Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Material Lab-22
Material Lab-22
Uploaded by
AhmadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Lab-22
Material Lab-22
Uploaded by
AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
MATERIALS LABORATORY 2006
METALLOGRAPHY
Objective
To study the structural characteristics or constitution of a metal or an alloy in
relation to its physical and mechanical properties.
Introduction
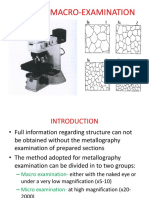
There are two examination methods in metallography:
I) Macroscopy
2) Microscopy
In macroscopy the examination of the structural characteristics or chemical
characteristics of a metal or an alloy is done by the unaided eye or with the aid of
a low-power microscope or binocular, usually under l0x.
In microscopy similar examination is done with the prepared metal specimens,
employing magnifications with the optical microscope of from 100x to as high as
2000x.
Specimen preparation
1. Grinding
A small piece of specimen is cut by a metal-cutting-saw. After cutting
operation, burrs on the edges of the specimen should be carefully removed by a
fine file or coarse grinding paper.
The silicon carbide grinding papers are held flat in a unit containing water
facility for lubrication purpose. Each unit contains four grades of papers, starting
with grade 400 (coarse) and finishing with grade 1200 (fine). Grinding of the
work piece is done by starting with the coarse papers and then continuing with the
fine papers. In each stage, grinding is done by rubbing the specimen backwards
and forwards on the grinding paper in one direction only, until the surface is
completely ground, that is, until only grinding marks due to this particular paper
can be seen to cover the whole surface.
The specimen is washed thoroughly to remove coarse silicon carbide particles
before proceeding to a finer paper.
The direction of grinding is changed from paper to paper, so that the removal
of previous grinding marks is easily observed. The extra time spent on each paper
should be increased as the finer papers are used. At the end of the grinding
sequence, the specimen is washed thoroughly and dried. Now, the specimen is
ready for polishing.
2. Polishing
The polishing is done on rotating wheels covered by a special cloth. Alumina is
employed as polishing agent. The 1-micron size is commonly used, but the total
polishing time shortened by starting on the 7 or 3 micron grade.
The pad should be kept well supplied with lubricant. The specimen should be held
23
You might also like
- Microstructure Examination of Steel Lab ReportDocument6 pagesMicrostructure Examination of Steel Lab ReportEmıły Wınıfred100% (4)
- Metallography Experiment ReportDocument11 pagesMetallography Experiment Reportsinabirecik83% (6)
- METALLOGRAPY Düzenlenmiş 1Document3 pagesMETALLOGRAPY Düzenlenmiş 1Doğukan CemaloğluNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document5 pagesLab 1AHMAD NAIM BIN AHMAD NAZRI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Metallography:: Steps To Reveal Microstructures of A SpecimenDocument7 pagesMetallography:: Steps To Reveal Microstructures of A SpecimenJoyce Saddhu MeettooNo ratings yet
- Microstructure AnalysisDocument4 pagesMicrostructure AnalysissgarrabNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 MICROSTRUCTURE OBSERVATIONDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 MICROSTRUCTURE OBSERVATIONhaziqaimanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Metallography1Document36 pagesLab Manual Metallography1prashant patilNo ratings yet
- Mos & Metallurgy LabDocument53 pagesMos & Metallurgy LabSrinu Arnuri100% (1)
- Lab 4 Metallography PDFDocument8 pagesLab 4 Metallography PDFjohn hayNo ratings yet
- Macro Micro - En.idDocument6 pagesMacro Micro - En.idYuliantari YuliantariNo ratings yet
- Kuliah IV. Preparasi Sampel MetalografiDocument20 pagesKuliah IV. Preparasi Sampel MetalografiDesi WidyawatiNo ratings yet
- National University of Science and TechnologyDocument6 pagesNational University of Science and TechnologyObrian TandiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials: Lab AssignmentDocument9 pagesEngineering Materials: Lab AssignmentASAD ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Specimen For Microscopic ExaminationDocument4 pagesPreparation of Specimen For Microscopic ExaminationsunfaceselvamNo ratings yet
- Microstructure of Low Carbon Steel and AluminiumDocument14 pagesMicrostructure of Low Carbon Steel and AluminiumFara NajwaNo ratings yet
- Metallography: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesMetallography: ObjectiveGosaye DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Study of Metallography StructureDocument8 pagesStudy of Metallography StructureMahrukh JavedNo ratings yet
- Metallography Lab Metallography Lab Metallography Lab Metallography LabDocument14 pagesMetallography Lab Metallography Lab Metallography Lab Metallography Labvishaly_450% (2)
- Material Lab Manual Experiments January2016 1Document47 pagesMaterial Lab Manual Experiments January2016 1gosaye desalegn100% (2)
- TADILODocument15 pagesTADILOSamiMasreshaNo ratings yet
- Ams - Metallography of SpecimenDocument8 pagesAms - Metallography of SpecimenkarthigeyanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metallurgy Laboratory Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Salahaddin-Erbil KurdistanDocument31 pagesEngineering Metallurgy Laboratory Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Salahaddin-Erbil KurdistanKarwan GoodNo ratings yet
- Metallography Report ZubairDocument5 pagesMetallography Report ZubairMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Microstructure Analysis EditedDocument6 pagesMicrostructure Analysis EditedHaikal ZikriNo ratings yet
- MicrostructureDocument8 pagesMicrostructureRamathi GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Final em Material ManualDocument43 pagesFinal em Material Manualprashant patilNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document13 pagesLab Report 5Jhon CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Discussion: From This Experiment Students Was Able To Understand TheDocument2 pagesDiscussion: From This Experiment Students Was Able To Understand TheKabuki MaskNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineering (ME 252) : Dr. Hany AmmarDocument19 pagesMaterials Engineering (ME 252) : Dr. Hany AmmarDanialNo ratings yet
- Grain Size PDFDocument4 pagesGrain Size PDFSarthak SachdevaNo ratings yet
- II B.Tech-MMS - Lab ManualDocument48 pagesII B.Tech-MMS - Lab Manualuma deviNo ratings yet
- Jj508 Engineering Laboratory 3 Lab Report: Title: Metallographic Specimen PreparationDocument10 pagesJj508 Engineering Laboratory 3 Lab Report: Title: Metallographic Specimen PreparationOnsen Ong Min XuanNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Metallography and HardnessDocument9 pagesLab 3 Metallography and HardnessTommy Miles100% (1)
- METALLURGY & MATERIAL SCIENCE Lab Manual PDFDocument44 pagesMETALLURGY & MATERIAL SCIENCE Lab Manual PDFRewat SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Topdown ApproachDocument8 pagesTopdown ApproachEbsiba Beaula JNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy LabDocument26 pagesMetallurgy LabSudarshan GNo ratings yet
- Material ManualDocument40 pagesMaterial ManualBenjie flor CalayegNo ratings yet
- Metallography: Dr. Mohd Arif Anuar Mohd SallehDocument22 pagesMetallography: Dr. Mohd Arif Anuar Mohd SallehNurulAtirahNoroziNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 - MSMDocument4 pagesExp 2 - MSMAmratPatelNo ratings yet
- Thermal Treatment Processes: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesThermal Treatment Processes: ObjectiveslppeaceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 4 PDFMohd FaizNo ratings yet
- Mee1005 Lab 19bma034 Da3Document6 pagesMee1005 Lab 19bma034 Da3Siva ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Mec 234Document48 pagesLab Manual Mec 234hemanth singhNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Lecture 3 1 Mikroskop OptikDocument48 pagesWeek 3 Lecture 3 1 Mikroskop OptikRadit N MobiliuNo ratings yet
- Me Laboratory Report Template IDocument36 pagesMe Laboratory Report Template IlinesitaNo ratings yet
- Grains May Be Coarse or FineDocument8 pagesGrains May Be Coarse or FineAshok ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Grains May Be Coarse or FineDocument8 pagesGrains May Be Coarse or FineAshok ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Determination of Composition of Steel ADocument6 pagesDetermination of Composition of Steel AJeetender MishraNo ratings yet
- Metallographic Sample Preparation Techniques: BackgroundDocument8 pagesMetallographic Sample Preparation Techniques: BackgroundQA LAB ISMNo ratings yet
- MM212 New Manual - FinalDocument30 pagesMM212 New Manual - FinalAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Micro & Macro ExaminationDocument51 pagesMicro & Macro ExaminationHernan Rodriguez50% (2)
- Ff14c Metallography Report 2019 2020 Spring e Taban 2020 Ef8Document8 pagesFf14c Metallography Report 2019 2020 Spring e Taban 2020 Ef8cetinkaytalhaenes23No ratings yet
- Advance Materials Lab Report: Name: - Aditya Bharadwaj Eyyunni Roll No.: 19126003Document10 pagesAdvance Materials Lab Report: Name: - Aditya Bharadwaj Eyyunni Roll No.: 19126003efflux 1990No ratings yet
- 3 MetallographyDocument5 pages3 MetallographyGaurav TripathiNo ratings yet
- MetallographyDocument7 pagesMetallographyMehmet Ali CanNo ratings yet
- Preparation Specimen For Metallographic ExaminationDocument7 pagesPreparation Specimen For Metallographic Examinationموسى هلال محسنNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy & Material Science Lab ManualDocument42 pagesMetallurgy & Material Science Lab ManualrameshNo ratings yet
- Tensile Testing of Metals: ObjectiveDocument1 pageTensile Testing of Metals: ObjectiveAhmadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Safety: Materials Laboratory 2006Document1 pageMechanical Safety: Materials Laboratory 2006AhmadNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Tensile Report: Materials Laboratory 2006Document1 pageChecklist For Tensile Report: Materials Laboratory 2006AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Lab-35Document1 pageMaterial Lab-35AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jominy Hardenability Test: ObjectiveDocument1 pageJominy Hardenability Test: ObjectiveAhmadNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection:: Materials Laboratory 2006Document1 pageVisual Inspection:: Materials Laboratory 2006AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Lab 9Document1 pageMaterial Lab 9AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aircraft 11Document1 pageAircraft 11AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Lab 3Document1 pageMaterial Lab 3AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Lab-32Document1 pageMaterial Lab-32AhmadNo ratings yet
- Materials Laboratory Attendance: Experiment Group Date ApprovalDocument1 pageMaterials Laboratory Attendance: Experiment Group Date ApprovalAhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Lab-31Document1 pageMaterial Lab-31AhmadNo ratings yet
- Table 14.2 Provides An Overview of The Cost Elements Included by DOC Methods. ATA 1967Document1 pageTable 14.2 Provides An Overview of The Cost Elements Included by DOC Methods. ATA 1967AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Lab 4Document1 pageMaterial Lab 4AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aircraft 13Document1 pageAircraft 13AhmadNo ratings yet
- 14.3.4 Calculation of DOC Cost Elements - Interest: P P K KDocument1 page14.3.4 Calculation of DOC Cost Elements - Interest: P P K KAhmadNo ratings yet
- Aircraft 16 PDFDocument1 pageAircraft 16 PDFAhmadNo ratings yet
- Equiva-Lent Ton-Mile Costs Can Be Calculated, in Which A Correction Factor Is Applied To The CargoDocument1 pageEquiva-Lent Ton-Mile Costs Can Be Calculated, in Which A Correction Factor Is Applied To The CargoAhmadNo ratings yet
- P That The Individual DOC Methods Assume and The Parameters of P Is Calculated Are Contained in Table 14.6. P P N N PDocument1 pageP That The Individual DOC Methods Assume and The Parameters of P Is Calculated Are Contained in Table 14.6. P P N N PAhmadNo ratings yet
- 14.3.6 Calculation of DOC Cost Elements - Fuel Costs: C Are Calculated According ToDocument1 page14.3.6 Calculation of DOC Cost Elements - Fuel Costs: C Are Calculated According ToAhmadNo ratings yet
- Fig. 14.3 AEA 1989bDocument1 pageFig. 14.3 AEA 1989bAhmadNo ratings yet