Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
Uploaded by
Srinivas VogguCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bus 1101 - Graded Quiz 3Document4 pagesBus 1101 - Graded Quiz 3kangwa stephenNo ratings yet
- Name: Nhlakanipho Surname: Khwela Student No.: 61541524 Module Code: BLG1502 Assignment No.: 02 Unique Number: 711357Document8 pagesName: Nhlakanipho Surname: Khwela Student No.: 61541524 Module Code: BLG1502 Assignment No.: 02 Unique Number: 711357Nhlakana Kay KhwelaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Bio 2022 P2 AnswersDocument9 pagesCSEC Bio 2022 P2 AnswersDhavani RankinNo ratings yet
- Good Hand Written NotesDocument8 pagesGood Hand Written Notessantunaskar948No ratings yet
- Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology SpecificationDocument21 pagesOxfordaqa International Gcse Biology Specificationjameelah santillanNo ratings yet
- UACE Biology 2010 Paper 2 GuideDocument11 pagesUACE Biology 2010 Paper 2 GuideRaidah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Biology Exercise For Final Test - Semester 1 - 2023 - 2024Document13 pagesBiology Exercise For Final Test - Semester 1 - 2023 - 2024zugagantengNo ratings yet
- 2006 Biology NotesDocument5 pages2006 Biology NotesroseNo ratings yet
- UACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2010 Marking GuideDocument10 pagesUACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2010 Marking GuideArthurNo ratings yet
- Bio sp3Document9 pagesBio sp3imrupnarayanNo ratings yet
- CBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument14 pagesCBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsMantri GNo ratings yet
- Biology - Part 1Document11 pagesBiology - Part 1hollymarieNo ratings yet
- Science Readings 2Document25 pagesScience Readings 2AericaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Exclude: 19,20,25,55,56Document31 pagesBiology: Exclude: 19,20,25,55,56Venessa PerpetuaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFDocument9 pages11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFRubhan kumarNo ratings yet
- Wa0007.Document70 pagesWa0007.onalennasethibaNo ratings yet
- Biology ExamDocument12 pagesBiology ExamRaulemarNo ratings yet
- Solution: WWW - Gradeup.coDocument46 pagesSolution: WWW - Gradeup.coFarewell Mech 17-21No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 12.36.52Document15 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 12.36.52ceec40479No ratings yet
- Paper 1 Taller 1Document12 pagesPaper 1 Taller 1Fco_Sandoval12No ratings yet
- 9 Science Cell The Basic Unit of Life Test 02 Answer m76bDocument2 pages9 Science Cell The Basic Unit of Life Test 02 Answer m76bNAVEEN DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument8 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSamar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell StandardsDocument5 pagesCell Standardsapi-300752528No ratings yet
- 2cytology 70 27Document4 pages2cytology 70 27rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes.Document263 pagesBiology Notes.Kelvin PhillipNo ratings yet
- Biology SpecificationDocument24 pagesBiology SpecificationJosh HallNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson NotesDocument8 pagesCell Lesson NotesNikshita KNo ratings yet
- Udaan 40 +1 Bio 13.08.2023Document6 pagesUdaan 40 +1 Bio 13.08.2023mohdhashim8789No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Laws: BiologyDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts and Laws: BiologyYasmien AldaveNo ratings yet
- Cyano-Bacteria ClassXIDocument22 pagesCyano-Bacteria ClassXISachin PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Notes Booklet SDA BIOLOGYDocument146 pagesNotes Booklet SDA BIOLOGYZeke Karl LondonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesDocument21 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesjanaNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument6 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- NEET - Biology - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesNEET - Biology - Cell Structure and Functionknlsinha67% (3)
- CHP 1,2Document4 pagesCHP 1,2MD MotinNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of Lifemunnithakur5285No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Laws: Biology PointersDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts and Laws: Biology PointersH Maranda100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSadik FsNo ratings yet
- Form 5 BiologyDocument13 pagesForm 5 BiologyLIU CHIEW NINGNo ratings yet
- Biology: Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesBiology: Organic CompoundsMockinjayNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 9 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesBiology Notes Class 9 The Fundamental Unit of LifeSai Uday Shankar BommakantiNo ratings yet
- Gi Embryo ComparativeDocument13 pagesGi Embryo ComparativemikeNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 07: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument11 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 07: Back of Chapter QuestionsTarandeep PawarNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Document7 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Ways by Which Paper Can Be SavedDocument37 pagesWays by Which Paper Can Be Savedsarthakrapartiwar3No ratings yet
- 482020104354AM-Class 9 Biology NotesDocument7 pages482020104354AM-Class 9 Biology Noteskmdmohideen2297No ratings yet
- Life Processes - Nutrition QB - 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesLife Processes - Nutrition QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Full NotesDocument259 pagesBiology Full NotesthaseiphologoNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument9 pagesBiological ClassificationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom EubacteriaDocument47 pagesKingdom EubacteriafarhanxxNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument13 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure & FunctionJ15No ratings yet
- Semep 2022 - Sample Test Questions BiologyDocument4 pagesSemep 2022 - Sample Test Questions BiologyJuliana PujanesNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument14 pagesCell: The Fundamental Unit of LifeSingh GurleenNo ratings yet
- Final Set A SolutionDocument14 pagesFinal Set A SolutionNirajan YadavNo ratings yet
- CH 6 BioDocument5 pagesCH 6 BioedwarddameNo ratings yet
- 9 Bio 1Document8 pages9 Bio 1Amisha SenapatiNo ratings yet
- NYA Practice Questions BiodiversityDocument7 pagesNYA Practice Questions Biodiversitymartin.kv4No ratings yet
- Biology CHP.17 Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesBiology CHP.17 Introduction To BiotechnologySanjay BandkarNo ratings yet
- Bio sp1Document10 pagesBio sp1deepmalabehera11No ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Name The Following Countries From Their Outlines BelowDocument2 pagesName The Following Countries From Their Outlines BelowSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Solved 05 New Sol JVQ PDFDocument16 pages11 Physics Solved 05 New Sol JVQ PDFSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesCbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper - 13 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesCbse Sample Paper - 13 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- Ciam T10Document3 pagesCiam T10Nino SilvaNo ratings yet
- PVC Sheet CatalogueDocument20 pagesPVC Sheet Cataloguerachel zulfiyatinNo ratings yet
- 1 StatDocument30 pages1 StatbutardoandreanicoleNo ratings yet
- Effects of Abm Subjects To The Content Knowledge in Abm StudentsDocument10 pagesEffects of Abm Subjects To The Content Knowledge in Abm StudentsJENNELLE LORILLANo ratings yet
- Adhesive Systems Important Aspects Related To TheiDocument8 pagesAdhesive Systems Important Aspects Related To TheiHachko GiragosyanNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity Analysis of Entrance Design Parameters of A Backward-Inclined Centrifugal Fan Using DOE Method and CFD CalculationsDocument8 pagesSensitivity Analysis of Entrance Design Parameters of A Backward-Inclined Centrifugal Fan Using DOE Method and CFD CalculationsHüseyin Atakan BaytaşNo ratings yet
- English FAL P2 Feb-March 2015 MemoDocument24 pagesEnglish FAL P2 Feb-March 2015 MemoRoxanneNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming: Labeling The Text OCC101Document8 pagesComputer Programming: Labeling The Text OCC101Marygin Esplana SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan For Senior HighDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For Senior HighSora HazelbitzNo ratings yet
- Sheet SamplingDocument3 pagesSheet SamplingAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Activity PR ItoDocument4 pagesActivity PR ItoSamantha Nicolle QuierraNo ratings yet
- Marien Van Westen Desmid Research in DrentheDocument24 pagesMarien Van Westen Desmid Research in DrentheMarien van WestenNo ratings yet
- Full Download Introduction To Measure Theoretic Probability 2nd Edition Roussas Solutions ManualDocument6 pagesFull Download Introduction To Measure Theoretic Probability 2nd Edition Roussas Solutions Manualirisybarrous100% (38)
- AMO Absolute Encoders Rotary AMOSINDocument36 pagesAMO Absolute Encoders Rotary AMOSINsanthoshkumar.sNo ratings yet
- ENG250 ChineseCreationMythsDocument6 pagesENG250 ChineseCreationMythsRishel Mae Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetBermonica Alvior SatuitoNo ratings yet
- Soil Spectroscopy: Training MaterialDocument28 pagesSoil Spectroscopy: Training MaterialAgustín DeviaNo ratings yet
- 5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsDocument5 pages5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsSendhil RevuluriNo ratings yet
- 2024 GeES 1011 Group AssignmentDocument1 page2024 GeES 1011 Group AssignmentLemma Deme ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Writing Style APA FormatDocument2 pagesWriting Style APA FormatsenyorakathNo ratings yet
- SeismoStruct User Manual PDFDocument325 pagesSeismoStruct User Manual PDFStr Engr Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Jensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewDocument11 pagesJensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewKarma TenzinNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations: Insoluble ChloridesDocument1 pageQualitative Analysis of Cations: Insoluble Chlorideskemhar jaminulNo ratings yet
- Individual Proposal Format-CSRI-2021Document12 pagesIndividual Proposal Format-CSRI-2021Dr. Manoj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Value Educatvdffion Mcqs Part 1Document20 pagesValue Educatvdffion Mcqs Part 1virupakshaNo ratings yet
- 7ICEGE Liquefaction Causesandeffects FsalgadoDocument9 pages7ICEGE Liquefaction Causesandeffects FsalgadoAbdifatah mohamed yusufNo ratings yet
- Sick - WT34 - R220Document7 pagesSick - WT34 - R220M MNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Writing Describing A PlaceDocument1 pageUnit 7 Writing Describing A PlaceXzit YassinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document28 pagesChapter 9api-2704505540% (1)
Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
Uploaded by
Srinivas VogguOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
Uploaded by
Srinivas VogguCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE SAMPLE PAPER – 12 (Solved)
Class-XI
BIOLOGY (THEORY)
Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70
ANSWERS
Section-A
1. There are plants for which flowering is either quantitatively or qualitatively dependent on
exposure to low temperature. This phenomenon is termed vernalisation.
2. Fibrinogen, globulins and albumins are the major proteins. Fibrinogens are needed for
clotting or coagulation of blood. Globulins primarly are involved in defense mechanisms
of the body and the albumins help in osmotic balance.
3. Both monera and protista contain species having unicellular organism and predominantly
aquatic organism.
4.
5. In some plants, like grass, Monstera and the banyan tree, roots arise from parts of the plant other
than the radicle and are called adventitious roots.
Section-B
6. Proteases are secreted in inactive form and pose no threat to the gut lining. The mucus
provides protection to the epithelial lining.
7.
a) The specimens are kept in suitable chemical solutions.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
b) Plant and animal specimens are also preserved as dry specimens.
c) Insects are normally dried and pinned in the insect boxes.
d) Larger animals (birds, mammals) are preserved as stuffed specimens.
Or
Ascus Basidia
Spores are produced endogenously Spores are produced exogenously
Eight spores are inside an ascus Four spores are produced by a basidium
8. When water is the limiting factor, photosynthesis is affected as – the stomata close and
entry carbon dioxide is restricted and the cells lose their turgidity and so leaves are not
fully exposed to light.
9. Kinetochores are small disc-shaped structures at the surface of centromere. They serve as
the sites of attachment of the spindle fibres to the centromere of chromosomes
Section-C
10.
Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
The cells are alive at maturity The cells are dead at maturity
Cell wall is unevenly thickened, thickening are Cell wall is unevenly thickened; sometimes
prominent in the corners. lumen in obliterated.
It gives strength and flexibility to growing It gives mechanical support to the organ and
organs the fibres are used for making opes / threads.
It may posses chloroplates and photosynthesis It never possesses chloroplasts.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
11.
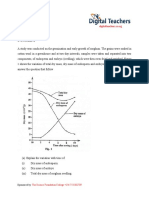
12. Respiratory quotient is defined as the ratio of the volume of carbon dioxide evolved to
the volume of oxygen consumed in respiration. RQ varies with the respiratory
substrates, as shown below:
(i) When a carbohydrate is the respiratory substrate the RQ is one
(ii) When fats are the respiratory substrate the RQ is less than one.
13. A brain is formed by the fusion of a pair of suprapharyngeal / cerebal ganglia; it lies in
the anterior and dorsal part of the third segment. It is connected to two sub-pharyngeal
ganglia’ lying below the pharynx, with the help of a pair of ircumpharyngeal
connectives, which form a nerve ring. A double ventral nerve cord runs up to the last
segment. Ganglia are segmentally arranged on the nerve cord and they give of nerves
tot eh organs of that segment.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Or
14. He employed purple and green photosynthetic bacteria. He demonstrated that
photosynthesis is essentially a light-dependent reaction in which hydrogen from a suitable
oxidisable compound reduces carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
This can expressed as 2 H2A + CO2 2 A + CH2O + H2O.
Green plants, water is the hydrogen donor as it is oxidised to oxygen. Photosynthetic
bacteria used hydrogen sulphide (H2S) as hydrogen donor and so the oxidation product
is sulphur or sulphate depending on the organism.
15.
(a) Presence of mammary glands is a characteristic feature, they are functional in
females and vestigial in males.
(b) External ear is present.
(c) Trunk is internally partitioned by a muscular diaphragm into thoracic and
abdominal cavities.
(d) Skin possesses sweat glands and sebaceous glands; skin has hair a unique feature
of the class.
(e) Heart is four – chambered with two auricles and two ventricles, there is double
circulation.
(f) Animals are viviparous and give birth to young ones. The foetus is nourished by
the mother through the placenta.
16. When a protein has many subunits (polypeptide) each having a primary , secondary or
tertiary structure of its own, the protein is said to be in its quaternary structure. E.g
Haemoglobin, Insulin, Myoglobin.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
17. Juxta glomercular apparatus (JGA) is a specialized cellular structure located where the
distal convoluted tubule passes close to the Bowman’s capsule near the afferent article,
where the two come in contact with each other. A fall in the GFR activities the cells of
TGA to release rennin. Rennin acts through a complex series of reactions called rein-
angiotension-aldosterone mechanism. This increases the blood volume and blood
pressure and the GFR is brought back to normal.
18.
19. Proteases are secreted in inactive form and pose no threat to the gut lining. The mucus
provides protection to the epithelial lining. The juice secreted by gastric gland contain
mucus that help protection of inner layer of gut.
20.
a) The specimens are kept in suitable chemical solutions.
b) Plant and animal specimens are also preserved as dry specimens.
c) Insects are normally dried and pinned in the insect boxes.
d) Larger animals (birds, mammals) are preserved as stuffed specimens.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
21.
a) Prabha is very concerned about the society and hygiene of locality.
b) The public hygiene is essential to prevent the spread of disease and make
the surrounding neat and clean.
c) Disease like malaria and cholera spread due to unhygienic condition.
Section-D
22. Imbibition is a special type of diffusion when water is absorbed by solids – colloids –
causing them to enormously increase in volume. The classical examples of imbibition are
absorption of water by seeds and dry wood. The pressure that is produced by the swelling of
wood had been used by prehistoric man to split rocks and boulders. If it were not for the
pressure due to imbibition, seedlings would not have been able to emerge out of the soil into
the open. Imbibition is also diffusion since water movement is along a concentration
gradient; the seeds and other such materials have almost no water hence they absorb water
easily. Water potential gradient between the absorbent and the liquid imbibed is essential for
imbibition. In addition, for any substance to imbibe any liquid, affinity between the
adsorbant and the liquid is also a pre-requisite.
Or
a)
b)
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
23. The outermost covering of a seed is the seed coat. The seed coat has two layers, the outer
testa and the inner tegmen. The hilum is a scar on the seed coat through which the
developing seeds
were attached to
the fruit. Above
the hilum is a
small pore called
the micropyle.
Within the seed coat is the embryo, consisting of an embryonal axis and two cotyledons.
The cotyledons are often fleshy and full of reserve food materials. At the two ends of the
embryonal axis are present the radicle and the plumule. In some seeds such as castor the
endosperm formed as a result of double fertilisation, is a food storing tissue. In plants
such as bean, gram and pea, the endosperm is not present in mature seeds and such seeds
are called non-endospermous.
Or
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- Bus 1101 - Graded Quiz 3Document4 pagesBus 1101 - Graded Quiz 3kangwa stephenNo ratings yet
- Name: Nhlakanipho Surname: Khwela Student No.: 61541524 Module Code: BLG1502 Assignment No.: 02 Unique Number: 711357Document8 pagesName: Nhlakanipho Surname: Khwela Student No.: 61541524 Module Code: BLG1502 Assignment No.: 02 Unique Number: 711357Nhlakana Kay KhwelaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Bio 2022 P2 AnswersDocument9 pagesCSEC Bio 2022 P2 AnswersDhavani RankinNo ratings yet
- Good Hand Written NotesDocument8 pagesGood Hand Written Notessantunaskar948No ratings yet
- Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology SpecificationDocument21 pagesOxfordaqa International Gcse Biology Specificationjameelah santillanNo ratings yet
- UACE Biology 2010 Paper 2 GuideDocument11 pagesUACE Biology 2010 Paper 2 GuideRaidah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Biology Exercise For Final Test - Semester 1 - 2023 - 2024Document13 pagesBiology Exercise For Final Test - Semester 1 - 2023 - 2024zugagantengNo ratings yet
- 2006 Biology NotesDocument5 pages2006 Biology NotesroseNo ratings yet
- UACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2010 Marking GuideDocument10 pagesUACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2010 Marking GuideArthurNo ratings yet
- Bio sp3Document9 pagesBio sp3imrupnarayanNo ratings yet
- CBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument14 pagesCBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsMantri GNo ratings yet
- Biology - Part 1Document11 pagesBiology - Part 1hollymarieNo ratings yet
- Science Readings 2Document25 pagesScience Readings 2AericaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Exclude: 19,20,25,55,56Document31 pagesBiology: Exclude: 19,20,25,55,56Venessa PerpetuaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFDocument9 pages11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFRubhan kumarNo ratings yet
- Wa0007.Document70 pagesWa0007.onalennasethibaNo ratings yet
- Biology ExamDocument12 pagesBiology ExamRaulemarNo ratings yet
- Solution: WWW - Gradeup.coDocument46 pagesSolution: WWW - Gradeup.coFarewell Mech 17-21No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 12.36.52Document15 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 12.36.52ceec40479No ratings yet
- Paper 1 Taller 1Document12 pagesPaper 1 Taller 1Fco_Sandoval12No ratings yet
- 9 Science Cell The Basic Unit of Life Test 02 Answer m76bDocument2 pages9 Science Cell The Basic Unit of Life Test 02 Answer m76bNAVEEN DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument8 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSamar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell StandardsDocument5 pagesCell Standardsapi-300752528No ratings yet
- 2cytology 70 27Document4 pages2cytology 70 27rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes.Document263 pagesBiology Notes.Kelvin PhillipNo ratings yet
- Biology SpecificationDocument24 pagesBiology SpecificationJosh HallNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson NotesDocument8 pagesCell Lesson NotesNikshita KNo ratings yet
- Udaan 40 +1 Bio 13.08.2023Document6 pagesUdaan 40 +1 Bio 13.08.2023mohdhashim8789No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Laws: BiologyDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts and Laws: BiologyYasmien AldaveNo ratings yet
- Cyano-Bacteria ClassXIDocument22 pagesCyano-Bacteria ClassXISachin PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Notes Booklet SDA BIOLOGYDocument146 pagesNotes Booklet SDA BIOLOGYZeke Karl LondonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesDocument21 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesjanaNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument6 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- NEET - Biology - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesNEET - Biology - Cell Structure and Functionknlsinha67% (3)
- CHP 1,2Document4 pagesCHP 1,2MD MotinNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of Lifemunnithakur5285No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Laws: Biology PointersDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts and Laws: Biology PointersH Maranda100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSadik FsNo ratings yet
- Form 5 BiologyDocument13 pagesForm 5 BiologyLIU CHIEW NINGNo ratings yet
- Biology: Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesBiology: Organic CompoundsMockinjayNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 9 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesBiology Notes Class 9 The Fundamental Unit of LifeSai Uday Shankar BommakantiNo ratings yet
- Gi Embryo ComparativeDocument13 pagesGi Embryo ComparativemikeNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 07: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument11 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 07: Back of Chapter QuestionsTarandeep PawarNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Document7 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Ways by Which Paper Can Be SavedDocument37 pagesWays by Which Paper Can Be Savedsarthakrapartiwar3No ratings yet
- 482020104354AM-Class 9 Biology NotesDocument7 pages482020104354AM-Class 9 Biology Noteskmdmohideen2297No ratings yet
- Life Processes - Nutrition QB - 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesLife Processes - Nutrition QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Full NotesDocument259 pagesBiology Full NotesthaseiphologoNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument9 pagesBiological ClassificationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom EubacteriaDocument47 pagesKingdom EubacteriafarhanxxNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument13 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure & FunctionJ15No ratings yet
- Semep 2022 - Sample Test Questions BiologyDocument4 pagesSemep 2022 - Sample Test Questions BiologyJuliana PujanesNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument14 pagesCell: The Fundamental Unit of LifeSingh GurleenNo ratings yet
- Final Set A SolutionDocument14 pagesFinal Set A SolutionNirajan YadavNo ratings yet
- CH 6 BioDocument5 pagesCH 6 BioedwarddameNo ratings yet
- 9 Bio 1Document8 pages9 Bio 1Amisha SenapatiNo ratings yet
- NYA Practice Questions BiodiversityDocument7 pagesNYA Practice Questions Biodiversitymartin.kv4No ratings yet
- Biology CHP.17 Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesBiology CHP.17 Introduction To BiotechnologySanjay BandkarNo ratings yet
- Bio sp1Document10 pagesBio sp1deepmalabehera11No ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Name The Following Countries From Their Outlines BelowDocument2 pagesName The Following Countries From Their Outlines BelowSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Solved 05 New Sol JVQ PDFDocument16 pages11 Physics Solved 05 New Sol JVQ PDFSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesCbse Sample Paper - 12 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper - 13 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesCbse Sample Paper - 13 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsSrinivas VogguNo ratings yet
- Ciam T10Document3 pagesCiam T10Nino SilvaNo ratings yet
- PVC Sheet CatalogueDocument20 pagesPVC Sheet Cataloguerachel zulfiyatinNo ratings yet
- 1 StatDocument30 pages1 StatbutardoandreanicoleNo ratings yet
- Effects of Abm Subjects To The Content Knowledge in Abm StudentsDocument10 pagesEffects of Abm Subjects To The Content Knowledge in Abm StudentsJENNELLE LORILLANo ratings yet
- Adhesive Systems Important Aspects Related To TheiDocument8 pagesAdhesive Systems Important Aspects Related To TheiHachko GiragosyanNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity Analysis of Entrance Design Parameters of A Backward-Inclined Centrifugal Fan Using DOE Method and CFD CalculationsDocument8 pagesSensitivity Analysis of Entrance Design Parameters of A Backward-Inclined Centrifugal Fan Using DOE Method and CFD CalculationsHüseyin Atakan BaytaşNo ratings yet
- English FAL P2 Feb-March 2015 MemoDocument24 pagesEnglish FAL P2 Feb-March 2015 MemoRoxanneNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming: Labeling The Text OCC101Document8 pagesComputer Programming: Labeling The Text OCC101Marygin Esplana SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan For Senior HighDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For Senior HighSora HazelbitzNo ratings yet
- Sheet SamplingDocument3 pagesSheet SamplingAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Activity PR ItoDocument4 pagesActivity PR ItoSamantha Nicolle QuierraNo ratings yet
- Marien Van Westen Desmid Research in DrentheDocument24 pagesMarien Van Westen Desmid Research in DrentheMarien van WestenNo ratings yet
- Full Download Introduction To Measure Theoretic Probability 2nd Edition Roussas Solutions ManualDocument6 pagesFull Download Introduction To Measure Theoretic Probability 2nd Edition Roussas Solutions Manualirisybarrous100% (38)
- AMO Absolute Encoders Rotary AMOSINDocument36 pagesAMO Absolute Encoders Rotary AMOSINsanthoshkumar.sNo ratings yet
- ENG250 ChineseCreationMythsDocument6 pagesENG250 ChineseCreationMythsRishel Mae Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetBermonica Alvior SatuitoNo ratings yet
- Soil Spectroscopy: Training MaterialDocument28 pagesSoil Spectroscopy: Training MaterialAgustín DeviaNo ratings yet
- 5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsDocument5 pages5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsSendhil RevuluriNo ratings yet
- 2024 GeES 1011 Group AssignmentDocument1 page2024 GeES 1011 Group AssignmentLemma Deme ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Writing Style APA FormatDocument2 pagesWriting Style APA FormatsenyorakathNo ratings yet
- SeismoStruct User Manual PDFDocument325 pagesSeismoStruct User Manual PDFStr Engr Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Jensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewDocument11 pagesJensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewKarma TenzinNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations: Insoluble ChloridesDocument1 pageQualitative Analysis of Cations: Insoluble Chlorideskemhar jaminulNo ratings yet
- Individual Proposal Format-CSRI-2021Document12 pagesIndividual Proposal Format-CSRI-2021Dr. Manoj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Value Educatvdffion Mcqs Part 1Document20 pagesValue Educatvdffion Mcqs Part 1virupakshaNo ratings yet
- 7ICEGE Liquefaction Causesandeffects FsalgadoDocument9 pages7ICEGE Liquefaction Causesandeffects FsalgadoAbdifatah mohamed yusufNo ratings yet
- Sick - WT34 - R220Document7 pagesSick - WT34 - R220M MNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Writing Describing A PlaceDocument1 pageUnit 7 Writing Describing A PlaceXzit YassinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document28 pagesChapter 9api-2704505540% (1)