Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsStudyGuide ForwardGeneticsInFly - Ans
StudyGuide ForwardGeneticsInFly - Ans
Uploaded by
Ata-AlpLuxtratusThis document provides instructions for a forward genetic screen in fruit flies to identify mutations involved in depositing mRNA into eggs. It asks the reader to answer questions about the screening process, including what generation to examine for dominant versus recessive mutations and how to design a screen to identify genes required for this function. It also includes a practice problem to design such a screen by outlining the generations of crosses needed and predicting mutant phenotypes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: Drosophila Simulation - Patterns of HeredityDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Drosophila Simulation - Patterns of HeredityFUN PHYSICS FOR NEET67% (3)
- OB Case Studies With Answers 1Document37 pagesOB Case Studies With Answers 1Tara FG100% (7)
- Preclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- AP Biology Lab Seven: Genetics of OrganismsDocument8 pagesAP Biology Lab Seven: Genetics of OrganismsCoolAsianDude67% (15)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- The Taimanov Sicilian Puzzles PDFDocument6 pagesThe Taimanov Sicilian Puzzles PDFAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Mage - Guide To The TechnocracyDocument214 pagesMage - Guide To The TechnocracyDracinaDragonfire85% (13)
- Extra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisDocument2 pagesExtra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Practical QuestionDocument4 pagesPractical Questionzaidulkheir0796No ratings yet
- Fruit Fly LabDocument4 pagesFruit Fly LabBrian HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly GeneticsDocument5 pagesFruit Fly GeneticsFiqryNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1Ain SufizaNo ratings yet
- Exam1 - Final - Genome 361Document7 pagesExam1 - Final - Genome 361Bùi Thị Vân KhanhNo ratings yet
- MLL Xii BioDocument17 pagesMLL Xii Bioeverythingisgonnabeallright007No ratings yet
- Drosophila ExperimentDocument8 pagesDrosophila Experimenteizzah asriNo ratings yet
- Lelm 206Document5 pagesLelm 206Kritika MishraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8: ProcedureDocument5 pagesExercise 8: Proceduresuryansh bhantiNo ratings yet
- Lelm206 PDFDocument5 pagesLelm206 PDFPrakhar VermaNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Document3 pagesFruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Kieu MuNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions (Term I) 2021-22 Biology Class XiiDocument20 pagesPractice Questions (Term I) 2021-22 Biology Class XiiJdijNo ratings yet
- KRM Public School Biology - Exam Class Xii Date: 27.11.21 Duration: 90 MinutesDocument21 pagesKRM Public School Biology - Exam Class Xii Date: 27.11.21 Duration: 90 MinutesGaneshNo ratings yet
- MCB 104 - Quiz 1 Combined Answer Key PDFDocument5 pagesMCB 104 - Quiz 1 Combined Answer Key PDFazgaray7No ratings yet
- Instructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofDocument1 pageInstructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly Lab Report InformationDocument25 pagesFruit Fly Lab Report Informationhatdog adadaNo ratings yet
- Heredity - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document4 pagesHeredity - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024jyotikushwahasmart0222No ratings yet
- Cfa 3 Geology StationsDocument9 pagesCfa 3 Geology Stationsapi-293084509No ratings yet
- Heredity QuestionsDocument5 pagesHeredity QuestionsNawaz AlamNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document4 pagesHomework 1ButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- Short QuestionsDocument10 pagesShort QuestionsBijayalaxmi SamantrayNo ratings yet
- Injso Race-1Document5 pagesInjso Race-1Shah RukhNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1-3Document9 pagesExercise 1-3Patricia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2Document8 pagesLab Activity 2Mellya RizkiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 and 2 - Drosophila MelanogaterDocument12 pagesExercise 1 and 2 - Drosophila MelanogaterInactive greekNo ratings yet
- KEY Mutations and MeiosisDocument2 pagesKEY Mutations and MeiosiszraootNo ratings yet
- BLANK Mouse Genetics Gizmo SEDocument6 pagesBLANK Mouse Genetics Gizmo SEzari leeNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution - 2019 Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesHeredity and Evolution - 2019 Question Bank PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Genetics - IDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Genetics - ISouparna GhoshNo ratings yet
- Drosophila Lab ReportDocument4 pagesDrosophila Lab ReportAnthony100% (1)
- Monohybrid Exercise GeneticsDocument1 pageMonohybrid Exercise GeneticsAli DokmakNo ratings yet
- B. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewDocument8 pagesB. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewNagalla Umalatha100% (1)
- B. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewDocument8 pagesB. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewNagalla UmalathaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project BOI 116Document19 pagesMini Project BOI 116Michell LeeNo ratings yet
- Drosophila MelanogasterDocument6 pagesDrosophila Melanogasterdanielle_wolbert100% (1)
- Principles of Inheritance - Notes - MONOHYBRID CROSSDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance - Notes - MONOHYBRID CROSSTuaNandiNo ratings yet
- Biology 1001A Term Test Part A: IndividualDocument12 pagesBiology 1001A Term Test Part A: IndividualJennie LinNo ratings yet
- Monohybrid and Test Cross Practice Problems WS 1ADocument2 pagesMonohybrid and Test Cross Practice Problems WS 1ANathalia Jaimes Jerez100% (1)
- Punnett Square Practice Worksheet 2 - W3simontechnologyorgDocument3 pagesPunnett Square Practice Worksheet 2 - W3simontechnologyorgAronNo ratings yet
- More Information and StatisticsDocument2 pagesMore Information and StatisticsMinhNo ratings yet
- Issam Jaroudi - Genetics Worksheet 1 - DominanceDocument3 pagesIssam Jaroudi - Genetics Worksheet 1 - DominanceSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Heredity CWDocument4 pagesHeredity CWPikachuNo ratings yet
- Final Biology 9Document15 pagesFinal Biology 9marogammaNo ratings yet
- 221 Final Exam Answer KeyDocument14 pages221 Final Exam Answer KeyGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument30 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesSanmayaNo ratings yet
- 10 Test - HereditaryDocument2 pages10 Test - HereditaryOnline MoradabadNo ratings yet
- Biology 24 Flylab - Drosophila - Monohybrid Cross - Answer Sheet FormatDocument3 pagesBiology 24 Flylab - Drosophila - Monohybrid Cross - Answer Sheet FormatElleeze Gwyneth EmpialesNo ratings yet
- PS 1 AnswersDocument11 pagesPS 1 AnswersLucy LiNo ratings yet
- Bio WSDocument4 pagesBio WSrrathnagirisrvtrycbseviiNo ratings yet
- Independent Honors Dihybrid TasksDocument7 pagesIndependent Honors Dihybrid Tasksapi-428068416No ratings yet
- Exercise 9Document3 pagesExercise 9raghav pandeyNo ratings yet
- Ensembl Genes and TranscriptsDocument3 pagesEnsembl Genes and Transcriptsquique ddmNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In PlantsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 2 1 2 2 6 3 Area:: Chem 130B, Spring 2017 1Document4 pages2 1 2 2 6 3 Area:: Chem 130B, Spring 2017 1Ata-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofDocument1 pageInstructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- ExtraPracticeQuestion FlyGeneticAnalysis - AnsDocument4 pagesExtraPracticeQuestion FlyGeneticAnalysis - AnsAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisDocument2 pagesExtra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- 2016-Midterm1-ANSWER KEYDocument10 pages2016-Midterm1-ANSWER KEYAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- MCZ CMK 5 - MFC ModelDocument2 pagesMCZ CMK 5 - MFC ModelAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- Apa 6 DissertationDocument5 pagesApa 6 Dissertationriteampvendell1979100% (1)
- Environment Consists of All Living and Non Living Things Which Surround UsDocument7 pagesEnvironment Consists of All Living and Non Living Things Which Surround UsrashmiamittalNo ratings yet
- Mental Hospital Architecture ThesisDocument8 pagesMental Hospital Architecture Thesissabrinahendrickssalem100% (2)
- Rutland 1967Document35 pagesRutland 1967Sophia JoseNo ratings yet
- VVIP Report Format: Sensitivity: InternalDocument3 pagesVVIP Report Format: Sensitivity: InternalShain SalimNo ratings yet
- Streamlines: Streamlines Dialog Box, Providing The Results Contain Flow ResultsDocument2 pagesStreamlines: Streamlines Dialog Box, Providing The Results Contain Flow ResultsManuel LavinNo ratings yet
- Nylon Fabric - LearningDocument23 pagesNylon Fabric - LearningBD Mug HouseNo ratings yet
- Calculus: EC All GATE QuestionsDocument54 pagesCalculus: EC All GATE QuestionsjonahNo ratings yet
- Roboric InspectionDocument20 pagesRoboric Inspectiongezu gebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Fibers..Document14 pagesBamboo Fibers..vinese.althearNo ratings yet
- A Mini Project Report On: Innovation Start-Up IdeaDocument8 pagesA Mini Project Report On: Innovation Start-Up IdeaShilpa MouryaNo ratings yet
- Structure From MotionDocument11 pagesStructure From MotionAyesha HussainNo ratings yet
- Focus5 2E End of Year Test Listening UoE Reading GroupBDocument4 pagesFocus5 2E End of Year Test Listening UoE Reading GroupBNikola RozićNo ratings yet
- Dietary Recall Diana Putri Subroto 2Document7 pagesDietary Recall Diana Putri Subroto 2Rayyan HafizNo ratings yet
- Insulin Glargine Injection: Active IngredientDocument31 pagesInsulin Glargine Injection: Active Ingredient44abcNo ratings yet
- Final Yr ProjectDocument21 pagesFinal Yr ProjectSnehal VarbheNo ratings yet
- Common Prospectus EnglishDocument338 pagesCommon Prospectus EnglishDeepakNo ratings yet
- 11th English ProjectDocument4 pages11th English ProjectAadhya HarugeriNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisFatur RahmNNo ratings yet
- Balucuc High School Balucuc Apalit PampangaDocument7 pagesBalucuc High School Balucuc Apalit PampangaBerto LopezNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Waiting - Line PDFDocument5 pagesCase Study - Waiting - Line PDFAnushka KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Engg 411 Form 5 Delegation PlanDocument2 pagesEngg 411 Form 5 Delegation PlanSofiaJabadanEspulgarNo ratings yet
- Reader's Perspective: 2004) - Gopen, A Professor of Rhetoric at Duke University, Says ThatDocument6 pagesReader's Perspective: 2004) - Gopen, A Professor of Rhetoric at Duke University, Says ThatrezkyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Argumentative EssayDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Argumentative Essayapi-461399602No ratings yet
- Gayatri C. Spivak-The Letter As Cutting EdgeDocument20 pagesGayatri C. Spivak-The Letter As Cutting EdgeCristina Burneo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Physics (Work, Energy & Power)Document36 pagesPhysics (Work, Energy & Power)Shainee Delle PalmeraNo ratings yet
- Modeling Power Law Absortion - 06Document8 pagesModeling Power Law Absortion - 06Nilson EvilásioNo ratings yet
StudyGuide ForwardGeneticsInFly - Ans
StudyGuide ForwardGeneticsInFly - Ans
Uploaded by
Ata-AlpLuxtratus0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageThis document provides instructions for a forward genetic screen in fruit flies to identify mutations involved in depositing mRNA into eggs. It asks the reader to answer questions about the screening process, including what generation to examine for dominant versus recessive mutations and how to design a screen to identify genes required for this function. It also includes a practice problem to design such a screen by outlining the generations of crosses needed and predicting mutant phenotypes.
Original Description:
Original Title
StudyGuide_ForwardGeneticsInFly.ans
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides instructions for a forward genetic screen in fruit flies to identify mutations involved in depositing mRNA into eggs. It asks the reader to answer questions about the screening process, including what generation to examine for dominant versus recessive mutations and how to design a screen to identify genes required for this function. It also includes a practice problem to design such a screen by outlining the generations of crosses needed and predicting mutant phenotypes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageStudyGuide ForwardGeneticsInFly - Ans
StudyGuide ForwardGeneticsInFly - Ans
Uploaded by
Ata-AlpLuxtratusThis document provides instructions for a forward genetic screen in fruit flies to identify mutations involved in depositing mRNA into eggs. It asks the reader to answer questions about the screening process, including what generation to examine for dominant versus recessive mutations and how to design a screen to identify genes required for this function. It also includes a practice problem to design such a screen by outlining the generations of crosses needed and predicting mutant phenotypes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Instructions:
Please read the notes of “Forward genetic screens in flies” through the link, and
answer the following questions. Most questions can be answered in one sentence.
Study question:
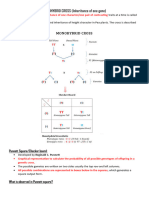
Look at the graphic:
1. What was mutagen used for this screen?
EMS
2. What is DTS? When would the flies die if they carry the allele?
Dominant temperature sensitive, die at 29C if the fly has >= 1 DTS
3. What is CYO? When would the flies die if they carry the allele?
CYO = dominant curly wing, recessive lethal. Fly dies if it is
homozygous for CYO.
4. The mutations on which chromosome will be balanced in this breeding
scheme? How do you know that?
Mutations on chromosome II, because you use balancer for chrm II.
5. In the screen described, if you want to identify a dominant mutation, which
generation should you look for mutants with the defects?
F1
6. In the screen described, if you want to identify a recessive mutation, which
generation should you look for mutants with the defects?
F3
7. Why is it important to backcross to the balancer female after F1?
To generate more flies with this particular mutation (The F2 contains
both male and female flies with the mutation. Note that among all the
F1s, there is only one fly in the whole world that contains this mutation.
Quick practice questions:
1. You are interested in identifying genes on chromosome II that are involved in
depositing mRNA into eggs of flies. If such genes were defective, then we’d
predict the fly to be sterile. Design a screen that will allow you to do this by
answering the following questions:
a. Will you mutagenize male or female? Male (it doesn’t really matter)
b. What would you predict your mutant to be if you have identified the
one that you want, sterile or fertile? Sterile female
c. What fly will you cross your F1 female to? What are the genotypes and
phenotypes of F2 generated by the F1 cross? A balancer male
(CYO/DTS). F2: m/CYO, +/CYO (all curly wings) at 29C
d. If you have found a dominant mutation, which generation should you
screen, and would you look at male fly or female fly? F2 embryos of
the F1 female.
e. If you have found a recessive mutation, do you need to generate an
F4 by crossing F3 to something else? If so, what will you cross the F3
to? Yes, because to examine if an F3 female is steile, you will
need to cross her to another fly. The genotype of this male fly
doesn’t matter.
Based on all your answers above, outline a diagram just like in the notes.
See extra practice problem on fly genetic analysis, question 3.
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: Drosophila Simulation - Patterns of HeredityDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Drosophila Simulation - Patterns of HeredityFUN PHYSICS FOR NEET67% (3)
- OB Case Studies With Answers 1Document37 pagesOB Case Studies With Answers 1Tara FG100% (7)
- Preclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- AP Biology Lab Seven: Genetics of OrganismsDocument8 pagesAP Biology Lab Seven: Genetics of OrganismsCoolAsianDude67% (15)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- The Taimanov Sicilian Puzzles PDFDocument6 pagesThe Taimanov Sicilian Puzzles PDFAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Mage - Guide To The TechnocracyDocument214 pagesMage - Guide To The TechnocracyDracinaDragonfire85% (13)
- Extra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisDocument2 pagesExtra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Practical QuestionDocument4 pagesPractical Questionzaidulkheir0796No ratings yet
- Fruit Fly LabDocument4 pagesFruit Fly LabBrian HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly GeneticsDocument5 pagesFruit Fly GeneticsFiqryNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1Ain SufizaNo ratings yet
- Exam1 - Final - Genome 361Document7 pagesExam1 - Final - Genome 361Bùi Thị Vân KhanhNo ratings yet
- MLL Xii BioDocument17 pagesMLL Xii Bioeverythingisgonnabeallright007No ratings yet
- Drosophila ExperimentDocument8 pagesDrosophila Experimenteizzah asriNo ratings yet
- Lelm 206Document5 pagesLelm 206Kritika MishraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8: ProcedureDocument5 pagesExercise 8: Proceduresuryansh bhantiNo ratings yet
- Lelm206 PDFDocument5 pagesLelm206 PDFPrakhar VermaNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Document3 pagesFruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Kieu MuNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions (Term I) 2021-22 Biology Class XiiDocument20 pagesPractice Questions (Term I) 2021-22 Biology Class XiiJdijNo ratings yet
- KRM Public School Biology - Exam Class Xii Date: 27.11.21 Duration: 90 MinutesDocument21 pagesKRM Public School Biology - Exam Class Xii Date: 27.11.21 Duration: 90 MinutesGaneshNo ratings yet
- MCB 104 - Quiz 1 Combined Answer Key PDFDocument5 pagesMCB 104 - Quiz 1 Combined Answer Key PDFazgaray7No ratings yet
- Instructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofDocument1 pageInstructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly Lab Report InformationDocument25 pagesFruit Fly Lab Report Informationhatdog adadaNo ratings yet
- Heredity - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document4 pagesHeredity - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024jyotikushwahasmart0222No ratings yet
- Cfa 3 Geology StationsDocument9 pagesCfa 3 Geology Stationsapi-293084509No ratings yet
- Heredity QuestionsDocument5 pagesHeredity QuestionsNawaz AlamNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document4 pagesHomework 1ButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- Short QuestionsDocument10 pagesShort QuestionsBijayalaxmi SamantrayNo ratings yet
- Injso Race-1Document5 pagesInjso Race-1Shah RukhNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1-3Document9 pagesExercise 1-3Patricia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2Document8 pagesLab Activity 2Mellya RizkiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 and 2 - Drosophila MelanogaterDocument12 pagesExercise 1 and 2 - Drosophila MelanogaterInactive greekNo ratings yet
- KEY Mutations and MeiosisDocument2 pagesKEY Mutations and MeiosiszraootNo ratings yet
- BLANK Mouse Genetics Gizmo SEDocument6 pagesBLANK Mouse Genetics Gizmo SEzari leeNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution - 2019 Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesHeredity and Evolution - 2019 Question Bank PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Genetics - IDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Genetics - ISouparna GhoshNo ratings yet
- Drosophila Lab ReportDocument4 pagesDrosophila Lab ReportAnthony100% (1)
- Monohybrid Exercise GeneticsDocument1 pageMonohybrid Exercise GeneticsAli DokmakNo ratings yet
- B. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewDocument8 pagesB. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewNagalla Umalatha100% (1)
- B. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewDocument8 pagesB. Sample Multiple Choice Questions: Genetics ReviewNagalla UmalathaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project BOI 116Document19 pagesMini Project BOI 116Michell LeeNo ratings yet
- Drosophila MelanogasterDocument6 pagesDrosophila Melanogasterdanielle_wolbert100% (1)
- Principles of Inheritance - Notes - MONOHYBRID CROSSDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance - Notes - MONOHYBRID CROSSTuaNandiNo ratings yet
- Biology 1001A Term Test Part A: IndividualDocument12 pagesBiology 1001A Term Test Part A: IndividualJennie LinNo ratings yet
- Monohybrid and Test Cross Practice Problems WS 1ADocument2 pagesMonohybrid and Test Cross Practice Problems WS 1ANathalia Jaimes Jerez100% (1)
- Punnett Square Practice Worksheet 2 - W3simontechnologyorgDocument3 pagesPunnett Square Practice Worksheet 2 - W3simontechnologyorgAronNo ratings yet
- More Information and StatisticsDocument2 pagesMore Information and StatisticsMinhNo ratings yet
- Issam Jaroudi - Genetics Worksheet 1 - DominanceDocument3 pagesIssam Jaroudi - Genetics Worksheet 1 - DominanceSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Heredity CWDocument4 pagesHeredity CWPikachuNo ratings yet
- Final Biology 9Document15 pagesFinal Biology 9marogammaNo ratings yet
- 221 Final Exam Answer KeyDocument14 pages221 Final Exam Answer KeyGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument30 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesSanmayaNo ratings yet
- 10 Test - HereditaryDocument2 pages10 Test - HereditaryOnline MoradabadNo ratings yet
- Biology 24 Flylab - Drosophila - Monohybrid Cross - Answer Sheet FormatDocument3 pagesBiology 24 Flylab - Drosophila - Monohybrid Cross - Answer Sheet FormatElleeze Gwyneth EmpialesNo ratings yet
- PS 1 AnswersDocument11 pagesPS 1 AnswersLucy LiNo ratings yet
- Bio WSDocument4 pagesBio WSrrathnagirisrvtrycbseviiNo ratings yet
- Independent Honors Dihybrid TasksDocument7 pagesIndependent Honors Dihybrid Tasksapi-428068416No ratings yet
- Exercise 9Document3 pagesExercise 9raghav pandeyNo ratings yet
- Ensembl Genes and TranscriptsDocument3 pagesEnsembl Genes and Transcriptsquique ddmNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In PlantsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 2 1 2 2 6 3 Area:: Chem 130B, Spring 2017 1Document4 pages2 1 2 2 6 3 Area:: Chem 130B, Spring 2017 1Ata-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofDocument1 pageInstructions:: C. Studying Whether The Effects of Neighboring Cells in Determining The Fate ofAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- ExtraPracticeQuestion FlyGeneticAnalysis - AnsDocument4 pagesExtraPracticeQuestion FlyGeneticAnalysis - AnsAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisDocument2 pagesExtra Practice Problems For Fly Genetic AnalysisAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- 2016-Midterm1-ANSWER KEYDocument10 pages2016-Midterm1-ANSWER KEYAta-AlpLuxtratusNo ratings yet
- MCZ CMK 5 - MFC ModelDocument2 pagesMCZ CMK 5 - MFC ModelAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- Apa 6 DissertationDocument5 pagesApa 6 Dissertationriteampvendell1979100% (1)
- Environment Consists of All Living and Non Living Things Which Surround UsDocument7 pagesEnvironment Consists of All Living and Non Living Things Which Surround UsrashmiamittalNo ratings yet
- Mental Hospital Architecture ThesisDocument8 pagesMental Hospital Architecture Thesissabrinahendrickssalem100% (2)
- Rutland 1967Document35 pagesRutland 1967Sophia JoseNo ratings yet
- VVIP Report Format: Sensitivity: InternalDocument3 pagesVVIP Report Format: Sensitivity: InternalShain SalimNo ratings yet
- Streamlines: Streamlines Dialog Box, Providing The Results Contain Flow ResultsDocument2 pagesStreamlines: Streamlines Dialog Box, Providing The Results Contain Flow ResultsManuel LavinNo ratings yet
- Nylon Fabric - LearningDocument23 pagesNylon Fabric - LearningBD Mug HouseNo ratings yet
- Calculus: EC All GATE QuestionsDocument54 pagesCalculus: EC All GATE QuestionsjonahNo ratings yet
- Roboric InspectionDocument20 pagesRoboric Inspectiongezu gebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Fibers..Document14 pagesBamboo Fibers..vinese.althearNo ratings yet
- A Mini Project Report On: Innovation Start-Up IdeaDocument8 pagesA Mini Project Report On: Innovation Start-Up IdeaShilpa MouryaNo ratings yet
- Structure From MotionDocument11 pagesStructure From MotionAyesha HussainNo ratings yet
- Focus5 2E End of Year Test Listening UoE Reading GroupBDocument4 pagesFocus5 2E End of Year Test Listening UoE Reading GroupBNikola RozićNo ratings yet
- Dietary Recall Diana Putri Subroto 2Document7 pagesDietary Recall Diana Putri Subroto 2Rayyan HafizNo ratings yet
- Insulin Glargine Injection: Active IngredientDocument31 pagesInsulin Glargine Injection: Active Ingredient44abcNo ratings yet
- Final Yr ProjectDocument21 pagesFinal Yr ProjectSnehal VarbheNo ratings yet
- Common Prospectus EnglishDocument338 pagesCommon Prospectus EnglishDeepakNo ratings yet
- 11th English ProjectDocument4 pages11th English ProjectAadhya HarugeriNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisFatur RahmNNo ratings yet
- Balucuc High School Balucuc Apalit PampangaDocument7 pagesBalucuc High School Balucuc Apalit PampangaBerto LopezNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Waiting - Line PDFDocument5 pagesCase Study - Waiting - Line PDFAnushka KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Engg 411 Form 5 Delegation PlanDocument2 pagesEngg 411 Form 5 Delegation PlanSofiaJabadanEspulgarNo ratings yet
- Reader's Perspective: 2004) - Gopen, A Professor of Rhetoric at Duke University, Says ThatDocument6 pagesReader's Perspective: 2004) - Gopen, A Professor of Rhetoric at Duke University, Says ThatrezkyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Argumentative EssayDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Argumentative Essayapi-461399602No ratings yet
- Gayatri C. Spivak-The Letter As Cutting EdgeDocument20 pagesGayatri C. Spivak-The Letter As Cutting EdgeCristina Burneo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Physics (Work, Energy & Power)Document36 pagesPhysics (Work, Energy & Power)Shainee Delle PalmeraNo ratings yet
- Modeling Power Law Absortion - 06Document8 pagesModeling Power Law Absortion - 06Nilson EvilásioNo ratings yet