Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010
Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010
Uploaded by
Jack TorresCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Management Consulting Club Casebook 2017-18 EditionDocument293 pagesManagement Consulting Club Casebook 2017-18 Editionshrmarcheline_641022No ratings yet
- Group 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFDocument24 pagesGroup 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFAnanditaKarNo ratings yet
- MexicocompetividadDocument2 pagesMexicocompetividadgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Greece: Key IndicatorsDocument1 pageGreece: Key Indicatorsapi-26143576No ratings yet
- ParaguayDocument2 pagesParaguaymalonso1234No ratings yet
- United States: Key IndicatorsDocument2 pagesUnited States: Key IndicatorsgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesPhilippines: Key Indicators, 2014alelie_germanNo ratings yet
- India: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesIndia: Key Indicators, 2014Gokul BaskerNo ratings yet
- Key Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesDocument2 pagesKey Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesluisrengNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesMalaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Rudy QuismorioNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesEgypt: Key Indicators, 2013Alhassan GamalNo ratings yet
- Switzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesSwitzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Dinu Maria-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesHonduras: Key Indicators, 2013Bladimir BastidaNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SDocument2 pagesIndonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SStefie Laimeheriwa KybernNo ratings yet
- QMS RequirementsDocument60 pagesQMS Requirementsvishwas salunkheNo ratings yet
- En WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessDocument196 pagesEn WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessPedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- En CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookDocument197 pagesEn CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookNhat Ngoc TrinhNo ratings yet
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDocument2 pages8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334No ratings yet
- EF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB6Document83 pagesEF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB6BharatNo ratings yet
- Cotton GinningDocument48 pagesCotton GinningTariq ShafiNo ratings yet
- Adventure TravelDocument35 pagesAdventure TravelArsimNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 - 2015Document41 pagesIso 9001 - 2015katyayini tembadmaniNo ratings yet
- Vision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportDocument198 pagesVision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportRyan RoweNo ratings yet
- Colombia GiiDocument1 pageColombia GiiDiana Yate VirguesNo ratings yet
- Work X Whitepaper V5Document47 pagesWork X Whitepaper V5ibrahimmohammed6702No ratings yet
- The Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2Document289 pagesThe Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2CRISTIAN MAURICIO GONZALES MURILLONo ratings yet
- CATALOG OF TECHNICAL STANDARDS FOR DIGITAL IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMS - Shared by WorldLine TechnologyDocument40 pagesCATALOG OF TECHNICAL STANDARDS FOR DIGITAL IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMS - Shared by WorldLine TechnologyRobert HaiNo ratings yet
- Booklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Document131 pagesBooklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Zamizan BNo ratings yet
- 2005 Evaluating and Improving WebsitesDocument56 pages2005 Evaluating and Improving WebsitesPantazis PastrasNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Final 2005Document56 pagesBusiness Plan Final 2005ryan pacinioNo ratings yet
- Iso 37120 2018Document15 pagesIso 37120 2018Anant PataniNo ratings yet
- International Mineral Property Valuation Standards TemplateDocument21 pagesInternational Mineral Property Valuation Standards TemplateVíctor Daniel QuispeNo ratings yet
- Supermarkets and Retail Shops PDFDocument45 pagesSupermarkets and Retail Shops PDFYusaf ButtNo ratings yet
- Mn7182 Report SampleDocument28 pagesMn7182 Report SampleDarshani KumariNo ratings yet
- Cak Strategic PlanDocument98 pagesCak Strategic PlanFednandNo ratings yet
- The Primary Drivers of Profitability Across The Digital ShelfDocument24 pagesThe Primary Drivers of Profitability Across The Digital ShelfAshick AliNo ratings yet
- Group 15 Merger ProposalDocument41 pagesGroup 15 Merger ProposalJohnny LamNo ratings yet
- Sai 2007 FrameworkDocument56 pagesSai 2007 FrameworkSuzanne Chang100% (1)
- Iso 22000 2018Document13 pagesIso 22000 2018Daniela Gerevini PereiraNo ratings yet
- BusinessPlan BangadBakeroBagongSikatBagongBuhay 2Document41 pagesBusinessPlan BangadBakeroBagongSikatBagongBuhay 2Clark WaganNo ratings yet
- A Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Diagnosis Module For Application in Value Chain Analysis (VCA)Document80 pagesA Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Diagnosis Module For Application in Value Chain Analysis (VCA)NatuvelaNo ratings yet
- The Eco-Marathon: Academic VersionDocument21 pagesThe Eco-Marathon: Academic Versionstevehead57No ratings yet
- June 2002: IMC Plan Pro®, IMC Planning Software Published by Palo Alto Software. Names, Locations andDocument31 pagesJune 2002: IMC Plan Pro®, IMC Planning Software Published by Palo Alto Software. Names, Locations andNiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Online Business Start ReportDocument41 pagesOnline Business Start ReportFazalur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Clean Energy Market Entry Project IndiaDocument133 pagesClean Energy Market Entry Project Indiaapurva_mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Entreperneurship ASM 3 FinalDocument25 pagesEntreperneurship ASM 3 Finalngongocquoc895No ratings yet
- CanineCritterCollege MPPDocument18 pagesCanineCritterCollege MPPMinh DuongNo ratings yet
- South Africa’s Renewable Energy IPP Procurement ProgramFrom EverandSouth Africa’s Renewable Energy IPP Procurement ProgramNo ratings yet
- BMI Vietnam Information Technology Report Q2 2014 PDFDocument84 pagesBMI Vietnam Information Technology Report Q2 2014 PDFBiểnLêNo ratings yet
- EF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB10Document76 pagesEF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB10Aaira TanveerNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFDocument61 pagesInnovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFripperblowes100% (3)
- 1490full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Investment Analysis & Portfolio Management All ChapterDocument43 pages1490full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Investment Analysis & Portfolio Management All Chapterkhanzizyri100% (6)
- Supply Chain Energy Efficiency Through Iso 50001 How Guide Your Company enDocument56 pagesSupply Chain Energy Efficiency Through Iso 50001 How Guide Your Company enalan_smoNo ratings yet
- Dry Cleaners and Laundry ServicesDocument47 pagesDry Cleaners and Laundry Servicessohaibmuzaffar007100% (1)
- Food and Beverages Sector PDFDocument126 pagesFood and Beverages Sector PDFsamydudeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Iso 9001:2008 HandbookDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Iso 9001:2008 HandbookRavi GeepunNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12From EverandEvaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12No ratings yet
- Some Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandFrom EverandSome Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandNo ratings yet
Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010
Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010
Uploaded by
Jack TorresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010
Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010
Uploaded by
Jack TorresCopyright:
Available Formats
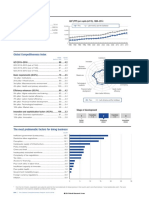
Colombia
2.1: Country/Economy Profiles
Key indicators, 2010
GDP (PPP) per capita (int’l $), 1985–2010
Population (millions).................................................46.3
GDP (US$ billions)...................................................285.5 Colombia Latin America and the Caribbean
12,000
GDP per capita (US$) .............................................6,273
10,000
GDP (PPP) as share (%) of world total..................0.58
8,000
6,000
4,000
2,000
1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010
Global Competitiveness Index
Rank Score Stage of development
(out of 142) (1–7)
GCI 2011–2012 ........................................................ 68......4.2 Transition Transition
1 1–2 2 2–3 3
GCI 2010–2011 (out of 139)..................................................68........ 4.1
GCI 2009–2010 (out of 133)..................................................69........ 4.1 Factor Efficiency Innovation
driven driven driven
Basic requirements (40.0%)...............................................73........ 4.5
Institutions...........................................................................100........ 3.5
Institutions
Infrastructure........................................................................85........ 3.7 7
Macroeconomic environment ...........................................42........ 5.2 Innovation Infrastructure
6
Health and primary education...........................................78........ 5.6 5
Business Macroeconomic
4
Efficiency enhancers (50.0%)............................................60........ 4.1 sophistication environment
150 3
Higher education and training...........................................60........ 4.3
2 Health and
Goods market efficiency.....................................................99........ 3.9 Market size 1 primary
Labor market efficiency......................................................88........ 4.1 education
Financial market development ..........................................68........ 4.1
Technological readiness.....................................................75........ 3.6 Technological Higher education
Market size ...........................................................................32........ 4.6 readiness and training
Innovation and sophistication factors (10.0%) ..............56........ 3.7 Financial market Goods market
development efficiency
Business sophistication .....................................................61........ 4.0
Labor market efficiency
Innovation..............................................................................57........ 3.3
Colombia Efficiency-driven economies
The most problematic factors for doing business
Corruption..............................................................................18.0
Inadequate supply of infrastructure.................................12.1
Inefficient government bureaucracy................................10.6
Access to financing.............................................................10.1
Tax rates ..................................................................................9.0
Crime and theft.......................................................................7.5
Restrictive labor regulations................................................7.3
Inadequately educated workforce .....................................5.9
Tax regulations .......................................................................5.5
Inflation....................................................................................4.0
Foreign currency regulations ..............................................3.9
Policy instability .....................................................................2.8
Poor work ethic in national labor force.............................1.8
Poor public health..................................................................0.7
Government instability/coups..............................................0.5
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Percent of responses
Note: From a list of 15 factors, respondents were asked to select the five most problematic for doing business in their country and to rank them between
1 (most problematic) and 5. The bars in the figure show the responses weighted according to their rankings.
The Global Competitiveness Report 2011-2012 © 2011 World Economic Forum
Colombia
2.1: Country/Economy Profiles
The Global Competitiveness Index in detail
INDICATOR VALUE RANK/142 INDICATOR VALUE RANK/142
1st pillar: Institutions 6th pillar: Goods market efficiency
1.01 Property rights....................................................... 3.9 ............87 6.01 Intensity of local competition................................ 4.6 ............85
1.02 Intellectual property protection ............................. 3.2 ............86 6.02 Extent of market dominance................................. 3.4 ............94
1.03 Diversion of public funds ...................................... 2.5 .......... 118 6.03 Effectiveness of anti-monopoly policy................... 3.8 ............81
1.04 Public trust of politicians ....................................... 2.4 ............84 6.04 Extent and effect of taxation................................. 2.9 .......... 120
1.05 Irregular payments and bribes .............................. 3.6 ............89 6.05 Total tax rate, % profits*..................................... 78.7 .......... 135
1.06 Judicial independence........................................... 3.5 ............81 6.06 No. procedures to start a business*........................ 9 ............94
1.07 Favoritism in decisions of government officials .... 2.6 ............99 6.07 No. days to start a business* ................................ 14 ............58
1.08 Wastefulness of government spending ................ 2.9 ............89 6.08 Agricultural policy costs ........................................ 3.5 ............99
1.09 Burden of government regulation ......................... 2.9 .......... 100 6.09 Prevalence of trade barriers .................................. 4.0 ...........110
1.10 Efficiency of legal framework in settling disputes 3.3 ............88 6.10 Trade tariffs, % duty*........................................... 11.2 .......... 118
1.11 Efficiency of legal framework in challenging regs. 3.4 ............78 6.11 Prevalence of foreign ownership........................... 4.6 ............77
1.12 Transparency of government policymaking........... 4.3 ............65 6.12 Business impact of rules on FDI........................... 4.6 ............69
1.13 Business costs of terrorism .................................. 2.9 .......... 142 6.13 Burden of customs procedures ............................ 4.0 ............80
1.14 Business costs of crime and violence .................. 2.8 .......... 133 6.14 Imports as a percentage of GDP* ....................... 17.1 .......... 138
1.15 Organized crime .................................................... 2.7 .......... 138 6.15 Degree of customer orientation............................ 5.2 ............30
1.16 Reliability of police services.................................. 4.3 ............64 6.16 Buyer sophistication.............................................. 3.7 ............49
1.17 Ethical behavior of firms ....................................... 3.7 ............87
1.18 Strength of auditing and reporting standards ....... 4.4 ............80 7th pillar: Labor market efficiency
1.19 Efficacy of corporate boards ................................. 4.6 ............66 7.01 Cooperation in labor-employer relations................ 4.6 ............48
1.20 Protection of minority shareholders’ interests...... 4.1 ............75 7.02 Flexibility of wage determination .......................... 5.2 ............69
1.21 Strength of investor protection, 0–10 (best)* ....... 8.3 ..............5 7.03 Rigidity of employment index, 0–100 (worst)* ... 10.0 ............19
7.04 Hiring and firing practices ..................................... 3.9 ............67
2nd pillar: Infrastructure 7.05 Redundancy costs, weeks of salary* .................... 59 ............98
2.01 Quality of overall infrastructure ............................. 3.6 ............95 7.06 Pay and productivity .............................................. 3.6 ............94
2.02 Quality of roads..................................................... 2.9 .......... 108 7.07 Reliance on professional management ................. 4.2 ............72
2.03 Quality of railroad infrastructure.............................1.7 ............99 7.08 Brain drain ............................................................. 3.3 ............69
2.04 Quality of port infrastructure................................. 3.4 .......... 109 7.09 Women in labor force, ratio to men*.................. 0.55 .......... 122
2.05 Quality of air transport infrastructure .................... 4.1 ............94
2.06 Available airline seat kms/week, millions* ........ 464.4 ............39 8th pillar: Financial market development 151
2.07 Quality of electricity supply................................... 5.2 ............57 8.01 Availability of financial services............................. 4.6 ............65
2.08 Fixed telephone lines/100 pop.* ......................... 14.7 ............82 8.02 Affordability of financial services .......................... 4.0 ............77
2.09 Mobile telephone subscriptions/100 pop.* ......... 93.8 ............78 8.03 Financing through local equity market .................. 3.7 ............59
8.04 Ease of access to loans ........................................ 3.2 ............40
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic environment 8.05 Venture capital availability ..................................... 2.9 ............49
3.01 Government budget balance, % GDP*................ -2.8 ............56 8.06 Soundness of banks.............................................. 5.6 ............42
3.02 Gross national savings, % GDP* ........................ 19.3 ............79 8.07 Regulation of securities exchanges....................... 3.7 .......... 101
3.03 Inflation, annual % change*.................................. 2.3 ..............1 8.08 Legal rights index, 0–10 (best)* ............................ 5.0 ............ 76
3.04 Interest rate spread, %* ....................................... 5.7 ............ 74
3.05 General government debt, % GDP* ................... 36.5 ............56 9th pillar: Technological readiness
3.06 Country credit rating, 0–100 (best)* ................... 58.4 ............55 9.01 Availability of latest technologies .......................... 4.8 ............78
9.02 Firm-level technology absorption .......................... 4.6 ............83
4th pillar: Health and primary education 9.03 FDI and technology transfer.................................. 4.8 ............59
4.01 Business impact of malaria ................................... 5.2 ............96 9.04 Internet users/100 pop.*..................................... 36.5 ............70
4.02 Malaria cases/100,000 pop.* ............................ 896.3 .......... 106 9.05 Broadband Internet subscriptions/100 pop.* ........ 5.7 ............66
4.03 Business impact of tuberculosis ........................... 5.0 ............84 9.06 Internet bandwidth, kb/s/capita*........................... 3.7 ............70
4.04 Tuberculosis incidence/100,000 pop.* ................ 35.0 ............60
4.05 Business impact of HIV/AIDS ............................... 4.6 ............98 10th pillar: Market size
4.06 HIV prevalence, % adult pop.* ............................. 0.5 ............88 10.01 Domestic market size index, 1–7 (best)*.............. 4.6 ............28
4.07 Infant mortality, deaths/1,000 live births*........... 16.2 ............73 10.02 Foreign market size index, 1–7 (best)* ................. 4.7 ............57
4.08 Life expectancy, years*....................................... 73.2 ............72
4.09 Quality of primary education................................. 3.6 ............80 11th pillar: Business sophistication
4.10 Primary education enrollment, net %* ............... 89.6 .......... 100 11.01 Local supplier quantity .......................................... 4.8 ............66
11.02 Local supplier quality............................................. 4.9 ............45
5th pillar: Higher education and training 11.03 State of cluster development................................ 4.1 ............39
5.01 Secondary education enrollment, gross %*....... 94.6 ............47 11.04 Nature of competitive advantage .......................... 3.2 ............80
5.02 Tertiary education enrollment, gross %* .............37.0 ............64 11.05 Value chain breadth ............................................... 3.7 ............62
5.03 Quality of the educational system ........................ 3.7 ............72 11.06 Control of international distribution....................... 4.2 ............53
5.04 Quality of math and science education ................ 3.7 ............83 11.07 Production process sophistication ........................ 3.7 ............65
5.05 Quality of management schools ........................... 4.4 ............53 11.08 Extent of marketing............................................... 3.8 ............80
5.06 Internet access in schools..................................... 4.1 ............68 11.09 Willingness to delegate authority ......................... 3.9 ............49
5.07 Availability of research and training services ........ 4.1 ............70
5.08 Extent of staff training .......................................... 3.7 ............84 12th pillar: Innovation
12.01 Capacity for innovation.......................................... 3.2 ............59
12.02 Quality of scientific research institutions .............. 3.6 ............69
12.03 Company spending on R&D.................................. 3.0 ............ 76
12.04 University-industry collaboration in R&D............... 4.1 ............43
12.05 Gov’t procurement of advanced tech products..... 4.0 ............45
12.06 Availability of scientists and engineers ................. 4.0 ............77
12.07 Utility patents granted/million pop.* ..................... 0.1 ............ 76
Notes: Values are on a 1-to-7 scale unless otherwise annotated with an asterisk (*). For further details and explanation, please refer to the section “How to
Read the Country/Economy Profiles” on page 89.
The Global Competitiveness Report 2011-2012 © 2011 World Economic Forum
You might also like
- Management Consulting Club Casebook 2017-18 EditionDocument293 pagesManagement Consulting Club Casebook 2017-18 Editionshrmarcheline_641022No ratings yet
- Group 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFDocument24 pagesGroup 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFAnanditaKarNo ratings yet
- MexicocompetividadDocument2 pagesMexicocompetividadgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Greece: Key IndicatorsDocument1 pageGreece: Key Indicatorsapi-26143576No ratings yet
- ParaguayDocument2 pagesParaguaymalonso1234No ratings yet
- United States: Key IndicatorsDocument2 pagesUnited States: Key IndicatorsgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesPhilippines: Key Indicators, 2014alelie_germanNo ratings yet
- India: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesIndia: Key Indicators, 2014Gokul BaskerNo ratings yet
- Key Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesDocument2 pagesKey Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesluisrengNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesMalaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Rudy QuismorioNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesEgypt: Key Indicators, 2013Alhassan GamalNo ratings yet
- Switzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesSwitzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Dinu Maria-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesHonduras: Key Indicators, 2013Bladimir BastidaNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SDocument2 pagesIndonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SStefie Laimeheriwa KybernNo ratings yet
- QMS RequirementsDocument60 pagesQMS Requirementsvishwas salunkheNo ratings yet
- En WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessDocument196 pagesEn WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessPedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- En CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookDocument197 pagesEn CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookNhat Ngoc TrinhNo ratings yet
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDocument2 pages8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334No ratings yet
- EF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB6Document83 pagesEF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB6BharatNo ratings yet
- Cotton GinningDocument48 pagesCotton GinningTariq ShafiNo ratings yet
- Adventure TravelDocument35 pagesAdventure TravelArsimNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 - 2015Document41 pagesIso 9001 - 2015katyayini tembadmaniNo ratings yet
- Vision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportDocument198 pagesVision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportRyan RoweNo ratings yet
- Colombia GiiDocument1 pageColombia GiiDiana Yate VirguesNo ratings yet
- Work X Whitepaper V5Document47 pagesWork X Whitepaper V5ibrahimmohammed6702No ratings yet
- The Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2Document289 pagesThe Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2CRISTIAN MAURICIO GONZALES MURILLONo ratings yet
- CATALOG OF TECHNICAL STANDARDS FOR DIGITAL IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMS - Shared by WorldLine TechnologyDocument40 pagesCATALOG OF TECHNICAL STANDARDS FOR DIGITAL IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMS - Shared by WorldLine TechnologyRobert HaiNo ratings yet
- Booklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Document131 pagesBooklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Zamizan BNo ratings yet
- 2005 Evaluating and Improving WebsitesDocument56 pages2005 Evaluating and Improving WebsitesPantazis PastrasNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Final 2005Document56 pagesBusiness Plan Final 2005ryan pacinioNo ratings yet
- Iso 37120 2018Document15 pagesIso 37120 2018Anant PataniNo ratings yet
- International Mineral Property Valuation Standards TemplateDocument21 pagesInternational Mineral Property Valuation Standards TemplateVíctor Daniel QuispeNo ratings yet
- Supermarkets and Retail Shops PDFDocument45 pagesSupermarkets and Retail Shops PDFYusaf ButtNo ratings yet
- Mn7182 Report SampleDocument28 pagesMn7182 Report SampleDarshani KumariNo ratings yet
- Cak Strategic PlanDocument98 pagesCak Strategic PlanFednandNo ratings yet
- The Primary Drivers of Profitability Across The Digital ShelfDocument24 pagesThe Primary Drivers of Profitability Across The Digital ShelfAshick AliNo ratings yet
- Group 15 Merger ProposalDocument41 pagesGroup 15 Merger ProposalJohnny LamNo ratings yet
- Sai 2007 FrameworkDocument56 pagesSai 2007 FrameworkSuzanne Chang100% (1)
- Iso 22000 2018Document13 pagesIso 22000 2018Daniela Gerevini PereiraNo ratings yet
- BusinessPlan BangadBakeroBagongSikatBagongBuhay 2Document41 pagesBusinessPlan BangadBakeroBagongSikatBagongBuhay 2Clark WaganNo ratings yet
- A Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Diagnosis Module For Application in Value Chain Analysis (VCA)Document80 pagesA Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Diagnosis Module For Application in Value Chain Analysis (VCA)NatuvelaNo ratings yet
- The Eco-Marathon: Academic VersionDocument21 pagesThe Eco-Marathon: Academic Versionstevehead57No ratings yet
- June 2002: IMC Plan Pro®, IMC Planning Software Published by Palo Alto Software. Names, Locations andDocument31 pagesJune 2002: IMC Plan Pro®, IMC Planning Software Published by Palo Alto Software. Names, Locations andNiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Online Business Start ReportDocument41 pagesOnline Business Start ReportFazalur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Clean Energy Market Entry Project IndiaDocument133 pagesClean Energy Market Entry Project Indiaapurva_mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Entreperneurship ASM 3 FinalDocument25 pagesEntreperneurship ASM 3 Finalngongocquoc895No ratings yet
- CanineCritterCollege MPPDocument18 pagesCanineCritterCollege MPPMinh DuongNo ratings yet
- South Africa’s Renewable Energy IPP Procurement ProgramFrom EverandSouth Africa’s Renewable Energy IPP Procurement ProgramNo ratings yet
- BMI Vietnam Information Technology Report Q2 2014 PDFDocument84 pagesBMI Vietnam Information Technology Report Q2 2014 PDFBiểnLêNo ratings yet
- EF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB10Document76 pagesEF4B HDT Sectors MFG EoD IPR MSME PCB10Aaira TanveerNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFDocument61 pagesInnovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFripperblowes100% (3)
- 1490full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Investment Analysis & Portfolio Management All ChapterDocument43 pages1490full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Investment Analysis & Portfolio Management All Chapterkhanzizyri100% (6)
- Supply Chain Energy Efficiency Through Iso 50001 How Guide Your Company enDocument56 pagesSupply Chain Energy Efficiency Through Iso 50001 How Guide Your Company enalan_smoNo ratings yet
- Dry Cleaners and Laundry ServicesDocument47 pagesDry Cleaners and Laundry Servicessohaibmuzaffar007100% (1)
- Food and Beverages Sector PDFDocument126 pagesFood and Beverages Sector PDFsamydudeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Iso 9001:2008 HandbookDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Iso 9001:2008 HandbookRavi GeepunNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12From EverandEvaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12No ratings yet
- Some Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandFrom EverandSome Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandNo ratings yet