Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guidelines For The Management of Pyloric Stenosis: Investigations
Guidelines For The Management of Pyloric Stenosis: Investigations
Uploaded by
DrThamma ShahiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Medical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide PDFDocument1 pageMedical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide PDFDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- Read Online 9781905812172 Medical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide To CT S PDFDocument1 pageRead Online 9781905812172 Medical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide To CT S PDFDrThamma Shahi0% (1)
- Pedia Small Notebook EditedDocument17 pagesPedia Small Notebook EditedStarlet Rhonadez Bito-onon Oriel100% (12)
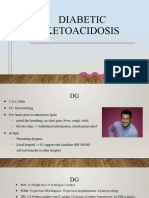
- Acute Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)Document21 pagesAcute Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)Madhu Sudhan Pandeya0% (1)
- NEONATOLOGYDocument8 pagesNEONATOLOGYmymamym100% (1)
- 1 FluidsDocument17 pages1 FluidsMae CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument38 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisAwatef AbushhiwaNo ratings yet
- The Medical Interview: Mastering Skills For Clinical Practice PDF - Marian R. BlockDocument1 pageThe Medical Interview: Mastering Skills For Clinical Practice PDF - Marian R. BlockDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ManagementDocument21 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ManagementRasYa DINo ratings yet
- Kuwait PICU Taskforce DKA V1 5 June 2022Document2 pagesKuwait PICU Taskforce DKA V1 5 June 2022Emad MashaalNo ratings yet
- InfusDocument29 pagesInfusfauzanNo ratings yet
- DKA Guidelines Version 4.0 28 Dec 2016FINALDocument4 pagesDKA Guidelines Version 4.0 28 Dec 2016FINALbenNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Emergencies: 1. Diabetic Ketoacidosis 2. Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State 3. HypoglycemiaDocument24 pagesDiabetic Emergencies: 1. Diabetic Ketoacidosis 2. Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State 3. HypoglycemiachooNo ratings yet
- Age PDFDocument26 pagesAge PDFJohanisa Benito ALawi-RakiinNo ratings yet
- Management of Convulsion in PaediatricsDocument21 pagesManagement of Convulsion in PaediatricsjuwelukgNo ratings yet
- Pedia Tickler 2 1 2Document106 pagesPedia Tickler 2 1 2Ma. Bernadette PinedaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: DiagnosisDocument1 pageDiabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: Diagnosislouglee9174100% (1)
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument35 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisTatik AgilaNo ratings yet
- Item 6f - Acute Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateDocument1 pageItem 6f - Acute Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateStef AnNo ratings yet
- Dka CalculatorDocument1 pageDka CalculatorTalib AdilNo ratings yet
- Revised DKA 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesRevised DKA 2015 PDFDr AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drips 2Document4 pagesDrips 2karen GoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in Pediatric: Dr. Wasnaa Hadi AbdullahDocument30 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in Pediatric: Dr. Wasnaa Hadi AbdullahLily AddamsNo ratings yet
- High CBS in Medical EmergencyDocument37 pagesHigh CBS in Medical EmergencyHansika GunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management of DKADocument4 pagesPrinciples of Management of DKAHassen Kavi IsseNo ratings yet
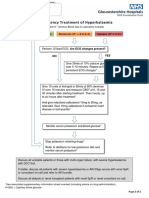
- Guideline For The Management of Adults Patients With DKA or HHSDocument3 pagesGuideline For The Management of Adults Patients With DKA or HHSJonard GiloNo ratings yet
- BIMC Adult DKA Protocol 2012Document5 pagesBIMC Adult DKA Protocol 2012djizhieeNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Hhs Adult PDFDocument4 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Hhs Adult PDFyayaNo ratings yet
- Pedia NotesDocument36 pagesPedia NotesmelNo ratings yet
- Condition Formula IV Fluid Acute Gastroenteritis A. Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) Source: WHO?? 1. in ShockDocument4 pagesCondition Formula IV Fluid Acute Gastroenteritis A. Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) Source: WHO?? 1. in ShockJohnPaulOliverosNo ratings yet
- 3-Management of DF-DHF2018Document36 pages3-Management of DF-DHF2018koengphearom9No ratings yet
- DKA Protocol With Calculation SheetDocument7 pagesDKA Protocol With Calculation SheetAmanda Marie Best OsbourneNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardsDocument9 pagesCourse in The WardsBea ValerioNo ratings yet
- Adult: Diabetic Emergencies: Care Protocol and ChartDocument4 pagesAdult: Diabetic Emergencies: Care Protocol and ChartvladhdNo ratings yet
- DKACalculatorDocument1 pageDKACalculatorRitch BassNo ratings yet
- 11.50 DR Stella George, Diabetic and Metabolic EmergenciesDocument49 pages11.50 DR Stella George, Diabetic and Metabolic Emergenciesamir ahmadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy in Paediatrics - RevisedDocument5 pagesFluid Therapy in Paediatrics - RevisedJehangir AllamNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Acute Management: A State of Absolute Insulin BankruptcyDocument24 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Acute Management: A State of Absolute Insulin BankruptcyGwEn LimNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal Pharmacologyashraf0% (1)
- Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Guideline South WestDocument6 pagesAdult Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Guideline South Westshada aaaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Care for Type1 Diabetes อ.พัฒน์Document10 pagesComprehensive Care for Type1 Diabetes อ.พัฒน์Pichamon SuwannachatNo ratings yet
- Idiot NotesDocument53 pagesIdiot NotesRay PerezNo ratings yet
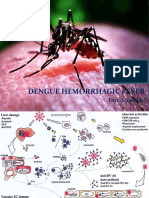
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Fazria NasriatiDocument19 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Fazria NasriatiElsa KarinasariNo ratings yet
- Diabetes EmergenciesDocument7 pagesDiabetes EmergenciesDr.Abdirahman DahirNo ratings yet
- AKI MBCHB VDocument64 pagesAKI MBCHB VSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- Dka CalculatorDocument1 pageDka CalculatordelfiaNo ratings yet
- 4 Fluid Therapy and Electrolyte Therapy in PicuDocument19 pages4 Fluid Therapy and Electrolyte Therapy in Picuyousif.med2234No ratings yet
- Parenteral Fluid Therapy: Know, Calculate and Be ComfortableDocument61 pagesParenteral Fluid Therapy: Know, Calculate and Be ComfortableDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Pedia Idiot Notes 1Document12 pagesPedia Idiot Notes 1David JonesNo ratings yet
- DKA Management-2Document7 pagesDKA Management-2NisaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Order Set DKA AdultDocument2 pagesClinical Order Set DKA AdultBashar Al-HamaidehNo ratings yet
- Kasus:: Dka: Keton 5 Meq/L, Blood Glucose 250, PH 7.3, Ketonemia and Ketonuria, Serum Bicarbonate 18 Meq/L or LessDocument3 pagesKasus:: Dka: Keton 5 Meq/L, Blood Glucose 250, PH 7.3, Ketonemia and Ketonuria, Serum Bicarbonate 18 Meq/L or LessSatya WangsaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis PathwayDocument22 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis PathwaySri Nath100% (1)
- OHSS Case Presentation Discussion - Jindal IVF CHDDocument41 pagesOHSS Case Presentation Discussion - Jindal IVF CHDJindal IVF ChandigarhNo ratings yet
- Fluid BalanceDocument28 pagesFluid BalancePragadesh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument2 pagesHyperkalaemiapaleviNo ratings yet
- Dehydration - PedsCase - v9Document1 pageDehydration - PedsCase - v9Chinenye ModestaNo ratings yet
- DKA AlgorismDocument2 pagesDKA AlgorismYohannes hailuNo ratings yet
- Management of Paediatric Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument21 pagesManagement of Paediatric Diabetic KetoacidosisAsad M AminNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal PharmacologyashrafNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NotesDocument45 pagesPediatric NoteskkkssbbNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm (Page 1-ED) : DKA Diagnosed DKA Not DiagnosedDocument2 pagesPediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm (Page 1-ED) : DKA Diagnosed DKA Not Diagnosedrolland_arrizaNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016Document6 pagesHow To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016DrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- 2020 F2 Stand-Alone Applicant Guidance - UPDATE Dec.2019Document32 pages2020 F2 Stand-Alone Applicant Guidance - UPDATE Dec.2019DrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- 150 Medical Interview Questions PDFDocument11 pages150 Medical Interview Questions PDFDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016Document6 pagesHow To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016DrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- So You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDocument2 pagesSo You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
Guidelines For The Management of Pyloric Stenosis: Investigations
Guidelines For The Management of Pyloric Stenosis: Investigations
Uploaded by
DrThamma ShahiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guidelines For The Management of Pyloric Stenosis: Investigations
Guidelines For The Management of Pyloric Stenosis: Investigations
Uploaded by
DrThamma ShahiCopyright:
Available Formats
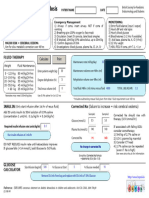
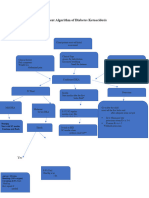
Guidelines for the management of Pyloric Stenosis
Investigations
Test feed
Capillary blood gas (CBG): hyponatraemic, hypokalaemic, hypochloraemic metabolic
alkalosis (may be normal)
Ultrasound abdomen: only needed if clinical diagnosis doubted (diagnostic if muscle
thickness >4mm and muscle length >14mm in term baby)
Management
Nil by mouth
Pass NG tube – free drainage and hourly aspiration
Replace losses ml for ml with 0.9% NaCl + 10mmol KCl
pH > 7.45, HCO3 >26, BE >2 (i.e. metabolic alkalosis)
Yes No
Give 150ml/Kg/day of 0.9% Give 120ml/Kg/day of 0.9% NaCl
NaCl + 5% dextrose + 10mmol + 5% dextrose
KCl Reduce fluids when normal CBG
+/- 10mmol KCl
Repeat CBG every 12 hours Normal CBG:
Daily U&E whilst NBM + IV fluids
HCO3 22 – 26
BE -2 – 2
Cl ≥ 100
Pyloromyotomy only when CBG normal
Post-operative
Remove NG tube at end of operation unless mucosa breached
IVI 0.9% saline + 5% Dextrose at 120ml/kg/day
Start 25% normal feed (milk) 6 hrs post op and increase as tolerated
Reduce IVI fluid as oral intake increases
Minor vomiting expected for one week post op
Ready for discharge once tolerated two full feeds (usually 150ml/kg/day) and no other
concerns
Authors: Dr Fulford-Smith, Miss Bradshaw and Miss Wagener, 2015
You might also like
- Medical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide PDFDocument1 pageMedical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide PDFDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- Read Online 9781905812172 Medical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide To CT S PDFDocument1 pageRead Online 9781905812172 Medical Interviews A Comprehensive Guide To CT S PDFDrThamma Shahi0% (1)
- Pedia Small Notebook EditedDocument17 pagesPedia Small Notebook EditedStarlet Rhonadez Bito-onon Oriel100% (12)
- Acute Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)Document21 pagesAcute Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)Madhu Sudhan Pandeya0% (1)
- NEONATOLOGYDocument8 pagesNEONATOLOGYmymamym100% (1)
- 1 FluidsDocument17 pages1 FluidsMae CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument38 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisAwatef AbushhiwaNo ratings yet
- The Medical Interview: Mastering Skills For Clinical Practice PDF - Marian R. BlockDocument1 pageThe Medical Interview: Mastering Skills For Clinical Practice PDF - Marian R. BlockDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ManagementDocument21 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ManagementRasYa DINo ratings yet
- Kuwait PICU Taskforce DKA V1 5 June 2022Document2 pagesKuwait PICU Taskforce DKA V1 5 June 2022Emad MashaalNo ratings yet
- InfusDocument29 pagesInfusfauzanNo ratings yet
- DKA Guidelines Version 4.0 28 Dec 2016FINALDocument4 pagesDKA Guidelines Version 4.0 28 Dec 2016FINALbenNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Emergencies: 1. Diabetic Ketoacidosis 2. Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State 3. HypoglycemiaDocument24 pagesDiabetic Emergencies: 1. Diabetic Ketoacidosis 2. Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State 3. HypoglycemiachooNo ratings yet
- Age PDFDocument26 pagesAge PDFJohanisa Benito ALawi-RakiinNo ratings yet
- Management of Convulsion in PaediatricsDocument21 pagesManagement of Convulsion in PaediatricsjuwelukgNo ratings yet
- Pedia Tickler 2 1 2Document106 pagesPedia Tickler 2 1 2Ma. Bernadette PinedaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: DiagnosisDocument1 pageDiabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: Diagnosislouglee9174100% (1)
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument35 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisTatik AgilaNo ratings yet
- Item 6f - Acute Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateDocument1 pageItem 6f - Acute Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateStef AnNo ratings yet
- Dka CalculatorDocument1 pageDka CalculatorTalib AdilNo ratings yet
- Revised DKA 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesRevised DKA 2015 PDFDr AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drips 2Document4 pagesDrips 2karen GoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in Pediatric: Dr. Wasnaa Hadi AbdullahDocument30 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in Pediatric: Dr. Wasnaa Hadi AbdullahLily AddamsNo ratings yet
- High CBS in Medical EmergencyDocument37 pagesHigh CBS in Medical EmergencyHansika GunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management of DKADocument4 pagesPrinciples of Management of DKAHassen Kavi IsseNo ratings yet
- Guideline For The Management of Adults Patients With DKA or HHSDocument3 pagesGuideline For The Management of Adults Patients With DKA or HHSJonard GiloNo ratings yet
- BIMC Adult DKA Protocol 2012Document5 pagesBIMC Adult DKA Protocol 2012djizhieeNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Hhs Adult PDFDocument4 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Hhs Adult PDFyayaNo ratings yet
- Pedia NotesDocument36 pagesPedia NotesmelNo ratings yet
- Condition Formula IV Fluid Acute Gastroenteritis A. Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) Source: WHO?? 1. in ShockDocument4 pagesCondition Formula IV Fluid Acute Gastroenteritis A. Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) Source: WHO?? 1. in ShockJohnPaulOliverosNo ratings yet
- 3-Management of DF-DHF2018Document36 pages3-Management of DF-DHF2018koengphearom9No ratings yet
- DKA Protocol With Calculation SheetDocument7 pagesDKA Protocol With Calculation SheetAmanda Marie Best OsbourneNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardsDocument9 pagesCourse in The WardsBea ValerioNo ratings yet
- Adult: Diabetic Emergencies: Care Protocol and ChartDocument4 pagesAdult: Diabetic Emergencies: Care Protocol and ChartvladhdNo ratings yet
- DKACalculatorDocument1 pageDKACalculatorRitch BassNo ratings yet
- 11.50 DR Stella George, Diabetic and Metabolic EmergenciesDocument49 pages11.50 DR Stella George, Diabetic and Metabolic Emergenciesamir ahmadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy in Paediatrics - RevisedDocument5 pagesFluid Therapy in Paediatrics - RevisedJehangir AllamNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Acute Management: A State of Absolute Insulin BankruptcyDocument24 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Acute Management: A State of Absolute Insulin BankruptcyGwEn LimNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal Pharmacologyashraf0% (1)
- Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Guideline South WestDocument6 pagesAdult Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Guideline South Westshada aaaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Care for Type1 Diabetes อ.พัฒน์Document10 pagesComprehensive Care for Type1 Diabetes อ.พัฒน์Pichamon SuwannachatNo ratings yet
- Idiot NotesDocument53 pagesIdiot NotesRay PerezNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Fazria NasriatiDocument19 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Fazria NasriatiElsa KarinasariNo ratings yet
- Diabetes EmergenciesDocument7 pagesDiabetes EmergenciesDr.Abdirahman DahirNo ratings yet
- AKI MBCHB VDocument64 pagesAKI MBCHB VSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- Dka CalculatorDocument1 pageDka CalculatordelfiaNo ratings yet
- 4 Fluid Therapy and Electrolyte Therapy in PicuDocument19 pages4 Fluid Therapy and Electrolyte Therapy in Picuyousif.med2234No ratings yet
- Parenteral Fluid Therapy: Know, Calculate and Be ComfortableDocument61 pagesParenteral Fluid Therapy: Know, Calculate and Be ComfortableDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Pedia Idiot Notes 1Document12 pagesPedia Idiot Notes 1David JonesNo ratings yet
- DKA Management-2Document7 pagesDKA Management-2NisaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Order Set DKA AdultDocument2 pagesClinical Order Set DKA AdultBashar Al-HamaidehNo ratings yet
- Kasus:: Dka: Keton 5 Meq/L, Blood Glucose 250, PH 7.3, Ketonemia and Ketonuria, Serum Bicarbonate 18 Meq/L or LessDocument3 pagesKasus:: Dka: Keton 5 Meq/L, Blood Glucose 250, PH 7.3, Ketonemia and Ketonuria, Serum Bicarbonate 18 Meq/L or LessSatya WangsaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis PathwayDocument22 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis PathwaySri Nath100% (1)
- OHSS Case Presentation Discussion - Jindal IVF CHDDocument41 pagesOHSS Case Presentation Discussion - Jindal IVF CHDJindal IVF ChandigarhNo ratings yet
- Fluid BalanceDocument28 pagesFluid BalancePragadesh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument2 pagesHyperkalaemiapaleviNo ratings yet
- Dehydration - PedsCase - v9Document1 pageDehydration - PedsCase - v9Chinenye ModestaNo ratings yet
- DKA AlgorismDocument2 pagesDKA AlgorismYohannes hailuNo ratings yet
- Management of Paediatric Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument21 pagesManagement of Paediatric Diabetic KetoacidosisAsad M AminNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal PharmacologyashrafNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NotesDocument45 pagesPediatric NoteskkkssbbNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm (Page 1-ED) : DKA Diagnosed DKA Not DiagnosedDocument2 pagesPediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm (Page 1-ED) : DKA Diagnosed DKA Not Diagnosedrolland_arrizaNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016Document6 pagesHow To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016DrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- 2020 F2 Stand-Alone Applicant Guidance - UPDATE Dec.2019Document32 pages2020 F2 Stand-Alone Applicant Guidance - UPDATE Dec.2019DrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- 150 Medical Interview Questions PDFDocument11 pages150 Medical Interview Questions PDFDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016Document6 pagesHow To Prepare For An Interview: Breathe November 2016DrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- So You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDocument2 pagesSo You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet