Professional Documents
Culture Documents
19 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2
19 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2
Uploaded by
PranayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
19 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2
19 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2
Uploaded by
PranayCopyright:
Available Formats
PROF.
RAKESH RATHI’S CHEMISTRY TUTORIALS
iv) H for the reverse reaction is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the value corresponding to the
o
forward reaction.
v) If the coefficient indicating the number of moles of all the substances in the thermochemical equation are
multiplied or divided by a numerical factor, the value of Ho must also be multiplied or divided by the same
factor
Types of heat of reaction
Standard enthalpy of formation (standard heat of formation) (fHo):
The standard enthalpy of formation of a compound is defined as the enthalpy change that accompanies a reaction
in which one mole of a substance in its standard state is formed from its elements also in their standard states.
e.g. H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l), fHo = -286 kJ
Enthalpies of elements in their standard states is assumed to be zero
Thus, heat of formation of compounds or substance is equal to their enthalpies
Enthalpies of formation of different compounds help to predict their relative stabilities:
i) Only those compounds are more stable than their elements whose fHo values are negative
ii) Greater the magnitude of the negative fHo value, i.e., more is the energy released, more stable is the
compound.
Standard enthalpy of combustion (∆cHo)
The standard enthalpy of combustion of a substance is the standard enthalpy change accompanying a reaction in
which one mole of the substance in the standard state reacts completely with oxygen or is completely burnt.
5
e.g. C2H2(g) + O2(g) ⎯→ 2CO2(g) + H2O(l), ∆cHo = −1300 kJ
2
Heat of combustion is always negative
Different fuels and foods produce different amount of heat on combustion. These are usually expressed in terms
of their calorific values.
The calorific value of a fuel or food is the amount of heat in calories or joules produced from the complete
combustion of one gram of the fuel or the food
Complete combustion i.e. carbon to CO2, Hydrogen to H2O, nitrogen to elemental nitrogen, sulphur to SO2 and
phosphorous to P2O5
Standard enthalpy of Neutralization (∆NHo)
The enthalpy of neutralization is defined as the heat change (usually the heat evolved) when one gram equivalent
of the acid is neutralized by a base, the reaction being carried out in dilute aqueous solution.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O, ∆NHo = -57.32 kJ mol-1
19
You might also like
- Enthalpy Changes: 2 1 2 C D 1 A BDocument21 pagesEnthalpy Changes: 2 1 2 C D 1 A BJue MayaNo ratings yet
- 16 7 PDF 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledDocument1 page16 7 PDF 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledPranayNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Class Notes-290 PDFDocument19 pagesThermochemistry Class Notes-290 PDFPallavi KhareNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument9 pagesThermochemistryZuhura RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - ThermochemistryDocument78 pagesSheet - 01 - ThermochemistrySushant VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsDocument12 pagesChapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsMohamed AkkashNo ratings yet
- A Thermochemistry1Document20 pagesA Thermochemistry1manasvii2006No ratings yet
- Chemical Thermo - CHAPTER 3Document86 pagesChemical Thermo - CHAPTER 3nickel2616No ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesSMPLFDDocument55 pagesEnthalpy ChangesSMPLFDtopherchandraNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy 093302Document22 pagesEnthalpy 093302Mikhoy RiveralNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument8 pagesFinal ExamermiasNo ratings yet
- 5.thermochemical EquationsDocument21 pages5.thermochemical EquationsKristine Joy BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Thermochemistry - Heat and Chemical Changes Part 1 - Notes: Enthalpy and Bond EnergiesDocument11 pagesChapter 11: Thermochemistry - Heat and Chemical Changes Part 1 - Notes: Enthalpy and Bond EnergiesSarthakNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics From Greek Thermo Dy'namis (Heat and Power) : DefinitionsDocument29 pagesThermodynamics From Greek Thermo Dy'namis (Heat and Power) : DefinitionsbalaaueNo ratings yet
- Energetics by Abhishek JaguessarDocument10 pagesEnergetics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21No ratings yet
- PhaseIII Chem L2 EnthalpyDocument27 pagesPhaseIII Chem L2 EnthalpyPrisha JainNo ratings yet
- Enthalpies of Reaction: Extensive PropertyDocument16 pagesEnthalpies of Reaction: Extensive PropertyKevinNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Physical ChemistryDocument21 pagesThermochemistry: Physical ChemistrySATYAM GAMINGNo ratings yet
- ISL EntalphyDocument9 pagesISL EntalphyJohnson EaNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy ChangesDoc_Croc100% (1)
- ThermochemistryDocument44 pagesThermochemistryAmi NatNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry-Jeemain GuruDocument20 pagesThermochemistry-Jeemain Gurushalini singhNo ratings yet
- 3 1 EnthalpyDocument30 pages3 1 EnthalpymahmoudNo ratings yet
- CPC Unit IvDocument50 pagesCPC Unit IvJAVAGAR M 20CHR023No ratings yet
- ChemDocument29 pagesChemPearl LingbawanNo ratings yet
- Hess's LawDocument31 pagesHess's Lawf4tim4islamNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy AsDocument9 pagesEnthalpy AsA LEVEL TOPNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggris Teknik - TerbaruDocument16 pagesTugas B.inggris Teknik - TerbaruMukhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Enthalpy (H)Document4 pagesThermochemistry: Enthalpy (H)Dedy SusantoNo ratings yet
- 7 Thermochemistry Short Question and Answers PDFDocument8 pages7 Thermochemistry Short Question and Answers PDFMARITIM GEOFFREY KIPLANGAT100% (2)
- Physics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesPhysics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsShubham JainNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument10 pagesEnergeticsEstrella RubioNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Notes (New)Document12 pagesTopic 4 Notes (New)amenaNo ratings yet
- W8 Energy Balance On Reactive ProcessesDocument52 pagesW8 Energy Balance On Reactive ProcessesZafirahAhmadFauzi0% (1)
- Heat Energy Is Absorbed And: Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed But Can Be Converted From One Form To AnotherDocument12 pagesHeat Energy Is Absorbed And: Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed But Can Be Converted From One Form To AnotherAeyyjayyNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Concept of Enthalpy PDFDocument32 pages9.1 Concept of Enthalpy PDFHaspreet GillNo ratings yet
- 04combustion TechnologyDocument70 pages04combustion TechnologySheensky V. SalasaNo ratings yet
- BS MME 2024 Lec#5Document8 pagesBS MME 2024 Lec#5maqsood3982No ratings yet
- Enthalpies of FormationDocument14 pagesEnthalpies of FormationAndrea BaduaNo ratings yet
- Theme 2 Lecture 6Document17 pagesTheme 2 Lecture 6ntokozocecilia81No ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument70 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic Reactionactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Panas Reaksi 3aDocument62 pagesPanas Reaksi 3aDahniarIkaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 - EnthalpyDocument1 pageGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 - EnthalpyparkleebusanNo ratings yet
- Chem 211-212 Hess's LawDocument17 pagesChem 211-212 Hess's LawRiff ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document52 pagesChapter 1MD NAYM MIANo ratings yet
- Energy Balance On Reactive ProcessesDocument21 pagesEnergy Balance On Reactive ProcessesSantosErnestoMamaniApazaNo ratings yet
- IB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topic 5Document4 pagesIB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topic 5AndrewNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT1Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT1NkemziNo ratings yet
- Hesss LawDocument15 pagesHesss LawAriAnggoroNo ratings yet
- Hesss LawDocument15 pagesHesss LawInês AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardDocument5 pages9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardmotivonovaNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument33 pagesThermo ChemistryMashnoor HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Enthalpy ChangesDocument18 pagesChapter 6-Enthalpy ChangesClarize Soo Hoo0% (1)
- KjlkjoijoijwefDocument31 pagesKjlkjoijoijwefAlbus SeverusNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument16 pagesHess LawAriAnggoroNo ratings yet
- Energetics and ThermochemistryDocument60 pagesEnergetics and ThermochemistryIsadora ThibauNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy (H)Document8 pagesEnthalpy (H)Prakhar GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Lecture Note On Thermo Chemical KineticsDocument24 pagesCHM 101 Lecture Note On Thermo Chemical Kineticsekanadefestus007100% (1)
- Lesson 4 ThermochemistryDocument8 pagesLesson 4 Thermochemistryaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Trends C. Diagonal Triangle Type 1: PatternDocument1 pageTrends C. Diagonal Triangle Type 1: PatternPranayNo ratings yet
- 37 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page37 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- Patterns: Classic Patterns vs. Modern Elliott Wave PatternsDocument1 pagePatterns: Classic Patterns vs. Modern Elliott Wave PatternsPranayNo ratings yet
- 37 - 7 PDF - 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledDocument1 page37 - 7 PDF - 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledPranayNo ratings yet
- 1 - 7 PDF - 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledDocument1 page1 - 7 PDF - 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledPranayNo ratings yet
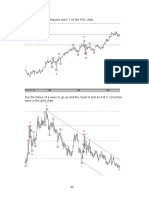
- See The Successful Impulse Wave 1 On The AOL ChartDocument1 pageSee The Successful Impulse Wave 1 On The AOL ChartPranayNo ratings yet
- 49 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page49 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- 31 - 7 PDF - 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledDocument1 page31 - 7 PDF - 8536693 Elliott Wave UnveiledPranayNo ratings yet
- 17: History of World War I: by Albert E. Mckinley, PH.DDocument1 page17: History of World War I: by Albert E. Mckinley, PH.DPranayNo ratings yet
- 34 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page34 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- 31 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page31 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- 40 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David Butler PDFDocument1 page40 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David Butler PDFPranayNo ratings yet
- 13 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page13 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 19 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page19 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- Phrase-Reading: Reading, Let Me Give You The Short Version of This TechniqueDocument1 pagePhrase-Reading: Reading, Let Me Give You The Short Version of This TechniquePranayNo ratings yet
- 22 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page22 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 25 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page25 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- 7 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David Butler PDFDocument1 page7 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David Butler PDFPranayNo ratings yet
- 1 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page1 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranay67% (3)
- 13 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page13 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- 16 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerDocument1 page16 - 7 PDF - 432352921 100 One Minute Speed Reading Drills by David ButlerPranayNo ratings yet
- 19 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page19 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 28 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page28 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 25 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page25 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- Preface To The Third Edition List of Abbreviations: Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument1 pagePreface To The Third Edition List of Abbreviations: Chapter 1. IntroductionPranayNo ratings yet
- 49 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page49 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 31 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page31 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 43 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page43 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet
- 16 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersDocument1 page16 - 7-PDF - Wiley CandleStick and Pivot Point Trading TriggersPranayNo ratings yet