Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4-Tutorial-Thick Cylinders
4-Tutorial-Thick Cylinders
Uploaded by
Mohsin BashirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4-Tutorial-Thick Cylinders
4-Tutorial-Thick Cylinders
Uploaded by
Mohsin BashirCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial – Thick Cylinders
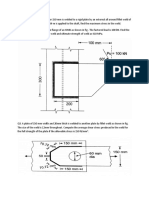
1. In an experiment of a thick cylinder of 100 mm external diameter and 50 mm internal
diameter the hoop and longitudinal strains as measured by strain gauges applied to the
outer surface of the cylinder were 240(10-6) and 60(10-6), respectively, for an internal
pressure of 90 MN/m2, the external pressure being zero. Determine the actual hoop and
longitudinal stresses present in the cylinder if E = 208 GN/m2 and ν = 0.29.
2. Assuming that the strain readings from Question 1 were obtained for a thick cylinder of
100 mm external diameter, calculate the internal diameter. Use all the information given
in Question 1.
3. A thick cylinder of 150 mm inside diameter and 200 mm outside diameter is subjected to
an internal pressure of 15 MN/m2. Determine the value of the maximum hoop stress set
up in the cylinder walls.
4. A cylinder of 100 mm internal radius and 125 mm external radius is subjected to an
external pressure of 14 bar (1.4 MN/m2). What will be the maximum stress set up in the
cylinder?
5. If the cylinder in Question 4 is now subjected to an additional internal pressure of 200 bar
(20 MN/m2), what will be the maximum stress value?
6. A steel thick cylinder of external diameter 150 mm has two strain gauges fixed externally,
one along the longitudinal axis and the other at right angles to read the hoop strain. The
cylinder is subjected to an internal pressure of and this causes the hoop strain of
+455(10-6) and longitudinal strain of +126(10-6). Given E = 208 GN/m2 and ν = 0.283,
find the internal diameter of the cylinder.
You might also like
- Problemas de Concentracion de EsfuerzosDocument7 pagesProblemas de Concentracion de EsfuerzosJonathan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Thick Cy FinalDocument5 pagesThick Cy FinalAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- ASM Tutorial 2Document2 pagesASM Tutorial 2martinsb76No ratings yet
- Assignment: Cylinders (Additional Problems) : By: Engr. Muhammad USMANDocument1 pageAssignment: Cylinders (Additional Problems) : By: Engr. Muhammad USMANRubab ZahraNo ratings yet
- Problems CH-10 Thick Cylinders (Blank)Document20 pagesProblems CH-10 Thick Cylinders (Blank)محمد خريبط100% (1)
- Unit 4B - Design of Pressur VesselDocument3 pagesUnit 4B - Design of Pressur VesselVikas RathodNo ratings yet
- Thick Cylinder Exercise AnswersDocument3 pagesThick Cylinder Exercise AnswersSimphiwe QuenethNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka Tutorial 2Document4 pagesFakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka Tutorial 2Hilmi YunosNo ratings yet
- Thick Cylinder ExercisesDocument2 pagesThick Cylinder ExercisesSimphiwe QuenethNo ratings yet
- Lab QuestionsDocument5 pagesLab QuestionsMohamed Salah0% (1)
- 4 Thick Cylinders AsgnDocument5 pages4 Thick Cylinders AsgnHILMAN NAZRINo ratings yet
- PS6 Mom IiDocument1 pagePS6 Mom IiMalik Ijaz Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- TyuijsgDocument2 pagesTyuijsgBibek ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Thin and Thick CylindersDocument6 pagesThin and Thick CylindersRamesh Akula80% (5)
- VisualizationDocument2 pagesVisualizationKIRAN H SNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- Question Bank SOM-IIDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank SOM-IISurjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- 12 09 2020Document2 pages12 09 2020nareshNo ratings yet
- MADE EASY (Welded Connections)Document2 pagesMADE EASY (Welded Connections)Swapnil KansayNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 2Document3 pagesTutorials 2Daemaro Liv Guud BremmerNo ratings yet
- SM Mid3 Model QuestionsDocument3 pagesSM Mid3 Model QuestionsSaitama BackupNo ratings yet
- CH3349 Tutorial - 3 Pressure Vessel DesignDocument3 pagesCH3349 Tutorial - 3 Pressure Vessel DesignLê Phạm HoàngNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - DPV - 2015Document5 pagesTutorial - DPV - 2015shuklameNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Design Problems (Undergrad Level)Document10 pagesChemical Engineering Design Problems (Undergrad Level)smeilyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 MoS Thin CylDocument3 pagesQuiz 4 MoS Thin CylSumesh SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Part B QDocument4 pagesModule 2 Part B Qjawad zamanNo ratings yet
- Dme Question Bank 2Document4 pagesDme Question Bank 2Ronak HadiyaNo ratings yet
- PS7 Mom 1Document2 pagesPS7 Mom 1Ahmed NaumanNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanic 2 - Assignment 4 GroupDocument2 pagesSolid Mechanic 2 - Assignment 4 GroupKelvin ThengNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2021Document3 pagesWorksheet 2021Layike AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- ExpectedDocument1 pageExpectedagdgaming100.mNo ratings yet
- PED AssignmentProblems 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesPED AssignmentProblems 2017 PDFSwapnil GudmalwarNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Stresses in Thin Walled Cylinder - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument13 pagesStrength of Materials - Stresses in Thin Walled Cylinder - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz Ameen100% (1)
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ce8395 Assignment No.4Document1 pageCe8395 Assignment No.4balaji muruganNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 6 NotesPonnada MarkandeyarajuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Ecs208 - Basic Solid Mechanics Learning Outcome: Thickness 30mmDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Ecs208 - Basic Solid Mechanics Learning Outcome: Thickness 30mmnurulselangorNo ratings yet
- Dme - Ii (17me64) : Assignement 01Document3 pagesDme - Ii (17me64) : Assignement 01NAVEEN H ENo ratings yet
- 15me53 Important Questions Paper-3Document3 pages15me53 Important Questions Paper-3Karthi SiddhNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PapersDocument23 pagesMechanical PapersSachin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument10 pagesQuestion BankNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- T2Document1 pageT2Muhammad Izzat AzimNo ratings yet
- Amd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017Document5 pagesAmd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017rip111176No ratings yet
- Bolt Head Stress Concentration Factors in Cylindrical Pressure VesselsDocument6 pagesBolt Head Stress Concentration Factors in Cylindrical Pressure VesselsLeandroNo ratings yet
- STL203SDocument6 pagesSTL203SClaudioNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids-II MEC-206ADocument3 pagesMechanics of Solids-II MEC-206AManish KumarNo ratings yet
- AMD Tutorial Stress StrainDocument3 pagesAMD Tutorial Stress Strainrip111176No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: MIDTERM ACTIVITIES: Pressure Vessels (Problem Set)Document2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: MIDTERM ACTIVITIES: Pressure Vessels (Problem Set)osas pasas100% (1)
- Problem Solving Session VDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Session VOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Spring QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesSpring QUESTIONSchetan guptaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Machine Design A: Numerical Problems: Problems On Pin, Cotter and Knuckle JointsDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Machine Design A: Numerical Problems: Problems On Pin, Cotter and Knuckle Jointsamol pogakeNo ratings yet
- Subject: E-Chamber Top Plate and Flange Strength AnalysisDocument10 pagesSubject: E-Chamber Top Plate and Flange Strength AnalysisJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Bearing & Thin WalledDocument17 pagesBearing & Thin WalledEmjay SevillaNo ratings yet
- AMD Tutorial ME CADCAM 2022-23Document6 pagesAMD Tutorial ME CADCAM 2022-23rip111176No ratings yet
- MD PPT For Review-1Document78 pagesMD PPT For Review-1Victor CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Exp. 5: Radiation Heat TransferDocument2 pagesExp. 5: Radiation Heat TransferMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab Project ReportDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics Lab Project ReportMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Test PDFDocument2 pagesTest PDFMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering Problem PDFDocument10 pagesComplex Engineering Problem PDFMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering Problem PDFDocument10 pagesComplex Engineering Problem PDFMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Measurement of PressureDocument51 pagesLecture 12 - Measurement of PressureMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Frame Fatigue Life: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Document5 pagesFrame Fatigue Life: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Mohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Calculations: 8Flq V 2 1 1.8 Log ( ( 3.7) + 6.9 )Document2 pagesExplanation of Calculations: 8Flq V 2 1 1.8 Log ( ( 3.7) + 6.9 )Mohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Production: Group MembersDocument13 pagesProduction: Group MembersMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- Guidelines PDFDocument1 pageGuidelines PDFMohsin BashirNo ratings yet
- S M & M E: Pring EmesterDocument1 pageS M & M E: Pring EmesterMohsin BashirNo ratings yet