Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Python GUI
Python GUI
Uploaded by
gopi99669571450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views2 pagestkinter is the most commonly used GUI module for Python. It provides a standard interface to the Tk GUI toolkit. To create a tkinter application, you import the tkinter module, create a main window container object, add widgets to the main window, apply event triggers to widgets, and run the main loop using mainloop(). There are different geometry managers like pack, grid, and place that control how widgets are organized in the parent window.
Original Description:
Original Title
Python GUI.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttkinter is the most commonly used GUI module for Python. It provides a standard interface to the Tk GUI toolkit. To create a tkinter application, you import the tkinter module, create a main window container object, add widgets to the main window, apply event triggers to widgets, and run the main loop using mainloop(). There are different geometry managers like pack, grid, and place that control how widgets are organized in the parent window.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views2 pagesPython GUI
Python GUI
Uploaded by
gopi9966957145tkinter is the most commonly used GUI module for Python. It provides a standard interface to the Tk GUI toolkit. To create a tkinter application, you import the tkinter module, create a main window container object, add widgets to the main window, apply event triggers to widgets, and run the main loop using mainloop(). There are different geometry managers like pack, grid, and place that control how widgets are organized in the parent window.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Python GUI – tkinter
Python offers multiple options for developing GUI (Graphical
User Interface). Out of all the GUI methods, tkinter is the most
commonly used method. It is a standard Python interface to the
Tk GUI toolkit shipped with Python. Python with tkinter is the
fastest and easiest way to create the GUI applications. Creating
a GUI using tkinter is an easy task.
To create a tkinter app:
1. Importing the module – tkinter
2. Create the main window (container)
3. Add any number of widgets to the main window
4. Apply the event Trigger on the widgets.
Importing tkinter is same as importing any other module in the
Python code. Note that the name of the module in Python 2.x is
‘Tkinter’ and in Python 3.x it is ‘tkinter’.
import tkinter
There are two main methods used which the user needs to
remember while creating the Python application with GUI.
1. Tk(screenName=None, baseName=None,
className=’Tk’, useTk=1): To create a main window,
tkinter offers a method ‘Tk(screenName=None,
baseName=None, className=’Tk’, useTk=1)’. To change
the name of the window, you can change the className
to the desired one. The basic code used to create the main
window of the application is:
m=tkinter.Tk() where m is the name of the main window object
2. mainloop(): There is a method known by the name
mainloop() is used when your application is ready to run.
mainloop() is an infinite loop used to run the application,
wait for an event to occur and process the event as long as
the window is not closed.
m.mainloop()
import tkinter
m = tkinter.Tk()
'''
widgets are added here
'''
m.mainloop()
tkinter also offers access to the geometric configuration of the
widgets which can organize the widgets in the parent windows.
There are mainly three geometry manager classes class.
1. pack() method:It organizes the widgets in blocks before
placing in the parent widget.
2. grid() method:It organizes the widgets in grid (table-like
structure) before placing in the parent widget.
3. place() method:It organizes the widgets by placing them
on specific positions directed by the programmer.
You might also like
- Automation Frameworks With Python Session 2: Sunny Khilare EricssonDocument8 pagesAutomation Frameworks With Python Session 2: Sunny Khilare EricssonBaluNo ratings yet
- Updated - Project 2 - GUIDocument65 pagesUpdated - Project 2 - GUIyoussefashraframadan2001No ratings yet
- Meeting11 12 GUI Programming NDocument46 pagesMeeting11 12 GUI Programming Nhusseinmesmar00No ratings yet
- Digital Clock FullDocument3 pagesDigital Clock FullSadab HussainNo ratings yet
- TK InterDocument16 pagesTK InterHoneyNo ratings yet
- Tkinter GuideDocument51 pagesTkinter GuideScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8-GUIDocument38 pagesLecture 8-GUIBezalel OwusuNo ratings yet
- Python GUI Programming With Tkinter - Real PythonDocument62 pagesPython GUI Programming With Tkinter - Real PythonPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Samritha It-2 ReportDocument16 pagesSamritha It-2 ReportKishore KNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 PythonDocument89 pagesUnit-4 PythonBessy Bijo100% (2)
- GUI Programming Using TkinterDocument62 pagesGUI Programming Using TkinterDudala NishithaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document45 pagesUnit 5susan babuNo ratings yet
- PWP ReportDocument6 pagesPWP ReportPriya NarsugadeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Dr. JPSM PPT - PythonDocument31 pagesUNIT 5 Dr. JPSM PPT - Pythonmorenikhil2024No ratings yet
- GUI Programming Using Tkinter PDFDocument62 pagesGUI Programming Using Tkinter PDFErick FelipeNo ratings yet
- GUI Programming Using Tkinter PDFDocument62 pagesGUI Programming Using Tkinter PDFalgorhythmNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 GUI Programming TkinterDocument26 pagesUnit 5 GUI Programming TkinterAsli memerNo ratings yet
- Python GUIDocument26 pagesPython GUIRafae DhopawakarNo ratings yet
- Python Gui TkinterDocument20 pagesPython Gui TkinterMasud SarkerNo ratings yet
- GUI Programming Additional MaterialDocument11 pagesGUI Programming Additional MaterialAnusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tkinter Tutorial For BeginnersDocument23 pagesTkinter Tutorial For BeginnersA Walí DexentNo ratings yet
- TK InterDocument5 pagesTK InterAntônio Carlos Fernandes da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Projects With Python (GUI & Tkinter)Document168 pagesProjects With Python (GUI & Tkinter)peacegroupng100% (1)
- Report Chat ApplicationDocument15 pagesReport Chat ApplicationBritish EmpireNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10psDocument16 pagesTutorial 10psAnand DhanaNo ratings yet
- Python Notes1Document17 pagesPython Notes1Dearly WurtzbachNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction PythonDocument24 pagesChapter 1-Introduction PythonNitesh JainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TkinterDocument8 pagesIntroduction To TkinterHaydz DulayNo ratings yet
- Python ProwDocument18 pagesPython ProwINJURED GAMER YTNo ratings yet
- Python - Gui Programming (Tkinter)Document12 pagesPython - Gui Programming (Tkinter)Franz Lee RamosNo ratings yet
- Mod 5Document113 pagesMod 5Abhinav JainNo ratings yet
- DIP Lab 3Document10 pagesDIP Lab 3Golam DaiyanNo ratings yet
- EX - NO: GUI (Graphical User Interface) Date: A. GUI With Python ProgramDocument4 pagesEX - NO: GUI (Graphical User Interface) Date: A. GUI With Python ProgramEssaki MuthuNo ratings yet
- Getting Started Programming With QT 5 WidgetsDocument17 pagesGetting Started Programming With QT 5 WidgetsMarcel Chis100% (2)
- 01 Introduction To TKinter - Windows, Labels, Entry Boxes, Buttons and Text BoxesDocument21 pages01 Introduction To TKinter - Windows, Labels, Entry Boxes, Buttons and Text Boxesemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- Aim: Developing A GUI Chat Application Theory:: Experiment:9 Date:6/07/2021Document7 pagesAim: Developing A GUI Chat Application Theory:: Experiment:9 Date:6/07/2021veduNo ratings yet
- Tkinter GUIDocument30 pagesTkinter GUISanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document83 pagesUnit 4VISHNU SHANKAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Uzair SMPDocument13 pagesUzair SMPSana MalikNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument24 pagesReportChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- Tkinter GUI Programming in PythonDocument38 pagesTkinter GUI Programming in PythonParul ThalquotraNo ratings yet
- Title Page:-Name of Group MembersDocument22 pagesTitle Page:-Name of Group MembersMit MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Phython TkinterDocument15 pagesPhython TkinterPabora KennethNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Worksheet - Tkinter - 1Document5 pagesSession 4 Worksheet - Tkinter - 1AarishiNo ratings yet
- Basic Features of Python IIIDocument13 pagesBasic Features of Python IIIKurnia SetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Student Management SystemDocument18 pagesStudent Management SystemAbhiram Bharadwaj SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- User Interfaces: Spring 2018Document155 pagesUser Interfaces: Spring 2018Micky CNo ratings yet
- Twitter: Iimt Engineering ColegeDocument77 pagesTwitter: Iimt Engineering ColegeMixmax12345No ratings yet
- Materi Minggu 12 TPB Alpro - GUIDocument20 pagesMateri Minggu 12 TPB Alpro - GUI16211007No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentUK creationsNo ratings yet
- LA1 - Introduction To Tkinter GUIDocument6 pagesLA1 - Introduction To Tkinter GUISiegrique Ceasar A. JalwinNo ratings yet
- Python - Gui Programming (Tkinter)Document33 pagesPython - Gui Programming (Tkinter)Franz Lee RamosNo ratings yet
- Android App DevelopmentDocument67 pagesAndroid App DevelopmentMoga Ion100% (1)
- Android Pro - Blogspot.com 2011 05 Threading in Android Part1Document6 pagesAndroid Pro - Blogspot.com 2011 05 Threading in Android Part1crxz0193No ratings yet
- Report Chat ApplicationDocument15 pagesReport Chat ApplicationBritish EmpireNo ratings yet
- The Ring Programming Language Version 1.5 Book - Part 67 of 180Document10 pagesThe Ring Programming Language Version 1.5 Book - Part 67 of 180Mahmoud Samir FayedNo ratings yet
- SizzDocument14 pagesSizzivan lapuzNo ratings yet
- Pythonnangcao - 4.gui - Data and ClassesDocument58 pagesPythonnangcao - 4.gui - Data and ClassesĐặng Thanh CườngNo ratings yet
- Address Book Using Python - SouradeepGupta - FinalpptDocument13 pagesAddress Book Using Python - SouradeepGupta - FinalpptSouradeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- RAID Detailed NotesDocument6 pagesRAID Detailed Notesgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Resume 002Document1 pageResume 002gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Resume 002Document1 pageResume 002gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Abstract Methods and Abstract Classes: Abstract MethodsDocument4 pagesAbstract Methods and Abstract Classes: Abstract Methodsgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Normalization Data AnomaliesDocument15 pagesNormalization Data Anomaliesgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Command Line ArgumentsDocument2 pagesCommand Line Argumentsgopi9966957145No ratings yet
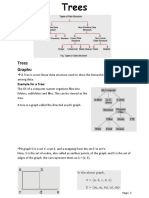
- Applications of Binary TreesDocument4 pagesApplications of Binary Treesgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- File Example XLSX 50Document2 pagesFile Example XLSX 50gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- A Spanning Tree Is A Subset of Graph GDocument9 pagesA Spanning Tree Is A Subset of Graph Ggopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Transaction PropertiesDocument3 pagesTransaction Propertiesgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- SQL Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesSQL Questions & Answersgopi9966957145100% (1)
- BSC 2 Unit III TreeDocument3 pagesBSC 2 Unit III Treegopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Unit 2 TCL CommandsDocument1 pageUnit 2 TCL Commandsgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Normalization Data AnomaliesDocument15 pagesNormalization Data Anomaliesgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- 11028/N M.Sc. II Semester Examination, April/May 2005 Paper I (2.1)Document2 pages11028/N M.Sc. II Semester Examination, April/May 2005 Paper I (2.1)gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Atria Convergence Technologies Limited, Due Date: 10/06/2020Document2 pagesAtria Convergence Technologies Limited, Due Date: 10/06/2020gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Telangana State Board of Intermediate Education: I Year General Results IPE MARCH-2020Document2 pagesTelangana State Board of Intermediate Education: I Year General Results IPE MARCH-2020gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- ALL ANY and EXISTS NOT EXISTSDocument5 pagesALL ANY and EXISTS NOT EXISTSgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Unions Enum PointersDocument12 pagesUnions Enum Pointersgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Basic Input Output in CPPDocument4 pagesBasic Input Output in CPPgopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Computer Networks Andrew S. Tanenbaum David J. Wetherall Fifth EditionDocument7 pagesComputer Networks Andrew S. Tanenbaum David J. Wetherall Fifth Editiongopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Facultyof Science M.Sc. II Semester Examination, April/May 2007Document1 pageFacultyof Science M.Sc. II Semester Examination, April/May 2007gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- Passenger Insurance: Your Ride With Rapido On 23 Nov 2019 at 04:08PM Is Now Insured!Document4 pagesPassenger Insurance: Your Ride With Rapido On 23 Nov 2019 at 04:08PM Is Now Insured!gopi9966957145No ratings yet
- 22 Annual Day Celebrations Shantiniketan Women's College: Program ListDocument1 page22 Annual Day Celebrations Shantiniketan Women's College: Program Listgopi9966957145No ratings yet