Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reference: Past Exam Paper - November 2012 Paper 23 Q3: (For Constant Speed, The Resultant Force Is Zero.) ( FV)
Reference: Past Exam Paper - November 2012 Paper 23 Q3: (For Constant Speed, The Resultant Force Is Zero.) ( FV)
Uploaded by
sumit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document provides information to calculate the resistive force acting on a cyclist traveling at 8.0 m/s, given the total mass of the cyclist and bicycle is 80 kg and the acceleration provided in an earlier part. It also states that using the information given, the resistive force R can be shown to be proportional to the speed v of the cyclist in this situation.
Original Description:
Original Title
New Microsoft Word Document.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information to calculate the resistive force acting on a cyclist traveling at 8.0 m/s, given the total mass of the cyclist and bicycle is 80 kg and the acceleration provided in an earlier part. It also states that using the information given, the resistive force R can be shown to be proportional to the speed v of the cyclist in this situation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageReference: Past Exam Paper - November 2012 Paper 23 Q3: (For Constant Speed, The Resultant Force Is Zero.) ( FV)
Reference: Past Exam Paper - November 2012 Paper 23 Q3: (For Constant Speed, The Resultant Force Is Zero.) ( FV)
Uploaded by
sumitThe document provides information to calculate the resistive force acting on a cyclist traveling at 8.0 m/s, given the total mass of the cyclist and bicycle is 80 kg and the acceleration provided in an earlier part. It also states that using the information given, the resistive force R can be shown to be proportional to the speed v of the cyclist in this situation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
(iv) The total mass of the cyclist and bicycle is 80 kg.
Calculate the resistive force R acting on
the cyclist when his speed is 8.0 m s–1. Use the value for the acceleration given in (iii).
(v) Use the information given in (ii) and your answer to (iv) to show that, in this situation, the
resistive force R is proportional to the speed v of the cyclist.
Reference: Past Exam Paper – November 2012 Paper 23 Q3
Solution 1003:
(a) Power is defined as the rate of doing work OR power = work done / time (taken)
OR power = energy transferred / time (taken)
(b)
(i) As the speed increases drag / air resistance increases. The resultant force reduces and hence
the acceleration is less. A constant speed is reached when the resultant force is zero.
(ii)
{For constant speed, the resultant force is zero.}
Force F from cyclist = drag force / resistive force
Power P {= Fv} = 12 × 48
Power P = 576 W
You might also like
- Solution Manual For An Introduction To Mechanical Engineering 4th EditionDocument45 pagesSolution Manual For An Introduction To Mechanical Engineering 4th EditionJayStewartmsie100% (45)
- Wind EnergyDocument9 pagesWind Energyharika mandadapuNo ratings yet
- Lifting MachinesDocument23 pagesLifting Machineskalpanaadhi75% (8)
- Inertia LoadsDocument10 pagesInertia LoadsBerns DulamNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Assignment 1 1 2Document4 pagesModule 6 Assignment 1 1 2sanjeev.rajoriaNo ratings yet
- A2 41a MomentumDocument29 pagesA2 41a MomentumChrise RajNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument7 pagesContinuekenfackNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Mechanics and HeatDocument50 pages2.2 Mechanics and HeataffeezNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 4Document18 pagesLecture14 4Mohannad BayadoNo ratings yet
- Power and EfficiencyDocument17 pagesPower and EfficiencyzakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 PDFDocument17 pagesLecture 15 PDFzakNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Flight Strategies: David Arterburn, Michael Jaye, Joseph Myers, Kip NygrenDocument10 pagesAircraft Flight Strategies: David Arterburn, Michael Jaye, Joseph Myers, Kip NygrenKiller_RNo ratings yet
- 7 4 PowerDocument4 pages7 4 Powergenetamane6No ratings yet
- Differential Axle and WheelDocument2 pagesDifferential Axle and WheelPolytechnic KatiharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Work, Energy UpdatedDocument43 pagesChapter 7-Work, Energy UpdatedNoor BlNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections Extended Version With Modern 1St Edition Katz Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections Extended Version With Modern 1St Edition Katz Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFBrendaTaylorwzab100% (7)
- Propulsion ResistanceDocument14 pagesPropulsion ResistanceEduardo LopesNo ratings yet
- 3314 Ijmech 11Document8 pages3314 Ijmech 11Burak KoyuncuogluNo ratings yet
- Propulsion ResistanceDocument15 pagesPropulsion ResistanceAnonymous QiMB2lBCJLNo ratings yet
- Mech 1Document18 pagesMech 1S MalinguNo ratings yet
- Wind Speed, Wind Yaw and The Aerodynamic Drag Acting On A Bicycle and RiderDocument9 pagesWind Speed, Wind Yaw and The Aerodynamic Drag Acting On A Bicycle and RidermaorpeNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy: Younes SinaDocument49 pagesWork and Energy: Younes SinayounessinaNo ratings yet
- Momentum Mass X VelocityDocument17 pagesMomentum Mass X VelocityHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Cycling: To Cite This VersionDocument10 pagesMechanics of Cycling: To Cite This Versionvalentina mejíaNo ratings yet
- Tractor Performance (Empirical) : Agus Haryanto VisitDocument23 pagesTractor Performance (Empirical) : Agus Haryanto VisitNizam AuliaNo ratings yet
- Examples On NotesDocument8 pagesExamples On NotesAbdulmalik JuneydiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Prediction of PowerDocument74 pagesPreliminary Prediction of PowerTullio OpattiNo ratings yet
- National University of SingaporeDocument4 pagesNational University of SingaporeTan Gin HuiNo ratings yet
- Keywords:: Performance Analysis II - Steady Climb, Descent and Glide (Lectures 21,22 and 23)Document12 pagesKeywords:: Performance Analysis II - Steady Climb, Descent and Glide (Lectures 21,22 and 23)Chegrani AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Internal Combustion Engine Performance ParametersDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Internal Combustion Engine Performance ParametersFlancNo ratings yet
- Torque and Power Delivered in Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)Document12 pagesTorque and Power Delivered in Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)ahmadhamada0511No ratings yet
- Utilisation of Electric Power Electric Traction: Course Code: EE702 Co Ordinator: Dr. Nandita SanyalDocument14 pagesUtilisation of Electric Power Electric Traction: Course Code: EE702 Co Ordinator: Dr. Nandita SanyalAditya PaulNo ratings yet
- Indirect Calculation of Mechanical and Propelling Efficiency During Freestyle SvihhingDocument4 pagesIndirect Calculation of Mechanical and Propelling Efficiency During Freestyle SvihhingleonardocascallarNo ratings yet
- Tractive Effort For Propulsion of TrainDocument4 pagesTractive Effort For Propulsion of TrainSandip MondalNo ratings yet
- PHYS 0100 Dynamics - Part III: Conservation of Linear Momentum and Energy Ms. Nalini DookieDocument17 pagesPHYS 0100 Dynamics - Part III: Conservation of Linear Momentum and Energy Ms. Nalini DookieJohn McNellNo ratings yet
- (MS) Yr 9-Revision WS-2023Document10 pages(MS) Yr 9-Revision WS-2023nisalielisha rodrigoNo ratings yet
- Bodies Moving On Inclined Planes - Acting ForcesDocument8 pagesBodies Moving On Inclined Planes - Acting Forcespalkan.emsysNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics Impulse WorkDocument16 pagesEngg Mechanics Impulse WorkAkash WeaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Roll Bar Design and Material Selection For THDocument3 pagesAnti-Roll Bar Design and Material Selection For TH8794 Dimplekunwar SolankiNo ratings yet
- Islam College of Engineering & Management Sciences Sialkot, (Icems) - Mechanics of Machine (Lab) - (4 Semester, Spring2022)Document5 pagesIslam College of Engineering & Management Sciences Sialkot, (Icems) - Mechanics of Machine (Lab) - (4 Semester, Spring2022)Ayesha MunnirNo ratings yet
- Anti Roll Bar DesignDocument3 pagesAnti Roll Bar DesignpgmaisheriNo ratings yet
- Samplex: Kiara S. Esguerra September 2019Document3 pagesSamplex: Kiara S. Esguerra September 2019Merlin MendozaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For An Introduction To Mechanical Engineering 3rd Edition by WickertDocument38 pagesSolution Manual For An Introduction To Mechanical Engineering 3rd Edition by WickertScottWyattognje100% (44)
- Physics QuestionsDocument6 pagesPhysics QuestionsUswa ChNo ratings yet
- Development of Low Cost Pellet Loading and Unloading AGVDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Low Cost Pellet Loading and Unloading AGVDaniel Garnando KristianNo ratings yet
- Stealth 316 - Force, Work, and PowerDocument3 pagesStealth 316 - Force, Work, and PowerAnthony PomaredeNo ratings yet
- Discussion Quiz 4 (40 Points) : 500 (KM/H) 800 (KM) 20.0 2.00 (H)Document4 pagesDiscussion Quiz 4 (40 Points) : 500 (KM/H) 800 (KM) 20.0 2.00 (H)Jan Adrian Galang FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument12 pagesSimple MachinesR MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter3pp021 030 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter3pp021 030 PDFInderMaheshNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Research PaperDocument6 pagesElectric Vehicle Research PaperHarshil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics (Work, Energy and Power)Document5 pagesDynamics (Work, Energy and Power)YadanaNo ratings yet
- Lemon Miracle DE2018 X1218 MAR523Document10 pagesLemon Miracle DE2018 X1218 MAR523Lemon MiracleNo ratings yet
- Odev 51Document5 pagesOdev 51Sami TükekNo ratings yet
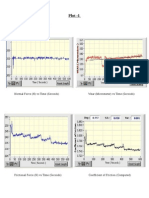
- Plot - 1Document7 pagesPlot - 1Suman MandalNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 PhysicsDocument3 pagesDPP 1 PhysicsSanjay Verma100% (1)
- Propeller Performance CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesPropeller Performance CharacteristicsNaga Manohar UmmadiNo ratings yet
- Design of Small Electric Car: P. Prochazka, I. Pazdera, P. Vorel and D. CervinkaDocument6 pagesDesign of Small Electric Car: P. Prochazka, I. Pazdera, P. Vorel and D. Cervinkashivendra singhNo ratings yet
- Episode 218: Mechanical Power: × VelocityDocument10 pagesEpisode 218: Mechanical Power: × VelocityAnonymous QvdxO5XTRNo ratings yet
- Overall Allotment R1+R2+MA - Open Elective III As On 26.07.2023Document50 pagesOverall Allotment R1+R2+MA - Open Elective III As On 26.07.2023sumitNo ratings yet
- ApplicantProfile2023-07-11 - 23 35 57Document2 pagesApplicantProfile2023-07-11 - 23 35 57sumitNo ratings yet
- Interview FormDocument2 pagesInterview FormsumitNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument2 pagesApplicationsumitNo ratings yet
- Paushtech Event ParticipantsDocument1 pagePaushtech Event ParticipantssumitNo ratings yet
- Packaging TechnologyDocument5 pagesPackaging TechnologysumitNo ratings yet
- Invitation EtterDocument1 pageInvitation EttersumitNo ratings yet
- Masters DataDocument72 pagesMasters DatasumitNo ratings yet
- Initial Pages S B LagareDocument4 pagesInitial Pages S B LagaresumitNo ratings yet
- AD Patil Sir SynopsisDocument13 pagesAD Patil Sir SynopsissumitNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Dye Removal by Adsorption Method and Nanocrystalline Tio Thin FilmsDocument11 pagesComparative Study of Dye Removal by Adsorption Method and Nanocrystalline Tio Thin FilmssumitNo ratings yet
- Assignmaint 1Document4 pagesAssignmaint 1sumitNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: (PRN No. 201502677)Document12 pagesSynopsis: (PRN No. 201502677)sumitNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engieering SME Test - 2021 - NEW OneDocument2 pagesChemical Engieering SME Test - 2021 - NEW OnesumitNo ratings yet
- Renuka Chemicals ProjectDocument3 pagesRenuka Chemicals ProjectsumitNo ratings yet
- Journal For Research: First Author Second AuthorDocument7 pagesJournal For Research: First Author Second AuthorsumitNo ratings yet
- Dept. of Chemical Engineering: Class-S.Y. (Chemical) 2018-19 Micro - Project GroupsDocument3 pagesDept. of Chemical Engineering: Class-S.Y. (Chemical) 2018-19 Micro - Project GroupssumitNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Esterification Reaction Using Ion-Exchange Resin CatalystDocument5 pagesKinetics of Esterification Reaction Using Ion-Exchange Resin CatalystsumitNo ratings yet
- Major Equations: Major Equation Used in ModelsDocument3 pagesMajor Equations: Major Equation Used in ModelssumitNo ratings yet
- List Project Topics For Final Year Chemical Engg. StudentsDocument4 pagesList Project Topics For Final Year Chemical Engg. StudentssumitNo ratings yet
- List of projects-BYBDocument10 pagesList of projects-BYBsumitNo ratings yet
- Jublient Training ReportDocument33 pagesJublient Training ReportsumitNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 7 Manufacturing of Butyl Acetate by Esterification ReactionDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 7 Manufacturing of Butyl Acetate by Esterification ReactionsumitNo ratings yet
- Process Simulation of Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesProcess Simulation of Heat ExchangersumitNo ratings yet
- List of Chemical Engineering Project TopicsDocument2 pagesList of Chemical Engineering Project TopicssumitNo ratings yet
- Renuka Chemicals ProjectDocument3 pagesRenuka Chemicals ProjectsumitNo ratings yet
- Process Simulation of Stirred Tank ReactorDocument4 pagesProcess Simulation of Stirred Tank ReactorsumitNo ratings yet