Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soil P Reaction
Soil P Reaction
Uploaded by
myp20Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Distribution Profile: FerralsolsDocument1 pageDistribution Profile: FerralsolstoporoachoNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Agricultural Soil ManagementDocument74 pagesSustainable Agricultural Soil ManagementVan PradanaNo ratings yet
- Fosfitos en Aguacate, Mejor Que El FosfatoDocument3 pagesFosfitos en Aguacate, Mejor Que El FosfatoLady CasallasNo ratings yet
- Clima y SueloDocument1 pageClima y SueloJhessica Salazar HerreraNo ratings yet
- Soil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension ServiceDocument8 pagesSoil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension Servicemyp20No ratings yet
- Understanding Phosphorus Forms and Their Cycling in The SoilDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Phosphorus Forms and Their Cycling in The SoilMichelle CastroNo ratings yet
- Review of Sorption-Desorption Kinetics of Phosphorus in A Highly Variable Charge Tropical SoilDocument17 pagesReview of Sorption-Desorption Kinetics of Phosphorus in A Highly Variable Charge Tropical SoilRtr Ahmed Abidemi CertifiedNo ratings yet
- v02 23 PDFDocument25 pagesv02 23 PDFUsi Nur PamilianiNo ratings yet
- cssc3 - Manual 121 131Document11 pagescssc3 - Manual 121 131mawvfrwbNo ratings yet
- Importance of Farm Phosphorus Mass Balance and Management OptionsDocument5 pagesImportance of Farm Phosphorus Mass Balance and Management OptionsuserNo ratings yet
- 14.6 Solubility of Inorganic Soil Phosphorus: Precipitation by Iron, Aluminum, and Manganese IonsDocument3 pages14.6 Solubility of Inorganic Soil Phosphorus: Precipitation by Iron, Aluminum, and Manganese IonsLilis AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- The Phosphorus CycleDocument6 pagesThe Phosphorus CycleGeri-Ann TagalogNo ratings yet
- 222Document4 pages222Amir Masoud SamaniNo ratings yet
- GHGS 08Document2 pagesGHGS 08Ainry BiscochoNo ratings yet
- Soil PH and Plant NutrientsDocument2 pagesSoil PH and Plant Nutrientsmohd ameerNo ratings yet
- Silicon Increases The Phosphorus Availability of Arctic SoilsDocument14 pagesSilicon Increases The Phosphorus Availability of Arctic SoilsGabriel CespedesNo ratings yet
- DCP ProductionDocument7 pagesDCP ProductionNadeem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 3.acid SoilsDocument13 pages3.acid Soilsanmollkamboz911No ratings yet
- Phosphorus Cycle ReportDocument40 pagesPhosphorus Cycle ReportBation, Lorjie B.No ratings yet
- The Effects of PH On Phosphate Uptake From The Soil: Regular ArticleDocument10 pagesThe Effects of PH On Phosphate Uptake From The Soil: Regular ArticleMagdalena QuirogaNo ratings yet
- Lec 08Document9 pagesLec 08musa ballah koromaNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Rock PropertiesDocument40 pagesPhosphate Rock PropertiesAdios ANo ratings yet
- Lec34 Soil P and KDocument24 pagesLec34 Soil P and KDIBINo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Pupuk Pada TanahDocument12 pagesMekanisme Pupuk Pada TanahPutri Indra NovianiNo ratings yet
- Soil Phosphorus and Potassium: - P N, C, España enDocument53 pagesSoil Phosphorus and Potassium: - P N, C, España enCamila PortillaNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Fertilizers and Soil AcidityDocument4 pagesFactsheet Fertilizers and Soil AcidityjeffreyNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. The Phosphorus CycleDocument2 pagesFigure 1. The Phosphorus Cyclefunky goodNo ratings yet
- Iron Toxicity in Wetland Rice: Rashmi C. M. and PradeepDocument4 pagesIron Toxicity in Wetland Rice: Rashmi C. M. and PradeepRashmi C M RashmiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Phosphorus CycleDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Phosphorus CycleAhnJelloNo ratings yet
- PhosphorusDocument6 pagesPhosphorusvumejisukiNo ratings yet
- Sac 503 Soil Chemistry (2+1) Name: J. Lekhavarshinee Id No: 2022520009 Biological Phosphorus FixationDocument11 pagesSac 503 Soil Chemistry (2+1) Name: J. Lekhavarshinee Id No: 2022520009 Biological Phosphorus FixationJ.lekha VarshineeNo ratings yet
- 1383 Full PDFDocument4 pages1383 Full PDFRoshmiNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus Sources For Field Crops: Fact Sheet 73 Agronomy Fact Sheet SeriesDocument2 pagesPhosphorus Sources For Field Crops: Fact Sheet 73 Agronomy Fact Sheet SeriesGregory BakasNo ratings yet
- B-268 Phosphate Hideout PDFDocument4 pagesB-268 Phosphate Hideout PDFJayanath Nuwan SameeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Phosphorus in SoilDocument5 pagesChemistry of Phosphorus in SoilAbubakar Auwalu KwalamNo ratings yet
- Fluorspar: Definition, Mineralogy and DepositsDocument18 pagesFluorspar: Definition, Mineralogy and Depositsmushava nyokaNo ratings yet
- Phoslock, Overview-V3Document16 pagesPhoslock, Overview-V3Suprapto NsNo ratings yet
- Fluorides in DentistryDocument50 pagesFluorides in DentistryهجرسNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Phosphorus Fixation Training Module. Click To Next SlideDocument26 pagesWelcome To The Phosphorus Fixation Training Module. Click To Next SlideKirti SumanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 20 PDFGuido LarcherNo ratings yet
- 7part1 4 1 PDFDocument18 pages7part1 4 1 PDFRyan WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of SoilDocument3 pagesChemical Properties of SoilNoob KidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Behaviour of Red Phosphorus in Water PDFDocument16 pagesChemical Behaviour of Red Phosphorus in Water PDFChris MainNo ratings yet
- Arsenic in RiceDocument3 pagesArsenic in RiceSustainable SushiNo ratings yet
- CP1Document4 pagesCP1Roahliza NalazaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Extractions of Soil Phosphorus Do Not Reflect The Fact That Liming Increases Rye Phosphorus Content and Yield in An Acidic SoilDocument18 pagesLaboratory Extractions of Soil Phosphorus Do Not Reflect The Fact That Liming Increases Rye Phosphorus Content and Yield in An Acidic Soil1ab4cNo ratings yet
- Biological Interactions: Forms of Soil PhosphorusDocument7 pagesBiological Interactions: Forms of Soil PhosphorusrutuparnnaNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus and Sulfur CyclesDocument2 pagesPhosphorus and Sulfur CyclesRonaldNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus CycleDocument16 pagesPhosphorus CycleNorman Honorio Aguila CelesteNo ratings yet
- Plants 04 00253Document14 pagesPlants 04 00253muhammadrafiqyNo ratings yet
- JM cocos,+Jurnal+Noviane+Stela+TampilDocument6 pagesJM cocos,+Jurnal+Noviane+Stela+TampilkarsamahaNo ratings yet
- PhosphorusDocument14 pagesPhosphorusfeevee20No ratings yet
- Phosphoric: Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer FromDocument6 pagesPhosphoric: Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer FromFatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus CycleDocument11 pagesPhosphorus CycleDevika Hemalatha DeviNo ratings yet
- JPN Fe MNDocument15 pagesJPN Fe MNprofni2001No ratings yet
- Shen2011 (Article) (Obs. Título - Phosphorus Dynamics - From Soil To Plant)Document9 pagesShen2011 (Article) (Obs. Título - Phosphorus Dynamics - From Soil To Plant)Very TrueNo ratings yet
- Humic Acid Enhances Phosphorus Transport in Soil and UptakeDocument14 pagesHumic Acid Enhances Phosphorus Transport in Soil and UptakeKassandraNo ratings yet
- Infosheet Phosphorus in Soils - 2021 05Document2 pagesInfosheet Phosphorus in Soils - 2021 05Maqsood KhalidNo ratings yet
- Phosporus Cycle - Kent SGDocument7 pagesPhosporus Cycle - Kent SGKent S. G.No ratings yet
- Edgar: A. SlagleDocument4 pagesEdgar: A. SlagleAlexNo ratings yet
- Conserving Bogs The Management Handbook 2nd EditionDocument207 pagesConserving Bogs The Management Handbook 2nd Editionmyp20No ratings yet
- Haynes 1981Document12 pagesHaynes 1981myp20No ratings yet
- Guía Experimentos de CampoDocument67 pagesGuía Experimentos de Campomyp20No ratings yet
- Soil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension ServiceDocument8 pagesSoil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension Servicemyp20No ratings yet
- Soil Testing Procedures For Calcareous SoilsDocument5 pagesSoil Testing Procedures For Calcareous SoilsDoThanhTungNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The Humus Layer Mineral S-Wageningen University and Research 17739Document112 pagesChemical Composition of The Humus Layer Mineral S-Wageningen University and Research 17739farinoosh askariNo ratings yet
- Inland CIBADocument88 pagesInland CIBAvineet vermaNo ratings yet
- Management of Acid Soils of NE RegionDocument6 pagesManagement of Acid Soils of NE Regionsoumyarm942No ratings yet
- Tanaman SteviaDocument5 pagesTanaman Steviatoru rakaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Management of Mango Nutrition For Better Yield and QualityDocument30 pagesSustainable Management of Mango Nutrition For Better Yield and QualityHuy Vũ GiaNo ratings yet
- Triticum Aesativum: Screening of Wheat (L.) Genotypes at Germination and Seedling Stage For Aluminum Toxicity ToleranceDocument8 pagesTriticum Aesativum: Screening of Wheat (L.) Genotypes at Germination and Seedling Stage For Aluminum Toxicity ToleranceSurender KumarNo ratings yet
- Garden Alchemy80 Recipes and Concoctions For Organic Fertilizers Plant Elixirs Potting Mixes, Pest Deterrents (True PDFDocument132 pagesGarden Alchemy80 Recipes and Concoctions For Organic Fertilizers Plant Elixirs Potting Mixes, Pest Deterrents (True PDFBerlin Andrew SionNo ratings yet
- Grow Bible 2019 DownloadDocument73 pagesGrow Bible 2019 DownloadalexsseverinoNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness Magazine October 2023-1Document42 pagesAgribusiness Magazine October 2023-1PrevilageNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and Fertilizer UseDocument17 pagesSoil Fertility and Fertilizer UseAshaNo ratings yet
- Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium - CycleDocument25 pagesPotassium, Calcium and Magnesium - CycleFajar NNo ratings yet
- Jungle JuiceDocument3 pagesJungle Juicemurciano207No ratings yet
- Related Lit. of NPK SoilDocument17 pagesRelated Lit. of NPK SoilVeejay Soriano CuevasNo ratings yet
- EGG SHELL As Acid NeutralizerDocument9 pagesEGG SHELL As Acid NeutralizerRene RamiloNo ratings yet
- ChlorosisDocument2 pagesChlorosiscesar7771No ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Strategies of Crop ProductionDocument5 pagesBasic Principles and Strategies of Crop ProductionFrancesca AmeliáNo ratings yet
- Djeneba Thesis Final 28 OctoberDocument197 pagesDjeneba Thesis Final 28 OctoberHajar IsahNo ratings yet
- Insight SUB CSP21T6Q GEODocument26 pagesInsight SUB CSP21T6Q GEOkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Rbcsoils ScienceDocument17 pagesRbcsoils ScienceRayge HarbskyNo ratings yet
- Central Travancore JaggeryDocument11 pagesCentral Travancore JaggeryAnoop RNo ratings yet
- Alok Ranjan - Environmental GeographyDocument83 pagesAlok Ranjan - Environmental GeographySiddramNo ratings yet
- The New Composition of Liquid Organic Fertilizer For Improving Organic Tomato Yield and QualityDocument5 pagesThe New Composition of Liquid Organic Fertilizer For Improving Organic Tomato Yield and QualityShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentofaLow CostWastewater PDFDocument11 pagesDevelopmentofaLow CostWastewater PDFAini ZahraNo ratings yet
- Wood Ash Use in Forestry - A Review PDFDocument26 pagesWood Ash Use in Forestry - A Review PDFyasir majeedNo ratings yet
- Mung BeanDocument24 pagesMung BeanCaleb VoosNo ratings yet
- Brewery and Municipal Wastewater Irrigation Quality Impacts On Selected Soil Properties Around Harar City Eastern EthiopDocument4 pagesBrewery and Municipal Wastewater Irrigation Quality Impacts On Selected Soil Properties Around Harar City Eastern EthiopDerejeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Mid-Term Exam 2019 NAUDocument8 pages3rd Sem Mid-Term Exam 2019 NAUharrygmar harrydonNo ratings yet
- NRAES-165 - Web - Organic Vegetable Production PDFDocument171 pagesNRAES-165 - Web - Organic Vegetable Production PDFJackophiliNo ratings yet
Soil P Reaction
Soil P Reaction
Uploaded by
myp20Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil P Reaction
Soil P Reaction
Uploaded by
myp20Copyright:
Available Formats
Soil Phosphorus Reactions pH
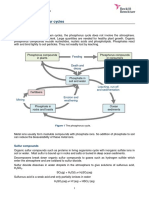
Phosphorus is required by the plant to form vital compounds Notice the hills and valleys of phosphorus fixation in Figure 1.
and to store and transfer energy for growth and reproduction. The highest fixation occurs in acid soils due to high iron
However, soil minerals and organic matter react quickly concentrations when the pH is less than 5. On the other end of
with soluble phosphorus fertilizer to create compounds with the spectrum, alkaline soils also create phosphorus-fixation
very low solubility. Because soil components and conditions problems due to high concentrations of calcium. In the
significantly affect the amount of phosphorus available, the following paragraphs, you will see what can be done in
ability to estimate soil phosphorus reactions is crucial. The each circumstance.
challenge is to manage these reactions so that crops have
Figure 1. Phosphorus Fixation
adequate supplies of available phosphorus.
Phosphorus Reactions with Soil Minerals Hill NO.1
Greatest
Am o unt o f P ho s pho rus F ix a tio n in the S o il
Fixation
Availability of phosphorus is primarily dependent upon the VERY HIGH
Range For Highest
Phosphorus Availability
pH of the soil. However, soil pH doesn’t affect phosphorus Hill NO.2
High
availability directly. Instead, soil pH levels indicate how certain Fixation
minerals – iron, aluminum, and calcium – interact with HIGH
Valley
NO.1
phosphorus in the soil, and it is this interaction that affects Hill NO.3
Medium
phosphorus availability.
Phosphorus Valley
Phosphorus Fixation
Fixation Due NO.2
MEDIUM Fixation To Aluminum
By Iron
Most soils contain abundant quantities of iron and aluminum; Phosphorus
Fixation
{
some soils, depending on soil pH, also contain an abundance
By Calcium
of calcium. The amount of iron, aluminum, and calcium present
LOW
pH3 pH4 pH5 pH6 pH7 pH8 pH9
in the soil are important because, in certain circumstances,
each mineral is capable of “fixing” the phosphorus, making it Acid Soils Neutral Alkaline Soils
unavailable to the crop.
When the soil pH is less than 5, iron and aluminum
In alkaline soils, iron and aluminum minerals are nearly concentrations are very high and react very quickly with
insoluble, while soluble calcium is abundant. In acid soils, iron phosphorus, creating iron or aluminum phosphate minerals.
and aluminum concentrations are high because the minerals The best way to correct this problem is to correct the pH
are soluble, while calcium concentrations are low because with lime. Lime neutralizes the soil acidity and decreases the
the mineral has been dissolved and leached out of the soil. concentration of iron and aluminum in the soil solution. In
High concentrations of any of these minerals will result in the short, lime reduces phosphorus fixation due to iron
phosphorus being fixed in the soil and unavailable to the crop. and aluminum.
(continued on reverse)
AgSource Testing today for a BETTER TOMORROW.
Laboratories labinfo@agsource.com | agsource.com/agronomy | 800.236.4995 |
A Subsidiary of Cooperative Resources International
When the soil pH is more than 7, calcium concentrations are soil requires more than 25 pounds of P 2 O5 to raise the
very high. Therefore, phosphorus fixation due to calcium soil-test levels, then perhaps normal fertilizer applications are
is a problem. The obvious solution is to lower soil pH. insufficient for your situation. Instead, consider correcting soil
Unfortunately, the amount of acid needed to neutralize many pH and/or band-applying phosphorus fertilizer to meet your
alkaline soils is cost prohibitive. For example, a typical alkaline crop’s requirements.
soil with 5% lime would contain 50 tons of lime in the top 6
2/3 inches of soil. It would require 16 tons of elemental sulfur
Phosphorus Reactions with Soil Organic Matter
Soil microbes require phosphorus as a part of their diet. As
to neutralize 50 tons of lime. If the soil were 50% lime, that
a result, microbes compete with crops for soil phosphorus.
would be 500 tons of lime and 160 tons of elemental sulfur.
This is especially true if a residue with a high carbon-to-
However, more cost effective solutions do exist:
phosphorus ratio has been applied to the soil. In this case,
• Acknowledge the high pH, and plant the microbes will need extra phosphorus to help them
a low-phosphorus-demand crop. decompose the residue. During decomposition, phosphorus is
• Band-apply phosphorus fertilizer. temporarily unavailable to the crop. This is called phosphorus
immobilization. When decomposition nears completion,
• When severe phosphorus stratification is evident, thoroughly phosphorus will once again become available for plant uptake.
incorporate the applied phosphorus throughout the root zone.
It is important to monitor phosphorus immobilization carefully
Phosphorus fixation occurs to some degree for all soils-even because it can result in purple corn or similar deficiencies. If
for pH levels from 6 to 7. This pH range is where phosphorus the residue has a high carbon to phosphorus ratio (e.g., 300:1),
availability is at its highest and fixation due to iron, aluminum, apply additional phosphorus fertilizer to prevent phosphorus
and calcium is at its lowest. At this range and in the very best of deficiencies.
circumstances, the crops may use 15% of the broadcast-applied
phosphorus fertilizer and 30% of the band-applied phosphorus Conclusion
fertilizer. When the soil is acidic or alkaline, these numbers Soil minerals and organic matter react quickly with soluble
could drop to 5% for broadcast and 15% for banded. phosphorus. In order for crops to have adequate supplies
of available phosphorus, soil pH must be managed, and
The best way to know if your soil has a high phosphorus-fixation phosphorus immobilization must be monitored.
capacity is to monitor the rate at which the soil-test levels
Copyright © by AgSource Harris, a Division of Cooperative Resources International
build when extra phosphorus fertilizer is applied. On the
average, it requires 18 pounds of P 2 O5 to raise the soil test
1 ppm for the Bray test and 0.5 ppm for the Olsen test. If your
AgSource Testing today for a BETTER TOMORROW.
Laboratories labinfo@agsource.com | agsource.com/agronomy | 800.236.4995 |
A Subsidiary of Cooperative Resources International
©2015 CRI F-10957-15
You might also like
- Distribution Profile: FerralsolsDocument1 pageDistribution Profile: FerralsolstoporoachoNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Agricultural Soil ManagementDocument74 pagesSustainable Agricultural Soil ManagementVan PradanaNo ratings yet
- Fosfitos en Aguacate, Mejor Que El FosfatoDocument3 pagesFosfitos en Aguacate, Mejor Que El FosfatoLady CasallasNo ratings yet
- Clima y SueloDocument1 pageClima y SueloJhessica Salazar HerreraNo ratings yet
- Soil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension ServiceDocument8 pagesSoil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension Servicemyp20No ratings yet
- Understanding Phosphorus Forms and Their Cycling in The SoilDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Phosphorus Forms and Their Cycling in The SoilMichelle CastroNo ratings yet
- Review of Sorption-Desorption Kinetics of Phosphorus in A Highly Variable Charge Tropical SoilDocument17 pagesReview of Sorption-Desorption Kinetics of Phosphorus in A Highly Variable Charge Tropical SoilRtr Ahmed Abidemi CertifiedNo ratings yet
- v02 23 PDFDocument25 pagesv02 23 PDFUsi Nur PamilianiNo ratings yet
- cssc3 - Manual 121 131Document11 pagescssc3 - Manual 121 131mawvfrwbNo ratings yet
- Importance of Farm Phosphorus Mass Balance and Management OptionsDocument5 pagesImportance of Farm Phosphorus Mass Balance and Management OptionsuserNo ratings yet
- 14.6 Solubility of Inorganic Soil Phosphorus: Precipitation by Iron, Aluminum, and Manganese IonsDocument3 pages14.6 Solubility of Inorganic Soil Phosphorus: Precipitation by Iron, Aluminum, and Manganese IonsLilis AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- The Phosphorus CycleDocument6 pagesThe Phosphorus CycleGeri-Ann TagalogNo ratings yet
- 222Document4 pages222Amir Masoud SamaniNo ratings yet
- GHGS 08Document2 pagesGHGS 08Ainry BiscochoNo ratings yet
- Soil PH and Plant NutrientsDocument2 pagesSoil PH and Plant Nutrientsmohd ameerNo ratings yet
- Silicon Increases The Phosphorus Availability of Arctic SoilsDocument14 pagesSilicon Increases The Phosphorus Availability of Arctic SoilsGabriel CespedesNo ratings yet
- DCP ProductionDocument7 pagesDCP ProductionNadeem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 3.acid SoilsDocument13 pages3.acid Soilsanmollkamboz911No ratings yet
- Phosphorus Cycle ReportDocument40 pagesPhosphorus Cycle ReportBation, Lorjie B.No ratings yet
- The Effects of PH On Phosphate Uptake From The Soil: Regular ArticleDocument10 pagesThe Effects of PH On Phosphate Uptake From The Soil: Regular ArticleMagdalena QuirogaNo ratings yet
- Lec 08Document9 pagesLec 08musa ballah koromaNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Rock PropertiesDocument40 pagesPhosphate Rock PropertiesAdios ANo ratings yet
- Lec34 Soil P and KDocument24 pagesLec34 Soil P and KDIBINo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Pupuk Pada TanahDocument12 pagesMekanisme Pupuk Pada TanahPutri Indra NovianiNo ratings yet
- Soil Phosphorus and Potassium: - P N, C, España enDocument53 pagesSoil Phosphorus and Potassium: - P N, C, España enCamila PortillaNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Fertilizers and Soil AcidityDocument4 pagesFactsheet Fertilizers and Soil AcidityjeffreyNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. The Phosphorus CycleDocument2 pagesFigure 1. The Phosphorus Cyclefunky goodNo ratings yet
- Iron Toxicity in Wetland Rice: Rashmi C. M. and PradeepDocument4 pagesIron Toxicity in Wetland Rice: Rashmi C. M. and PradeepRashmi C M RashmiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Phosphorus CycleDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Phosphorus CycleAhnJelloNo ratings yet
- PhosphorusDocument6 pagesPhosphorusvumejisukiNo ratings yet
- Sac 503 Soil Chemistry (2+1) Name: J. Lekhavarshinee Id No: 2022520009 Biological Phosphorus FixationDocument11 pagesSac 503 Soil Chemistry (2+1) Name: J. Lekhavarshinee Id No: 2022520009 Biological Phosphorus FixationJ.lekha VarshineeNo ratings yet
- 1383 Full PDFDocument4 pages1383 Full PDFRoshmiNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus Sources For Field Crops: Fact Sheet 73 Agronomy Fact Sheet SeriesDocument2 pagesPhosphorus Sources For Field Crops: Fact Sheet 73 Agronomy Fact Sheet SeriesGregory BakasNo ratings yet
- B-268 Phosphate Hideout PDFDocument4 pagesB-268 Phosphate Hideout PDFJayanath Nuwan SameeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Phosphorus in SoilDocument5 pagesChemistry of Phosphorus in SoilAbubakar Auwalu KwalamNo ratings yet
- Fluorspar: Definition, Mineralogy and DepositsDocument18 pagesFluorspar: Definition, Mineralogy and Depositsmushava nyokaNo ratings yet
- Phoslock, Overview-V3Document16 pagesPhoslock, Overview-V3Suprapto NsNo ratings yet
- Fluorides in DentistryDocument50 pagesFluorides in DentistryهجرسNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Phosphorus Fixation Training Module. Click To Next SlideDocument26 pagesWelcome To The Phosphorus Fixation Training Module. Click To Next SlideKirti SumanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 20 PDFGuido LarcherNo ratings yet
- 7part1 4 1 PDFDocument18 pages7part1 4 1 PDFRyan WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of SoilDocument3 pagesChemical Properties of SoilNoob KidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Behaviour of Red Phosphorus in Water PDFDocument16 pagesChemical Behaviour of Red Phosphorus in Water PDFChris MainNo ratings yet
- Arsenic in RiceDocument3 pagesArsenic in RiceSustainable SushiNo ratings yet
- CP1Document4 pagesCP1Roahliza NalazaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Extractions of Soil Phosphorus Do Not Reflect The Fact That Liming Increases Rye Phosphorus Content and Yield in An Acidic SoilDocument18 pagesLaboratory Extractions of Soil Phosphorus Do Not Reflect The Fact That Liming Increases Rye Phosphorus Content and Yield in An Acidic Soil1ab4cNo ratings yet
- Biological Interactions: Forms of Soil PhosphorusDocument7 pagesBiological Interactions: Forms of Soil PhosphorusrutuparnnaNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus and Sulfur CyclesDocument2 pagesPhosphorus and Sulfur CyclesRonaldNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus CycleDocument16 pagesPhosphorus CycleNorman Honorio Aguila CelesteNo ratings yet
- Plants 04 00253Document14 pagesPlants 04 00253muhammadrafiqyNo ratings yet
- JM cocos,+Jurnal+Noviane+Stela+TampilDocument6 pagesJM cocos,+Jurnal+Noviane+Stela+TampilkarsamahaNo ratings yet
- PhosphorusDocument14 pagesPhosphorusfeevee20No ratings yet
- Phosphoric: Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer FromDocument6 pagesPhosphoric: Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer FromFatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus CycleDocument11 pagesPhosphorus CycleDevika Hemalatha DeviNo ratings yet
- JPN Fe MNDocument15 pagesJPN Fe MNprofni2001No ratings yet
- Shen2011 (Article) (Obs. Título - Phosphorus Dynamics - From Soil To Plant)Document9 pagesShen2011 (Article) (Obs. Título - Phosphorus Dynamics - From Soil To Plant)Very TrueNo ratings yet
- Humic Acid Enhances Phosphorus Transport in Soil and UptakeDocument14 pagesHumic Acid Enhances Phosphorus Transport in Soil and UptakeKassandraNo ratings yet
- Infosheet Phosphorus in Soils - 2021 05Document2 pagesInfosheet Phosphorus in Soils - 2021 05Maqsood KhalidNo ratings yet
- Phosporus Cycle - Kent SGDocument7 pagesPhosporus Cycle - Kent SGKent S. G.No ratings yet
- Edgar: A. SlagleDocument4 pagesEdgar: A. SlagleAlexNo ratings yet
- Conserving Bogs The Management Handbook 2nd EditionDocument207 pagesConserving Bogs The Management Handbook 2nd Editionmyp20No ratings yet
- Haynes 1981Document12 pagesHaynes 1981myp20No ratings yet
- Guía Experimentos de CampoDocument67 pagesGuía Experimentos de Campomyp20No ratings yet
- Soil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension ServiceDocument8 pagesSoil, Plant, and Fertilizer: Cooperative Extension Servicemyp20No ratings yet
- Soil Testing Procedures For Calcareous SoilsDocument5 pagesSoil Testing Procedures For Calcareous SoilsDoThanhTungNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The Humus Layer Mineral S-Wageningen University and Research 17739Document112 pagesChemical Composition of The Humus Layer Mineral S-Wageningen University and Research 17739farinoosh askariNo ratings yet
- Inland CIBADocument88 pagesInland CIBAvineet vermaNo ratings yet
- Management of Acid Soils of NE RegionDocument6 pagesManagement of Acid Soils of NE Regionsoumyarm942No ratings yet
- Tanaman SteviaDocument5 pagesTanaman Steviatoru rakaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Management of Mango Nutrition For Better Yield and QualityDocument30 pagesSustainable Management of Mango Nutrition For Better Yield and QualityHuy Vũ GiaNo ratings yet
- Triticum Aesativum: Screening of Wheat (L.) Genotypes at Germination and Seedling Stage For Aluminum Toxicity ToleranceDocument8 pagesTriticum Aesativum: Screening of Wheat (L.) Genotypes at Germination and Seedling Stage For Aluminum Toxicity ToleranceSurender KumarNo ratings yet
- Garden Alchemy80 Recipes and Concoctions For Organic Fertilizers Plant Elixirs Potting Mixes, Pest Deterrents (True PDFDocument132 pagesGarden Alchemy80 Recipes and Concoctions For Organic Fertilizers Plant Elixirs Potting Mixes, Pest Deterrents (True PDFBerlin Andrew SionNo ratings yet
- Grow Bible 2019 DownloadDocument73 pagesGrow Bible 2019 DownloadalexsseverinoNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness Magazine October 2023-1Document42 pagesAgribusiness Magazine October 2023-1PrevilageNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and Fertilizer UseDocument17 pagesSoil Fertility and Fertilizer UseAshaNo ratings yet
- Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium - CycleDocument25 pagesPotassium, Calcium and Magnesium - CycleFajar NNo ratings yet
- Jungle JuiceDocument3 pagesJungle Juicemurciano207No ratings yet
- Related Lit. of NPK SoilDocument17 pagesRelated Lit. of NPK SoilVeejay Soriano CuevasNo ratings yet
- EGG SHELL As Acid NeutralizerDocument9 pagesEGG SHELL As Acid NeutralizerRene RamiloNo ratings yet
- ChlorosisDocument2 pagesChlorosiscesar7771No ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Strategies of Crop ProductionDocument5 pagesBasic Principles and Strategies of Crop ProductionFrancesca AmeliáNo ratings yet
- Djeneba Thesis Final 28 OctoberDocument197 pagesDjeneba Thesis Final 28 OctoberHajar IsahNo ratings yet
- Insight SUB CSP21T6Q GEODocument26 pagesInsight SUB CSP21T6Q GEOkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Rbcsoils ScienceDocument17 pagesRbcsoils ScienceRayge HarbskyNo ratings yet
- Central Travancore JaggeryDocument11 pagesCentral Travancore JaggeryAnoop RNo ratings yet
- Alok Ranjan - Environmental GeographyDocument83 pagesAlok Ranjan - Environmental GeographySiddramNo ratings yet
- The New Composition of Liquid Organic Fertilizer For Improving Organic Tomato Yield and QualityDocument5 pagesThe New Composition of Liquid Organic Fertilizer For Improving Organic Tomato Yield and QualityShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentofaLow CostWastewater PDFDocument11 pagesDevelopmentofaLow CostWastewater PDFAini ZahraNo ratings yet
- Wood Ash Use in Forestry - A Review PDFDocument26 pagesWood Ash Use in Forestry - A Review PDFyasir majeedNo ratings yet
- Mung BeanDocument24 pagesMung BeanCaleb VoosNo ratings yet
- Brewery and Municipal Wastewater Irrigation Quality Impacts On Selected Soil Properties Around Harar City Eastern EthiopDocument4 pagesBrewery and Municipal Wastewater Irrigation Quality Impacts On Selected Soil Properties Around Harar City Eastern EthiopDerejeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Mid-Term Exam 2019 NAUDocument8 pages3rd Sem Mid-Term Exam 2019 NAUharrygmar harrydonNo ratings yet
- NRAES-165 - Web - Organic Vegetable Production PDFDocument171 pagesNRAES-165 - Web - Organic Vegetable Production PDFJackophiliNo ratings yet