pagesBOBATHCatherine A.No ratings yet
- Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) and AutismDocument19 pagesAvoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) and AutismMarietta_MonariNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionDocument33 pagesColorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionNesyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Pediatric Surgery 2010Document454 pagesHandbook of Pediatric Surgery 2010Clau Jorquera Castillo100% (1)
- Psych Drugs - From MedbulletsDocument2 pagesPsych Drugs - From MedbulletsFazeyfazeNo ratings yet
- ALERTEC (Modafinil) Product Monograph For CanadaDocument38 pagesALERTEC (Modafinil) Product Monograph For Canadajennabush100% (2)
- Nitrofurantoin - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 pagesNitrofurantoin - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfJose ZulaNo ratings yet
- DR. B R Ambedkar Medical Aid SchemeDocument7 pagesDR. B R Ambedkar Medical Aid Schemevineet shendeNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of A Neck Mass - UpToDateDocument16 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of A Neck Mass - UpToDatezzellowknifeNo ratings yet
- 05 - 203perkembangan Terkini Diagnosis Dan Penatalaksanaan Imflammatory Bowel Disease PDFDocument6 pages05 - 203perkembangan Terkini Diagnosis Dan Penatalaksanaan Imflammatory Bowel Disease PDFrisda aulia putriNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Kadar Interleukin 6 Dan Interleukin 10 Serum Pada Pasien Cedera Otak Berat Akibat TraumaDocument9 pagesHubungan Kadar Interleukin 6 Dan Interleukin 10 Serum Pada Pasien Cedera Otak Berat Akibat TraumaanggiNo ratings yet
- PDF Fish S Clinical Psychopathology Signs and Symptoms in Psychiatry Fourth Edition Patricia Casey Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Fish S Clinical Psychopathology Signs and Symptoms in Psychiatry Fourth Edition Patricia Casey Ebook Full Chapterkrystal.driscoll313100% (3)
- Nsaids and DmardsDocument59 pagesNsaids and DmardsBaidawu Weso-amo IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Assessment Three: Analysis of Legal and Professional Issues (2,200-Word Assignment, 50% of Available Mark)Document2 pagesAssessment Three: Analysis of Legal and Professional Issues (2,200-Word Assignment, 50% of Available Mark)Ayesha NaseerNo ratings yet