Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MP PDF
MP PDF
Uploaded by
Raman GoyalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MP PDF
MP PDF
Uploaded by
Raman GoyalCopyright:
Available Formats
31.
Which one of the following is true in of rock from the moon was found to contain both
photoelectric emission the elements X and Y which were in the ratio of
1 : 7. The age of the rock is
(a) Photoelectric current is directly proportional (a) 1.96 × 108 years
to the amplitude of light of a given frequency
(b) 3.85 × 109 years
(b) Photoelectric current is directly proportional
to the intensity of light of a given frequency (c) 4.11 × 109 years
at moderate intensities
(d) 9.59 × 109 years
(c) Above the threshold frequency, the maximum
39. Radioactive element decays to form a stable
K.E. of photoelectrons is inversely
nuclide, then the rate of decay of reactant
proportional to the frequency of incident light
dN
will vary with time (t) as shown in figure
(d) The threshold frequency depends upon the dt
wavelength of incident light
dN dN
32. For intensity I of a light of wavelength 5000Å the dt dt
photoelectron saturation current is 0.40 µA and
stopping potential is 1.36 V, the work function of
metal is
(a) t (b) t
(a) 2.47 eV (b) 1.36 eV
dN dN
(c) 1.10 eV (d) 0.43 eV dt dt
33. An electron has a mass of 9.1 × 10–31 kg. It
revolves round the nucleus in a circular orbit of (c) t (d) t
radius 0.529 × 10–10 metre at a speed of 2.2 × 40. A particle of mass M at rest decays into two
106 m/s. The magnitude of its linear momentum particles of masses m1 and m2, having non zero
in this motion is velocities. The ratio of the de Broglie
wavelengths of the particles, λ1/λ2is
(a) 1.1 × 10–34 kg–m/s
m1 m2
(a) (b)
m2 m1
(b) 2.0 × 10–24 kg–m/s
m2
(c) 1.0 (d)
(c) 4.0 × 10–24 kg–m/s m1
41. Imagine an atom made up of a proton and a
(d) 4.0 × 10–31 kg–m/s
hypothetical particle of double the mass of the
34. If λmax is 6563 Å, then wave length of second electron but having the same charge as the
line for Balmer series will be electron. Apply the Bohr atom model and
16 36 consider all possible transitions of this
(a) λ = (b) λ = hypothetical particle to the first excited level.
3R 5R The longest wavelength photon that will be
4 emitted has wavelength λ (given in terms of the
(c) λ = (d) None of the above Rydberg constant R for the hydrogen atom equal
3R to)
35. If the wavelength of the first line of the Balmer
series of hydrogen is 6561 Å, the wavelength of
9 36
(a) (b)
the second line of the series should be 5R 5R
(a) 13122 Å (b) 3280 Å 18 4
(c) (d)
(c) 4860 Å (d) 2187 Å 5R R
36. If an X–ray tube operates at the voltage of 10kV,
42. A nucleus of mass number 220, initially at rest,
find the ratio of the de–Brogle wavelength of the
emits an α-particle. If the Q value of the reaction
incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of
is 5.5 MeV, the energy of the emitted α-particle
X–rays produce(d) The specific charge of electron
will be
11
is 1.8 × 10 C/kg. (a) 4.8 MeV (b) 5.4 MeV
(a) 1 (b) 0.1 (c) 1.8 (d) 1.2
(c) 6.0 MeV (d) 6.8 MeV
2
37. The binding energy of deuteron 1 H is 1.112 43. Kα wavelength emitted by an atom of atomic
MeV per nucleon and an α–particle has a number Z = 11 is λ. Find the atomic number for
binding energy of 7.047 MeV per nucleon. Then an atom that emits Kα radiation with wavelength
2
in the fusion reaction 1 H + 12H → 24 He + Q, the 4λ
energy Q released is (a) Z = 6 (b) Z = 4
(a) 1 MeV (b) 11.9 MeV (c) Z = 11 (d) Z = 44
(c) 23.8 MeV (d) 931 MeV 44. Half-life of a radioactive substance A is 4 days.
The probability that a nucleus will decay in two
half-lives is :
38. A radioactive isotope X with a half–life of 1.37 ×
109 years decays to Y which is stable. A sample
1 3 1 55. A small mirror of mass m is suspended by a
(a) (b) (c) (d) 1 light thread of length l. A short pulse of laser
2 4 2 falls on the mirror with energy E. Then, which of
45. The electron in a hydrogen atom jumps from the following statement is correct ?
ground state to the higher energy state where its
velocity is reduced to one-third its initial value.
If the radius of the orbit in the ground state is r,
the radius of new orbit will be :
r r
(a) 3r (b) 9r (c) (d)
3 9
46. If λ1 and λ2 are the wavelength of the first (a) If the pulse falls normally on the mirror, it
member of the Lyman and Paschen series,
respectively, then λ1 : λ2 is :
(
deflects by θ =2E/ mc 2g )
(a) 1 : 3 (b) 1 : 30 (b) If the pulse falls normally on the mirror, it
(c) 7 : 50 (d) 7 : 108 (
deflects by θ =2E/ mc 2g )
47. Difference between and ( n +
nth Bohr’s 1)th
radius of hydrogen atom is equal to (n –1)th (c) Impulse in thread depends on angle at
Bohr’s radius. The value of n is which the pulse falls on the mirror
(a) 1 (b) 2 (d) None of the above
(c) 3 (d) 4 56. A nozzle throws a stream of gas against a wall
with a velocity v much larger than the thermal
48. An X-ray tube is operating at 150 kV and 10 agitation of the molecules. The wall deflects the
mA. If only 1% of the electric power is converted molecules without changing the magnitude of
into X-rays, the rate at which the target is their velocity. Also, assume that the force
heated, in cal s–1, is exerted on the wall by the molecules is
(a) 3.57 (b) 35.7 (c) 4.57 (d) 15 perpendicular to the wall. (This is not strictly
49. If elements of quantum number greater than n true for a rough wall). Find the force exerted on
were not allowed, the number of possible the wall.
elements in nature would have been
2
1 n ( n + 1)
(a) n ( n + 1) (b)
2
2
1 1
(c) n ( n + 1) ( 2n + 1) (d) n ( n + 1) ( 2n + 1)
6 3
50. Magnetic field at the center (at nucleus) of the (a) Anmv2 cos2 θ (b) 2Anmv2 cos2 θ
hydrogen-like atoms (atomic number = z) due to (c) 2Anmv2 sin2 θ (d) Anmv2 cos θ
the motion of electron in nth orbit is proportional 57. An α-particle and a proton are fired through the
to same magnetic field which is perpendicular to
n3 n4 z2 z3 their velocity vectors. The α-particle and the
(a) (b) (c) (d) proton move such that radius of curvature of
z5 z n3 n5 their paths is same. Find the ratio of their de
51. What is the de Brogle wavelength of the a- Broglie wavelengths.
particle accelerated through a potential (a) 2 : 3 (b) 3 : 4 (c) 5 : 7 (d) 1 : 2
difference V ?
58. If first excitation potential of a hydrogen-like
(a) 0.287/ V Å (b) 12.27/ V Å atom is V electron volt, then the ionization
energy of this atom will be :
(c) 0.101/ V Å (d) 0.202/ V Å
3V
52. If 5% of the energy supplied to a bulb is (a) V electron volt (b) electron volt
4
irradiated as visible light, how many quanta are
emitted per second by a 100 W lamp ? Assume 4V
(c) electron volt
wavelength of visible light as 5.6 × 10–5 cm. 3
(a) 1.4 × 1019 (b) 3 × 103 (d) cannot be calculated by given information
(c) 1.4 × 10 –19 (d) 3 × 104 59. The wavelength of KαX-rays of two metals ‘A’ and
53. An electron and a photon, each has a ‘B’ are 4/1875 R and 4/675 R, respectively,
wavelength of 1.2 Å. What is the ratio of their where ‘R’ is Rydberg’s constant. The number of
energies ? elements lying between ‘A’ and ‘B’ according to
(a) 1 : 10 (b) 1 : 102 their atomic numbers is :
(c) 1 : 103 (d) 1 : 104 (a) 3 (b) 6
54. Work function of nickel is 5.01 eV. When (c) 5 (d) 4
ultraviolet radiation of wavelength 200 Å is 60. The angular momentum of an electron in a
incident on it, electron are emitted. What will be hydrogen atom is proportional to :
the maximum velocity of emitted electrons ?
(a) 1/ r (b) 1/r (c) r (d) r2
(a) 3 × 108 ms–1 (b) 6.46 × 105 ms–1
(c) 10.36 × 105 ms–1 (d) 8.54 × 106 ms–1
You might also like
- Chemistry Malaysian Matriculation Full Notes & Slides For Semester 1 and 2Document1,743 pagesChemistry Malaysian Matriculation Full Notes & Slides For Semester 1 and 2Jay Bee90% (58)
- Spectroscopy For AmateurDocument165 pagesSpectroscopy For AmateurJulio ZebaduaNo ratings yet
- TEST 24 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument4 pagesTEST 24 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matternivasininiva0No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument29 pagesStructure of AtomSayantan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- AIEEE - Atomic Nucleus - 2Document3 pagesAIEEE - Atomic Nucleus - 2Amit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-04 - Objective Unsolved LevelDocument4 pagesModern Physics-04 - Objective Unsolved LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 7: (Dual Nature of Matter, Atoms and Nuclei)Document6 pagesUnit Test 7: (Dual Nature of Matter, Atoms and Nuclei)padhi8480No ratings yet
- Physics Set 1 2022-23 BoardDocument11 pagesPhysics Set 1 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- 13Document30 pages13riosjerit1234No ratings yet
- Maha Pralay DPP - Dual Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesMaha Pralay DPP - Dual Nature of MatterKOVIDH CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- 10 Atomic StructureDocument9 pages10 Atomic StructurearcNo ratings yet
- Question Set 2 Chap 11 Dual Nature of Radiation An - 78449 - 2023 - 01 - 16 - 17 - 46Document7 pagesQuestion Set 2 Chap 11 Dual Nature of Radiation An - 78449 - 2023 - 01 - 16 - 17 - 46RajneeshNo ratings yet
- AIIMS 2017 Solved PaperDocument31 pagesAIIMS 2017 Solved PaperhritikNo ratings yet
- 27. ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND X-RAYSDocument5 pages27. ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND X-RAYSShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 2024-04-18-0.2327351069944701Document35 pages2024-04-18-0.2327351069944701Devansh DodaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper (Physics)Document10 pagesSample Question Paper (Physics)Milanjyoti BorahNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument10 pagesModern Physicsmike vineyardNo ratings yet
- V.neet Full Syllabus Mock Test 1Document69 pagesV.neet Full Syllabus Mock Test 150005akpNo ratings yet
- AIEEE - Atomic Nucleus - 1Document3 pagesAIEEE - Atomic Nucleus - 1Amit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Exercise-4 Qs. - Sol. - .PMDDocument34 pagesModern Physics Exercise-4 Qs. - Sol. - .PMDAbhinav ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom-1Document126 pagesStructure of Atom-1mohdhashim8789No ratings yet
- Phy - Dpp-Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument10 pagesPhy - Dpp-Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterPIYUSH SHARMANo ratings yet
- 23 March 2024 NEET Practice Questions Vedantu NEET SankalpDocument30 pages23 March 2024 NEET Practice Questions Vedantu NEET Sankalpmfhaque0No ratings yet
- Sol Rep WT 2-10 JulyDocument10 pagesSol Rep WT 2-10 JulyMaster IdeasNo ratings yet
- Set QP 2019 FebDocument11 pagesSet QP 2019 Febsreejitha KNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFDocument24 pagesModern Physics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFAnanya DwivediNo ratings yet
- SQP 5Document7 pagesSQP 5Ips Maneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 2 2022-23 BoardDocument10 pagesPhysics Set 2 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems: C-B (Level-B)Document3 pagesDaily Practice Problems: C-B (Level-B)Ved NarsekarNo ratings yet
- Atom McqsDocument13 pagesAtom McqsMrunmayee ManeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure T-1Document5 pagesAtomic Structure T-1gwnangborokNo ratings yet
- 04 - Physics - July 2007Document6 pages04 - Physics - July 2007Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaNo ratings yet
- 50Q - AtomsDocument9 pages50Q - AtomsNaman MahawarNo ratings yet
- Matter-Wave Exercise 1 - 4 Module-6Document14 pagesMatter-Wave Exercise 1 - 4 Module-6Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 11thDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure 11thAshwani kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Sem VI - PHSH - CC13 PDFDocument3 pagesSem VI - PHSH - CC13 PDFÂřîjìť PāłNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 3 2022-23 BoardDocument11 pagesPhysics Set 3 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure TestDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure TestSanika PahujaNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Chap 20Document3 pagesMCQ's Chap 20Arham MunirNo ratings yet
- Higher Secondary Second Year Physics Model Question Paper-IiiDocument5 pagesHigher Secondary Second Year Physics Model Question Paper-IiiVelmurugan PNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Chap 19Document3 pagesMCQ's Chap 19Arham MunirNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature MCQDocument6 pagesDual Nature MCQPrateek KhareNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 23 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document6 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 23 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22abcdNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - AIEEE Maths Sample Paper 7Document20 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - AIEEE Maths Sample Paper 7Aditya RamNo ratings yet
- Magnetism - Practice SheetDocument5 pagesMagnetism - Practice Sheetpurva pawarNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2003Document20 pagesAieee 2003gunjan kadelNo ratings yet
- Qbank PHYSICSDocument36 pagesQbank PHYSICSBishnu gopal DasNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect-1Document2 pagesPhotoelectric Effect-1dddddNo ratings yet
- Sura Publications: Neet Based QuestionsDocument16 pagesSura Publications: Neet Based QuestionsSubash_SaradhaNo ratings yet
- AM QBank - AtomsDocument7 pagesAM QBank - Atomsmeghanapatil864No ratings yet
- Atmoic Structure 11thDocument33 pagesAtmoic Structure 11thiitianwasimNo ratings yet
- Paper 22 23 Dual Nature and AtomDocument6 pagesPaper 22 23 Dual Nature and AtomSunil BalaniNo ratings yet
- QM Problem Set 1Document18 pagesQM Problem Set 1Arnab BhowmikNo ratings yet
- 02 - Atomic Structure - (Exercises)Document13 pages02 - Atomic Structure - (Exercises)Nishant JanuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Assig (Xi 2021-23) (Print) 26 08 21Document3 pagesAtomic Structure Assig (Xi 2021-23) (Print) 26 08 21Ramkrushna khandareNo ratings yet
- January 29 - EveningDocument12 pagesJanuary 29 - Eveningadhyayan.learning.2021No ratings yet
- Atomic STRDocument3 pagesAtomic STRveerlocusNo ratings yet
- FVST-10(Question) - 30.04.2024Document21 pagesFVST-10(Question) - 30.04.2024JAGATBALLAV SAHOONo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Problem Sheets NewDocument20 pagesModern Physics Problem Sheets NewXyzNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsFrom EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Ray Opitics Disha Solns PDFDocument5 pagesRay Opitics Disha Solns PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- MEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFDocument4 pagesMEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- MEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFDocument4 pagesMEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Part - Iii: PhysicsDocument9 pagesPart - Iii: PhysicsRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Ray 1 PDFDocument6 pagesRay 1 PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions: Section (A) : Measurement and Calculation of PressureDocument8 pagesObjective Questions: Section (A) : Measurement and Calculation of PressureRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument7 pagesFluids PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- DPP - Daily Practice Problems: Name: DateDocument8 pagesDPP - Daily Practice Problems: Name: DateRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Heat PDFDocument20 pagesHeat PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Ray Opitics Disha PDFDocument4 pagesRay Opitics Disha PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation of Centre of MassDocument14 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation of Centre of MassRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Test Series: Test - 9 (Objective) : PhysicsDocument4 pagesTest Series: Test - 9 (Objective) : PhysicsRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer Solutions PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Serbia Србија: Fast FactsDocument18 pagesSerbia Србија: Fast FactsRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe Bulgaria v1 m56577569830516522Document29 pagesEastern Europe Bulgaria v1 m56577569830516522Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern-Europe-Moldova v1 m56577569830516538Document13 pagesEastern-Europe-Moldova v1 m56577569830516538Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe 9 Getting StartedDocument14 pagesEastern Europe 9 Getting StartedRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe Czech Republic v1 m56577569830516526Document33 pagesEastern Europe Czech Republic v1 m56577569830516526Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe CroatiaDocument31 pagesEastern Europe CroatiaTanya KorolovNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe 9 ContentsDocument9 pagesEastern Europe 9 ContentsRaman Goyal0% (1)
- Eastern Europe Bosnia Hercegovina v1 m56577569830516521Document18 pagesEastern Europe Bosnia Hercegovina v1 m56577569830516521Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern-Europe-Poland v1 m56577569830516543Document40 pagesEastern-Europe-Poland v1 m56577569830516543Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern-Europe-Latvia v1 m56577569830516532Document13 pagesEastern-Europe-Latvia v1 m56577569830516532Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe Montenegro v1 m56577569830516541Document9 pagesEastern Europe Montenegro v1 m56577569830516541Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern-Europe-Estonia v1 m56577569830516529Document19 pagesEastern-Europe-Estonia v1 m56577569830516529Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe Slovakia v1 m56577569830516564Document22 pagesEastern Europe Slovakia v1 m56577569830516564Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern-Europe-Hungary v1 m56577569830516530Document32 pagesEastern-Europe-Hungary v1 m56577569830516530Josep G. CollNo ratings yet
- Eastern-Europe-Romania v1 m56577569830516555Document38 pagesEastern-Europe-Romania v1 m56577569830516555Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Eastern Europe Macedonia v1 m56577569830516536Document13 pagesEastern Europe Macedonia v1 m56577569830516536Raman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12th Question Bank PhysicsDocument6 pagesCbse 12th Question Bank Physicsramayodi223No ratings yet
- Atomic Spectrum of HydrogenDocument3 pagesAtomic Spectrum of HydrogenlovemynaturecountryNo ratings yet
- 2014 Physics - Sydney Grammar Trial With SolutionsDocument56 pages2014 Physics - Sydney Grammar Trial With SolutionsWilliam Hou0% (1)
- Quantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument58 pagesQuantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of AtomsAsudeNo ratings yet
- Sem1 Unit3 Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesSem1 Unit3 Atomic Structureshehdilanun100% (1)
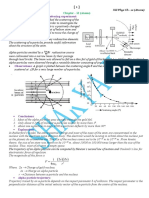
- Rutherford's α-particle scattering experiment:: 엠 radioactive sourceDocument6 pagesRutherford's α-particle scattering experiment:: 엠 radioactive sourcerohit chakNo ratings yet
- 2 - Structure of Atom-01 - TheoryDocument36 pages2 - Structure of Atom-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 - Atomic Structure ExerciseDocument18 pages1 - Atomic Structure Exercisesanket sinhaNo ratings yet
- Test For Xii EngkDocument5 pagesTest For Xii EngkKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Chap 4Document49 pagesModern Physics Chap 4Minte MuluNo ratings yet
- Active Galactic Nuclei Fueling and FeedbackDocument44 pagesActive Galactic Nuclei Fueling and FeedbackShambhavi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ModuleDocument182 pagesChemistry ModuletesfayeNo ratings yet
- Lang AstrophysicalFormulae TextDocument760 pagesLang AstrophysicalFormulae TextJairNo ratings yet
- Jee Main-2023 - Important Replica QS - PhysicsDocument106 pagesJee Main-2023 - Important Replica QS - PhysicsAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Hydrogen Spectrum and The Bohr ModelDocument13 pagesThe Hydrogen Spectrum and The Bohr Modeljuso_jusicNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spec of Hydrogen Nov 8Document6 pagesAtomic Spec of Hydrogen Nov 8Bimal Ale MagarNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document37 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3Peth alambatinNo ratings yet
- Iit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1Document48 pagesIit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1MD IMRAN100% (1)
- 1.atomic Structure 1-24Document16 pages1.atomic Structure 1-24eamcetmaterials67% (15)
- Line Spectra: Institute of Chemistry, University of The Philippines-Los BanosDocument5 pagesLine Spectra: Institute of Chemistry, University of The Philippines-Los BanosKimberly DelicaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science: C. Letty, A. Pastore, E. Mastorakos, R. Balachandran, S. CourisDocument8 pagesExperimental Thermal and Fluid Science: C. Letty, A. Pastore, E. Mastorakos, R. Balachandran, S. CourisCarolina BalderramaNo ratings yet
- Christopher R. Kitchin-Optical Astronomical Spectroscopy-IOP Institute of Physics 1995 (1995)Document268 pagesChristopher R. Kitchin-Optical Astronomical Spectroscopy-IOP Institute of Physics 1995 (1995)carolinasilvagNo ratings yet
- Physics Unique Concepts & Questions Sub Topic WiseDocument728 pagesPhysics Unique Concepts & Questions Sub Topic Wiseushashiva.1973No ratings yet
- Questions For Structure of Atom - CBSE Chemistry Class 11Document4 pagesQuestions For Structure of Atom - CBSE Chemistry Class 11The DealerNo ratings yet
- Atoms ExercisesDocument12 pagesAtoms ExercisesAditi VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 101 - 2001 Answers Assignment #2 and Quiz 2Document7 pagesChemistry 101 - 2001 Answers Assignment #2 and Quiz 2Victoria MooreNo ratings yet
- Inogranic Chem 11TDocument116 pagesInogranic Chem 11T0.1hacker0123No ratings yet