Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
Uploaded by
رائد عبد العزيز فرحانCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Review Problems For 3rd LE (Mass Transfer Problems)Document2 pagesReview Problems For 3rd LE (Mass Transfer Problems)Julie Anne del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Mass Transfer OperationsDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Mass Transfer OperationsAnonymous Yxmo6eFNo ratings yet
- 13 ME525 Practice Problems For Final Exam Partial Solutions 42313 PDFDocument7 pages13 ME525 Practice Problems For Final Exam Partial Solutions 42313 PDFalibaba011No ratings yet
- Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays TowersDocument6 pagesPacked Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towersرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 11 GasesDocument17 pages11 Gasespuja ritongaNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Experiment Labrotary ManualDocument16 pagesThin Film Experiment Labrotary ManualSishir JanaNo ratings yet
- Chen Inves NewDocument6 pagesChen Inves NewSanu JosephNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Part2Document28 pagesUnit 5-Part2Nobukhosi NdlovuNo ratings yet
- NOx RecyclingDocument5 pagesNOx RecyclingsureshNo ratings yet
- Absorption Operation and Equipment DesignDocument24 pagesAbsorption Operation and Equipment DesignDEEP HIRPARANo ratings yet
- 9 GRL-XG PDFDocument4 pages9 GRL-XG PDFjenianmarinNo ratings yet
- Removal of NO From Coke Oven GasDocument3 pagesRemoval of NO From Coke Oven Gasmuthu kujmarNo ratings yet
- Steam Reforming of Methane in A Membrane Reactor: S.Laegsgaardj Rgensen, P.E.H@Jlund Nielsen, P. LehrmannDocument5 pagesSteam Reforming of Methane in A Membrane Reactor: S.Laegsgaardj Rgensen, P.E.H@Jlund Nielsen, P. LehrmannVytha MarmoetNo ratings yet
- 8 Absorber DesignDocument16 pages8 Absorber DesignilhamriswandaaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Design Analysis of A Liquid Hydrogen VesselDocument9 pagesThermal Design Analysis of A Liquid Hydrogen Vessel이경률No ratings yet
- Chemistry Study SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Study SheetSteph PiperNo ratings yet
- Dai 1995Document6 pagesDai 1995Ukhty Thiyyu SaiianqBundaNo ratings yet
- 4.ideal GasDocument27 pages4.ideal GasSam KumarNo ratings yet
- Removal of Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Sulphur From Tool Steel During Vacuum DegassingDocument7 pagesRemoval of Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Sulphur From Tool Steel During Vacuum DegassingRasul BzNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document2 pagesTutorial 8prajjwal rastogiNo ratings yet
- Torres de AbsorcionDocument5 pagesTorres de AbsorcionSebastian BaqueroNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-13-08 - 11th (PQRS) SpaceDocument22 pagesCHEMISTRY-13-08 - 11th (PQRS) SpaceRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Gas Density CalculationDocument10 pagesGas Density CalculationKhurshid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Final SelectionDocument8 pagesFinal SelectionFahad KhokharNo ratings yet
- Design of Packed Towers For AbsorptionDocument36 pagesDesign of Packed Towers For AbsorptionFaisal RidhoNo ratings yet
- Liquefaction WorkbookDocument10 pagesLiquefaction WorkbookMJ100% (1)
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- Analysis of The Characteristics of The Blast Furnace Peripheral Zone.Document4 pagesAnalysis of The Characteristics of The Blast Furnace Peripheral Zone.Samanway DasNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument15 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasesmuddu00007No ratings yet
- States of Matter Jee Mains 2Document28 pagesStates of Matter Jee Mains 2Hirishik Sarkar 10ANo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument3 pagesAdsorptionHarySetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document1 pageTutorial 5David Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Subjective and Objective Questions With Answers of Chemical Equilibrium For PracticeDocument21 pagesSubjective and Objective Questions With Answers of Chemical Equilibrium For PracticehappyNo ratings yet
- Composition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesComposition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeNgoc Le LeNo ratings yet
- Vapour Breakthrough in Activated CarbonDocument9 pagesVapour Breakthrough in Activated CarbonDomenico BarillariNo ratings yet
- Prediction of NOx Emissions in Recovery Boilers PDFDocument14 pagesPrediction of NOx Emissions in Recovery Boilers PDFNilesh KhadeNo ratings yet
- Teaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Document7 pagesTeaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Solin HawreNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations 1Document2 pagesMass Transfer Operations 1Uday KiranNo ratings yet
- Principles of Extractive Metallurgy - Docx - CopyDocument104 pagesPrinciples of Extractive Metallurgy - Docx - CopyFelix TinasheNo ratings yet
- Vol 47 - 2 0008 PDFDocument37 pagesVol 47 - 2 0008 PDFSahil DaradeNo ratings yet
- Vacuum System Design, CERNDocument15 pagesVacuum System Design, CERNjfejfeNo ratings yet
- 01 1stlaw ExessolsDocument29 pages01 1stlaw Exessolsblanca.pegueraNo ratings yet
- Air Stripping: The Removal of Volatile Contaminants From Water and Contaminated SoilsDocument39 pagesAir Stripping: The Removal of Volatile Contaminants From Water and Contaminated SoilsMohammed Al-DahlanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 121: Topic 5 - The Gaseous StateDocument24 pagesChemistry 121: Topic 5 - The Gaseous StateImranMalikNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture 10: For Dilute Concentrations, Over A Small Height DZ of Column, The Absorption Is Given by (Eq. 12.53)Document10 pagesOnline Lecture 10: For Dilute Concentrations, Over A Small Height DZ of Column, The Absorption Is Given by (Eq. 12.53)shamsul aminNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359431116305142 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1359431116305142 MainDiego MorenoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Unit - 3 Surface ChemistryDocument9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Unit - 3 Surface ChemistryAnish Babu100% (1)
- Adsorptive Purification of Large Waste Gas StreamsDocument5 pagesAdsorptive Purification of Large Waste Gas StreamsAMEY MAJLEKARNo ratings yet
- Assignment IVDocument2 pagesAssignment IVAbhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- Annotated Solution 2019 USNCO National Exam Part I: SolutionsDocument13 pagesAnnotated Solution 2019 USNCO National Exam Part I: SolutionsĐình Thư LêNo ratings yet
- Air Pool Protection From Emissions Of The Power Industry: 1.1.2.1.3. Burners Out оf Service - BOOSDocument1 pageAir Pool Protection From Emissions Of The Power Industry: 1.1.2.1.3. Burners Out оf Service - BOOSJagdeep ArryNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law 5684f195af3e6Document38 pagesIdeal Gas Law 5684f195af3e6Jose GulitiwNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Document20 pagesChemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Alina Syedd32No ratings yet
- C13 TutorialDocument9 pagesC13 TutorialAdam MrsmNo ratings yet
- Oden Thal 2010Document18 pagesOden Thal 2010Prakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Elsevier - Sensitivity of Joule Thomson Cooling To Impure CO2 Injection in Depleted Gas Reservoirs - Ziabakhsh - Ganji - 2013Document18 pagesElsevier - Sensitivity of Joule Thomson Cooling To Impure CO2 Injection in Depleted Gas Reservoirs - Ziabakhsh - Ganji - 2013wordindustriesNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry-02 Solved ProblemsDocument11 pagesSurface Chemistry-02 Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- To My FriendsDocument14 pagesTo My Friendsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- DoubleVision PpsDocument6 pagesDoubleVision Ppsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Double VisionDocument6 pagesDouble Visionرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- B) To Feel Shy and Silly, A Big Cup Make Liquid Flow OutDocument1 pageB) To Feel Shy and Silly, A Big Cup Make Liquid Flow Outرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- (Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age) : Design, Production, and Utilization of MaterialsDocument8 pages(Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age) : Design, Production, and Utilization of Materialsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Pipe Friction Losses: Fundamental Principles For Project WorkDocument3 pagesPipe Friction Losses: Fundamental Principles For Project Workرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Exp3 DensityDocument1 pageExp3 Densityرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Viscosity and Density Measurement Methods For Polymer Melts: R. Kažys, R. RekuvienėDocument6 pagesViscosity and Density Measurement Methods For Polymer Melts: R. Kažys, R. Rekuvienėرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 518d163be4b062a8d1d9f903-.Sam.-1368204347334-4 Factors Affecting Viscosity PDFDocument5 pages518d163be4b062a8d1d9f903-.Sam.-1368204347334-4 Factors Affecting Viscosity PDFرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 08-Mechanical Properties-BU-HandoutsDocument13 pages08-Mechanical Properties-BU-Handoutsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Changes in Matter: Hot Ice and The Carbon Snake: Grade 8 Activity PlanDocument7 pages8.4 Changes in Matter: Hot Ice and The Carbon Snake: Grade 8 Activity Planرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- ChemicalDocument1 pageChemicalرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Interest and Investment CostDocument6 pagesChapter Two Interest and Investment Costرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
Uploaded by
رائد عبد العزيز فرحانOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
Uploaded by
رائد عبد العزيز فرحانCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept.
Equipment Design
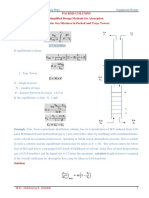
PACKED COLUMNS
Simplified Design Methods for Absorption
of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towers
1. Packed Tower
Z = H OG N OG
If equilibrium is linear
2. Tray Tower
Z :- heigh of tower
N :- number of trays
ℓ :- distance between two trays = 0.5 m
If the equilibrium is liner Y∗ = mX
Example :Gas, from a petroleum distillation column, has its concentration of H2S reduced from 0.03
kmol H2S/kmol of inert hydrocarbon gas to 1 per cent of this value, by scrubbing with a triethanolamine-
water solvent in a countercurrent tower, operating at 300 K and at atmospheric pressure. H2S is soluble
in such a solution and the equilibrium relation may be taken as Y = 2X . The solvent enters the tower
free of H2S and leaves containing 0.013 kmol of H2S/kmol of solvent. If the flow of inert hydrocarbon
gas is 0.015 kmol/m2s and the liquid rate is 1.7 times the minimum , calculate height of tower is required
if the overall coefficient for absorption KOG.a may be taken as 0.04 kmol/sm3 .
Solution
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 1
You might also like
- Review Problems For 3rd LE (Mass Transfer Problems)Document2 pagesReview Problems For 3rd LE (Mass Transfer Problems)Julie Anne del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Mass Transfer OperationsDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Mass Transfer OperationsAnonymous Yxmo6eFNo ratings yet
- 13 ME525 Practice Problems For Final Exam Partial Solutions 42313 PDFDocument7 pages13 ME525 Practice Problems For Final Exam Partial Solutions 42313 PDFalibaba011No ratings yet
- Packed Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays TowersDocument6 pagesPacked Columns Simplified Design Methods For Absorption of Dilute Gas Mixtures in Packed and Trays Towersرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 11 GasesDocument17 pages11 Gasespuja ritongaNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Experiment Labrotary ManualDocument16 pagesThin Film Experiment Labrotary ManualSishir JanaNo ratings yet
- Chen Inves NewDocument6 pagesChen Inves NewSanu JosephNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Part2Document28 pagesUnit 5-Part2Nobukhosi NdlovuNo ratings yet
- NOx RecyclingDocument5 pagesNOx RecyclingsureshNo ratings yet
- Absorption Operation and Equipment DesignDocument24 pagesAbsorption Operation and Equipment DesignDEEP HIRPARANo ratings yet
- 9 GRL-XG PDFDocument4 pages9 GRL-XG PDFjenianmarinNo ratings yet
- Removal of NO From Coke Oven GasDocument3 pagesRemoval of NO From Coke Oven Gasmuthu kujmarNo ratings yet
- Steam Reforming of Methane in A Membrane Reactor: S.Laegsgaardj Rgensen, P.E.H@Jlund Nielsen, P. LehrmannDocument5 pagesSteam Reforming of Methane in A Membrane Reactor: S.Laegsgaardj Rgensen, P.E.H@Jlund Nielsen, P. LehrmannVytha MarmoetNo ratings yet
- 8 Absorber DesignDocument16 pages8 Absorber DesignilhamriswandaaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Design Analysis of A Liquid Hydrogen VesselDocument9 pagesThermal Design Analysis of A Liquid Hydrogen Vessel이경률No ratings yet
- Chemistry Study SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Study SheetSteph PiperNo ratings yet
- Dai 1995Document6 pagesDai 1995Ukhty Thiyyu SaiianqBundaNo ratings yet
- 4.ideal GasDocument27 pages4.ideal GasSam KumarNo ratings yet
- Removal of Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Sulphur From Tool Steel During Vacuum DegassingDocument7 pagesRemoval of Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Sulphur From Tool Steel During Vacuum DegassingRasul BzNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document2 pagesTutorial 8prajjwal rastogiNo ratings yet
- Torres de AbsorcionDocument5 pagesTorres de AbsorcionSebastian BaqueroNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-13-08 - 11th (PQRS) SpaceDocument22 pagesCHEMISTRY-13-08 - 11th (PQRS) SpaceRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Gas Density CalculationDocument10 pagesGas Density CalculationKhurshid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Final SelectionDocument8 pagesFinal SelectionFahad KhokharNo ratings yet
- Design of Packed Towers For AbsorptionDocument36 pagesDesign of Packed Towers For AbsorptionFaisal RidhoNo ratings yet
- Liquefaction WorkbookDocument10 pagesLiquefaction WorkbookMJ100% (1)
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- Analysis of The Characteristics of The Blast Furnace Peripheral Zone.Document4 pagesAnalysis of The Characteristics of The Blast Furnace Peripheral Zone.Samanway DasNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument15 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasesmuddu00007No ratings yet
- States of Matter Jee Mains 2Document28 pagesStates of Matter Jee Mains 2Hirishik Sarkar 10ANo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument3 pagesAdsorptionHarySetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document1 pageTutorial 5David Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Subjective and Objective Questions With Answers of Chemical Equilibrium For PracticeDocument21 pagesSubjective and Objective Questions With Answers of Chemical Equilibrium For PracticehappyNo ratings yet
- Composition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesComposition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeNgoc Le LeNo ratings yet
- Vapour Breakthrough in Activated CarbonDocument9 pagesVapour Breakthrough in Activated CarbonDomenico BarillariNo ratings yet
- Prediction of NOx Emissions in Recovery Boilers PDFDocument14 pagesPrediction of NOx Emissions in Recovery Boilers PDFNilesh KhadeNo ratings yet
- Teaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Document7 pagesTeaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Solin HawreNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations 1Document2 pagesMass Transfer Operations 1Uday KiranNo ratings yet
- Principles of Extractive Metallurgy - Docx - CopyDocument104 pagesPrinciples of Extractive Metallurgy - Docx - CopyFelix TinasheNo ratings yet
- Vol 47 - 2 0008 PDFDocument37 pagesVol 47 - 2 0008 PDFSahil DaradeNo ratings yet
- Vacuum System Design, CERNDocument15 pagesVacuum System Design, CERNjfejfeNo ratings yet
- 01 1stlaw ExessolsDocument29 pages01 1stlaw Exessolsblanca.pegueraNo ratings yet
- Air Stripping: The Removal of Volatile Contaminants From Water and Contaminated SoilsDocument39 pagesAir Stripping: The Removal of Volatile Contaminants From Water and Contaminated SoilsMohammed Al-DahlanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 121: Topic 5 - The Gaseous StateDocument24 pagesChemistry 121: Topic 5 - The Gaseous StateImranMalikNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture 10: For Dilute Concentrations, Over A Small Height DZ of Column, The Absorption Is Given by (Eq. 12.53)Document10 pagesOnline Lecture 10: For Dilute Concentrations, Over A Small Height DZ of Column, The Absorption Is Given by (Eq. 12.53)shamsul aminNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359431116305142 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1359431116305142 MainDiego MorenoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Unit - 3 Surface ChemistryDocument9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Unit - 3 Surface ChemistryAnish Babu100% (1)
- Adsorptive Purification of Large Waste Gas StreamsDocument5 pagesAdsorptive Purification of Large Waste Gas StreamsAMEY MAJLEKARNo ratings yet
- Assignment IVDocument2 pagesAssignment IVAbhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- Annotated Solution 2019 USNCO National Exam Part I: SolutionsDocument13 pagesAnnotated Solution 2019 USNCO National Exam Part I: SolutionsĐình Thư LêNo ratings yet
- Air Pool Protection From Emissions Of The Power Industry: 1.1.2.1.3. Burners Out оf Service - BOOSDocument1 pageAir Pool Protection From Emissions Of The Power Industry: 1.1.2.1.3. Burners Out оf Service - BOOSJagdeep ArryNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law 5684f195af3e6Document38 pagesIdeal Gas Law 5684f195af3e6Jose GulitiwNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Document20 pagesChemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Alina Syedd32No ratings yet
- C13 TutorialDocument9 pagesC13 TutorialAdam MrsmNo ratings yet
- Oden Thal 2010Document18 pagesOden Thal 2010Prakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Elsevier - Sensitivity of Joule Thomson Cooling To Impure CO2 Injection in Depleted Gas Reservoirs - Ziabakhsh - Ganji - 2013Document18 pagesElsevier - Sensitivity of Joule Thomson Cooling To Impure CO2 Injection in Depleted Gas Reservoirs - Ziabakhsh - Ganji - 2013wordindustriesNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry-02 Solved ProblemsDocument11 pagesSurface Chemistry-02 Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- To My FriendsDocument14 pagesTo My Friendsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- DoubleVision PpsDocument6 pagesDoubleVision Ppsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Double VisionDocument6 pagesDouble Visionرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- B) To Feel Shy and Silly, A Big Cup Make Liquid Flow OutDocument1 pageB) To Feel Shy and Silly, A Big Cup Make Liquid Flow Outرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- (Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age) : Design, Production, and Utilization of MaterialsDocument8 pages(Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age) : Design, Production, and Utilization of Materialsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Pipe Friction Losses: Fundamental Principles For Project WorkDocument3 pagesPipe Friction Losses: Fundamental Principles For Project Workرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Exp3 DensityDocument1 pageExp3 Densityرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Viscosity and Density Measurement Methods For Polymer Melts: R. Kažys, R. RekuvienėDocument6 pagesViscosity and Density Measurement Methods For Polymer Melts: R. Kažys, R. Rekuvienėرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 518d163be4b062a8d1d9f903-.Sam.-1368204347334-4 Factors Affecting Viscosity PDFDocument5 pages518d163be4b062a8d1d9f903-.Sam.-1368204347334-4 Factors Affecting Viscosity PDFرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 08-Mechanical Properties-BU-HandoutsDocument13 pages08-Mechanical Properties-BU-Handoutsرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Changes in Matter: Hot Ice and The Carbon Snake: Grade 8 Activity PlanDocument7 pages8.4 Changes in Matter: Hot Ice and The Carbon Snake: Grade 8 Activity Planرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- ChemicalDocument1 pageChemicalرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Interest and Investment CostDocument6 pagesChapter Two Interest and Investment Costرائد عبد العزيز فرحانNo ratings yet