Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDF
MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDF
Uploaded by
zinzinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDF
MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDF
Uploaded by
zinzinCopyright:
Available Formats
Motivation and Study Techniques to help Cisco
you learn, remember, and pass your
CISSP
technical exams!
CEH
More coming soon...
Visit us www.mindcert.com
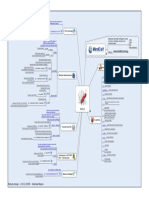
IKE Phase One
Router(config)#crypto isakmp enable Enable ISAKMP Step 1
ISAKMP is enabled by default Provides security services at the IP layer
Define the ISAKMP policy A framework of services
3DES Adds security to the upper
layers in the OSI model By Implementing a new set of headers
DES
Definition
128-bit Encryption One SA is required per direction
1932-bit AES Utilizes Security Associations (SA) A router to router IPsec VPN
will use two SA's One in each direction
256-bit
MD5
Hash AH
SHA Authentication Header
Have to set a pre-shared key Both change the datagram
Parameters that are used during ESP
Encapsulating Security Payload
Router(config)#crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 1.1.1.1 Pre-Share ISAKMP negotiation
Would set the key cisco123 for the peer 1.1.1.1 Authentication AH
RSA-Encr IP Protocol 51
RSA-Sig Origin authentication Does a one-way hash of the packet
1 Step 2 Provides
2 DH Group DOES NOT OFFER DATA CONFIDENTIALITY
Encryption
5
Authentication Header Adds a new header
60-86400 Seconds SA Lifetime Tunnel Mode
Authenticates the whole new datagram
Supports
56-bit DES
Encryption Transport Mode Authenticates the whole existing datagram
SHA Hash Not compliant with NAT As NAT changes the IP Header
RSA-Sig Authentication Two Frame Formats The will break AH authentication
Defaults
ESP
768-bit 1
DH Group IP Protocol 50
Confidentiality Encryption
One Day 86400 Seconds Provides
SA Lifetime Integrity
Origin Authentication
Router(config)#crypto isakmp identity {address | hostname} Configure the ISAKMP Identity method
Original datagram is placed in the
IP Address Encapsulating Security Payload encrypted ESP payload
Options Step 3 Tunnel Mode Cannot detect tampering whilst delivered
Hostname
Uses encrypted ESP headers
Although payload is fully secure
IP Address Default Supports
Keeps the existing IP header and
IKE Phase Two encrypts the original payload
Cisco IPsec Transport Mode cannot detect tampering whilst delivered
Router(config)#crypto ipsec transform-set myset esp-des esp-md5-hmac Only authenticates the ESP header and payload
Although payload is fully secure
This would create a transform set called myset
Define IPsec Transform Sets Configuration Is Compliant with NAT
using ESP and DES for Encryption
using ESP and MD5 for Authentication
Step 4 Protects the payload of the original IP datagram
You are then in crypto transform
configuration mode Transport Mode Used for end to end sessions
Router(cfg-crypto-trans)#mode {transport | tunnel} Cannot be used When NAT is required
Sets the mode to either Transport or Tunnel Further configuration
Two Protection Modes Protects entire datagram
Default is Tunnel
Tunnel Mode Places whole datagram in a new datagram
Define Crypto ACL
Works with NAT
Crypto ACL is the Access Control
List that specifies the traffic to be
sent over the VPN Step 5 In IPsec, Key Exchange is provided by
the Internet Key Exchange IKE
Would encrypt traffic with IPsec from
host 1.1.1.1 to host 2.2.2.2 Router(config)#access-list 199 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 IKE provides scalability for
exchanging keys between IPsec
Router(config)#crypto map mymap 10 ipsec-isakmp
IKE is synonymous with ISAKMP
Configures a Crypto Map with a
The Crypto Map will use ISAKMP No security is currently in place
sequence number of 10
Master secret is exchanged to
Description of the Crypto Map authenticate the peers
description
IKE Phase One sets the secure channel
Dialer related commands for the data encryption key exchange
dialer IKe Phase One negotiates IKE SAs
which is done in IKE Phase Two
Match crypto ACL match Hash
IKE SA parameters are agreed at Phase One
Define Crypto Maps Authentication
Commands for reverse route injection reverse-route
IKE Phase One Eliminates several Phase One steps
Identifies the IPsec peer Crypto Map configuration commands
peer Aggressive Mode Faster but less secure Three way packet exchange
Identifies which transform set to use transform-set Typically used in Remote Access VPNs
Key Exchange Two Modes
set Step 6 Slower but more secure Six way packet exchange
Use PFS or not pfs
IKE has two phases
Main Mode Can respond to peers that use
Lifetime Set SA parameters aggressive mode
security-association Cisco devices use main mode
Crypto maps pull together various Uses Diffie-Hellman (DH) to create the secure channel
parts used to set up the IPsec SAs IKE negotiates the IPsec SAs and generates
All entries are pre-configured Static the required key material for IPsec
Transform set and all other IPsec
Entries are configured dynamically as Types parameters are agreed at Phase Two
the result of IPsec negotiation Dynamic Reinitiates to refresh the SA
Quick Mode
One Mode
IKE Phase Two
Crypto Maps are applied to the interface where the
traffic leaves and enters a router PFS
You must apply the crypto map both Apply the Crypto Map If enabled, occurs at IKE Phase Two
Perfect Forward Secrecy
the the physical and logical interface
Carries out a new DH exchange with
when using GRE tunnels
each Quick Mode
You might also like
- Torrent Magnet LinkDocument1 pageTorrent Magnet LinkDamon Vector0% (3)
- Practice Exam Cpanel FundamentalsDocument9 pagesPractice Exam Cpanel FundamentalsVpnku 20% (1)
- Practical 01Document7 pagesPractical 01AndyXai0% (1)
- Simu5G: A System-Level Simulator For 5G Networks: Giovanni Nardini, Giovanni Stea, Antonio Virdis and Dario SabellaDocument13 pagesSimu5G: A System-Level Simulator For 5G Networks: Giovanni Nardini, Giovanni Stea, Antonio Virdis and Dario SabellaaymenayariNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Access Control MindMap PDFZeeshan RanaNo ratings yet
- Threat ModellingDocument3 pagesThreat ModellingayeshashafeeqNo ratings yet
- Learn Cyber SecurityDocument1 pageLearn Cyber SecurityPHẠM MINH TRÍNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Development ModelDocument9 pagesLife Cycle Development Modelapi-256677991No ratings yet
- CISO MindMap 2022 1651468241Document1 pageCISO MindMap 2022 1651468241Hashem HabibiNo ratings yet
- Secret Server Installation Windows 5Document24 pagesSecret Server Installation Windows 5smart_eagle44No ratings yet
- Network Security Essentials: Fifth Edition by William StallingsDocument31 pagesNetwork Security Essentials: Fifth Edition by William StallingsMuhammad Imran ButtNo ratings yet
- Google Cybersecurity Coursera Study Materials NotesDocument416 pagesGoogle Cybersecurity Coursera Study Materials NotesDhaleshwar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Alpha Group Appsec Testing PropoalDocument10 pagesAlpha Group Appsec Testing PropoalIndian OpinionNo ratings yet
- Cysa+ Cs0-002 Exam Topics Notes: 1.0 Threat and Vulnerability ManagementDocument15 pagesCysa+ Cs0-002 Exam Topics Notes: 1.0 Threat and Vulnerability ManagementainzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Threat Solution: Tentokrát Více o Koncovém ZařízeníDocument65 pagesAdvanced Threat Solution: Tentokrát Více o Koncovém ZařízeníJaved HashmiNo ratings yet
- MindCert Netcat MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert Netcat MindMap PDFzinzinNo ratings yet
- CSE Curriculum - IIIT HyderabadDocument20 pagesCSE Curriculum - IIIT HyderabadSuperdudeGauravNo ratings yet
- ADVERSARY EMULATION MATRIX by JoasDocument1 pageADVERSARY EMULATION MATRIX by JoasMD. MAHABUB RANA SAIKATNo ratings yet
- Cryptography, Network Security, and CyberlawDocument234 pagesCryptography, Network Security, and Cyberlaw1am17ec014 ashnal ahmedNo ratings yet
- 2019 Cloud Security Report Sponsored by (ISC) .Document20 pages2019 Cloud Security Report Sponsored by (ISC) .qadir147No ratings yet
- NS - 12 Incident ResponseDocument24 pagesNS - 12 Incident ResponseYogaRizwanNo ratings yet
- SIEM With Tactical AnalyticsDocument2 pagesSIEM With Tactical AnalyticsKoti EshwarNo ratings yet
- Security CisspDocument14 pagesSecurity CisspLaptop salesNo ratings yet
- Web Application Security Standard PDFDocument5 pagesWeb Application Security Standard PDFyshprasdNo ratings yet
- Firewall Penetration TestingDocument52 pagesFirewall Penetration TestingColin FancesNo ratings yet
- Scoping Questionnaire TemplateDocument3 pagesScoping Questionnaire Templatelagib78166No ratings yet
- Cyber Kill ChainDocument4 pagesCyber Kill ChainAbhi NairNo ratings yet
- CISSP Domain One: Security and Risk Management-What You Need To Know For The ExamDocument14 pagesCISSP Domain One: Security and Risk Management-What You Need To Know For The ExamLaptop salesNo ratings yet
- Professional Summary: - : Eswar Reddy - Sr. Vulnerability Management Engineer Phone: +1 704-920-9339 E-Mail IDDocument5 pagesProfessional Summary: - : Eswar Reddy - Sr. Vulnerability Management Engineer Phone: +1 704-920-9339 E-Mail IDAshwani kumarNo ratings yet
- SentinelOne DV Cheatsheet Opt2-2Document3 pagesSentinelOne DV Cheatsheet Opt2-2gobfNo ratings yet
- Abhishek: 20BCS3591@cuchd - in Chandel-B682061b8Document1 pageAbhishek: 20BCS3591@cuchd - in Chandel-B682061b8madhu jhaNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapjayarajan100% (1)
- Network Security EngineeringDocument17 pagesNetwork Security EngineeringGeorge PrintezisNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Vulnerability Management AnalystDocument3 pagesJob Description - Vulnerability Management AnalystMaher AyariNo ratings yet
- BIG-IP Application Security Manager Getting Started GuideDocument89 pagesBIG-IP Application Security Manager Getting Started GuidejavirodzNo ratings yet
- Try Latest & Free CompTIA CySA+ CS0-002 Real DumpsDocument11 pagesTry Latest & Free CompTIA CySA+ CS0-002 Real DumpskaronbillNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cybersecurity: Nanodegree Program SyllabusDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Cybersecurity: Nanodegree Program SyllabusaamirNo ratings yet
- Thread ModelingDocument41 pagesThread ModelingMervNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity RoadmapDocument23 pagesCybersecurity Roadmapshy.bu9No ratings yet
- Exabeam SecurityDocument32 pagesExabeam SecurityAbie Widyatmojo100% (1)
- An Approach To Vulnerability Management: by Umesh Chavan, CISSPDocument3 pagesAn Approach To Vulnerability Management: by Umesh Chavan, CISSPRaju PatleNo ratings yet
- Threat Protection - Windows 10Document3,502 pagesThreat Protection - Windows 10tetkaCNo ratings yet
- Baba Sai Eswara Reddy Satti: Cybersecurity Student AmbassadorDocument2 pagesBaba Sai Eswara Reddy Satti: Cybersecurity Student AmbassadorEswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Request Response Anything Something: (Can Be The Same or Different Hosts)Document20 pagesRequest Response Anything Something: (Can Be The Same or Different Hosts)nik4uNo ratings yet
- SANS Security AwarenessDocument2 pagesSANS Security AwarenessfredelNo ratings yet
- Eco-479 Exam Practice (Dumps)Document33 pagesEco-479 Exam Practice (Dumps)Sulaiman GbadamosiNo ratings yet
- OWASP SCP Quick Reference Guide - en-USDocument17 pagesOWASP SCP Quick Reference Guide - en-USheloNo ratings yet
- MindCert Wireshark MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Wireshark MindMapacehussainNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security AnalystDocument4 pagesCyber Security AnalystJu FiksonNo ratings yet
- Opmanager Standard UserguideDocument717 pagesOpmanager Standard Userguidemikrotik kemantanNo ratings yet
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 8Document30 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 8baby100% (1)
- Dynamic Malware AnalysisDocument6 pagesDynamic Malware AnalysisBik AshNo ratings yet
- BRKCRS 2891 PDFDocument140 pagesBRKCRS 2891 PDFNitinNo ratings yet
- Managing A Secure Network: CCNA Security v2.0Document41 pagesManaging A Secure Network: CCNA Security v2.0Youssef YLNo ratings yet
- Soc RaciDocument2 pagesSoc RaciLyu SeyNo ratings yet
- OWASP The Application Security Help DeskDocument598 pagesOWASP The Application Security Help Desksomendas100% (1)
- Incident Response Playbooks AND WorkflowsDocument62 pagesIncident Response Playbooks AND WorkflowsCleórbete SantosNo ratings yet
- Cyber Information Security Analyst in Seattle WA Resume Robin GarrettDocument3 pagesCyber Information Security Analyst in Seattle WA Resume Robin GarrettRobinGarrettNo ratings yet
- PAS Install and Configure 4 DaysDocument5 pagesPAS Install and Configure 4 DaysJESTIN JOYNo ratings yet
- 01a - General Security ConceptsDocument61 pages01a - General Security ConceptsMa Hoàng Hải KhôiNo ratings yet
- GIAC Certified Unix Security Administrator Standard RequirementsFrom EverandGIAC Certified Unix Security Administrator Standard RequirementsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lab 11 Title: RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument45 pagesLab 11 Title: RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramAhmed HameedNo ratings yet
- Brkarc-2350 - 2014Document128 pagesBrkarc-2350 - 2014Sarah AnandNo ratings yet
- Wcdma ChannelsDocument19 pagesWcdma ChannelsRitesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent ISA ES16 DatasheetDocument8 pagesAlcatel-Lucent ISA ES16 DatasheetZekita StrausNo ratings yet
- 04 AG - OC001 - E02 - 1 ZXMSG 5200 Data Configuration CLI-58pDocument58 pages04 AG - OC001 - E02 - 1 ZXMSG 5200 Data Configuration CLI-58pwael hamdy100% (1)
- Troubleshooting OSI Layers 4 7Document8 pagesTroubleshooting OSI Layers 4 7flyingccie datacenterNo ratings yet
- MentDocument14 pagesMenthamza syahoNo ratings yet
- FortiAuthenticator 5.4 Study Guide-OnlineDocument362 pagesFortiAuthenticator 5.4 Study Guide-OnlineDimitris GiannoulakisNo ratings yet
- Label Distribution ProtocolsDocument38 pagesLabel Distribution ProtocolsArie UtomoNo ratings yet
- Task SummaryDocument4 pagesTask SummaryRayed Al marshdNo ratings yet
- Ccna 1Document16 pagesCcna 1aboubakrysyNo ratings yet
- SignalingDocument96 pagesSignalingJeansel KahelNo ratings yet
- Fastiron 08070 L2guide 2Document353 pagesFastiron 08070 L2guide 2Suresh VNNo ratings yet
- Sendmail: Introduction and ConfigurationDocument9 pagesSendmail: Introduction and ConfigurationSrinivas ChNo ratings yet
- (SRX) Active Session Timeout Value Is Longer Than Backup Session After Chassis Cluster Failover - Juniper NetworksDocument3 pages(SRX) Active Session Timeout Value Is Longer Than Backup Session After Chassis Cluster Failover - Juniper NetworksLi KangNo ratings yet
- IP Camera Quick Start GuideDocument13 pagesIP Camera Quick Start GuideDarren BorgNo ratings yet
- 01-09 Basic IPv6 Configuration PDFDocument49 pages01-09 Basic IPv6 Configuration PDFHamoud BourjNo ratings yet
- RSG2488 Vs RSG2200 Ruggedcom 1 SLDDocument1 pageRSG2488 Vs RSG2200 Ruggedcom 1 SLDYahya ZabenNo ratings yet
- Introducción A La Tecnología GPONDocument39 pagesIntroducción A La Tecnología GPONJohannaNo ratings yet
- Internet Sharing Using Fire StarterDocument3 pagesInternet Sharing Using Fire StarterSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- CPSC 441 Test 2 Review: Iterative RecursiveDocument8 pagesCPSC 441 Test 2 Review: Iterative RecursiveGuransh MangatNo ratings yet
- CN MCQ Unit 1 Set 1Document5 pagesCN MCQ Unit 1 Set 1Makbool Shah W.No ratings yet
- Character Stuffing GuideDocument4 pagesCharacter Stuffing Guidemerlin664No ratings yet
- NetworkDelay Problems B10Document5 pagesNetworkDelay Problems B10SadiholicNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting GPRS Modem GMS-XXDocument6 pagesTroubleshooting GPRS Modem GMS-XXAurora DenitaNo ratings yet
- DP LAN Network wnt5 x86 32 903Document13 pagesDP LAN Network wnt5 x86 32 903Samwel KaranjaNo ratings yet