Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?
What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?
Uploaded by
AqilahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ebook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesEbook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (17)
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument2 pagesBiochem Reviewerrealistic0830No ratings yet
- Types of RespirationDocument5 pagesTypes of RespirationJevelyn Mendoza FarroNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDocument4 pagesMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism in Fish: o o o oDocument4 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism in Fish: o o o oMD. SAKIB MUBALLIGNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument45 pagesCarbohydratescropion_78No ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)Document11 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)soumyajitghosh289No ratings yet
- Respiration A LevelDocument30 pagesRespiration A LevelSamuel HarvNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8Document7 pagesHsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8diyakozhimalaNo ratings yet
- HMS 4601 NUTRITION TO FUEL SPORTS PERFORMANCE - Case 1Document23 pagesHMS 4601 NUTRITION TO FUEL SPORTS PERFORMANCE - Case 1stijn.berkmortel1No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CarbonDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 CarbonBlessingNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Ex Physiology Group1Document31 pagesBioenergetics Ex Physiology Group1arham mujahidNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13. Introduction To Metabolism: - Catabolism - Degradation - Anabolism (Aka Biosynthesis) - EnergyDocument20 pagesLecture 13. Introduction To Metabolism: - Catabolism - Degradation - Anabolism (Aka Biosynthesis) - EnergyAnonymous Bh9NrU77No ratings yet
- Respiration ppt1Document15 pagesRespiration ppt1api-244168124No ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION & Principle of Energy MetabolismDocument84 pagesBIOLOGICAL OXIDATION & Principle of Energy MetabolismAnikusaSaniariNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument33 pages(Download PDF) Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapterjadidbrmawi100% (5)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsjanakiramannadesanNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesKey ConceptsHikaru IshiiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration Is, in Its Broadest Definition, The Process in Which TheDocument1 pageCellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration Is, in Its Broadest Definition, The Process in Which TheBriana Munoz-MorganNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-3bDocument10 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-3bAnnejhel Mae PoralanNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesCampbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manualkevinrodriguezcnytfpaskx100% (27)
- Exercise Physiology Course Notes PDFDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course Notes PDFPRAJINIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - RESPIRATION IN PLANTSDocument10 pagesChapter 14 - RESPIRATION IN PLANTSprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- ATP Production From Carbs Protein FatsDocument16 pagesATP Production From Carbs Protein Fatshuraira bhattiNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Is AnDocument4 pagesGlycolysis Is AnKarla RubinNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document6 pagesQ2 Module 5joseantoniolcastro408No ratings yet
- Energy Transformation (N)Document56 pagesEnergy Transformation (N)Princess Lorreine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- HW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismDocument2 pagesHW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismyanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Group1Document53 pagesCellular Respiration Group1Erline Suzette GabrielNo ratings yet
- Bio1610 Discussion q2Document1 pageBio1610 Discussion q2api-241205310No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 pagesCellular RespirationromiifreeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyDocument10 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyManoj PantaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Class 11Document21 pagesRespiration Class 11madhavi goswamiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Respiration in DetailsDocument9 pagesRespiration in DetailsasifaqtabsaifNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- PPT On Respiration in Plants Xi BioDocument46 pagesPPT On Respiration in Plants Xi BioRiya NarangNo ratings yet
- Atp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasDocument12 pagesAtp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasIan AusejoNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument100 pagesRespirationColin RiddellNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022Document59 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 2022Catherine SilokaNo ratings yet
- Plantrespiration 220508070537 Cd11ce93Document58 pagesPlantrespiration 220508070537 Cd11ce93lee863713No ratings yet
- Resp and Photo Study GuideDocument3 pagesResp and Photo Study GuidenikvNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23Document13 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23tytytfbfvhbvb dhbvNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument49 pagesCellular RespirationJohn Paul RoaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Fermentation (2 Files Merged) PDFDocument93 pagesCellular Respiration and Fermentation (2 Files Merged) PDFeddula ganeshNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: The Photosynthetic ApparatusDocument1 pageWhat Is Photosynthesis?: The Photosynthetic ApparatusAqilahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Elephant Part 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Elephant Part 1AqilahNo ratings yet
- Four Stages of Respiration: What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?Document1 pageFour Stages of Respiration: What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?AqilahNo ratings yet
- Gorgeous Images of Australian 'Rainbow' Bees Will Blow Your MindDocument1 pageGorgeous Images of Australian 'Rainbow' Bees Will Blow Your MindAqilahNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions and DiagramDocument4 pagesAnimal Cell - Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions and DiagramAqilahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Short or Slender ColumnDocument3 pagesDetermination of Short or Slender ColumnAqilahNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument19 pagesBeam DesignAqilahNo ratings yet
- IDM SerialDocument1 pageIDM SerialAqilahNo ratings yet
What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?
What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?
Uploaded by
AqilahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?
What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?
Uploaded by
AqilahCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is the Formula for Cellular Respiration?
Updated April 23, 2019
By Chris Deziel
The cellular processes inside the bodies of humans, animals and even fish depend on the
formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This complex organic chemical can convert into
less complex mono- and di-phosphates, releasing energy that the organism consumes. It is
also involved in the production of DNA and RNA. ATP is one of the by-products of cellular
respiration, for which the raw ingredients are glucose and oxygen.
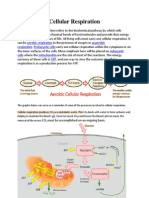
Chemical Formula for Respiration
Glucose, a complex sugar, combines with oxygen during respiration to produce water, carbon
dioxide and ATP. The combination of one glucose molecule with six molecules of gaseous
oxygen produces six water molecules, six carbon dioxide molecules and 38 molecules of
ATP. The chemical equation for the reaction is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 or 38 ATP molecules
While glucose is the main fuel for respiration, energy can also come from fats and proteins, although
the process is not as efficient. Respiration proceeds in four discrete stages and releases about 39
percent of the energy stored in the glucose molecules.
Reference
1. https://sciencing.com/formula-cellular-respiration-5513197.html
You might also like
- Ebook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesEbook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (17)
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument2 pagesBiochem Reviewerrealistic0830No ratings yet
- Types of RespirationDocument5 pagesTypes of RespirationJevelyn Mendoza FarroNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDocument4 pagesMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism in Fish: o o o oDocument4 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism in Fish: o o o oMD. SAKIB MUBALLIGNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument45 pagesCarbohydratescropion_78No ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)Document11 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)soumyajitghosh289No ratings yet
- Respiration A LevelDocument30 pagesRespiration A LevelSamuel HarvNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8Document7 pagesHsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8diyakozhimalaNo ratings yet
- HMS 4601 NUTRITION TO FUEL SPORTS PERFORMANCE - Case 1Document23 pagesHMS 4601 NUTRITION TO FUEL SPORTS PERFORMANCE - Case 1stijn.berkmortel1No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CarbonDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 CarbonBlessingNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Ex Physiology Group1Document31 pagesBioenergetics Ex Physiology Group1arham mujahidNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13. Introduction To Metabolism: - Catabolism - Degradation - Anabolism (Aka Biosynthesis) - EnergyDocument20 pagesLecture 13. Introduction To Metabolism: - Catabolism - Degradation - Anabolism (Aka Biosynthesis) - EnergyAnonymous Bh9NrU77No ratings yet
- Respiration ppt1Document15 pagesRespiration ppt1api-244168124No ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION & Principle of Energy MetabolismDocument84 pagesBIOLOGICAL OXIDATION & Principle of Energy MetabolismAnikusaSaniariNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument33 pages(Download PDF) Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapterjadidbrmawi100% (5)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsjanakiramannadesanNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesKey ConceptsHikaru IshiiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration Is, in Its Broadest Definition, The Process in Which TheDocument1 pageCellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration Is, in Its Broadest Definition, The Process in Which TheBriana Munoz-MorganNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-3bDocument10 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-3bAnnejhel Mae PoralanNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesCampbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manualkevinrodriguezcnytfpaskx100% (27)
- Exercise Physiology Course Notes PDFDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course Notes PDFPRAJINIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - RESPIRATION IN PLANTSDocument10 pagesChapter 14 - RESPIRATION IN PLANTSprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- ATP Production From Carbs Protein FatsDocument16 pagesATP Production From Carbs Protein Fatshuraira bhattiNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Is AnDocument4 pagesGlycolysis Is AnKarla RubinNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document6 pagesQ2 Module 5joseantoniolcastro408No ratings yet
- Energy Transformation (N)Document56 pagesEnergy Transformation (N)Princess Lorreine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- HW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismDocument2 pagesHW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismyanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Group1Document53 pagesCellular Respiration Group1Erline Suzette GabrielNo ratings yet
- Bio1610 Discussion q2Document1 pageBio1610 Discussion q2api-241205310No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 pagesCellular RespirationromiifreeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyDocument10 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyManoj PantaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Class 11Document21 pagesRespiration Class 11madhavi goswamiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Respiration in DetailsDocument9 pagesRespiration in DetailsasifaqtabsaifNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- PPT On Respiration in Plants Xi BioDocument46 pagesPPT On Respiration in Plants Xi BioRiya NarangNo ratings yet
- Atp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasDocument12 pagesAtp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasIan AusejoNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument100 pagesRespirationColin RiddellNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022Document59 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 2022Catherine SilokaNo ratings yet
- Plantrespiration 220508070537 Cd11ce93Document58 pagesPlantrespiration 220508070537 Cd11ce93lee863713No ratings yet
- Resp and Photo Study GuideDocument3 pagesResp and Photo Study GuidenikvNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23Document13 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23tytytfbfvhbvb dhbvNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument49 pagesCellular RespirationJohn Paul RoaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Fermentation (2 Files Merged) PDFDocument93 pagesCellular Respiration and Fermentation (2 Files Merged) PDFeddula ganeshNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: The Photosynthetic ApparatusDocument1 pageWhat Is Photosynthesis?: The Photosynthetic ApparatusAqilahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Elephant Part 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Elephant Part 1AqilahNo ratings yet
- Four Stages of Respiration: What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?Document1 pageFour Stages of Respiration: What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?AqilahNo ratings yet
- Gorgeous Images of Australian 'Rainbow' Bees Will Blow Your MindDocument1 pageGorgeous Images of Australian 'Rainbow' Bees Will Blow Your MindAqilahNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions and DiagramDocument4 pagesAnimal Cell - Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions and DiagramAqilahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Short or Slender ColumnDocument3 pagesDetermination of Short or Slender ColumnAqilahNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument19 pagesBeam DesignAqilahNo ratings yet
- IDM SerialDocument1 pageIDM SerialAqilahNo ratings yet