Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification of Differential Equation
Classification of Differential Equation
Uploaded by
Elaph Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis document classifies and defines different types of differential equations. It defines ordinary differential equations as involving derivatives of dependent variables with respect to a single independent variable, and partial differential equations as involving derivatives with respect to more than one independent variable. The order of a differential equation is defined as the order of the highest derivative it contains, and its degree as the highest power of the highest order derivative. An equation is nonlinear if it contains products of dependent variables or their derivatives.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document classifies and defines different types of differential equations. It defines ordinary differential equations as involving derivatives of dependent variables with respect to a single independent variable, and partial differential equations as involving derivatives with respect to more than one independent variable. The order of a differential equation is defined as the order of the highest derivative it contains, and its degree as the highest power of the highest order derivative. An equation is nonlinear if it contains products of dependent variables or their derivatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesClassification of Differential Equation
Classification of Differential Equation
Uploaded by
Elaph AhmedThis document classifies and defines different types of differential equations. It defines ordinary differential equations as involving derivatives of dependent variables with respect to a single independent variable, and partial differential equations as involving derivatives with respect to more than one independent variable. The order of a differential equation is defined as the order of the highest derivative it contains, and its degree as the highest power of the highest order derivative. An equation is nonlinear if it contains products of dependent variables or their derivatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
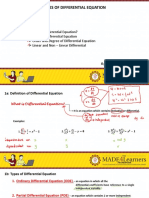
Lecture 12
Classification of D.E
We will classify of the following differential equations as ordinary or partial
differential equations, state the order of each equation, and determine
whether the equation under consideration is linear or nonlinear.
➢ Ordinary differential equation ( O.D.E. ) is the differential equation
involving ordinary derivatives of one or more dependent variables
with respect to a single independent variable.
➢ Partial differential equation is the differential equation involving
ordinary derivatives of one or more dependent variables with respect
to more than one independent variable.
➢ The order of a differential equation is equal to the order of the
highest differential coefficient that it contains.
This differential equation is of third order.
➢ The degree of a differential equation is the highest power of the
highest order differential coefficient that the equation contains after
it has been rationalized.
This differential equation is of first degree.
➢ The differential equation is nonlinear if there is a product between
dependent variable themselves, or a product between the dependant
variable and/or any of its derivatives, its various derivatives occur to
the any degree other than first degree, or there is a trancendental
function of y and/ or its derivatives occur.
This equation is linear differential equation.
This equation is nonlinear differential equation.
You might also like
- Module 1 Notes - Introduction To Differential EquationDocument19 pagesModule 1 Notes - Introduction To Differential EquationMia NicoleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document9 pagesLesson 1luizNo ratings yet
- Definitions:: A Differential Equations Is A Equations Which Contains The Derivative or Differentials ofDocument3 pagesDefinitions:: A Differential Equations Is A Equations Which Contains The Derivative or Differentials ofMina W. SayedNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesDifferential Equationsseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Solving Differential EquationsDocument9 pagesSolving Differential EquationsJong CruzNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 1.0Document12 pagesDifferential Equations 1.0Vans HpNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of DEDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts of DEHi HiNo ratings yet
- File 5189323594857419932Document10 pagesFile 5189323594857419932mike sanglitanNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 1.1Document12 pagesDifferential Equations 1.1Vans HpNo ratings yet
- MATH223 - Lecture1 With SolutionDocument19 pagesMATH223 - Lecture1 With SolutionRaymond AbesamisNo ratings yet
- ENDEQN30 - Module 1b MEC191Document22 pagesENDEQN30 - Module 1b MEC191Ian Arnold FamiNo ratings yet
- Problem Setof Differential EquationDocument73 pagesProblem Setof Differential EquationpicugaNo ratings yet
- Grade: XI Mathematics-Differential Equations NotesDocument2 pagesGrade: XI Mathematics-Differential Equations NotesVenakadalakshmi KannappanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set & Solutions: Differential Equation: Ibnu RafiDocument73 pagesProblem Set & Solutions: Differential Equation: Ibnu RafiAllan Mugisha100% (1)
- Differentian EquationChapter 1 Basic ConceptsDocument23 pagesDifferentian EquationChapter 1 Basic ConceptsHassan GandamraNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods and Its Applications: Introduction To Linear Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesMathematical Methods and Its Applications: Introduction To Linear Differential EquationsVarsha DangeNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Module 1Document17 pagesUnit I - Module 1Anyanna MunderNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 22. Differential EquationsDocument332 pagesChapter - 22. Differential Equationsgimoc51465No ratings yet
- DE Module 1Document33 pagesDE Module 1Miguel BernabeNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Method of PhysicsDocument4 pagesMathematical Method of PhysicsPro ProductNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Part 1 Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument22 pagesLesson 1 Part 1 Introduction To Differential EquationsAlexah Marie BibatNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Two-Way ANOVADocument14 pagesUnderstanding The Two-Way ANOVAMaridil Joy IsidroNo ratings yet
- Umar Zahid 2022-MBA-628 Applied Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesUmar Zahid 2022-MBA-628 Applied Data AnalysisTECH CENTRALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Mathematics - Class 12 - Formula - SheetDocument1 pageChapter 9 Mathematics - Class 12 - Formula - SheetAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ice 2105 Module 1.1 1.2 Lecture Video NotesDocument22 pagesIce 2105 Module 1.1 1.2 Lecture Video NotesCyam DashNo ratings yet
- 9 Differential Equations 1Document35 pages9 Differential Equations 1princevashi1123No ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument8 pagesDifferential Equationkpmhydro10No ratings yet
- Calculus 3 5Document31 pagesCalculus 3 5Tùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Researc H: Reporters: Irish Angel B. Ancanan Jihann Sydney D. JavierDocument12 pagesResearc H: Reporters: Irish Angel B. Ancanan Jihann Sydney D. JavierIrish Angel B. AncananNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations-IDocument13 pagesDifferential Equations-IMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesDifferential Equationsapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Lesson 1aDocument7 pagesLesson 1aNiño Bryle M. LimotanNo ratings yet
- EMAT 2163 Presentation 1 - Part ADocument5 pagesEMAT 2163 Presentation 1 - Part AIsuru LakshanNo ratings yet
- ODEs 2024Document16 pagesODEs 2024Ahtasham ArshadNo ratings yet
- Notes of ODEDocument14 pagesNotes of ODEWinnie MutukuNo ratings yet
- Types of VariablesDocument2 pagesTypes of VariablesCheindy Mae Santos II100% (1)
- 3.1 - Experimental MethodsDocument39 pages3.1 - Experimental MethodsKhae PadiernosNo ratings yet
- Math 7Document5 pagesMath 7Christian Laurenz AndradeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesClassification of Differential EquationsChristian Laurenz AndradeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear RegressionDocument2 pagesMultiple Linear RegressionFizatahirNo ratings yet
- Choosing Statistical TedsdstDocument7 pagesChoosing Statistical TedsdstHimanshParmarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1: Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesLecture Notes 1: Introduction To Differential EquationsTaanzNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - IntroductionsDocument2 pagesDifferential Equations - IntroductionsTaanzNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation 2Document21 pagesDifferential Equation 2بشار الراشديNo ratings yet
- 44 Diffrential Equations Part 2 of 3Document14 pages44 Diffrential Equations Part 2 of 3ayushNo ratings yet
- A. Independent and Dependent VariableDocument4 pagesA. Independent and Dependent VariableJeromeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 01 - Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument8 pagesMODULE 01 - Introduction To Differential Equationsruveldoroy6No ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework and VariablesDocument21 pagesTheoretical Framework and VariablesFawad LatifNo ratings yet
- Experimental Pyschology: Experimental MethodsDocument11 pagesExperimental Pyschology: Experimental MethodsShekaina YaniNo ratings yet
- Two Way Anova: Welly Ernando Septian Rezy Nurul NatasaDocument19 pagesTwo Way Anova: Welly Ernando Septian Rezy Nurul Natasaheri wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: NomenclatureDocument3 pagesDifferential Equations: Nomenclaturera02No ratings yet
- Applications of Differential Equations in EngineeringDocument4 pagesApplications of Differential Equations in EngineeringSammas Sham ZeaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesDifferential Equation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaVinod BabuNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 8614Document35 pagesUnit 7 8614My ThoughtsNo ratings yet
- Concept of Basic Differential EquationsDocument12 pagesConcept of Basic Differential EquationsSayan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Multilpe RegressionDocument17 pagesMultilpe RegressionArnette Joy BachillerNo ratings yet
- Part 1 of Applied Mathematics - Eimartis - 1Document53 pagesPart 1 of Applied Mathematics - Eimartis - 1عمر الحكيميNo ratings yet
- Discriminant Analysis: Prepared By-Sumit JainDocument44 pagesDiscriminant Analysis: Prepared By-Sumit Jainsumitjain_amcap5571No ratings yet
- Module 9 - Simple Linear Regression & CorrelationDocument29 pagesModule 9 - Simple Linear Regression & CorrelationRoel SebastianNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Computer Function: Reads (Fetches) InstructionsDocument20 pages3.2 Computer Function: Reads (Fetches) InstructionsElaph AhmedNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 EditionDocument4 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 EditionElaph AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Organization and Architecture Computer Architecture:: Refers To Those Attributes of ADocument10 pages1.1 Organization and Architecture Computer Architecture:: Refers To Those Attributes of AElaph AhmedNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument5 pagesEigenvalues and EigenvectorsElaph AhmedNo ratings yet