Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem Lab Report
Chem Lab Report
Uploaded by
jhoana melendrezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem Lab Report
Chem Lab Report
Uploaded by
jhoana melendrezCopyright:
Available Formats
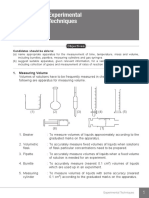
Basic Laboratory Techniques
Measurement of volume and weight
1. Mass of empty graduated cylinder
__________25.0g______________
2. Mass of graduated cylinder and water _________
30.0g______________
3. Mass of water
__________5.0g_______________
4. Volume of water
____________________________
5. Density of water at room temperature ____________________________
Handling of solutions and precipitates
1. Describe what was formed after mixing the solutions.
There is a brown particle formed after mixing ferric chloride with
sodium hydroxide because when these solutions react with each other,
ferric hydroxide will be present which on the other hand is not soluble in
water that is why there was a precipitate that was formed.
2. Draw the filtration set-up and label the equipment used.
3. Which of the two separation is better – filtration or decantation?
Filtration is better than decantation because filtration can filter or
separate all small or coarse particles that is cannot be done by
decantation. In the process of decantation, the chance of the particles to
mix back with the liquid is high which proves that filtration is way better
than this separation process.
Generalization/Conclusion
Therefore, this laboratory activity showed how important for you to
know the basic laboratory equipment and apparatus in able for you to do the tasks
properly. Proper laboratory attire is also important to ensure the safety of everyone who
are working in the lab. Doing different separation techniques taught us what is the best
technique you can use at different separating scenarios to ensure that your solution is
properly filtrated or decantated for the result’s betterment.
Documentation
Questions and Problems
1. Name all the equipment you will need when heating 5 ml water in the laboratory.
Bunsen burner, test tube, test tube clamp.
2. Define the following terms:
a. Precipitate – the solid particle that was formed after the reaction occurs in
a liquid solution.
b. Evaporation – it is the process of converting liquid into gas.
c. Filtrate – it is a liquid which has passed through a filter.
d. Filtration – it is a process of separating the components of a suspension.
e. Residue – it is the remains on the filter paper after the filtration process.
f. Decantation – it is the process of separating heterogeneous mixtures.
The solid particles are allowed to settle first at the bottom and later the
liquid is called supernatant is poured into another container leaving
behind the solid particles
g. Decantate – the liquid decantated after the solid particles settled at the
bottom in the decantation process.
h. Sublimation – process of changing solid to gas without passing the liquid
state.
i. Supernatant liquid – it is the resulting liquid after a mixture of liquid and
solid has been left to settle out to separate the two.
j. Precipitation – it is the process of changing gas into liquid.
3. How will you determine the density of a solid like a piece of wood?
You can determine the density of a solid like a piece of wood by
measuring its mass and volume and divide the mass by the volume.
4. Name the standard unit of measurement used in scientific investigation by
chemists for length, volume, mass and temperature. What other units are used
for each of these?
Standard Unit Other units
a. Length Meter Kilometer
b. Volume Cubic meter Liter
c. Mass Kilogram Gram
d. Temperature Kelvin Celsius
5. What is the dominant color of the flame of properly adjusted burner? Why?
The dominant color of the flame of properly adjusted burner is blue
because of the reaction of the air with the gas which creates a complete
combustion.
6. If you want to melt a glass rod fastest, which of the region of the burner flame will
you use? Why?
I will use the non-luminous flame region or the blue flame because it is
the hottest region of the flame and can melt a glass rod fastest.
7. Why is density of a substance not the same at the temperature varying by 10⁰ to
15⁰ C?
Density changes the temperature because volume changes with
temperature. The higher the temperature, the volume increase and as the
volume increases, the density decreases because volume is in the denominator
of the formula of the density.
8. If 50 ml alcohol weights 120 g, what is its density at that temperature?
120g/50ml = 2.4g/ml
You might also like
- Collaborative Environmental Governance Frameworks-A Practical Guide (Timothy Gieseke (Author) ) (Z-Library) - 1Document211 pagesCollaborative Environmental Governance Frameworks-A Practical Guide (Timothy Gieseke (Author) ) (Z-Library) - 1kiemwanzNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Total Solid and Total Suspended SolidDocument3 pagesExperiment On Total Solid and Total Suspended SolidRosa Chelley77% (26)
- Experiment 1 CHM207 Intermediate Organic Chemistry Heating by Reflux and Filtering Using Buchner FunnelDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 CHM207 Intermediate Organic Chemistry Heating by Reflux and Filtering Using Buchner FunnelFazsroul100% (3)
- A Complete Guide to M.C.Q,Science (C.B.S.E & N.C.E.R.T),Class 9: CBSE MCQ Series, #2From EverandA Complete Guide to M.C.Q,Science (C.B.S.E & N.C.E.R.T),Class 9: CBSE MCQ Series, #2Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Physics Lab 2 CapacitorssssDocument9 pagesPhysics Lab 2 Capacitorssssjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory OperationsDocument5 pagesCommon Laboratory OperationsbenanangelieNo ratings yet
- Physical TechniquesDocument22 pagesPhysical TechniquesJerielita MartirezNo ratings yet
- Dwi Nur F - Assignment 3 - 1ED4Document3 pagesDwi Nur F - Assignment 3 - 1ED4Dwi Nur FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Module 3: Simple Separation Technique: Name: Anya S. Salik Grade and Section: G12-STEM - SisonDocument6 pagesQuarter 1 Module 3: Simple Separation Technique: Name: Anya S. Salik Grade and Section: G12-STEM - SisonNaila SalikNo ratings yet
- 1 Experimental Chemistry: ATP Paper 4Document14 pages1 Experimental Chemistry: ATP Paper 4malahim ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SeparationDocument12 pagesChemistry SeparationKashifntcNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 3 - Cindi Noviani - 1C D4-TKI - 06Document4 pagesASSIGNMENT 3 - Cindi Noviani - 1C D4-TKI - 06Cindi NovianiNo ratings yet
- ECE Lab Manual Requirements Sep 2021Document10 pagesECE Lab Manual Requirements Sep 2021supinya bieNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Density of LiquidDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1 Density of LiquidPeetah MorrisNo ratings yet
- CHEM 130 Lab Manual Fall 2011Document64 pagesCHEM 130 Lab Manual Fall 2011CaledoniaHearthPipesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Q1 Gen Chem I v.2Document17 pagesModule 1 Q1 Gen Chem I v.2Gweneth BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument4 pagesSeparation TechniquesNicola Faye BronNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Techniques Lab Report: Option One: Density Measurements Virtual LabDocument4 pagesLaboratory Techniques Lab Report: Option One: Density Measurements Virtual LabGloomieNo ratings yet
- Ma. Jade R. Agres - Full Report No. 2Document7 pagesMa. Jade R. Agres - Full Report No. 2Ma. Jade AgresNo ratings yet
- Methods of PurificationDocument10 pagesMethods of PurificationhadysuciptoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Group 5Document10 pagesExperiment 1 - Group 5Paul RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BMMV1013 Lab 2 20212022 2Document17 pagesBMMV1013 Lab 2 20212022 2Blue BeatleNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1:: Purification of Benzoic Acid by RecrystallizationDocument51 pagesExperiment #1:: Purification of Benzoic Acid by RecrystallizationStephanie Ann Marie DueñasNo ratings yet
- Exp1 LabreportDocument23 pagesExp1 Labreportbhing koNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ProcessesDocument7 pagesUnit 3 ProcessesNovitaNo ratings yet
- CDB 3082 Chemical Engineering Lab Iv: - Solid DeterminationDocument6 pagesCDB 3082 Chemical Engineering Lab Iv: - Solid DeterminationFarhan HazeeqNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Chemistry/Concepts in Chemistry Practicals (18CYB101J/18CYB102J)Document48 pagesLaboratory Manual For Chemistry/Concepts in Chemistry Practicals (18CYB101J/18CYB102J)googlu bbsNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Separation and Purification TechniqueDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Separation and Purification TechniqueSobi SitjarNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document7 pagesActivity 4Louela Jean EspirituNo ratings yet
- Chem205 Lab Report 1Document6 pagesChem205 Lab Report 1Isra MallaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Determination of Density PDFDocument6 pagesExperiment 3 - Determination of Density PDFOxford North100% (1)
- Z Notes Chemistry ATP 2023-25Document11 pagesZ Notes Chemistry ATP 2023-25Zoya100% (1)
- APAVB17060 Wastewater and Sludge ManagementDocument27 pagesAPAVB17060 Wastewater and Sludge ManagementLuqman Mazlan100% (1)
- GLT111 PratDocument21 pagesGLT111 Pratmetasynthronos748No ratings yet
- Bmmv1013 Lab 2Document18 pagesBmmv1013 Lab 2Blue BeatleNo ratings yet
- Laporan Minyak NabatiDocument10 pagesLaporan Minyak Nabatiputri wildanaNo ratings yet
- Score:: Noveleta, Cavite High School Department First Mid-Quarter ExaminationDocument3 pagesScore:: Noveleta, Cavite High School Department First Mid-Quarter ExaminationTimothyPaul13No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (NIVETHA)Document22 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project (NIVETHA)lakmi260107No ratings yet
- Reporte de CristalizacionDocument3 pagesReporte de Cristalizaciondavid liraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report OutlineDocument2 pagesLab Report OutlineMajestic RavenNo ratings yet
- Joyce Exp7 ChemlabDocument7 pagesJoyce Exp7 ChemlabKristine Joyce CaloNo ratings yet
- Methods of PurificationDocument11 pagesMethods of PurificationSalma kanwal - 66639/TCHR/BHQSMNo ratings yet
- Anachem Answer SheetsDocument8 pagesAnachem Answer SheetsBai Rihan PangolimaNo ratings yet
- Recryst4lliz4tion and Melting Point Determin4ti0nDocument6 pagesRecryst4lliz4tion and Melting Point Determin4ti0nTimothy DrakeNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument10 pagesSample Lab ReportHuỳnh TẤn PhátNo ratings yet
- Methods of PurificationDocument12 pagesMethods of Purificationanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques Chem.Document5 pagesExperimental Techniques Chem.mayaNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory OperationsDocument5 pagesCommon Laboratory OperationsRosales Joseph M.No ratings yet
- Org Lab 5Document8 pagesOrg Lab 5Bacillus SubtilisNo ratings yet
- Science 5124 (Chemistry) 10-12 Final PDFDocument83 pagesScience 5124 (Chemistry) 10-12 Final PDFComfort Mubanga100% (1)
- POC Lab Activity 3 Separations of Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesPOC Lab Activity 3 Separations of Organic CompoundsSha ZaenudinNo ratings yet
- Liquid Liquidextraction1 150510001558 Lva1 App6892Document27 pagesLiquid Liquidextraction1 150510001558 Lva1 App6892Ranjani J DeepakNo ratings yet
- Org Chem LabDocument7 pagesOrg Chem LabCriselda CarinoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Week1Document13 pagesGeneral Chemistry Week1Eljane PaniloNo ratings yet
- Science8 q3 Mod2 Week3-4 Phasesofmatter v4.PDF-For-studentsDocument32 pagesScience8 q3 Mod2 Week3-4 Phasesofmatter v4.PDF-For-studentsLawrence BianesNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Worksheet VSDocument2 pagesActivity 6 Worksheet VSJayson P. JalbunaNo ratings yet
- LAP 11 Separating Mixtures GR 6Document3 pagesLAP 11 Separating Mixtures GR 6Hannah Mariel CabañeroNo ratings yet
- Expt. 3 - Separation and Purification of Org. Compounds (Part 2) (20230214121826)Document5 pagesExpt. 3 - Separation and Purification of Org. Compounds (Part 2) (20230214121826)Kaye SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1.4Document2 pagesExperiment 1.4anthony.sisonNo ratings yet
- Heath Effects of RadiationDocument1 pageHeath Effects of Radiationjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Policy Paper AssignmentDocument2 pagesPolicy Paper Assignmentjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Ensci Research ProposalDocument2 pagesEnsci Research Proposaljhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Radiation EffectsDocument3 pagesRadiation Effectsjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- MELENDREZ ENSCI1110 FactorsAffectingTheSpheresDocument1 pageMELENDREZ ENSCI1110 FactorsAffectingTheSpheresjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Ensci 1110Document1 pageEnsci 1110jhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
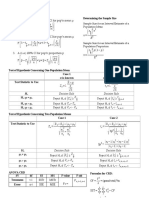
- x−Z s n μ<´x +Z s n n= z σ E: Sample Size for an Interval Estimate of a Population MeanDocument2 pagesx−Z s n μ<´x +Z s n n= z σ E: Sample Size for an Interval Estimate of a Population Meanjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number 4 Uniform Accelerated Motion IIDocument4 pagesExperiment Number 4 Uniform Accelerated Motion IIjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Void Struct Int Int Int Struct Char Int Int Int Struct Struct IntDocument16 pagesVoid Struct Int Int Int Struct Char Int Int Int Struct Struct Intjhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Jhoana A. Melendrez BSMET 1-1Document2 pagesJhoana A. Melendrez BSMET 1-1jhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Waste: A Review About Radioactive Waste DisposalDocument4 pagesNuclear Waste: A Review About Radioactive Waste Disposaljhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- "Understanding Ozone Depletion" Prepared By: Aqiuno, Mikhaella Melendrez, Jhoana Pengson, Crishia MaeDocument4 pages"Understanding Ozone Depletion" Prepared By: Aqiuno, Mikhaella Melendrez, Jhoana Pengson, Crishia Maejhoana melendrezNo ratings yet
- Recursive Least-Squares Adaptive Filters: Dr. Yogananda IsukapalliDocument28 pagesRecursive Least-Squares Adaptive Filters: Dr. Yogananda IsukapalliAkilesh MDNo ratings yet
- Accounting Technologies and SustainabilityDocument13 pagesAccounting Technologies and Sustainabilitycharme4109No ratings yet
- Marketing Internship ReportDocument32 pagesMarketing Internship ReportParveshNo ratings yet
- Book Review of I Love You Since 1892Document2 pagesBook Review of I Love You Since 1892hannah100% (1)
- VaricoceleDocument10 pagesVaricoceleDenny SetyadiNo ratings yet
- Double Wedding Ring Size Fabric Requirements EditedDocument3 pagesDouble Wedding Ring Size Fabric Requirements EditedfrapatchNo ratings yet
- 3 Combine Wiring Diagram Pad BDocument7 pages3 Combine Wiring Diagram Pad BDimas FirmanNo ratings yet
- NCP For GERD (Risk For Aspiration)Document2 pagesNCP For GERD (Risk For Aspiration)Ma Kristina Apolonio63% (8)
- Lab Report2 Keil SimulatorDocument11 pagesLab Report2 Keil SimulatorKhubaib WaqarNo ratings yet
- GCV - SRV Overhauling and Calibration - Automation & Control Engineering ForumDocument1 pageGCV - SRV Overhauling and Calibration - Automation & Control Engineering Forumعبدالسلام المبروك ابوزنادNo ratings yet
- Chapter 75Document2 pagesChapter 75Quranic ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Yahoo Mail - PCN Number Request For - WV20UOYDocument2 pagesYahoo Mail - PCN Number Request For - WV20UOYVicky RathodNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumejohn DaqueNo ratings yet
- 2014-08 Delphi Test EquipmentDocument41 pages2014-08 Delphi Test EquipmentDerek Jewett100% (2)
- Capstone Project ProposalDocument7 pagesCapstone Project Proposalapi-596258184No ratings yet
- Roof Fall Protection EngineeringDocument3 pagesRoof Fall Protection EngineeringfallsafetyNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual SinotruckDocument21 pagesMaintenance Manual SinotruckCôn LuânNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids: By: DR Dolapo AduDocument35 pagesUterine Fibroids: By: DR Dolapo AduAdu DolapoNo ratings yet
- Quiz SubsystemDocument7 pagesQuiz SubsystemReyes CzarinaNo ratings yet
- Topic Review Question and Case Study TopDocument6 pagesTopic Review Question and Case Study TopNorainah Abdul GaniNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication NetworksDocument4 pagesOptical Communication Networksarivurp100% (1)
- Sample Research PaperDocument71 pagesSample Research PaperminueeesimeNo ratings yet
- Ads Member 2Document28 pagesAds Member 2Kevin TtitoNo ratings yet
- Guía Didáctica - Profesionalización Inglés A1Document60 pagesGuía Didáctica - Profesionalización Inglés A1Fernanda AndradeNo ratings yet
- Major Kpi ImpDocument7 pagesMajor Kpi ImpImran AslamNo ratings yet
- 126105601chutuburu Jamshedpur 18Document3 pages126105601chutuburu Jamshedpur 18Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Insight in Inpatients With Psychotic Mania Demographic and Clinical FactorsDocument13 pagesInsight in Inpatients With Psychotic Mania Demographic and Clinical FactorsmusdalifahNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion StoryboardsDocument7 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion StoryboardsJudy AndalNo ratings yet
- RMA Planing Guide 200708 v1 1-1-36Document36 pagesRMA Planing Guide 200708 v1 1-1-36viswanath_manjulaNo ratings yet