Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Description: Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE)
Description: Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE)
Uploaded by
Yaho HosCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Polyols & Aspartics For Reaction With Polyisocyanates Nonreactive ResinsDocument32 pagesPolyols & Aspartics For Reaction With Polyisocyanates Nonreactive Resinssriatul2006No ratings yet
- DIAGRID WAFFLE SLAB-Layout1Document1 pageDIAGRID WAFFLE SLAB-Layout1shriya joshi100% (3)
- Electrode Selection Excel SheetDocument1 pageElectrode Selection Excel Sheetchandrakit047No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Exercice Au ChoixDocument6 pagesStainless Steel Exercice Au ChoixFabrice Haoulassa HamanNo ratings yet
- BIOMATERIALDocument6 pagesBIOMATERIALXabier LázaroNo ratings yet
- NaturalDocument2 pagesNaturalLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Epoxy Jeren LegiDocument2 pagesEpoxy Jeren Legimerlin margridNo ratings yet
- Epoxy (Glass Filler) : GeneralDocument2 pagesEpoxy (Glass Filler) : Generalmerlin margridNo ratings yet
- Poli MeroDocument3 pagesPoli MeroLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- PEPolyethylene20 30GlassFilledDocument3 pagesPEPolyethylene20 30GlassFilledshizu monNo ratings yet
- Description: LeatherDocument6 pagesDescription: LeatherTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- MetalDocument3 pagesMetalLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- CES ExerciseDocument49 pagesCES ExerciseDing HangNo ratings yet
- CeramicoDocument3 pagesCeramicoLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Description: LeatherDocument6 pagesDescription: LeatherTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- Description: Hardwood: Oak, Along GrainDocument7 pagesDescription: Hardwood: Oak, Along GrainTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- Description: Polystyrene (PS)Document5 pagesDescription: Polystyrene (PS)Murilo SanchesNo ratings yet
- Bronze Data SheetDocument3 pagesBronze Data SheetAnonymous xkKyD8fBouNo ratings yet
- Technical Data of Adtech Fluoroplastic Polymers: Servicios E Importaciones Especializadas S.A. de C.VDocument1 pageTechnical Data of Adtech Fluoroplastic Polymers: Servicios E Importaciones Especializadas S.A. de C.VEdgar LucianoNo ratings yet
- Typical Engineering Properties of High Density Polyethylene: General Properties English Units SI UnitsDocument2 pagesTypical Engineering Properties of High Density Polyethylene: General Properties English Units SI UnitsAnil AmrawanshiNo ratings yet
- Description: ImageDocument4 pagesDescription: ImageTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- CES Selector Acrylobutadienestyrene (ABS) - High Impact: GeneralDocument1 pageCES Selector Acrylobutadienestyrene (ABS) - High Impact: GeneralCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: (BR) (WR-2) (Special F)Document1 pageTechnical Information: (BR) (WR-2) (Special F)johnNo ratings yet
- Aisi 4140 (0.40% C)Document5 pagesAisi 4140 (0.40% C)BernardoNo ratings yet
- Ppte Acier Fiablement AllierDocument3 pagesPpte Acier Fiablement AllierConception & Fabrication MécaniqueNo ratings yet
- 1 Wa-Catalog9Document1 page1 Wa-Catalog9johnNo ratings yet
- SYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer: Features & Benefits ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer: Features & Benefits ApplicationsZhan FangNo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector Low Alloy SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector Low Alloy SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- AISI 410: Stainless Steel, Martensitic, AISI 410S, Wrought, AnnealedDocument4 pagesAISI 410: Stainless Steel, Martensitic, AISI 410S, Wrought, AnnealedLinus LooNo ratings yet
- 1 Wa-Catalog13Document1 page1 Wa-Catalog13johnNo ratings yet
- TDS SW 901 3Document5 pagesTDS SW 901 3Frans Hendra WinartaNo ratings yet
- Brief Introduction of UHMWPEDocument3 pagesBrief Introduction of UHMWPEFatima NusserNo ratings yet
- Devcon Plastic Steel Putty ADocument3 pagesDevcon Plastic Steel Putty AAZLAN ABDULLAINo ratings yet
- Acero Medio CDocument1 pageAcero Medio CCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector Medium Carbon SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector Medium Carbon SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Properties of Common Optical Polymers: F D C DDocument1 pageProperties of Common Optical Polymers: F D C DHugo MakNo ratings yet
- Epofine 740 - Finehard 5200Document4 pagesEpofine 740 - Finehard 5200Karishma PrabhuNo ratings yet
- UHMW Mechanical Properties: Comparison of Dynamic Coefficient of Friction On Polished SteelDocument4 pagesUHMW Mechanical Properties: Comparison of Dynamic Coefficient of Friction On Polished SteeldangdinhthyNo ratings yet
- 410 Tech DataDocument1 page410 Tech DataAbraham FernandezNo ratings yet
- HT Swancor 901-Pt-Ve-30Document3 pagesHT Swancor 901-Pt-Ve-30Fernando Cesar PérezNo ratings yet
- Inox 316 L: (Stainless Steel, Austenitic, AISI 316L, Annealed)Document3 pagesInox 316 L: (Stainless Steel, Austenitic, AISI 316L, Annealed)Hamid AZZOUZINo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector High Carbon SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector High Carbon SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- CES Selector Wrought Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steel: GeneralDocument1 pageCES Selector Wrought Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steel: GeneralCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Alloy 410s Spec SheetDocument2 pagesAlloy 410s Spec SheetALONSO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector Low Carbon SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector Low Carbon SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Acero Bajo CDocument1 pageAcero Bajo CCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- TOTAL Polystyrene 1441: Material DatasheetDocument3 pagesTOTAL Polystyrene 1441: Material DatasheetAlbert FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Encapsulants and Impregnation Resins For E-Motor: Advanced MaterialsDocument2 pagesEncapsulants and Impregnation Resins For E-Motor: Advanced Materialsمحمد مقلدNo ratings yet
- Alloy 410S Spec SheetDocument2 pagesAlloy 410S Spec SheetPrakash SundharamNo ratings yet
- 11 3508 01 Dowsil Ei 1184 Optical EncapsulantDocument5 pages11 3508 01 Dowsil Ei 1184 Optical Encapsulantyusuf KhanNo ratings yet
- Hojas TécnicasDocument2 pagesHojas TécnicasalejandrocharlescollNo ratings yet
- Bronze Putty: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesBronze Putty: Technical Data SheetSharad ShahNo ratings yet
- Pei 0270 RTP 2183Document2 pagesPei 0270 RTP 2183Vincent NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers: (Use The Table in The PPT As Your Guide in Accomplishing Table 1.)Document8 pagesChemistry For Engineers: (Use The Table in The PPT As Your Guide in Accomplishing Table 1.)Aivan Lloyd CapuleNo ratings yet
- TeflonDocument1 pageTeflonSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition: ASTM B103Document1 pageChemical Composition: ASTM B103MarcoAntonioNo ratings yet
- Ecoalube642TDS PDFDocument2 pagesEcoalube642TDS PDFDkC gunsNo ratings yet
- Ineos Typical Engineering Properties of HdpeDocument3 pagesIneos Typical Engineering Properties of HdpePhát Lê TiếnNo ratings yet
- Morflo 170Document2 pagesMorflo 170baselNo ratings yet
- Rigid 10k DatasheetDocument2 pagesRigid 10k DatasheetAna Maria RodrigoNo ratings yet
- The Three P's of Safe Winter DrivingDocument1 pageThe Three P's of Safe Winter DrivingYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Finding Safety and Support ENGLISHDocument2 pagesFinding Safety and Support ENGLISHYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Office ErgonomicsDocument14 pagesOffice ErgonomicsYaho HosNo ratings yet
- SFTV Safety ManualDocument7 pagesSFTV Safety ManualYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Apitalisn't: The Sticky Side of Teflon: Kate Waldock Luigi ZingalesDocument13 pagesApitalisn't: The Sticky Side of Teflon: Kate Waldock Luigi ZingalesYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Meatpacking Workers InfectedDocument2 pagesMeatpacking Workers InfectedYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Ejaculation ProblemDocument4 pagesEjaculation ProblemYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Envelope Formats, Sizes & EnclosuresDocument2 pagesEnvelope Formats, Sizes & EnclosuresYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Not All Beach Muck Is Created Equal: Michigan State University ExtensionDocument2 pagesNot All Beach Muck Is Created Equal: Michigan State University ExtensionYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Lawns: On This PageDocument4 pagesLawns: On This PageYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Waste Disposal PolicyDocument2 pagesWaste Disposal PolicyYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Paperbag RRLDocument5 pagesPaperbag RRLDonita Gloria100% (2)
- Riopipeline2019 1112 FM 1112 FinalDocument10 pagesRiopipeline2019 1112 FM 1112 FinalMarcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- High Strength Low Alloy Structural SteelsDocument16 pagesHigh Strength Low Alloy Structural SteelsTuan DangNo ratings yet
- Fisa Tehnica Linoleum Natural MarmoretteDocument1 pageFisa Tehnica Linoleum Natural MarmoretteSurdu AncaNo ratings yet
- News JournalDocument3 pagesNews Journal4D25 LUXIMON AMELIA DIONNo ratings yet
- Co 0016 (In)Document2 pagesCo 0016 (In)Antonio Perez MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nullifire B270 - High Strength Compound: 1. Product DescriptionDocument4 pagesNullifire B270 - High Strength Compound: 1. Product Descriptionnewnse2008No ratings yet
- Refractor Storage RecommendationsDocument3 pagesRefractor Storage RecommendationsWael IsmaelNo ratings yet
- CDG Technical PresentationDocument26 pagesCDG Technical Presentationar desNo ratings yet
- Steel 4140Document116 pagesSteel 4140KarenMar DCNo ratings yet
- C Purlin Data SheetDocument6 pagesC Purlin Data SheetAkhil VNNo ratings yet
- CO2 FloodingDocument15 pagesCO2 FloodingUzumaki28No ratings yet
- Molecular Weight of Carbopol and PemulenDocument3 pagesMolecular Weight of Carbopol and PemulenMawarniNo ratings yet
- Soldering, Brazing & WeldingDocument52 pagesSoldering, Brazing & WeldingChandrakantha K100% (1)
- The Special Steel Book - V08.00.1119 - WEBDocument52 pagesThe Special Steel Book - V08.00.1119 - WEBkevin honiballNo ratings yet
- What Is AEROPERL® 300 Pharma Mesoporous Silica?Document3 pagesWhat Is AEROPERL® 300 Pharma Mesoporous Silica?Salman BasheerNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022Document22 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2022Rose RamisaNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Rates, Zone Contracts - General Building Works BHRDocument38 pagesSchedule of Rates, Zone Contracts - General Building Works BHRnadeeshlakmalNo ratings yet
- Aic Asf PQR 0120Document2 pagesAic Asf PQR 0120AHMED MEDANYNo ratings yet
- SECTION 15150 Sanitary Waste and Vent Piping Rev 0Document18 pagesSECTION 15150 Sanitary Waste and Vent Piping Rev 0mohamad damerlyNo ratings yet
- A1 Karanja Oil MSDSDocument3 pagesA1 Karanja Oil MSDSSahil VoraNo ratings yet
- Sika ViscoCrete-225 SDocument2 pagesSika ViscoCrete-225 SMajid AlzubadyNo ratings yet
- Restore /restore Plus Heavy-Duty Coolant Cleaners: The Safe and Efficient Way To Clean Heavy-Duty Cooling SystemsDocument2 pagesRestore /restore Plus Heavy-Duty Coolant Cleaners: The Safe and Efficient Way To Clean Heavy-Duty Cooling SystemsemezibNo ratings yet
- Birla Cellulose, TechnotexDocument43 pagesBirla Cellulose, Technotexsuresh_parmar_9No ratings yet
- Batik L3 CoCU-4 - Batik Contemporary (86-103)Document18 pagesBatik L3 CoCU-4 - Batik Contemporary (86-103)azman hilmiNo ratings yet
- Water LeakageDocument34 pagesWater LeakageKousalya Mk100% (2)
Description: Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE)
Description: Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE)
Uploaded by
Yaho HosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Description: Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE)
Description: Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE)
Uploaded by
Yaho HosCopyright:
Available Formats
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE) Page 1 of 6
Description
Image
Caption
PTFE is widely used for non-stick pans and spatulas. © Granta Design
The material
PTFE (Teflon) is a member of the fluoroplastic family, which includes chlorotrifluoroethylene, CTFE or CFE, polyvinyl
fluoride, PVF, and polyvinylidene fluoride PVF2. PTFE has exceptionally low friction, is water repellant, and extremely
stable. It was first commercialized in the late 1940's as Teflon. Non-stick cooking utensils (Tefal = Teflon coated
aluminum) exploiting its chemical inertness, its thermal stability and its non-wettability - the reason nothing sticks to
it. It is expensive as polymers go, but it is used in high-value applications (non-stick pans; Gore-Tex rain gear;
artificial arteries).
Composition (summary)
(CF2-CF2)n
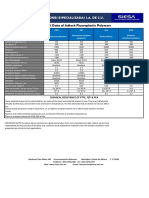
General properties
Density 134 - 137 lb/ft^3
Price * 6.71 - 7.67 USD/lb
Date first used 1938
Mechanical properties
Young's modulus 0.058 - 0.0801 10^6 psi
Shear modulus * 0.02 - 0.0276 10^6 psi
Bulk modulus 0.218 - 0.232 10^6 psi
Poisson's ratio 0.44 - 0.46
Yield s trength (elas tic limit) 2.18 - 3.63 ksi
Tensile strength 2.9 - 4.35 ksi
Compressive strength 2.39 - 3.99 ksi
Elongation 200 - 400 % strain
Hardness - Vickers 5.9 - 6.5 HV
Fatigue strength at 10^7 cycles 0.834 - 1.02 ksi
Values marked * are estimates.
No warranty is given for the accuracy of this data
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE) Page 2 of 6
Fracture toughness * 1.2 - 1.64 ksi.in^0.5
Mechanical loss coefficient (tan delta) * 0.0725 - 0.1
Thermal properties
Melting point 599 - 642 °F
Glass temperature 224 - 253 °F
Maximum service temperature 482 - 520 °F
Minimum service temperature * -442 - -424 °F
Thermal conductor or insulator? Good insulator
Thermal conductivity 0.14 - 0.151 BTU.ft/h.ft^2.F
Specific heat capacity * 0.242 - 0.252 BTU/lb.°F
Thermal expansion coefficient 70 - 120 µstrain/°F
Electrical properties
Electrical conductor or insulator? Good insulator
Electrical resistivity 3.3e23 - 3e24 µohm.cm
Dielectric constant (relative permittivity) 2.1 - 2.24
Dissipation factor (dielectric loss tangent) * 1.5e-4 - 2.5e-4
Dielectric strength (dielectric breakdown) 462 - 500 V/mil
Optical properties
Transparenc y Translucent
Refractive index 1.31 - 1.35
Critical Materials Risk
High critical material risk? No
Processability
Castability 1 - 2
Moldability 4
Machinability 3 - 4
Weldability 3 - 4
Durability: water and aqueous solutions
Water (fresh) Excellent
Water (salt) Excellent
Soils, acidic (peat) Excellent
Soils, alkaline (clay) Excellent
Wine Excellent
Durability: acids
Acetic acid (10%) Excellent
Values marked * are estimates.
No warranty is given for the accuracy of this data
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE) Page 3 of 6
Acetic acid (glacial) Excellent
Citric acid (10%) Excellent
Hydrochloric acid (10%) Excellent
Hydrochloric acid (36%) Excellent
Hydrofluoric acid (40%) Excellent
Nitric acid (10%) Excellent
Nitric acid (70%) Excellent
Phosphoric acid (10%) Excellent
Phosphoric acid (85%) Excellent
Sulfuric acid (10%) Excellent
Sulfuric acid (70%) Excellent
Durability: alkalis
Sodium hydroxide (10%) Excellent
Sodium hydroxide (60%) Excellent
Durability: fuels, oils and solvents
Amyl acetate Excellent
Benzene Excellent
Carbon tetrachloride Excellent
Chloroform Excellent
Crude oil Excellent
Diesel oil Excellent
Lubricating oil Excellent
Paraffin oil (kerosene) Excellent
Petrol (gasoline) Excellent
Silicone fluids Excellent
Toluene Excellent
Turpentine Excellent
Vegetable oils (general) Excellent
White spirit Excellent
Durability: alcohols, aldehydes, ketones
Acetaldehyde Excellent
Acetone Excellent
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Excellent
Ethylene glycol Excellent
Formaldehyde (40%) Excellent
Glycerol Excellent
Methyl alcohol (methanol) Excellent
Values marked * are estimates.
No warranty is given for the accuracy of this data
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE) Page 4 of 6
Durability: halogens and gases
Chlorine gas (dry) Excellent
Fluorine (gas) Excellent
O2 (oxygen gas) Acceptable
Sulfur dioxide (gas) Excellent
Durability: built environments
Industrial atmosphere Excellent
Rural atmosphere Excellent
Marine atmosphere Excellent
UV radiation (sunlight) Good
Durability: flammability
Flammability Non-flammable
Durability: thermal environments
Tolerance to cryogenic temperatures Excellent
Tolerance up to 150 C (302 F) Excellent
Tolerance up to 250 C (482 F) Excellent
Tolerance up to 450 C (842 F) Unacceptable
Tolerance up to 850 C (1562 F) Unacceptable
Tolerance above 850 C (1562 F) Unacceptable
Primary material production: energy, CO2 and water
Embodied energy, primary production * 1.17e4 - 1.3e4 kcal/lb
CO2 footprint, primary production * 5.69 - 6.29 lb/lb
Water usage * 52 - 57.5 gal(US)/lb
Eco-indicator 99 2.44e3 millipoints/kg
Material processing: energy
Polymer extrusion energy * 870 - 959 kcal/lb
Polymer molding energy * 2.24e3 - 2.47e3 kcal/lb
Coarse machining energy (per unit wt removed) * 57 - 63.1 kcal/lb
Fine machining energy (per unit wt removed) * 107 - 118 kcal/lb
Grinding energy (per unit wt removed) * 163 - 180 kcal/lb
Material processing: CO2 footprint
Polymer extrusion CO2 * 0.642 - 0.708 lb/lb
Polymer molding CO2 * 1.66 - 1.83 lb/lb
Coarse machining CO2 (per unit wt removed) * 0.0395 - 0.0436 lb/lb
Fine machining CO2 (per unit wt removed) * 0.0742 - 0.082 lb/lb
Values marked * are estimates.
No warranty is given for the accuracy of this data
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE) Page 5 of 6
Grinding CO2 (per unit wt removed) * 0.113 - 0.125 lb/lb
Material recycling: energy, CO2 and recycle fraction
Recycle
Embodied energy, recycling * 3.02e3 - 3.35e3 kcal/lb
CO2 footprint, recycling * 2.2 - 2.43 lb/lb
Recycle fraction in current supply * 0.5 - 1 %
Downcycle
Combust for energy recovery
Heat of combustion (net) * 508 - 533 kcal/lb
Combustion CO2 * 0.859 - 0.903 lb/lb
Landfill
Biodegrade
Toxicity rating Non-toxic
A renewable resource?
Environmental notes
PTFE is non-flammable and FDA approved. Like all thermoplastics, simple PTFE can be recycled. But in making it
into non-stick surfaces, or in transforming it into Gore-Tex, additives are made which prevent further recycling.
Recycle mark
Supporting information
Design guidelines
PTFE is 2.7 times denser than polyethylene and 12 times more expensive. But it is much more resistant to chemical
attack; it can safely be used from -270 to + 250 C. It has remarkably low friction; and it has an exceptional ability to
resist wetting. All fluoroplastics are white, and to some degree, translucent. They give long-term resistance to attacks
of all sorts, including ultraviolet radiation. PTFE itself has a characteristically soft, waxy feel, partly because of the
low coefficient of friction. It is an excellent electrical insulator, with low dielectric loss. It can be "foamed" to give a
light, micro-porous film that rejects liquid water but allows water vapor to pass - the principle of Gore-Tex. The
mechanical properties of PTFE are not remarkable, but it can be made more abrasive resistant by filling with inert
ceramic and it can be reinforced with glass, nylon or Kevlar fibers to give a leather-like skin of exceptional toughness,
strength and weather-resistance (exploited in tensile roofs). Bonding PTFE is difficult; thermal or ultrasonic methods
are good; epoxy, nitrile-phenolic and silicone adhesives can be used. The use of Gore-Tex deriv atives in fabrics is
expanding, with new variants being developed. The pore size in these fabrics can be controlled to reject not merely
water, but bacteria, with potential for protective clothing for surgeons, and possibly against certain kinds of biological
weapons. PTFE itself has FDA approval. Its architectural use for dramatic, tent-like, roofing of large structures is
increasing.
Technical notes
Values marked * are estimates.
No warranty is given for the accuracy of this data
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTFE) Page 6 of 6
Fluorine is the most reactive of gasses, yet combined with carbon to form fluoropolymers and it becomes the most
stable of molecules, resistant to practically everything except excessive heat. Polytetrafluoroethylene, PTFE, the
simplest of these, is just polyethylene with all the hydrogens stripped off and replaced by fluorine: (-CF2)n. The others
are variants on this.
Typical uses
Wire and cable covers, high-quality insulating tape, corrosion resistant lining for pipes and valves, protective
coatings, seals and gaskets, low friction bearings and skis, transparent roofing and weather protection for other
polymers (e.g. ABS), non-stick cooking products, water repellent fabrics.
Tradenames
Aflas, Algoflon, Duroid, Dyneon, Fluon, Fluorel, Hostaflon TF, Polyflon, Soreflon, THV, Teflon, Tetraflon, Tetrafluor
Links
Reference
ProcessUniverse
Producers
Values marked * are estimates.
No warranty is given for the accuracy of this data
You might also like
- Polyols & Aspartics For Reaction With Polyisocyanates Nonreactive ResinsDocument32 pagesPolyols & Aspartics For Reaction With Polyisocyanates Nonreactive Resinssriatul2006No ratings yet
- DIAGRID WAFFLE SLAB-Layout1Document1 pageDIAGRID WAFFLE SLAB-Layout1shriya joshi100% (3)
- Electrode Selection Excel SheetDocument1 pageElectrode Selection Excel Sheetchandrakit047No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Exercice Au ChoixDocument6 pagesStainless Steel Exercice Au ChoixFabrice Haoulassa HamanNo ratings yet
- BIOMATERIALDocument6 pagesBIOMATERIALXabier LázaroNo ratings yet
- NaturalDocument2 pagesNaturalLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Epoxy Jeren LegiDocument2 pagesEpoxy Jeren Legimerlin margridNo ratings yet
- Epoxy (Glass Filler) : GeneralDocument2 pagesEpoxy (Glass Filler) : Generalmerlin margridNo ratings yet
- Poli MeroDocument3 pagesPoli MeroLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- PEPolyethylene20 30GlassFilledDocument3 pagesPEPolyethylene20 30GlassFilledshizu monNo ratings yet
- Description: LeatherDocument6 pagesDescription: LeatherTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- MetalDocument3 pagesMetalLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- CES ExerciseDocument49 pagesCES ExerciseDing HangNo ratings yet
- CeramicoDocument3 pagesCeramicoLivio EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Description: LeatherDocument6 pagesDescription: LeatherTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- Description: Hardwood: Oak, Along GrainDocument7 pagesDescription: Hardwood: Oak, Along GrainTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- Description: Polystyrene (PS)Document5 pagesDescription: Polystyrene (PS)Murilo SanchesNo ratings yet
- Bronze Data SheetDocument3 pagesBronze Data SheetAnonymous xkKyD8fBouNo ratings yet
- Technical Data of Adtech Fluoroplastic Polymers: Servicios E Importaciones Especializadas S.A. de C.VDocument1 pageTechnical Data of Adtech Fluoroplastic Polymers: Servicios E Importaciones Especializadas S.A. de C.VEdgar LucianoNo ratings yet
- Typical Engineering Properties of High Density Polyethylene: General Properties English Units SI UnitsDocument2 pagesTypical Engineering Properties of High Density Polyethylene: General Properties English Units SI UnitsAnil AmrawanshiNo ratings yet
- Description: ImageDocument4 pagesDescription: ImageTạ Minh Phương BảoNo ratings yet
- CES Selector Acrylobutadienestyrene (ABS) - High Impact: GeneralDocument1 pageCES Selector Acrylobutadienestyrene (ABS) - High Impact: GeneralCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: (BR) (WR-2) (Special F)Document1 pageTechnical Information: (BR) (WR-2) (Special F)johnNo ratings yet
- Aisi 4140 (0.40% C)Document5 pagesAisi 4140 (0.40% C)BernardoNo ratings yet
- Ppte Acier Fiablement AllierDocument3 pagesPpte Acier Fiablement AllierConception & Fabrication MécaniqueNo ratings yet
- 1 Wa-Catalog9Document1 page1 Wa-Catalog9johnNo ratings yet
- SYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer: Features & Benefits ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer: Features & Benefits ApplicationsZhan FangNo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector Low Alloy SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector Low Alloy SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- AISI 410: Stainless Steel, Martensitic, AISI 410S, Wrought, AnnealedDocument4 pagesAISI 410: Stainless Steel, Martensitic, AISI 410S, Wrought, AnnealedLinus LooNo ratings yet
- 1 Wa-Catalog13Document1 page1 Wa-Catalog13johnNo ratings yet
- TDS SW 901 3Document5 pagesTDS SW 901 3Frans Hendra WinartaNo ratings yet
- Brief Introduction of UHMWPEDocument3 pagesBrief Introduction of UHMWPEFatima NusserNo ratings yet
- Devcon Plastic Steel Putty ADocument3 pagesDevcon Plastic Steel Putty AAZLAN ABDULLAINo ratings yet
- Acero Medio CDocument1 pageAcero Medio CCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector Medium Carbon SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector Medium Carbon SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Properties of Common Optical Polymers: F D C DDocument1 pageProperties of Common Optical Polymers: F D C DHugo MakNo ratings yet
- Epofine 740 - Finehard 5200Document4 pagesEpofine 740 - Finehard 5200Karishma PrabhuNo ratings yet
- UHMW Mechanical Properties: Comparison of Dynamic Coefficient of Friction On Polished SteelDocument4 pagesUHMW Mechanical Properties: Comparison of Dynamic Coefficient of Friction On Polished SteeldangdinhthyNo ratings yet
- 410 Tech DataDocument1 page410 Tech DataAbraham FernandezNo ratings yet
- HT Swancor 901-Pt-Ve-30Document3 pagesHT Swancor 901-Pt-Ve-30Fernando Cesar PérezNo ratings yet
- Inox 316 L: (Stainless Steel, Austenitic, AISI 316L, Annealed)Document3 pagesInox 316 L: (Stainless Steel, Austenitic, AISI 316L, Annealed)Hamid AZZOUZINo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector High Carbon SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector High Carbon SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- CES Selector Wrought Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steel: GeneralDocument1 pageCES Selector Wrought Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steel: GeneralCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Alloy 410s Spec SheetDocument2 pagesAlloy 410s Spec SheetALONSO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- General: CES Selector Low Carbon SteelDocument1 pageGeneral: CES Selector Low Carbon SteelCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- Acero Bajo CDocument1 pageAcero Bajo CCristhianGeovannyNo ratings yet
- TOTAL Polystyrene 1441: Material DatasheetDocument3 pagesTOTAL Polystyrene 1441: Material DatasheetAlbert FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Encapsulants and Impregnation Resins For E-Motor: Advanced MaterialsDocument2 pagesEncapsulants and Impregnation Resins For E-Motor: Advanced Materialsمحمد مقلدNo ratings yet
- Alloy 410S Spec SheetDocument2 pagesAlloy 410S Spec SheetPrakash SundharamNo ratings yet
- 11 3508 01 Dowsil Ei 1184 Optical EncapsulantDocument5 pages11 3508 01 Dowsil Ei 1184 Optical Encapsulantyusuf KhanNo ratings yet
- Hojas TécnicasDocument2 pagesHojas TécnicasalejandrocharlescollNo ratings yet
- Bronze Putty: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesBronze Putty: Technical Data SheetSharad ShahNo ratings yet
- Pei 0270 RTP 2183Document2 pagesPei 0270 RTP 2183Vincent NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers: (Use The Table in The PPT As Your Guide in Accomplishing Table 1.)Document8 pagesChemistry For Engineers: (Use The Table in The PPT As Your Guide in Accomplishing Table 1.)Aivan Lloyd CapuleNo ratings yet
- TeflonDocument1 pageTeflonSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition: ASTM B103Document1 pageChemical Composition: ASTM B103MarcoAntonioNo ratings yet
- Ecoalube642TDS PDFDocument2 pagesEcoalube642TDS PDFDkC gunsNo ratings yet
- Ineos Typical Engineering Properties of HdpeDocument3 pagesIneos Typical Engineering Properties of HdpePhát Lê TiếnNo ratings yet
- Morflo 170Document2 pagesMorflo 170baselNo ratings yet
- Rigid 10k DatasheetDocument2 pagesRigid 10k DatasheetAna Maria RodrigoNo ratings yet
- The Three P's of Safe Winter DrivingDocument1 pageThe Three P's of Safe Winter DrivingYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Finding Safety and Support ENGLISHDocument2 pagesFinding Safety and Support ENGLISHYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Office ErgonomicsDocument14 pagesOffice ErgonomicsYaho HosNo ratings yet
- SFTV Safety ManualDocument7 pagesSFTV Safety ManualYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Apitalisn't: The Sticky Side of Teflon: Kate Waldock Luigi ZingalesDocument13 pagesApitalisn't: The Sticky Side of Teflon: Kate Waldock Luigi ZingalesYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Meatpacking Workers InfectedDocument2 pagesMeatpacking Workers InfectedYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Ejaculation ProblemDocument4 pagesEjaculation ProblemYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Envelope Formats, Sizes & EnclosuresDocument2 pagesEnvelope Formats, Sizes & EnclosuresYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Not All Beach Muck Is Created Equal: Michigan State University ExtensionDocument2 pagesNot All Beach Muck Is Created Equal: Michigan State University ExtensionYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Lawns: On This PageDocument4 pagesLawns: On This PageYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Waste Disposal PolicyDocument2 pagesWaste Disposal PolicyYaho HosNo ratings yet
- Paperbag RRLDocument5 pagesPaperbag RRLDonita Gloria100% (2)
- Riopipeline2019 1112 FM 1112 FinalDocument10 pagesRiopipeline2019 1112 FM 1112 FinalMarcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- High Strength Low Alloy Structural SteelsDocument16 pagesHigh Strength Low Alloy Structural SteelsTuan DangNo ratings yet
- Fisa Tehnica Linoleum Natural MarmoretteDocument1 pageFisa Tehnica Linoleum Natural MarmoretteSurdu AncaNo ratings yet
- News JournalDocument3 pagesNews Journal4D25 LUXIMON AMELIA DIONNo ratings yet
- Co 0016 (In)Document2 pagesCo 0016 (In)Antonio Perez MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nullifire B270 - High Strength Compound: 1. Product DescriptionDocument4 pagesNullifire B270 - High Strength Compound: 1. Product Descriptionnewnse2008No ratings yet
- Refractor Storage RecommendationsDocument3 pagesRefractor Storage RecommendationsWael IsmaelNo ratings yet
- CDG Technical PresentationDocument26 pagesCDG Technical Presentationar desNo ratings yet
- Steel 4140Document116 pagesSteel 4140KarenMar DCNo ratings yet
- C Purlin Data SheetDocument6 pagesC Purlin Data SheetAkhil VNNo ratings yet
- CO2 FloodingDocument15 pagesCO2 FloodingUzumaki28No ratings yet
- Molecular Weight of Carbopol and PemulenDocument3 pagesMolecular Weight of Carbopol and PemulenMawarniNo ratings yet
- Soldering, Brazing & WeldingDocument52 pagesSoldering, Brazing & WeldingChandrakantha K100% (1)
- The Special Steel Book - V08.00.1119 - WEBDocument52 pagesThe Special Steel Book - V08.00.1119 - WEBkevin honiballNo ratings yet
- What Is AEROPERL® 300 Pharma Mesoporous Silica?Document3 pagesWhat Is AEROPERL® 300 Pharma Mesoporous Silica?Salman BasheerNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022Document22 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2022Rose RamisaNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Rates, Zone Contracts - General Building Works BHRDocument38 pagesSchedule of Rates, Zone Contracts - General Building Works BHRnadeeshlakmalNo ratings yet
- Aic Asf PQR 0120Document2 pagesAic Asf PQR 0120AHMED MEDANYNo ratings yet
- SECTION 15150 Sanitary Waste and Vent Piping Rev 0Document18 pagesSECTION 15150 Sanitary Waste and Vent Piping Rev 0mohamad damerlyNo ratings yet
- A1 Karanja Oil MSDSDocument3 pagesA1 Karanja Oil MSDSSahil VoraNo ratings yet
- Sika ViscoCrete-225 SDocument2 pagesSika ViscoCrete-225 SMajid AlzubadyNo ratings yet
- Restore /restore Plus Heavy-Duty Coolant Cleaners: The Safe and Efficient Way To Clean Heavy-Duty Cooling SystemsDocument2 pagesRestore /restore Plus Heavy-Duty Coolant Cleaners: The Safe and Efficient Way To Clean Heavy-Duty Cooling SystemsemezibNo ratings yet
- Birla Cellulose, TechnotexDocument43 pagesBirla Cellulose, Technotexsuresh_parmar_9No ratings yet
- Batik L3 CoCU-4 - Batik Contemporary (86-103)Document18 pagesBatik L3 CoCU-4 - Batik Contemporary (86-103)azman hilmiNo ratings yet
- Water LeakageDocument34 pagesWater LeakageKousalya Mk100% (2)