Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Lecture 2 (Week 3) : OH DD in DD OL OH OL
Summary of Lecture 2 (Week 3) : OH DD in DD OL OH OL
Uploaded by
Hammad Satti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThe document discusses a lecture on the electronic analysis of inverters made of NMOS and PMOS transistors. It explains that for DC analysis, the input voltage is slowly varied to measure the output, while transient analysis assumes a time-varying input voltage. It then analyzes the behavior of NMOS and PMOS transistors at different input voltages to determine the output voltage levels and explain the logic levels. Threshold voltages and saturation regions of the transistors are also analyzed to determine the voltage level at which both transistors operate in saturation, which is defined as the midpoint voltage.
Original Description:
Original Title
FA17-EEE-008_Week3_Lecture2.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses a lecture on the electronic analysis of inverters made of NMOS and PMOS transistors. It explains that for DC analysis, the input voltage is slowly varied to measure the output, while transient analysis assumes a time-varying input voltage. It then analyzes the behavior of NMOS and PMOS transistors at different input voltages to determine the output voltage levels and explain the logic levels. Threshold voltages and saturation regions of the transistors are also analyzed to determine the voltage level at which both transistors operate in saturation, which is defined as the midpoint voltage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesSummary of Lecture 2 (Week 3) : OH DD in DD OL OH OL
Summary of Lecture 2 (Week 3) : OH DD in DD OL OH OL
Uploaded by
Hammad SattiThe document discusses a lecture on the electronic analysis of inverters made of NMOS and PMOS transistors. It explains that for DC analysis, the input voltage is slowly varied to measure the output, while transient analysis assumes a time-varying input voltage. It then analyzes the behavior of NMOS and PMOS transistors at different input voltages to determine the output voltage levels and explain the logic levels. Threshold voltages and saturation regions of the transistors are also analyzed to determine the voltage level at which both transistors operate in saturation, which is defined as the midpoint voltage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Sir I am not feeling well due to vomiting and severe headache I may not be able to take session if I will
not be able to take it then I am sorry.
SUMMARY OF LECTURE 2 (WEEK
3)
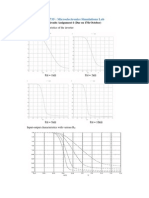
In this lecture we have learnt about the electronic analysis of inverter (made up of nmos and
pmos) so in case of DC analysis we have to take input slowly but for output it is not measured
immediately whether it is measure when the input is stabilized but for transient analysis the
scenario is different we have to assume a function of a time for input, hence output changes
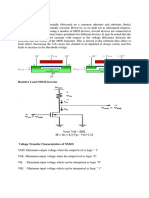
respectively. For Dc analysis consider a low voltage for input then Vin will be zero hence nmos
will be off while pmos will be conducting current so output (V OH=VDD). While when the input
voltage is high (Vin= VDD) then it will be opposite to the case of low voltage for input hence the
VOL will be zero. While logic swing output will be the difference btw V OH and VOL . Hence we can
say that:
VGSN = Vin
VSGp = VDD - Vin
The nmos remains in cut off region until following condition is met V in <= VTH hence the pmos will
be the conducting so the output voltage will be equal to V DD. As Vin increases the nFet is on while
the Pfet is still conducting hence we will see decrease in V SGp hence the efficiency of the device
decreases. The pmos remain in cut off region if V in = VDD - |VTp| then output voltage will be zero,
hence it is high logic. To make sure that input voltage does not overlap the output voltage then
we use voltage noise margins
1. VNMH= VOH – VlH
2. VNMHL= VIL - VOL
These noise margins tell us about the stability of inputs and lesser the Nosie margin is better
will be the efficiency of the device.
If the input voltage is greater than the voltage at the mid-point then it is considered as the logic
high side and vice versa. If we say that mid-point voltage, input voltage, output voltage is same
then all transistor have equal drain currents. In order to calculate the mid-point voltage we have
to find the mode of operation of the Mosfets.
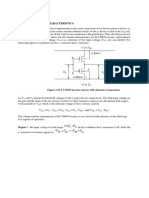
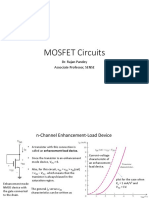
Consider a Nmos then
Vsat= VGSn - VTH
VGSn= Vin =VM
So,
Vsat= VM - VTH
And
VDSn= Vout = VM
So, for checking saturation region
Vsat< VDSn
So by putting equations of Vsat and VDSn we get:
VM> VM - VTH
Its true, hence the condition is satisfied so we can say that the nmos is in saturation region.
Consider Pmos then
Vsat= VSDp - |VTp|= VDD - Vin - |VTp|
VSDp= VDD – Vout = VM – Vout
And
Vsat <= VSDp
Put euqations of Vsat and VSDp then we get
- |VTp|<= 0
The condition is satisfied hence the pmos is in the saturation region.
As
IDN =IDP
Hence bu putting values and re-arranging them we get final result as
Bn/Bp =[ Kn* *(W/L)n]/[ Kp* *(W/L)p]
You might also like
- ECM3701 Electronic Communcation Technology: Minor Test No: 01 Year ModuleDocument4 pagesECM3701 Electronic Communcation Technology: Minor Test No: 01 Year ModuleTale Banks0% (1)
- Ferrite Transformer Turns Calculation For HighDocument67 pagesFerrite Transformer Turns Calculation For HighJaiParkash100% (1)
- Ferrite Transformer Turns Calculation For HighDocument67 pagesFerrite Transformer Turns Calculation For Highjaigodara0% (1)
- Lab#7 Block Diagram Reduction and Analysis and Design of Feedback SystemsDocument19 pagesLab#7 Block Diagram Reduction and Analysis and Design of Feedback SystemsHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- English Bullseye ChartDocument1 pageEnglish Bullseye ChartBaloo Nick CastlesNo ratings yet
- Retail ProjectDocument114 pagesRetail ProjectSowjanya KunareddyNo ratings yet
- VM EnginesDocument7 pagesVM EnginesraulNo ratings yet
- Cad of Electronics Lab: MbreaknDocument4 pagesCad of Electronics Lab: MbreaknAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- VLSI LabDocument44 pagesVLSI LabPoulami RoyNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document19 pagesLec 6vibhorkrnitrklNo ratings yet
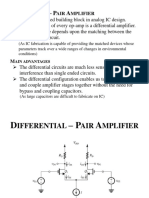
- Diff AmplDocument13 pagesDiff AmplAdeel AnsariNo ratings yet
- Lecture On TTLDocument16 pagesLecture On TTLAkhil M PNo ratings yet
- U 3Document13 pagesU 3Maheshwar Reddy100% (1)
- Ferrite Transformer Turns CalculationDocument6 pagesFerrite Transformer Turns CalculationMaher Mansour100% (2)
- Unit 5Document6 pagesUnit 5Tarun SinghalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document24 pagesUnit 3Indrajeet GautamNo ratings yet
- Arjun PL Vlsi2Document73 pagesArjun PL Vlsi2Tony StarkNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DDocument31 pagesUnit 2 DShaleva SinghNo ratings yet
- P 1 P and The Derivation Is Shown in Below FigureDocument8 pagesP 1 P and The Derivation Is Shown in Below FigureItsy BitsyNo ratings yet
- Vlsi10 Cmos Transmission GateDocument15 pagesVlsi10 Cmos Transmission GateGaurav MehraNo ratings yet
- Lpvlsi Ii UnitDocument16 pagesLpvlsi Ii UnitrakeshNo ratings yet
- CMOS Inverter LectureDocument16 pagesCMOS Inverter LectureAmr YassinNo ratings yet
- ICA-UNIT-III - R19-CompleteDocument28 pagesICA-UNIT-III - R19-CompleteBhanu Kiran BKNo ratings yet
- OPampDocument16 pagesOPampDarshan Iyer NNo ratings yet
- Digital Integrated CircuitsDocument17 pagesDigital Integrated CircuitsumeshkhetaNo ratings yet
- File PIbpjDENlDocument8 pagesFile PIbpjDENlSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- CMOS INVERTER-WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesCMOS INVERTER-WPS OfficekusumaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential Amplifier: Common Mode & Differential ModeDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Differential Amplifier: Common Mode & Differential ModeMalik JameelNo ratings yet
- Triangular Wave GeneratorDocument7 pagesTriangular Wave Generatorsourav_cybermusicNo ratings yet
- 03 CMOS DC Characteristics PDFDocument28 pages03 CMOS DC Characteristics PDFbalukiran2008No ratings yet
- Comparator CircuitDocument6 pagesComparator CircuitMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Nmos and Pmos Plot Using VlsiDocument13 pagesNmos and Pmos Plot Using VlsiSaathvik R KhatavkarNo ratings yet
- Midterm CircuitosDocument7 pagesMidterm CircuitosSantiago G. TorresNo ratings yet
- ECE 334 Lecture Chapter 16 InverterDocument20 pagesECE 334 Lecture Chapter 16 InverterSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- EL-225 Electronic Devices and Circuits: National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, FASTDocument5 pagesEL-225 Electronic Devices and Circuits: National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, FASTTanzeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Resistive Load InverterDocument3 pagesResistive Load InverterKing EverestNo ratings yet
- Dual Slope ADCDocument3 pagesDual Slope ADCHero HeroNo ratings yet
- Dual Slope Type ADC - Electronics TutorialDocument3 pagesDual Slope Type ADC - Electronics TutorialAvinashSharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Calibrateda Oscilloscope - HTMLDocument8 pagesHow To Calibrateda Oscilloscope - HTMLWahyu DinNo ratings yet
- Lec 28Document7 pagesLec 28Piyush KumarNo ratings yet
- To Study Comparator: Ikjot Dhawan, 13 Btech ECE A Lovely Professional UniversityDocument7 pagesTo Study Comparator: Ikjot Dhawan, 13 Btech ECE A Lovely Professional UniversityikjotdhawanNo ratings yet
- Name: Vikash Gupta Roll No.: 17EC01022 Experiment - 3 (ESD Lab)Document9 pagesName: Vikash Gupta Roll No.: 17EC01022 Experiment - 3 (ESD Lab)Soumya Kanti BeraNo ratings yet
- P E Lab FinalDocument63 pagesP E Lab FinalARVIND100% (1)
- EE 735: Microelectronics Simulations Lab: 1. Input-Output Characteristics of The InverterDocument13 pagesEE 735: Microelectronics Simulations Lab: 1. Input-Output Characteristics of The InverterRonik JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2Nicholas JyrwaNo ratings yet
- Static CMOS Inverter DC Characteristics: Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryDocument1 pageStatic CMOS Inverter DC Characteristics: Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- ECE 334-Lecture 30-nMOS - Inverter-DepletionloadDocument7 pagesECE 334-Lecture 30-nMOS - Inverter-DepletionloadBretuoba Nana Yaw YeboahNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and E.M. Waves Lec 10Document31 pagesTransmission Lines and E.M. Waves Lec 10Vishnu ShashankNo ratings yet
- CMOSDocument15 pagesCMOSVinesh JayaramanNo ratings yet
- 368463600-JFET-Summary - PPT 20240314 132059 0000Document91 pages368463600-JFET-Summary - PPT 20240314 132059 0000Yanis SlimaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4Document63 pagesUnit 3 & 4Indrajeet GautamNo ratings yet
- JFETDocument12 pagesJFETsujoneeesustNo ratings yet
- Linear Amplifiers and Opamps: I + Av - + V I Z V Z R RDocument19 pagesLinear Amplifiers and Opamps: I + Av - + V I Z V Z R RAnimesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2023 - AnsDocument3 pagesTutorial 2023 - Anschetannp121No ratings yet
- Lec02 Ae Ms14Document59 pagesLec02 Ae Ms14Mohsin Abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 ECE1002 ETH VL2020210506889 Reference Material I 25-Jun-2021 MOSFET-circuits-ApplicationsDocument19 pagesWINSEM2020-21 ECE1002 ETH VL2020210506889 Reference Material I 25-Jun-2021 MOSFET-circuits-Applicationsrisith royNo ratings yet
- Example - Relaxatn OscDocument5 pagesExample - Relaxatn Oscsourav_cybermusicNo ratings yet
- Varun Sharma 2018eeb1193 Analog Lab Exp - 2 ReportDocument16 pagesVarun Sharma 2018eeb1193 Analog Lab Exp - 2 ReportVarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: A B A BDocument10 pagesDigital Electronics: A B A BVehap CurriNo ratings yet
- Chap16 1 NMOS InverterDocument50 pagesChap16 1 NMOS Invertervlsijp100% (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Multi-Class Disease Classification in Brain MRIsDocument14 pagesMulti-Class Disease Classification in Brain MRIsHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Thesis Final VersionDocument97 pagesThesis Final VersionHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using FPGA PlatformDocument16 pagesAutomatic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using FPGA PlatformHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University IslamabadDocument2 pagesCOMSATS University IslamabadHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document8 pagesLab Report 1Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Hamad Ul Haq Fa17-Eee-008Document3 pagesAssignment 1: Hamad Ul Haq Fa17-Eee-008Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam ScheduleDocument8 pagesMidterm Exam ScheduleHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- In Lab Tasks:: Task 1Document5 pagesIn Lab Tasks:: Task 1Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3: Hamad Ul HaqDocument9 pagesLab Report 3: Hamad Ul HaqHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab Tasks:: Task 1Document13 pagesPre Lab Tasks:: Task 1Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: HAMAD UL HAQ (FA17-EEE-008)Document5 pagesAssignment 2: HAMAD UL HAQ (FA17-EEE-008)Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- FA17-EEE-037 Control Lab Report 11Document6 pagesFA17-EEE-037 Control Lab Report 11Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Lab#9: Steady State Error Analysis and DesignDocument9 pagesLab#9: Steady State Error Analysis and DesignHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Lab#9 Steady State Error Analysis and DesignDocument7 pagesLab#9 Steady State Error Analysis and DesignHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Fa17-Eee-008 - Asssignment 4Document6 pagesFa17-Eee-008 - Asssignment 4Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Fa17-Eee-008 - Asssignment 3Document6 pagesFa17-Eee-008 - Asssignment 3Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture 3 (Week 4) : PR PF P PF PR F N DD Out R P DD DD OutDocument2 pagesSummary of Lecture 3 (Week 4) : PR PF P PF PR F N DD Out R P DD DD OutHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture 2 (Week 4) : 1. Fall TimeDocument3 pagesSummary of Lecture 2 (Week 4) : 1. Fall TimeHammad SattiNo ratings yet
- Fa17-Eee-008 - Asssignment 2Document7 pagesFa17-Eee-008 - Asssignment 2Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- RuttDocument6 pagesRuttJustinian FiloteosNo ratings yet
- Ernst Gombrich - Power and Glory I (Ch. 21)Document11 pagesErnst Gombrich - Power and Glory I (Ch. 21)Kraftfeld100% (1)
- Redox Equilibria: Electrochemical CellsDocument11 pagesRedox Equilibria: Electrochemical CellsThiranisesh JeyakanthanNo ratings yet
- Recognition and Extinction of StatesDocument4 pagesRecognition and Extinction of StatesCristy C. BangayanNo ratings yet
- Online QDA - How and What To CodeDocument5 pagesOnline QDA - How and What To CodeRockyNo ratings yet
- Fire PreventionDocument2 pagesFire PreventionMarlon Arian Conde AhorroNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards The Retail Footwear Industry: A Project Report OnDocument27 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards The Retail Footwear Industry: A Project Report Onangelamonteiro1234No ratings yet
- Ingovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction ManualDocument44 pagesIngovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction Manualfelipe floresNo ratings yet
- "The Pedestrian" By: Rey BradburyDocument7 pages"The Pedestrian" By: Rey BradburyGabBragatNo ratings yet
- Oracle Enterprise Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesOracle Enterprise Asset ManagementMH.SezanNo ratings yet
- For ConsultationDocument11 pagesFor ConsultationClarisse PoliciosNo ratings yet
- Silvia Rey Resume OkDocument3 pagesSilvia Rey Resume Okapi-489656705No ratings yet
- Kindergarten Writing Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesKindergarten Writing Lesson Planapi-332051194No ratings yet
- Summer Farm: By: Norman Maccaig Group: Camila Luna and Estrella LinDocument8 pagesSummer Farm: By: Norman Maccaig Group: Camila Luna and Estrella LinJamieDuncanNo ratings yet
- Torque Link Kit EligibilityDocument15 pagesTorque Link Kit EligibilityoscarNo ratings yet
- Dio125 and Hornet2 RepsolDocument2 pagesDio125 and Hornet2 RepsolSibi SundarNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System StimulantsDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System StimulantsNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Coin FlipDocument10 pagesCoin Flip林丽莹No ratings yet
- March of The Metro Gnome Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMarch of The Metro Gnome Lesson Planapi-607297153No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Creating and Editing Screens: 2.1 Scredit (Screen Editor) SetupDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Creating and Editing Screens: 2.1 Scredit (Screen Editor) SetupryoNo ratings yet
- Monday 09-12-2019 2pm To 5pm: Date & Time SEM Sub Code SubjectDocument3 pagesMonday 09-12-2019 2pm To 5pm: Date & Time SEM Sub Code SubjectSabaNo ratings yet
- CDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideDocument18 pagesCDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideJulio RodanesNo ratings yet
- Upcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 2 - Science Proficiency v.5.26Document14 pagesUpcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 2 - Science Proficiency v.5.26Regina MercurioNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Gesture Controlled Wireless Wheelchair For The Physically HandicappedDocument6 pagesIntelligent Gesture Controlled Wireless Wheelchair For The Physically HandicappedshivaramreddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To JainismDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To JainismVertika guptaNo ratings yet
- CC Err DSP LogDocument7 pagesCC Err DSP LogdegfabioNo ratings yet