Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M M Average Translational KE Per Molecule
M M Average Translational KE Per Molecule
Uploaded by
jonas ho0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document discusses gas laws and the kinetic theory of gases. It defines gas pressure and introduces Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, and the combined gas law. The ideal gas law relates pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas. The kinetic theory of gases is based on assumptions about gas molecules being in random motion and collisions being elastic. The kinetic theory equation relates pressure, volume, number of moles, and average molecular kinetic energy.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses gas laws and the kinetic theory of gases. It defines gas pressure and introduces Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, and the combined gas law. The ideal gas law relates pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas. The kinetic theory of gases is based on assumptions about gas molecules being in random motion and collisions being elastic. The kinetic theory equation relates pressure, volume, number of moles, and average molecular kinetic energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageM M Average Translational KE Per Molecule
M M Average Translational KE Per Molecule
Uploaded by
jonas hoThis document discusses gas laws and the kinetic theory of gases. It defines gas pressure and introduces Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, and the combined gas law. The ideal gas law relates pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas. The kinetic theory of gases is based on assumptions about gas molecules being in random motion and collisions being elastic. The kinetic theory equation relates pressure, volume, number of moles, and average molecular kinetic energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
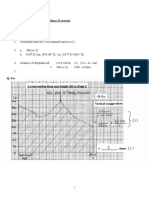
1.
Gas pressure (unit: Pa)
- P = F/A (force is perpendicular to the contact area)
2. Gas Laws
- Boyle’s Law: fixed T and m: pv=pv
- Pressure law: fixed V and m: P/T = P/T
- Charle’s law: V/T = V/T
→ pV/T = pV/T
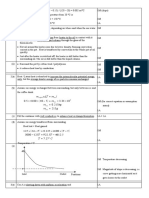
3. Ideal gas law
- pV = nRT
● *use SI units: p(Pa), V(m^3), T (K)*
- Gas that obeys ideal gas law → ideal gas; gas that doesn’t obey ideal gas law → real
gas
- Good ideal gas approximation when the gas is at high temperature and low pressure
4. Kinetic theory
- Assumptions
● The gas consists of a huge number of gas molecules and the molecules are in random
motion
● The size of each gas molecule is very small, so it can be neglected
● The gas molecules are far apart, so the interaction between them can be neglected
● The gas molecules are far apart, so the interaction between them can be neglected
● The collisions between gas molecules and the wall of the container are elastic
● The collision time is negligible compared with the time between collisions
● The effect of gravity is negligible
- Kinetic theory equation: pV = ⅓ Nm<v^2>
- Average translational KE per mole = Avogadro’s constant X ½ m<v^2> - 3/2 RT (m =
mass a gas molecule, ½ m<v^2> = average translational KE per molecule)
4. Mechanical model of a gas
You might also like
- F.3 First Term Revision Exercise For Christmas ANSDocument3 pagesF.3 First Term Revision Exercise For Christmas ANSjonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 Final Exam 11-12Document23 pagesF3 Final Exam 11-12jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Form Three Final Examination 2010-2011 Biology Question-Answer SheetsDocument15 pagesForm Three Final Examination 2010-2011 Biology Question-Answer Sheetsjonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 Final Exam 11-12 AnsDocument20 pagesF3 Final Exam 11-12 Ansjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 11 Ideal GasesDocument47 pages11 Ideal Gaseslc1999227No ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORYDocument6 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORYRitu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Topic 15 Ideal Gases - CAIE Physics A-LevelDocument5 pagesNotes - Topic 15 Ideal Gases - CAIE Physics A-LevelGulwarina SaleemNo ratings yet
- KINETICDocument6 pagesKINETICSahil baggaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument6 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesSecret SantaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Kinetic Theory of GasDocument41 pagesChapter 8 Kinetic Theory of GasHarry JakeNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Kinetic Theory of GaesDocument7 pagesCH 13 Kinetic Theory of GaeskhwaishwalterNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument46 pagesIdeal Gasesrameesa sufiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document21 pagesLecture 2Joe ParkNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSDocument6 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSSk ShivamNo ratings yet
- Ch01-Slides-1 Gas LawsDocument60 pagesCh01-Slides-1 Gas LawsDoreen BenezethNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Sayed Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Gases After-Lecture-NoteDocument30 pagesChapter 9 Gases After-Lecture-NoteElvis ChanNo ratings yet
- Part 4: Gases Ideal Gas LawDocument7 pagesPart 4: Gases Ideal Gas LawdtjjyyhjtfyNo ratings yet
- 2-Real Gases LectureDocument38 pages2-Real Gases Lecturemahmoud50% (2)
- Gaseous State: Ideal GasesDocument13 pagesGaseous State: Ideal GasesM.S.A. Mobashwer HossenNo ratings yet
- Class-11 Chemistry Chapter-5 States of Matter Part-IIDocument7 pagesClass-11 Chemistry Chapter-5 States of Matter Part-IINevin ShajiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectdarshna100% (5)
- Revision Notes On Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Kinetic Theory of Gasesvermarashmi2780No ratings yet
- CHM 111 - States of MatterDocument81 pagesCHM 111 - States of MatterBABATIMILEYIN OLLANo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry 01 2015 1stDocument33 pagesPhysical Chemistry 01 2015 1stAzkha AvicenaNo ratings yet
- 13 Kinetic Theory of Gases - 231221 - 212353Document4 pages13 Kinetic Theory of Gases - 231221 - 212353Shlok MishraNo ratings yet
- Heat FinalDocument14 pagesHeat Finalapi-231880547No ratings yet
- CH 10 Gases StudentDocument48 pagesCH 10 Gases StudentTrọng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- List of ContentDocument5 pagesList of Contenthassanmasud hassanNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Pressure: Chapter 5: GasesDocument4 pages5.1 Pressure: Chapter 5: GasesSam ChungNo ratings yet
- 2 Vacuum TechnologyDocument71 pages2 Vacuum TechnologyyounessNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document16 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!DineshNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of Gases CH13Document17 pagesKinetic Theory of Gases CH13Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Theory of GasesDocument11 pagesKinematic Theory of GasesShlok MishraNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws and Kinetic TheoryDocument14 pagesGas Laws and Kinetic Theorybrianouko25No ratings yet
- 3.3. Kinetic TheoryDocument7 pages3.3. Kinetic TheorySumia QuashieNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Aim: The Foundation of Everyday Engineering Aerodynamics WorkDocument27 pagesIntroduction: Aim: The Foundation of Everyday Engineering Aerodynamics WorkJarief Safawat FarabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 18 PDFSarah MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of An Ideal GASDocument45 pagesKinetic Theory of An Ideal GASTâm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Prepared by N.C. PomalDocument40 pagesPrepared by N.C. PomalNandan PomalNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument12 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasesvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- XI Phy Ch12 Kinetic Theory Chapter NotesDocument2 pagesXI Phy Ch12 Kinetic Theory Chapter NotesGokul Vijayan100% (3)
- Low Pressure Effusion of GasesDocument10 pagesLow Pressure Effusion of Gasesglen-576661No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument46 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesRosmaya MokhtarNo ratings yet
- School of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Document4 pagesSchool of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Francisco De León-Sotelo EstebanNo ratings yet
- For 2nd Year CK&EC Chapter 4 Final PDFDocument51 pagesFor 2nd Year CK&EC Chapter 4 Final PDFbahru demekeNo ratings yet
- Phy 9 PDFDocument14 pagesPhy 9 PDFDAKSHPREET17No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document46 pagesChapter 10Parth GandhiNo ratings yet
- For Chapter 444 ForDocument94 pagesFor Chapter 444 FortizitaNo ratings yet
- Revised States of MatterDocument82 pagesRevised States of MatterGaurav PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument4 pagesLab ReportIoana PinzaruNo ratings yet
- CHP3 Hysical States of MatterDocument45 pagesCHP3 Hysical States of Matternasec38602No ratings yet
- 3.2 Modelling A Gas - NewDocument58 pages3.2 Modelling A Gas - NewUlung Gondo Kusumo KhoeNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Ideal GasesDocument22 pages4.1 Ideal GasesAnonymous o97HYLpe0No ratings yet
- One Mark Questions:: SBMJC, VV Puram Department of Physics ND Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument3 pagesOne Mark Questions:: SBMJC, VV Puram Department of Physics ND Kinetic Theory of GasesAryan SaiNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Chapter 5Document6 pagesZumdahl Chapter 5drzachcrossNo ratings yet
- 2 GasesDocument38 pages2 Gasesbaran.sarsinNo ratings yet
- SHS Gr.12 Chap 9Document23 pagesSHS Gr.12 Chap 9Cj NacarioNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Gas LawsDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Gas LawsAdamNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes 09 Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument14 pages11 Physics Notes 09 Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory of GasesAnu Radha100% (2)
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- F3 Deserts Exercise 2018-2019 (With Answers)Document5 pagesF3 Deserts Exercise 2018-2019 (With Answers)jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Form Three Final Examination 2010-2011 Biology Question-Answer SheetsDocument12 pagesForm Three Final Examination 2010-2011 Biology Question-Answer Sheetsjonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - WT Ans - Final - 110526Document14 pagesF3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - WT Ans - Final - 110526jonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 CHP 1, 3 Test (Ans)Document8 pagesF3 CHP 1, 3 Test (Ans)jonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - For Ss - Final - 110526Document13 pagesF3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - For Ss - Final - 110526jonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 Final Exam Feedback - 3ADocument37 pagesF3 Final Exam Feedback - 3Ajonas hoNo ratings yet
- F.3 17-18 1st Term Bio Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesF.3 17-18 1st Term Bio Exam Answersjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Answers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple ChoicesDocument13 pagesAnswers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple Choicesjonas hoNo ratings yet
- F.3 FeedbackDocument29 pagesF.3 Feedbackjonas hoNo ratings yet
- F.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV ShortDocument2 pagesF.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV Shortjonas hoNo ratings yet
- P S CL K Ca: F3 First Term RevisionDocument6 pagesP S CL K Ca: F3 First Term Revisionjonas hoNo ratings yet
- F3 Chemistry Final Revision - 1617Document6 pagesF3 Chemistry Final Revision - 1617jonas hoNo ratings yet
- 13-14 F3 Geog 1st Term Exam (Answers)Document4 pages13-14 F3 Geog 1st Term Exam (Answers)jonas hoNo ratings yet
- 2009 - 2010 Form 3 First Term Exam: Cross-SectionDocument2 pages2009 - 2010 Form 3 First Term Exam: Cross-Sectionjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Form 3 Final ExaminationDocument23 pagesChemistry: Form 3 Final Examinationjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer For Form 3 Final Examination 2012Document3 pagesSuggested Answer For Form 3 Final Examination 2012jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question-Answer BookDocument16 pagesPhysics: Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer BookDocument15 pagesForm 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 2013 F3 Final Exam MSDocument3 pages2013 F3 Final Exam MSjonas hoNo ratings yet