Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Slope : Water Pressure and Ice Wedge Factor - J
Slope : Water Pressure and Ice Wedge Factor - J
Uploaded by
Daniel soto aOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Slope : Water Pressure and Ice Wedge Factor - J
Slope : Water Pressure and Ice Wedge Factor - J
Uploaded by
Daniel soto aCopyright:
Available Formats
= RQD x
Jr J wice
Qslope x
Jn Ja o
SRFslope
Orientation adjustment for joints in rock slopes (Jr/Ja)o SRF
slope
For Jr “contact” categories a) and b) Slope surface condition (now or expected due to
Ja “contact” categories a) and b)
susceptibility to wethering and erosion
SRFslope
Note: Use A) and B) when wedges are formed:
A) slight loosening due to surface location 2.5
For A) the least favourable set or discontinuity B) Loose blocks, signs of tension cracks and joint
5.0
multiply Jr/Ja by following: shearing, but susceptibility to weathering
o-factor C) As B but strong susceptibility to weathering 10
if v. favourably oriented 2 D) Slope is in advanced stage of erosion and
quite favourable 1 15
loosening due to periodic water erosion and/or
unfavourable 0.75 ice-wedging effects
very unfavourable 0.5 E) Residual slope with significant transport of
20
causing failure if unsupported 0.25 material down-slope
For B) the second least favourable set or discontinuity Adverse stress-strength range
multiply Jr/Ja by following: / SRFslope
C 1
o-factor
J) Moderate stress-strength range 50-200 2.5
if v. favourably oriented 1.5
K) High stress-strength range 10-50 5-2.5
quite favourable 1
unfavourable 0.9 L) Localized intact rock failure 5-10 10-5
very unfavourable 0.8 M) Crushing or plastic yield 2.5-5 15-10
causing failure if unsupported 0.7 N) Plastic flow of strain softened material 1-2.5 20-15
Example: set 1 dominant, least favourable Jr = 1.5 Ja = 2 Major discontinuities i.e. faults, weakness zones and
set 2 less dominant Jr = 2 Ja=1
joint swarms which may also contain clay filling that
Wedges structures are formed by these two sets adversely affect the slope stability
A) Jr/Ja = 1.5/2 o- factor = 0.5
B) Jr/Ja = 2/1 o- factor = 0.9 K) Major discontinuity with little or no day with orientation
The total “Jr/Ja” term used in Qslope is the combined term: SRFslope
1.5/2 * 0.5 * 2/1 * 0.9 = 0.68 e) favourable 1
f) unfavourable 2
g) very unfavourable 4
Water pressure and ice wedge factor - J wice h) causing failure if unsupported 8
Desert Wet Tropical Ice L) Major discontinuity with RDQ100= 0 due to clay and
environment environment storms wedging crushed rock, with orientation
SRFslope
Stable structure
1.0 0.7 0.5 0.9
competent rock e) favourable 2
Stable structure 0.7 0.6 0.3 0.5 f) unfavourable 4
incompetent rock
g) very unfavourable 8
Unstable structure
competent rock 0.8 0.5 0.1 0.3 h) causing failure if unsupported 16
Unstable structure
0.5 0.3 0.05 0.2
M) Major discontinuity with RDQ300
= 0 due to clay and
incompetent rock crushed rock, with orientation
SRFslope
Note: e) favourable 4
When drainage measures are installed
f) unfavourable 8
apply J wice x 1.5
g) very unfavourable 12
When slope reinforcement measures are installed h) causing failure if unsupported 24
apply Jwice x 1.3
When drainage and reinforcement is installed RQD
100
= 1 meter perpendicular sample of discontinuity
apply both factor: J w x 1.5 x 1.3 RQD 300= 1 meter perpendicular sample of discontinuity
You might also like
- Change On The Rise: Transcribed by David LiuDocument7 pagesChange On The Rise: Transcribed by David Liuveromejhdo57% (7)
- Checklist Audit ISO 22000Document18 pagesChecklist Audit ISO 22000Abhishek Kumar Singh95% (20)
- Mechanical Behavior Mostly Ceramics, Glasses and PolymersDocument26 pagesMechanical Behavior Mostly Ceramics, Glasses and PolymersNorozKhanNo ratings yet
- Trim Clean 2030-Msds (Bld-1656 v1)Document8 pagesTrim Clean 2030-Msds (Bld-1656 v1)Tri Febrianto PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Q Course For PERU PPT 2Document7 pagesQ Course For PERU PPT 2jhonaroniNo ratings yet
- Strengthening MechanismsDocument3 pagesStrengthening MechanismsGopinathNo ratings yet
- ISRM2019 BB QslopeFaultedRocksAndFaultZonesDocument9 pagesISRM2019 BB QslopeFaultedRocksAndFaultZonesJuan Fernando Joya NuñezNo ratings yet
- RMR Table ClassificationDocument22 pagesRMR Table ClassificationPrasetya Adi RinantoNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 Q-Rock Mass ClassificationDocument21 pagesLec-11 Q-Rock Mass ClassificationUmair AshrafNo ratings yet
- Q - Method 2013 Summary For Field UseDocument2 pagesQ - Method 2013 Summary For Field UsePatricio CisternasNo ratings yet
- Deformations and Cracking of R.C. StructuresDocument24 pagesDeformations and Cracking of R.C. StructuresTakis ApostolidesNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Rock Mass Classification: 4.6 Tunnelling Quality Index (Q)Document7 pagesModule 4: Rock Mass Classification: 4.6 Tunnelling Quality Index (Q)tanujaayerNo ratings yet
- Technological Possibilities For Improving The Strength of AlloysDocument12 pagesTechnological Possibilities For Improving The Strength of AlloysParijat MitraNo ratings yet
- CE 441 - Lec02 - Bearing Capacity Theories and Eqns V2Document117 pagesCE 441 - Lec02 - Bearing Capacity Theories and Eqns V2Md. Nahin Al ZakiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Fault Seal Analysis - An IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntegrated Fault Seal Analysis - An IntroductionSepribo Eugene BriggsNo ratings yet
- Markscheme Coba PhysicsDocument2 pagesMarkscheme Coba PhysicsDigilib Cambridge TazkiaNo ratings yet
- Aspirants AS1319 12th Physics Public Exam Answer Key For 2019 Question Paper English MediumDocument4 pagesAspirants AS1319 12th Physics Public Exam Answer Key For 2019 Question Paper English Medium5318819.sreejithNo ratings yet
- GlassProp Lecture7 Brow Part2Document57 pagesGlassProp Lecture7 Brow Part2patheony23No ratings yet
- WEEK 7-8 (Settlement Influenced by Foundation)Document25 pagesWEEK 7-8 (Settlement Influenced by Foundation)Mohammad Yunus SalehiNo ratings yet
- Discontinuity Characterization - QueensMineDesignWikiDocument4 pagesDiscontinuity Characterization - QueensMineDesignWikiImranNo ratings yet
- ENCE 647 ENCE 647 Stability of Slopes Dr. Ahmet AydilekDocument23 pagesENCE 647 ENCE 647 Stability of Slopes Dr. Ahmet AydilekHoracioCruiseNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Solution 2017 Set 1Document68 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Solution 2017 Set 1zakNo ratings yet
- Member Design - Columns Member Design - ColumnsDocument33 pagesMember Design - Columns Member Design - ColumnsxangNo ratings yet
- Complex PDFDocument23 pagesComplex PDFabtin pegahNo ratings yet
- Rock Stress and Failure BasicsDocument13 pagesRock Stress and Failure BasicsIgorCencičNo ratings yet
- Multi-Disciplinary Approach To Fault Seal Integrity Analysis: A Case Study From Jambusar Field Cambay Basin, IndiaDocument7 pagesMulti-Disciplinary Approach To Fault Seal Integrity Analysis: A Case Study From Jambusar Field Cambay Basin, IndiaUpendra SoniNo ratings yet
- Partial Dislocation of FCC MaterialsDocument17 pagesPartial Dislocation of FCC MaterialsIshtiaque Karim RobinNo ratings yet
- Modelling Brittle Failure of Rock: V. Hajiabdolmajid, P.K. Kaiser, C.D. MartinDocument11 pagesModelling Brittle Failure of Rock: V. Hajiabdolmajid, P.K. Kaiser, C.D. MartinKristi GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterDocument15 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterMuhammad HaroonNo ratings yet
- Determining Stress ReductionDocument4 pagesDetermining Stress Reductiontie.wangNo ratings yet
- 5 Underground Ecavation in Rock (Compatibility Mode)Document19 pages5 Underground Ecavation in Rock (Compatibility Mode)jialinnNo ratings yet
- Toughening Mechanisms: Brittle Materials:!Document17 pagesToughening Mechanisms: Brittle Materials:!Hunny GuptaNo ratings yet
- 4.4.2.1 Shallow Bearing Foundations: γ is the weightDocument13 pages4.4.2.1 Shallow Bearing Foundations: γ is the weightDone NikolovskiNo ratings yet
- 01 Nick BartonDocument46 pages01 Nick Bartonangel_maulwurfNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Code: C: Page - 1Document12 pagesMarking Scheme Code: C: Page - 1starrai3600No ratings yet
- Ppr12 152alr PDFDocument11 pagesPpr12 152alr PDFRavi MalikNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength of Soil: Lab. Report NO. 10Document6 pagesShear Strength of Soil: Lab. Report NO. 10علي الحسنNo ratings yet
- Application of The Q-Slope Method To Highly Weathered and Saprolitic RocksDocument6 pagesApplication of The Q-Slope Method To Highly Weathered and Saprolitic RocksWalt ArcherNo ratings yet
- Rock Quiz PaperDocument2 pagesRock Quiz Paperabhaysinghpratap2000No ratings yet
- Rock Tunelling Quality Index, QDocument8 pagesRock Tunelling Quality Index, QMilthonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document40 pagesLesson 2Marco NeveNo ratings yet
- Fault Seal AnalysisDocument8 pagesFault Seal AnalysisQaiser HafeezNo ratings yet
- Asentamiento 1Document93 pagesAsentamiento 1NURIA YULIYA DIAZ VELARDENo ratings yet
- SIN 411 Theme 5 Beams - 2012Document20 pagesSIN 411 Theme 5 Beams - 2012Johnnie StrydomNo ratings yet
- Is 13365 Part4 DraftDocument15 pagesIs 13365 Part4 DraftPalak Shivhare0% (1)
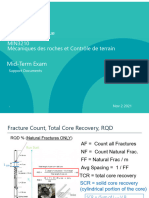
- Min3210 Support Doc Mid-Term Exam Nov 10 2022Document23 pagesMin3210 Support Doc Mid-Term Exam Nov 10 2022Abdelghafour ElmchiekNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Soil Description 2006-4Document10 pagesGuidelines For Soil Description 2006-4JOSENo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Restrained BeamDocument26 pagesLec 3 - Restrained Beammuhammadfarhat35No ratings yet
- L4 BC RetainingWalls HNDDocument4 pagesL4 BC RetainingWalls HNDDadi YashwantNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral RelaysDocument6 pagesQuadrilateral RelaysJOHN ANDERSON MU�OZ GOEZNo ratings yet
- Stress, Strain and Young's Modulus 2 MSDocument8 pagesStress, Strain and Young's Modulus 2 MSTimothy SeyaramNo ratings yet
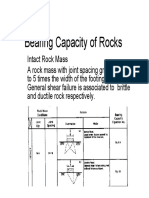
- Bearing Capacity of RockDocument19 pagesBearing Capacity of RockAhmad PooladiNo ratings yet
- Design For NSF by Harry PoulosDocument7 pagesDesign For NSF by Harry PoulosSantosoNo ratings yet
- RCC42 Post Tensioned Analysis & DesignDocument8 pagesRCC42 Post Tensioned Analysis & DesignShawkat Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Design Procedures For Dynamically Loaded Foundations Choice of Parameters For Equivalent Lumped SystemsDocument11 pagesDesign Procedures For Dynamically Loaded Foundations Choice of Parameters For Equivalent Lumped SystemsAnonymous osfiXqUkNo ratings yet
- 950 WKBK Ground MasterDocument28 pages950 WKBK Ground MasterVanessa CordovaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme PAPER 2Document11 pagesMarking Scheme PAPER 2Atharv TyagiNo ratings yet
- Design of BeamsDocument112 pagesDesign of BeamskbkwebsNo ratings yet
- Impedance Relays: Chapter 10 - Part 6Document48 pagesImpedance Relays: Chapter 10 - Part 6Mohamed ZekryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1Document2 pagesLecture 1-1Rhoda MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Ersoy2014Document7 pagesErsoy2014Roxana LencinaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Training Materials PDFDocument32 pages2012 Training Materials PDFWisam Ankah100% (1)
- Solubility Equilibrium HomeworkDocument2 pagesSolubility Equilibrium HomeworkEyayu ZewduNo ratings yet
- TheDocument12 pagesTheVictor PileggiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Turbine CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesExperiment 4 Turbine CharacteristicsChong Ru YinNo ratings yet
- Covellite PDFDocument1 pageCovellite PDFRyoga RizkyNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Air ConditioningDocument17 pagesTechnical Data: Air ConditioningTomaž BajželjNo ratings yet
- Panel Features: Square-D Fabricator and Control Systems EnterpriseDocument1 pagePanel Features: Square-D Fabricator and Control Systems EnterpriseCallista CollectionsNo ratings yet
- Geography & Resources of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesGeography & Resources of The PhilippinesPaulAliboghaNo ratings yet
- Abstracts: IAFRI Metaldehyde Conference - 13 September - Fera Science LTD, York YO41 1LZDocument6 pagesAbstracts: IAFRI Metaldehyde Conference - 13 September - Fera Science LTD, York YO41 1LZbendel_boyNo ratings yet
- EN ISO 13503-2 (2006) (E) CodifiedDocument8 pagesEN ISO 13503-2 (2006) (E) CodifiedEzgi PelitNo ratings yet
- AppliedchemistrylabmaualDocument23 pagesAppliedchemistrylabmaualYashwanth KasthuriNo ratings yet
- Aquion Battery Technology - 1216Document18 pagesAquion Battery Technology - 1216sinnlosNo ratings yet
- Individual Development WorkoutDocument3 pagesIndividual Development WorkoutmichelleNo ratings yet
- Turbodrain EnglDocument8 pagesTurbodrain EnglIonut BuzescuNo ratings yet
- Thoughts John DeeDocument353 pagesThoughts John DeeJ. Perry Stonne100% (1)
- GCRP TX InterruptionDocument13 pagesGCRP TX InterruptionPanNo ratings yet
- Circuito Integrado BA05STDocument10 pagesCircuito Integrado BA05STEstefano EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina Aubrey0% (1)
- Module 2 (People and The Earth's Ecosystem)Document11 pagesModule 2 (People and The Earth's Ecosystem)chris ian0% (2)
- Linear Wave ShapingDocument71 pagesLinear Wave ShapingArun Kumar DhupamNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EDocument9 pagesWeek 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EInstituto Centro de Desenvolvimento da GestãoNo ratings yet
- Gas Cyclone 2Document20 pagesGas Cyclone 2Para DiseNo ratings yet
- High Protein Foods List PDFDocument3 pagesHigh Protein Foods List PDFAnonymous P1FbQoqsHJ100% (1)
- PA2500Document10 pagesPA2500plaki_7No ratings yet
- Modding For Ysflight - Scenery EditorDocument92 pagesModding For Ysflight - Scenery Editordecaff_42No ratings yet
- Endovac BrochureDocument8 pagesEndovac BrochureGeorge MK100% (1)
- Chocolate From Cocoa - PPT 5.15Document21 pagesChocolate From Cocoa - PPT 5.15Sandhya ArulNo ratings yet