Professional Documents
Culture Documents
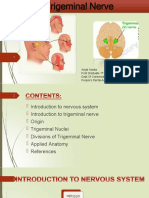
Pons: Abducens Nucleus Passes Through The Superior Orbital Fissure
Pons: Abducens Nucleus Passes Through The Superior Orbital Fissure
Uploaded by
Renz GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- KeNotes 2017 PDFDocument106 pagesKeNotes 2017 PDFDENTAL REVIEWER ONLY100% (3)
- Trigeminal Nerve Seminar FINALDocument54 pagesTrigeminal Nerve Seminar FINALAnji Satsangi100% (1)
- Perception and Coordination Module ADocument3 pagesPerception and Coordination Module ARosmary100% (1)
- Color PsychologyDocument8 pagesColor PsychologymuhamadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Sensory TestingDocument27 pagesQuantitative Sensory TestinghusynNo ratings yet
- Nervi KranialisDocument4 pagesNervi KranialisNarendra Ardea PradanaNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 AtrigeminalDocument2 pagesLec 9 AtrigeminalOodettaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Summary PDFDocument9 pagesCranial Nerves Summary PDFMudassar SattarNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemTanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Wand - Atlas Nerve CompressedDocument23 pagesThe Wand - Atlas Nerve CompressedAmina AganovićNo ratings yet
- CRANIAL NERVES and SPECIAL SENSESDocument8 pagesCRANIAL NERVES and SPECIAL SENSESanyaNo ratings yet
- Body Nervios CranealesDocument15 pagesBody Nervios CranealesEstrellaNo ratings yet
- Sensory InnervationDocument1 pageSensory InnervationProject NursingNo ratings yet
- Bio Psy Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesBio Psy Finals ReviewerZian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- 01 Head and Neck JMDocument16 pages01 Head and Neck JMJowi SalNo ratings yet
- 1cranial NervesDocument62 pages1cranial Nervesmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Nervus Cranialis Dan Basis Cranii: Praktikum Anatomi IIDocument42 pagesNervus Cranialis Dan Basis Cranii: Praktikum Anatomi IIRahayu OktalianiNo ratings yet
- I Olfactory Nerve Anterior Olfactory Nucleus Transmits The Sense of SmellDocument4 pagesI Olfactory Nerve Anterior Olfactory Nucleus Transmits The Sense of SmellalvinNo ratings yet
- Reporters: Marawh, Qasem Bin Jahlan, Salem Samantha BallesterosDocument56 pagesReporters: Marawh, Qasem Bin Jahlan, Salem Samantha Ballesterosjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Write The Name of The Cranial Nerve of Your Answer On The Blank Provided Before The NumberDocument2 pagesWrite The Name of The Cranial Nerve of Your Answer On The Blank Provided Before The NumberSHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOSNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- PNS and Special Online To Post For StudentsDocument15 pagesPNS and Special Online To Post For Studentspham vanNo ratings yet
- Describe The Different Types of Ganglia in The Head and NeckDocument2 pagesDescribe The Different Types of Ganglia in The Head and Neckmp658t952dNo ratings yet
- Gross B 2.17. FaceDocument5 pagesGross B 2.17. FaceShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- PNS PDFDocument14 pagesPNS PDFselesmabNo ratings yet
- Table Describing The Vestibulocochlear NerveDocument82 pagesTable Describing The Vestibulocochlear NerveIqtader hoque khan AkibNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 127 150Document23 pagesNervous System 127 150Claw GamerNo ratings yet
- anatomy 8 scalp تعلم بذكاءDocument8 pagesanatomy 8 scalp تعلم بذكاءmahmoud ezzeldeenNo ratings yet
- Adekunle Seminar in Cranial NervDocument34 pagesAdekunle Seminar in Cranial NervBamgbose OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Assessing Neurologic SystemDocument7 pagesAssessing Neurologic Systemjanikkakristal100% (1)
- Anat 1019 NeuroDocument37 pagesAnat 1019 NeurotakakamiseriaNo ratings yet
- LP KMB - Nurul Fadilah - 1811311034Document19 pagesLP KMB - Nurul Fadilah - 1811311034Indah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Cranial Anatomy RevisionDocument20 pagesCranial Anatomy Revisionbannanastew7975No ratings yet
- Cranial NervsDocument14 pagesCranial NervsluckyNo ratings yet
- Neurology of HmaDocument6 pagesNeurology of HmaJOHN HAROLD CABRADILLANo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Cranial NervesDocument1 pageNervous System and Cranial NervesnihalNo ratings yet
- PT Neuro Intro NotesDocument13 pagesPT Neuro Intro NotesSusan K100% (1)
- 3 TrigeminalwordDocument26 pages3 TrigeminalwordrajaniNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument51 pagesFacial NerveSwijalNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemPIOZRNo ratings yet
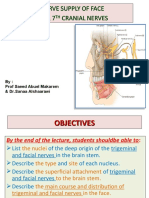
- By: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiDocument24 pagesBy: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiRakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve 2Document87 pagesFacial Nerve 2bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDavid Brillo0% (1)
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocument4 pages10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika50% (4)
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaphy ReviewerPrince Chester CamaliganNo ratings yet
- Skull Anterior View: The Frontal Bone (Or Forehead Bone) CurvesDocument22 pagesSkull Anterior View: The Frontal Bone (Or Forehead Bone) CurvesFatima JamalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Sensory SystemDocument3 pagesLesson 6 Sensory SystemElijah Melo FloresNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ReviewerDocument10 pagesHealth Assessment ReviewerZLKASMdlasmNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Classs 10th IcseDocument8 pagesNervous System Classs 10th IcsehrsanjeevanihireNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve, Face, and Scalp-3Document46 pagesThe Facial Nerve, Face, and Scalp-3renzvalorant28No ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Notes)Document3 pagesThe Nervous System (Notes)Trisha Laiden100% (1)
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesFunctions of The Nervous SystemnvhnygNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument4 pagesFacial NerveAppas SahaNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve, Face, and ScalpDocument47 pagesThe Facial Nerve, Face, and Scalprenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument33 pagesFacial NerveKesheni LemiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For RLE 101Document9 pagesReviewer For RLE 101ZLKASMdlasmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The Nervous Systemlengers poworNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Reviewer: Special Senses VisionDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Reviewer: Special Senses VisionAzodNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Contributes To The Lumpy and Thick Outer Layer of The EggDocument6 pagesContributes To The Lumpy and Thick Outer Layer of The EggRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaDocument4 pagesDioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phylum MolluscaDocument10 pagesPhylum MolluscaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and PhylogenyDocument7 pagesTaxonomy and PhylogenyRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument2 pagesPoriferaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Managing Learning EnviromentsDocument8 pagesChapter 13 Managing Learning EnviromentsRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Ego in Post-Freudinan Theory: - Three Interrelated Aspects of EgoDocument10 pagesThe Ego in Post-Freudinan Theory: - Three Interrelated Aspects of EgoRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Jangi JangerDocument2 pagesJangi JangerRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Piaget and NeoPiagetianDocument5 pagesPiaget and NeoPiagetianRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Post Freudian - EriksonDocument8 pagesPost Freudian - EriksonRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Retardation: Chapter 4: Learner Differences and Learning NeedsDocument3 pagesRetardation: Chapter 4: Learner Differences and Learning NeedsRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cognitivism and Gestalt ReviewerDocument4 pagesCognitivism and Gestalt ReviewerRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Midbrain: 1. TectumDocument7 pagesMidbrain: 1. TectumRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Congruent or Authentic, and Who Unconditional Positive RegardDocument5 pagesCongruent or Authentic, and Who Unconditional Positive RegardRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Brainstem 2Document2 pagesBrainstem 2Renz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Thoughts On Ocular Dominance-Is It Actually A Preference?: Daniel M. Laby, and David G. KirschenDocument5 pagesThoughts On Ocular Dominance-Is It Actually A Preference?: Daniel M. Laby, and David G. KirschenMaria FernandaNo ratings yet
- Smart Phone For Shade Selection in Fixed ProsthodonticsDocument2 pagesSmart Phone For Shade Selection in Fixed ProsthodonticsRajsandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Original Article: The Effect of Experimentally Induced Anisometropia On Binocularity and Bifoveal FixationDocument7 pagesOriginal Article: The Effect of Experimentally Induced Anisometropia On Binocularity and Bifoveal FixationNurul Falah KalokoNo ratings yet
- Sensory Evaluation in FoodDocument32 pagesSensory Evaluation in FoodAnonymous vVsidh3nNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Tatalaksana Pembedahan Pada Pasien Dengan Eksotropia Sensoris - Novaqua YandiDocument13 pagesLaporan Kasus Tatalaksana Pembedahan Pada Pasien Dengan Eksotropia Sensoris - Novaqua YandiMeliNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Gradual Loss of VisionDocument19 pages7.1 Gradual Loss of VisionparugandooNo ratings yet
- VSS2011 ProgramDocument95 pagesVSS2011 ProgramizzuddinhairolNo ratings yet
- Origins of KnowledgeDocument1 pageOrigins of Knowledgemosesdecierdo000No ratings yet
- Tinnitus Assessment The Key To Successful Tinnitus Patient ManagementDocument8 pagesTinnitus Assessment The Key To Successful Tinnitus Patient Managementanitaabreu123No ratings yet
- Color Vision Deficiency in Medical ProfessionDocument7 pagesColor Vision Deficiency in Medical ProfessionpathoTMNo ratings yet
- PSC 2014 June 15Document32 pagesPSC 2014 June 15Anoop AjaighoshNo ratings yet
- LR Vor VSRDocument53 pagesLR Vor VSRAlfira UlfaNo ratings yet
- Neuro OphthalmologyDocument23 pagesNeuro Ophthalmologysk100% (1)
- Human EarDocument38 pagesHuman Earshervlad75% (4)
- Physiological Psychology Lecture 3 MidtermDocument2 pagesPhysiological Psychology Lecture 3 MidtermAngelo SumaoyNo ratings yet
- Examination of Sensory SystemDocument27 pagesExamination of Sensory SystemÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Transducer MindrayDocument19 pagesTransducer MindrayNathaly CastilloNo ratings yet
- KeralaJOphthalmol28288-7254972 200909 PDFDocument8 pagesKeralaJOphthalmol28288-7254972 200909 PDFLukman HidayatNo ratings yet
- Graphic Design For Blind Users - An Industrial Case StudyDocument10 pagesGraphic Design For Blind Users - An Industrial Case StudyRonillo PormonNo ratings yet
- AudiogramDocument38 pagesAudiogramaarya12No ratings yet
- Cirrus 6000 - PosterDocument1 pageCirrus 6000 - PosterDim BoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12sprinkle50100% (1)
- Tuning Fork Tests: Name: Roll No: Assignment: Submitted ToDocument3 pagesTuning Fork Tests: Name: Roll No: Assignment: Submitted ToFizza AliNo ratings yet
- Otosclerosis Slides 061018Document96 pagesOtosclerosis Slides 061018Paraguay De La Cruz JoelNo ratings yet
- Aphakia SlideDocument44 pagesAphakia SlidepiterwiselyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Importance of Responses To Stimuli in AnimalsDocument5 pages1.4 Importance of Responses To Stimuli in AnimalsNaveen AlexanderNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Perception and PerspectiveDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Perception and Perspectivebday23100% (1)
- Non Organic Hearing Loss by DrtbaluDocument3 pagesNon Organic Hearing Loss by DrtbaluAnish RajNo ratings yet
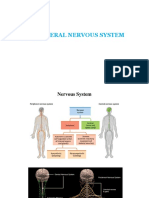
Pons: Abducens Nucleus Passes Through The Superior Orbital Fissure
Pons: Abducens Nucleus Passes Through The Superior Orbital Fissure
Uploaded by
Renz GarciaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pons: Abducens Nucleus Passes Through The Superior Orbital Fissure
Pons: Abducens Nucleus Passes Through The Superior Orbital Fissure
Uploaded by
Renz GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
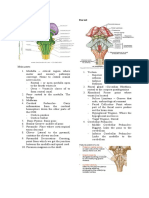
CN# Names Classification
1. Olfactory Does not originate from the brainstem, for sense Some
Smell of smell
(smallest/ Origin: Limbic System, Amygdala and Frontal
shortest Lobe
CN)
2. Optic Vision Say
Origin: Occipital Lobe
3. Oculomotor originates in the midbrain at the level of the Marry
superior colliculus, supplies all EOM except
lateral rectus and superior oblique
Pupil constriction Elevation of Upper lid
(superior to interior)
Pupil- Nonexistent anatomical part
Extra Occular Muscles (EOM) : (SISIML)
Superior Rectus
Inferior Rectus
Superior Oblique Rectus
Inferior Oblique Rectus
Medial Rectus - Converge
Lateral Rectus – Diverge
4. Trochlear Superior Oblique muscle Mone
originates in the midbrain at the level of the y
inferior colliculus, exit dorsally, supplies superior
oblique muscles
5. Trigeminal Controls muscles of mastication (to chew But
(Largest CN) without pain); Sensations for the entire face and
cornea
Trigeminal Neuroglia (MOM)
Opthalmic – Sensory
Maxillary
Mandibular - motor root of trigeminal from
pons
6. Abducens Superior Lateral Rectus Muscles My
Origin : pons: abducens nucleus
passes through the superior orbital
fissure
Originates from the dorsal lower portion of the
pons and supplies the lateral rectus muscle.
7. Facial Predominantly a motor nerve, although it does Broth
carry parasympathetic fibers to the lacrimal and er
salivary glands (the greater superficial petrosal
nerve and chorda tympani) as well as sensation
from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue (the
chorda tympani).
Controls muscles for facial expression Anterior
2/3 of the tongue
Lacrimal – Tears
Salivary Glands
Parotid- lie just under the skin, one in
front of each ear
Sublingual Glands- are the smallest of
the salivary glands. They lie in the floor
of the mouth underneath the tongue
Submandibular- The name of this
salivary gland is a bit confusing
because the gland does not, in fact, lie
under the mandible, but instead in a
small depression on the medial surface
of that bone. This depression is called
the submandibular fossa.
The motor nucleus for the facial nerve originates
in the pons, and supplies all the muscles of the
face except for those involved in mastication.
Corneal Abrasion- Corneal abrasions result
from a disruption or loss of cells in the top
layer of the cornea, called the corneal
epithelium. Due to dryness of eyes
8. Acoustic Balance and hearing Says
conveys information from the cochlea (the
auditory or cochlear nerve as well as the
semicircular canals and otolith organs
9. Glossopharyngeal Controls muscles of throat Posterior 1/3 of the Bad
tongue
Contains motor, sensory and parasympathetic
fibers.
Vocal Chords Control
Gag reflex
10. Vagus Controls muscles of throat PNS stimulation of Busin
thoracic & abdominal organs ess
Provides a motor input to the soft palate,
pharynx and larynx, which originates in the
dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and nucleus
ambiguus. It also has a minor sensory role,
conveying taste from the epiglottis and
sensation from the pinna, but has a significant
parasympathetic role
11. Spinal Controls sternocleidomastoid and trapezius Marry
Accessories muscles
Purely motor in nature and originates from the
nucleus ambiguus in the medulla and the
accessory nucleus in the upper cervical spinal
cord.
12. Hypoglossal Tongue movement Mone
provides the motor innervation of the tongue. Its y
fibers originate from the hypoglossal nucleus in
the posterior part of the medulla
You might also like
- KeNotes 2017 PDFDocument106 pagesKeNotes 2017 PDFDENTAL REVIEWER ONLY100% (3)
- Trigeminal Nerve Seminar FINALDocument54 pagesTrigeminal Nerve Seminar FINALAnji Satsangi100% (1)
- Perception and Coordination Module ADocument3 pagesPerception and Coordination Module ARosmary100% (1)
- Color PsychologyDocument8 pagesColor PsychologymuhamadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Sensory TestingDocument27 pagesQuantitative Sensory TestinghusynNo ratings yet
- Nervi KranialisDocument4 pagesNervi KranialisNarendra Ardea PradanaNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 AtrigeminalDocument2 pagesLec 9 AtrigeminalOodettaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Summary PDFDocument9 pagesCranial Nerves Summary PDFMudassar SattarNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemTanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Wand - Atlas Nerve CompressedDocument23 pagesThe Wand - Atlas Nerve CompressedAmina AganovićNo ratings yet
- CRANIAL NERVES and SPECIAL SENSESDocument8 pagesCRANIAL NERVES and SPECIAL SENSESanyaNo ratings yet
- Body Nervios CranealesDocument15 pagesBody Nervios CranealesEstrellaNo ratings yet
- Sensory InnervationDocument1 pageSensory InnervationProject NursingNo ratings yet
- Bio Psy Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesBio Psy Finals ReviewerZian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- 01 Head and Neck JMDocument16 pages01 Head and Neck JMJowi SalNo ratings yet
- 1cranial NervesDocument62 pages1cranial Nervesmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Nervus Cranialis Dan Basis Cranii: Praktikum Anatomi IIDocument42 pagesNervus Cranialis Dan Basis Cranii: Praktikum Anatomi IIRahayu OktalianiNo ratings yet
- I Olfactory Nerve Anterior Olfactory Nucleus Transmits The Sense of SmellDocument4 pagesI Olfactory Nerve Anterior Olfactory Nucleus Transmits The Sense of SmellalvinNo ratings yet
- Reporters: Marawh, Qasem Bin Jahlan, Salem Samantha BallesterosDocument56 pagesReporters: Marawh, Qasem Bin Jahlan, Salem Samantha Ballesterosjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Write The Name of The Cranial Nerve of Your Answer On The Blank Provided Before The NumberDocument2 pagesWrite The Name of The Cranial Nerve of Your Answer On The Blank Provided Before The NumberSHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOSNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- PNS and Special Online To Post For StudentsDocument15 pagesPNS and Special Online To Post For Studentspham vanNo ratings yet
- Describe The Different Types of Ganglia in The Head and NeckDocument2 pagesDescribe The Different Types of Ganglia in The Head and Neckmp658t952dNo ratings yet
- Gross B 2.17. FaceDocument5 pagesGross B 2.17. FaceShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- PNS PDFDocument14 pagesPNS PDFselesmabNo ratings yet
- Table Describing The Vestibulocochlear NerveDocument82 pagesTable Describing The Vestibulocochlear NerveIqtader hoque khan AkibNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 127 150Document23 pagesNervous System 127 150Claw GamerNo ratings yet
- anatomy 8 scalp تعلم بذكاءDocument8 pagesanatomy 8 scalp تعلم بذكاءmahmoud ezzeldeenNo ratings yet
- Adekunle Seminar in Cranial NervDocument34 pagesAdekunle Seminar in Cranial NervBamgbose OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Assessing Neurologic SystemDocument7 pagesAssessing Neurologic Systemjanikkakristal100% (1)
- Anat 1019 NeuroDocument37 pagesAnat 1019 NeurotakakamiseriaNo ratings yet
- LP KMB - Nurul Fadilah - 1811311034Document19 pagesLP KMB - Nurul Fadilah - 1811311034Indah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Cranial Anatomy RevisionDocument20 pagesCranial Anatomy Revisionbannanastew7975No ratings yet
- Cranial NervsDocument14 pagesCranial NervsluckyNo ratings yet
- Neurology of HmaDocument6 pagesNeurology of HmaJOHN HAROLD CABRADILLANo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Cranial NervesDocument1 pageNervous System and Cranial NervesnihalNo ratings yet
- PT Neuro Intro NotesDocument13 pagesPT Neuro Intro NotesSusan K100% (1)
- 3 TrigeminalwordDocument26 pages3 TrigeminalwordrajaniNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument51 pagesFacial NerveSwijalNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemPIOZRNo ratings yet
- By: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiDocument24 pagesBy: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiRakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve 2Document87 pagesFacial Nerve 2bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDavid Brillo0% (1)
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocument4 pages10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika50% (4)
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaphy ReviewerPrince Chester CamaliganNo ratings yet
- Skull Anterior View: The Frontal Bone (Or Forehead Bone) CurvesDocument22 pagesSkull Anterior View: The Frontal Bone (Or Forehead Bone) CurvesFatima JamalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Sensory SystemDocument3 pagesLesson 6 Sensory SystemElijah Melo FloresNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ReviewerDocument10 pagesHealth Assessment ReviewerZLKASMdlasmNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Classs 10th IcseDocument8 pagesNervous System Classs 10th IcsehrsanjeevanihireNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve, Face, and Scalp-3Document46 pagesThe Facial Nerve, Face, and Scalp-3renzvalorant28No ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Notes)Document3 pagesThe Nervous System (Notes)Trisha Laiden100% (1)
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesFunctions of The Nervous SystemnvhnygNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument4 pagesFacial NerveAppas SahaNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve, Face, and ScalpDocument47 pagesThe Facial Nerve, Face, and Scalprenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument33 pagesFacial NerveKesheni LemiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For RLE 101Document9 pagesReviewer For RLE 101ZLKASMdlasmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The Nervous Systemlengers poworNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Reviewer: Special Senses VisionDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Reviewer: Special Senses VisionAzodNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Contributes To The Lumpy and Thick Outer Layer of The EggDocument6 pagesContributes To The Lumpy and Thick Outer Layer of The EggRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaDocument4 pagesDioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phylum MolluscaDocument10 pagesPhylum MolluscaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and PhylogenyDocument7 pagesTaxonomy and PhylogenyRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument2 pagesPoriferaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Managing Learning EnviromentsDocument8 pagesChapter 13 Managing Learning EnviromentsRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Ego in Post-Freudinan Theory: - Three Interrelated Aspects of EgoDocument10 pagesThe Ego in Post-Freudinan Theory: - Three Interrelated Aspects of EgoRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Jangi JangerDocument2 pagesJangi JangerRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Piaget and NeoPiagetianDocument5 pagesPiaget and NeoPiagetianRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Post Freudian - EriksonDocument8 pagesPost Freudian - EriksonRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Retardation: Chapter 4: Learner Differences and Learning NeedsDocument3 pagesRetardation: Chapter 4: Learner Differences and Learning NeedsRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cognitivism and Gestalt ReviewerDocument4 pagesCognitivism and Gestalt ReviewerRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Midbrain: 1. TectumDocument7 pagesMidbrain: 1. TectumRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Congruent or Authentic, and Who Unconditional Positive RegardDocument5 pagesCongruent or Authentic, and Who Unconditional Positive RegardRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Brainstem 2Document2 pagesBrainstem 2Renz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Thoughts On Ocular Dominance-Is It Actually A Preference?: Daniel M. Laby, and David G. KirschenDocument5 pagesThoughts On Ocular Dominance-Is It Actually A Preference?: Daniel M. Laby, and David G. KirschenMaria FernandaNo ratings yet
- Smart Phone For Shade Selection in Fixed ProsthodonticsDocument2 pagesSmart Phone For Shade Selection in Fixed ProsthodonticsRajsandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Original Article: The Effect of Experimentally Induced Anisometropia On Binocularity and Bifoveal FixationDocument7 pagesOriginal Article: The Effect of Experimentally Induced Anisometropia On Binocularity and Bifoveal FixationNurul Falah KalokoNo ratings yet
- Sensory Evaluation in FoodDocument32 pagesSensory Evaluation in FoodAnonymous vVsidh3nNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Tatalaksana Pembedahan Pada Pasien Dengan Eksotropia Sensoris - Novaqua YandiDocument13 pagesLaporan Kasus Tatalaksana Pembedahan Pada Pasien Dengan Eksotropia Sensoris - Novaqua YandiMeliNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Gradual Loss of VisionDocument19 pages7.1 Gradual Loss of VisionparugandooNo ratings yet
- VSS2011 ProgramDocument95 pagesVSS2011 ProgramizzuddinhairolNo ratings yet
- Origins of KnowledgeDocument1 pageOrigins of Knowledgemosesdecierdo000No ratings yet
- Tinnitus Assessment The Key To Successful Tinnitus Patient ManagementDocument8 pagesTinnitus Assessment The Key To Successful Tinnitus Patient Managementanitaabreu123No ratings yet
- Color Vision Deficiency in Medical ProfessionDocument7 pagesColor Vision Deficiency in Medical ProfessionpathoTMNo ratings yet
- PSC 2014 June 15Document32 pagesPSC 2014 June 15Anoop AjaighoshNo ratings yet
- LR Vor VSRDocument53 pagesLR Vor VSRAlfira UlfaNo ratings yet
- Neuro OphthalmologyDocument23 pagesNeuro Ophthalmologysk100% (1)
- Human EarDocument38 pagesHuman Earshervlad75% (4)
- Physiological Psychology Lecture 3 MidtermDocument2 pagesPhysiological Psychology Lecture 3 MidtermAngelo SumaoyNo ratings yet
- Examination of Sensory SystemDocument27 pagesExamination of Sensory SystemÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Transducer MindrayDocument19 pagesTransducer MindrayNathaly CastilloNo ratings yet
- KeralaJOphthalmol28288-7254972 200909 PDFDocument8 pagesKeralaJOphthalmol28288-7254972 200909 PDFLukman HidayatNo ratings yet
- Graphic Design For Blind Users - An Industrial Case StudyDocument10 pagesGraphic Design For Blind Users - An Industrial Case StudyRonillo PormonNo ratings yet
- AudiogramDocument38 pagesAudiogramaarya12No ratings yet
- Cirrus 6000 - PosterDocument1 pageCirrus 6000 - PosterDim BoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12sprinkle50100% (1)
- Tuning Fork Tests: Name: Roll No: Assignment: Submitted ToDocument3 pagesTuning Fork Tests: Name: Roll No: Assignment: Submitted ToFizza AliNo ratings yet
- Otosclerosis Slides 061018Document96 pagesOtosclerosis Slides 061018Paraguay De La Cruz JoelNo ratings yet
- Aphakia SlideDocument44 pagesAphakia SlidepiterwiselyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Importance of Responses To Stimuli in AnimalsDocument5 pages1.4 Importance of Responses To Stimuli in AnimalsNaveen AlexanderNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Perception and PerspectiveDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Perception and Perspectivebday23100% (1)
- Non Organic Hearing Loss by DrtbaluDocument3 pagesNon Organic Hearing Loss by DrtbaluAnish RajNo ratings yet