Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective
Uploaded by
Sherlyn Kirisaki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
168 views3 pagesThe patient, Mario Magno, presented with dyspnea and was diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis. Assessments found decreased lung capacity and signs of infection related to the acute tuberculosis. The nursing care plan was to monitor his respiratory status, administer oxygen therapy as needed, and promote comfort through positioning while collecting sputum samples and administering physician-ordered drugs over 8 hours. This aimed to improve breathing and signs of infection while gauging the severity and treatment of the condition.
Original Description:
Original Title
36407612-Albuterol-Salbutamol
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient, Mario Magno, presented with dyspnea and was diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis. Assessments found decreased lung capacity and signs of infection related to the acute tuberculosis. The nursing care plan was to monitor his respiratory status, administer oxygen therapy as needed, and promote comfort through positioning while collecting sputum samples and administering physician-ordered drugs over 8 hours. This aimed to improve breathing and signs of infection while gauging the severity and treatment of the condition.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
168 views3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective
Uploaded by
Sherlyn KirisakiThe patient, Mario Magno, presented with dyspnea and was diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis. Assessments found decreased lung capacity and signs of infection related to the acute tuberculosis. The nursing care plan was to monitor his respiratory status, administer oxygen therapy as needed, and promote comfort through positioning while collecting sputum samples and administering physician-ordered drugs over 8 hours. This aimed to improve breathing and signs of infection while gauging the severity and treatment of the condition.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
NURSING CARE PLAN
Name of Patient: Llanto, Mario Magno Chief of Complaints: Dyspnea
Hospital: VSMMC Diagnosis: Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Ward and Bed No.: Miscellaneous Ward, Bed 11
Age: 58 yrs. old
Sex: Male
Civil Status: Married
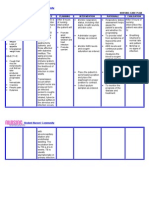
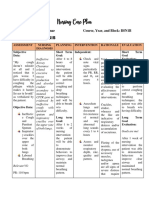
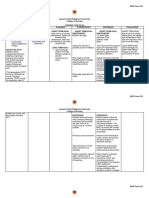
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: Ineffective The risk of TB is After 8 hours Independent: Respiratory status After 8 hours of
breathing a higher in older of nursing Monitor respiratory assessment helps nursing
“ Naglisod ko og pattern people who have intervention status, including vital gauge the intervention the
ginhawa “ as related to close contact the patient will signs, breath sounds, patient’s severity patient was
verbalized by the acute with a newly be: and skin color. and whether it’s able to:
patient. infection and
diagnosed TB progressing.
decreased
lung patient, those Promote To provide relief Breathing
OBJECTIVE:
capacity. who have TB good Administer oxygen from symptoms of returned to
before, respiratory therapy as ordered. hypoxemia and normal rate
Cough
gastrectomy function and hypoxia. and pattern
nonproductiv
patients, and treat
e at first but ABG levels and Minimal or
infection
later those affected Monitor ABG levels continuous pulse no signs of
Promote
produces with diabetes and oxygen oximetry infection.
comfort
sputum and mellitus. The saturation as ordered. measures the
progresses aging process blood’s oxygen
to weakens the content and are
hemoptysis. immune system,
Crackles Place the patient in good indicators of
further increasing semi-fowlers position the lung’s ability
Pleuritc pain the likelihood of
Dyspnea and place the to oxygenate the
tubercular diaphragm in proper blood.
infection in older position to contract. To increase chest
V/S taken: adults. Collect sputum expansion and to
samples as ordered. alleviate dyspnea.
T- 36.2 C Transmission
P- 74 bpm
occurs when
R- 24 cpm
BP- 120/80
droplet nuclei are To monitor the
mmHg produced form progress of the
an infected disease and
person’s coughs treatment.
or sneezes. If Source:
inhaled, tubercle (www.sribd.com)
bacillus settles in Dependent:
the alveolus and
infection occurs, Administer drugs as
with ordered by the physician.
alveolocapillary
dilation and Source:
endothelial (www.sribd.com)
swelling. The
incubation time
for TB is 4 to 8
weeks. TB is
usually
asymptomatic in
primary infection.
Source:
(Wikipedia.com)
You might also like
- Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesCase AnalysisDarlyn Amplayo100% (1)
- (Beginning Month) (Present Month) (End of Month) (Present Month) (Previous Month) (Present Month)Document7 pages(Beginning Month) (Present Month) (End of Month) (Present Month) (Previous Month) (Present Month)rapokzzz100% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeKen Simon100% (1)
- Disease Spread Gizmo HandoutDocument7 pagesDisease Spread Gizmo HandoutVicTroll YT50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan by MecDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan by MecMech CayananNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVen Belista86% (14)
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNCP PneumoniaMerliah LofrancoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianeDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- SNU54Document1 pageSNU54Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- A. Enrichment Activity 1 (Lesson 2: RHU)Document6 pagesA. Enrichment Activity 1 (Lesson 2: RHU)Yam Esor OsomrofNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis ReportDocument19 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis ReportKristel AnneNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument33 pagesPNEUMONIAgabrielle panganNo ratings yet
- IPPA SampleDocument28 pagesIPPA Samplekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Ptb-Case No. 3-Palmes, Judith P. BSN 3-HDocument21 pagesPtb-Case No. 3-Palmes, Judith P. BSN 3-HEduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Piguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24Document5 pagesPiguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24kc bpNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument15 pagesCOPDMary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis PneumoniaDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis PneumoniaPasa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument36 pagesPneumoniaMajed AlGhassabNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Respiratory HandoutDocument7 pagesNCM 112 Respiratory HandoutissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Scenario 3Document12 pagesScenario 3yunyastiti dwidyaNo ratings yet
- NCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Document8 pagesNCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- NCP ModsDocument5 pagesNCP ModsErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Assessment EditedDocument7 pagesAssessment Editedczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medicine CME: Lancelot Mark Pinto, Arpan Chandrakant Shah, Kushal Dipakkumar Shah, Zarir Farokh UdwadiaDocument3 pagesRespiratory Medicine CME: Lancelot Mark Pinto, Arpan Chandrakant Shah, Kushal Dipakkumar Shah, Zarir Farokh UdwadiaLintang SuroyaNo ratings yet
- EpiglDocument2 pagesEpiglfifiNo ratings yet
- Moleno April Mariebsn Ii F Case Scenario 1 Pediatric-Community Acquired Pneumonia Pcap-C IDocument11 pagesMoleno April Mariebsn Ii F Case Scenario 1 Pediatric-Community Acquired Pneumonia Pcap-C IyounggirldavidNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, MTB or TB (Short For TuberclesDocument4 pagesBacillus Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, MTB or TB (Short For TuberclesLeonelyn GeromoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection - NCPDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection - NCPHamil BanagNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionbijelNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Isoniazid Causing Pleural Effusion: Case ReportDocument2 pagesIsoniazid Causing Pleural Effusion: Case Reporttiti agniNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis G3Document12 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis G3Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumothorax in A Patient With COVID-19Document4 pagesTension Pneumothorax in A Patient With COVID-19Novie AstiniNo ratings yet
- Asthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesAsthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceEdmr SlzarNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic RiDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ristrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Assignment: Student Nurses' CommunityDocument3 pagesAssignment: Student Nurses' CommunityShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Article Endobronchial TuberculosisDocument4 pagesArticle Endobronchial TuberculosisFaruqi clinic OfficialNo ratings yet
- Acute Suppurative Parotitis Caused by Streptococcus Pneumoniae in An HIV-infected ManDocument4 pagesAcute Suppurative Parotitis Caused by Streptococcus Pneumoniae in An HIV-infected ManvaNo ratings yet
- Your Big IdeaDocument12 pagesYour Big Ideaapi-380169571No ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan Presented To The Faculty of The Nursing DepartmentDocument4 pagesA Nursing Care Plan Presented To The Faculty of The Nursing DepartmentAnge MinguitoNo ratings yet
- RLE Case PresentationDocument26 pagesRLE Case PresentationShaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument3 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Caso Aspergilosis NEJMDocument8 pagesCaso Aspergilosis NEJMSaidNo ratings yet
- Duran, Kayllien - SGD On CD GRP 14Document11 pagesDuran, Kayllien - SGD On CD GRP 14KAYLLIEN DURANNo ratings yet
- NCP Pneumonia May6 Ate KimDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia May6 Ate Kimiransevilla615No ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPKhatlen BagaresNo ratings yet
- NCP Not FinishDocument3 pagesNCP Not FinishJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXDocument2 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- Pulmonary Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient: Strategies for ManagementFrom EverandPulmonary Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient: Strategies for ManagementCarlos AgustiNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Endoscopy: Advances in Interventional PulmonologyFrom EverandThoracic Endoscopy: Advances in Interventional PulmonologyMichael J. SimoffNo ratings yet
- Jerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameDocument4 pagesJerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameSherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- What Is Malnutrition?Document4 pagesWhat Is Malnutrition?Sherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanMary Margarett BoadoNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning: M - MedicationDocument3 pagesDischarge Planning: M - MedicationSherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument1 pageDrug NameSherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pages3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism - Types: Type Primary Secondary Origin ThyroidDocument7 pagesHypothyroidism - Types: Type Primary Secondary Origin Thyroidboinklets100% (1)
- MalnutritionDocument1 pageMalnutritionSherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Diagnostics: A Guide For Diagnostic EvaluationsDocument5 pagesEvaluating Diagnostics: A Guide For Diagnostic EvaluationsYanneLewerissaNo ratings yet
- EmergencyDocument86 pagesEmergencyyazzNo ratings yet
- Expository Essay About Corona Virus PandemicDocument6 pagesExpository Essay About Corona Virus PandemicRas JemohNo ratings yet
- Model Intervensi Hipertensi Di Kabupaten Lebak Provinsi BantenDocument8 pagesModel Intervensi Hipertensi Di Kabupaten Lebak Provinsi Bantenyanuar anazdiNo ratings yet
- Low Level Laser Therapy LLLTDocument9 pagesLow Level Laser Therapy LLLTalamNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition by VanmeterDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition by Vanmetershriekacericg31u3100% (41)
- Unit - Three: HelminthsDocument177 pagesUnit - Three: HelminthsDembalu NuguseNo ratings yet
- Secure and Robust Machine Learning For HealthcareDocument22 pagesSecure and Robust Machine Learning For HealthcareJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- En UsDocument12 pagesEn UsYudhi NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Kangen Water BrochureDocument8 pagesKangen Water BrochureCTC GroupNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorder Mind MapDocument1 pageGenetic Disorder Mind MapEP Online classNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - SalbutamolDocument4 pagesDrug Study - SalbutamolReal TetisoraNo ratings yet
- Global Burden of DiseaseDocument82 pagesGlobal Burden of Diseaseangayarkanni100% (1)
- Minutes of 290th Meeting of Registration BoardDocument1,286 pagesMinutes of 290th Meeting of Registration BoardUsman DarNo ratings yet
- IDFC ABSLI Salaried Term Plan V01 BrochureDocument30 pagesIDFC ABSLI Salaried Term Plan V01 Brochuremantoo kumarNo ratings yet
- Pest and Disease Problems in Mushroom CultivationDocument6 pagesPest and Disease Problems in Mushroom CultivationJOSE ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Plant Pathogenic Organisms: Protozoa, Chromista, Fungi, Bacteria, and Candidatus PhytoplasmaDocument4 pagesPlant Pathogenic Organisms: Protozoa, Chromista, Fungi, Bacteria, and Candidatus Phytoplasmakeerthi vasanNo ratings yet
- Inseparable - Prospectus With 2021 BudgetDocument9 pagesInseparable - Prospectus With 2021 BudgetAralee HenighanNo ratings yet
- WHO, WIPO and WTO Trilateral Report (2020)Document352 pagesWHO, WIPO and WTO Trilateral Report (2020)Prof BorosNo ratings yet
- SurveillanceDocument61 pagesSurveillanceruthNo ratings yet
- Rescu Peds Simulation E-BookDocument594 pagesRescu Peds Simulation E-BookG SmithNo ratings yet
- CPHM-MIDTERM REVIeWERDocument10 pagesCPHM-MIDTERM REVIeWERJoise Daria Alabo100% (1)
- 2015 Revision: Dubai Health Authority Exam For G. DentistsDocument99 pages2015 Revision: Dubai Health Authority Exam For G. DentistsMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Ultrasonography 2020Document15 pagesNeuro-Ultrasonography 2020Santiago PovedaNo ratings yet
- Acl InjuryDocument8 pagesAcl InjuryFransiscaChelseaNatalieNo ratings yet
- Bio-Glass Filter Major ReportDocument58 pagesBio-Glass Filter Major ReportSiddharth ThakurNo ratings yet
- Sample Medical Incident Report: Section 1Document2 pagesSample Medical Incident Report: Section 1DS SystemsNo ratings yet
- 02-Incentive SpirometryDocument5 pages02-Incentive SpirometryPaloma CaneoNo ratings yet