Professional Documents
Culture Documents
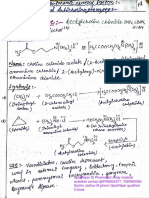
Toxicology and Antidote
Toxicology and Antidote
Uploaded by
Vikash KushwahaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Toxicology and Antidote
Toxicology and Antidote
Uploaded by
Vikash KushwahaCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTES ON DRUG POISONING AND ANTIDOTE @2018PPASagar [Copyright protected]
LIST OF ANTIDOTES FOR DRUG POISONING
Antidotes to Common Medications
No. Drugs Antidote
01 Acetaminophen N-Acetylcysteine or Mucomyst
02 Anticholinesterase Atropine or Pralidoxime
03 Anticholinergics, diphenhydramine, Physostigmine
dimenhydrinate
04 Antifreeze Fomepizole, Ethanol
05 BenzodiazepinesZaleplonZolpidem Flumazenil (Romazicon)
06 Beta-Blocking agents, Calcium channel Glucagon, Epinephrine
blockers, Hypoglycemia, Hypoglycemic
agents
07 Calcium Channel Blockers Calcium Chloride, Glucagon
08 Coumadin Phytonadione or Vitamin K
09 Cyanide Amyl nitrite, sodium nitrite, sodium
thiosulfate
10 Cyclophosphamide Mesna
11 Digoxin Digibind or Digoxin Immune Fab
13 Heroin Naloxone (Narcan) or Nalmefene
14 Iron Deferoxamine
15 Heparin Protamine Sulfate
16 Lead EDTA, dimercaprol, succimer
18 Methotrexate Leucovorin calcium
19 Potassium Insulin + Glucose, Kayexalate
20 Methanol Folic acid
21 Valproic acid L-Carnitine
22 Sulfonylureas Octreotide (Sandostatin )
23 Isoniazid, ethylene glycol Pyridoxine HCl (Vitamin B6)
24 Sodium channel blockers (e.g. cyclic Sodium Bicarbonate
antidepressants), salicylates
25 Ethylene glycol Thiamine
26 Calcium channel blockersFluoride salts (e.g., Calcium chloride andCalcium gluconate
NaF)Hydrofluoric acid (HF)Hyperkalemia
(not digoxin-induced)Hypermagnesemia
27 Ethylene glycolMethanol Ethanol
28 Alpha agonists (e.g., clonidine), Opioids (e.g., Naloxone
codeine, diphenoxylate, fentanyl, heroin,
meperidine, morphine and propoxyphene)
29 Arsenic, Copper, Lead, Mercury D-Penicillamine (Cuprimine )
30 Local anesthetics and possibly othercardiac Fat emulsion (Intralipid , Liposyn II , Liposyn
toxins (e.g., bupropion, calciumchannel III )
blockers, cocaine, beta blockers, tricyclic
antidepressants)
How The Poison Enter Into The Body?
The Poison In Any Form may be taken in by the breath Or swallowed, Absorbed
Through the thinner and more delicate mucous membranes, Or absorbed through the skin,
or implanted by stings, bites, or other wounds.
There Are A lot Of Antidotes In The Medical Field Today But Some Antidotes Are Very
Important And Need To Be Remembered Because Of Their Frequent Use In The Emergency
Situations. Knowledge About Antidotes
Is Very Important For All Medical Professionals Especially Those Who Are Working In
Health Care Settings.Here Are Some Of The Types And List Of Very Important And
Frequently Used Antidotes ;
Pioneer Pharma AcademySagar (M.P.)(1) 7000409969, 6264805074
NOTES ON DRUG POISONING AND ANTIDOTE @2018PPASagar [Copyright protected]
Types of Antidotes
1: Universal Antidotes :This type of antidote is Given when unknown poison is ingested
Composition:
(1):powdered charcoal 2 parts
(2):Magnesium oxide 1 part
(3):Tannic Acid 1 Part
2: Chemical Antidotes :These substances neutrilize the chemical action or oxidize the poison
into nontoxic or insolouble form
eg:
Dilute alkali(milk of magnesia)
Dilute acetic acid,
Potassium permangante
Tannin(strong tea).
3: Physiological or pharmacological Antidotes
These produce effects opposite to that of poison
eg:
Naloxone for morphine,
Atropine and oxime for organophosphorous poison,
N-acetylcysteine for acetaminophen
4: Mechanical or physical Antidotes :
These substances prevents the absorption of poison by their presence
eg: Activated charcoal is used for strychinine.
Emulcents(fats,oils,milk,eggalbumin) are used for corrosive and irritant poisoning,
Bulky food used for glass poisoning And mineral poisoning(dose 30-60 gms for children and 60-
100gms for adults)
5: Chelating agents:
These are substances which form chelates(non ionized complexes) with cations.These are
mostly used in heavy metal poisoning
eg:
N-pencillamine for mercury,lead,copper
BAL(dimercepol) is used in heavy metal poisons
EDTA is used in Arsenic,mercury,lead
Versenate is used in Arsenic,mercury and lead
Desferoxamine is used for iron.
Important Antidotes List
Antidotes For
Non-specific poisons except cyanide, iron, lithium, caustics and alcohol = Activated charcoal
Cobra bite = Snake Anti-Venin.
Heparin = Protamine Sulfate
Gas=Use artificial respiration,Remove patient to air, apply heat to extremities; send for doctor.
Absinthe = Give an active emetic; then flaxseed tea freely; stimulate
Insulin reaction = Glucose (Dextrose 50%)
Alkali, Volatile = Drink freely of water with vinegar or lemon juice in it.
Antimonial Wine = Give warm water freely to encourage vomiting.
Aqua Fortis = Magnesia or soap dissolved in water, every two minutes.
Bed Bug Poison = Give milk or white of eggs in large quantities.
Belladona = Active emetic; stimulate.
Acetaminophen/Paracetamol = N-Acetylcysteine or Mucomyst
Anticholinergics, diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate =Physostigmine
BenzodiazepinesZaleplonZolpidem = Flumazenil (Romazicon)
Calcium Channel Blockers = Calcium Chloride, Glucagon
Cyanide = Amyl nitrite, sodium nitrite, sodium thiosulfate
Iron = Deferoxamine
For Chemicals causing methemoglobinemia in patients with G6PD deficiency = Vitamin C
Pioneer Pharma AcademySagar (M.P.)(2) 7000409969, 6264805074
NOTES ON DRUG POISONING AND ANTIDOTE @2018PPASagar [Copyright protected]
For Lead = EDTA, dimercaprol, succimer
Methanol = Folic acid
Ammonia = Lemon juice, diluted vinegar or acetic acid.
Methotrexate = Leucovorin calcium
Potassium = Insulin + Glucose, Kayexalate
Mercury = White of eggs freely; afterwards evacuate; mild drinks
Valproic acid = L-Carnitine
Isoniazid, ethylene glycol = Pyridoxine HCl (Vitamin B6)
Tricyclic antidepressants = phyostigmine or NaHCO3
Sulfonylureas = Octreotide (Sandostatin )
Alpha agonists (e.g., clonidine), Opioids (e.g., codeine, diphenoxylate, fentanyl, heroin,
meperidine, morphine and propoxyphene = Naloxone
Arsenic, Copper, Lead, Mercury = D-Penicillamine (Cuprimine )
Neuromuscular blockade = anticholinesterase agents.
Anticholinesterase = atropine sulfate or pralidoxime.
Fluoride ingestion = Calcium salts
Digoxin = digibind digoxine immune fab
Beta blockers and calciumchannel blockers = glucagon
Ergotamine = Heparin
Dopamine = Phentolamine.
SUMMERY OF DRUG AND ANTIDOTE
Antidote Indication(POISONING) Mode of Action
acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) Acetaminophen/ Tylenol/ Restores depleted
Paracetamol glutathione stores and
protects against renal and
hepatic failure.
Activated charcoal Non-specific poisons except Absorption of drug in the
cyanide, iron, lithium, caustics gastric and intestinal tracts.
and alcohol. Interrupts the entero-hepatic
cycle with multiple dose.
albuterol inhaler, insulin & Potassium
glucose, NaHCO3, kayexalate
anticholinesterase agents Neuromuscular blockade
(paralytics)
atropine sulfate or Anticholinesterase Competitive inhibition of
pralidoxime muscarinic receptors.
Benzylpenicillin Amanita phalloides (Death cap Not known; partial
mushroom) protection against acute
hepatic failure; may displace
amatoxin from protein-
binding sites allowing
increased renal excretion;
may also inhibit penetration
of amatoxin to hepatocytes.
Calcium salts Fluoride ingestion Rapidly complexes with
fluoride ion.
deferoxamine Iron Deferoxamine acts by
binding free iron in the
bloodstream and enhancing
its elimination in the urine.
digibind Digoxin Binds molecules of digoxin,
digoxine immune fab making them unavailable for
binding at their site of action
on cells in the body.
Pioneer Pharma AcademySagar (M.P.)(3) 7000409969, 6264805074
NOTES ON DRUG POISONING AND ANTIDOTE @2018PPASagar [Copyright protected]
dimercapol, edetate calcium, Lead Chelation of lead ions and
disodium, endogenous metals (e.g.,
zinc, manganese, iron,
copper).
diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Extrapyramidal symptoms A potent antagonist to
(EPS) acetylcholine in muscarinic
receptors.
flumazenil Benzodiazepines Reverses the effects of
benzodiazepines by
competitive inhibition at the
benzodiazepine binding site
on the GABAA receptor.
fomepizole Ethylene glycol A competitive inhibitor of
the enzyme alcohol
dehydrogenase found in the
liver. This enzyme plays a
key role in the metabolism of
ethylene glycol and
methanol.
glucagon Beta blockers and calcium Stimulates the formation of
channel blockers adenyl cyclase causing
intracellular increase in
cycling AMP and enhanced
glycogenolysis and elevated
serum glucose
concentration.
Glucose (Dextrose 50%) Insulin reaction Dextrose (the
monosaccharide glucose) is
used, distributed and stored
by body tissues and is
metabolized to carbon
dioxide and water with the
release of energy.
Heparin Ergotamine Reverses hypercoagulable
state by interacting with
antithrombin III. Used in
combination with
vasodilator phentolamine or
nitroprusside to prevent
local thrombosis and
ischemia.
Hydroxocobalamin Cyanide Forms cyanocobalamin, a
non-toxic metabolite that is
easily excreted through the
kidneys.
leucovorin calcium Fluorouracil
Methotrexate Protects the healthy cells
from the effects of
methotrexate while allowing
methotrexate to enter and
kill cancer cells.
Magnesium sulfate calcium gluconate
mesna Cyclophosphamide A “chemoprotectant” drug
that reduces the undesired
Pioneer Pharma AcademySagar (M.P.)(4) 7000409969, 6264805074
NOTES ON DRUG POISONING AND ANTIDOTE @2018PPASagar [Copyright protected]
effects of certain
chemotherapy drugs.
Methylene blue Chemical producing severe Reduces methemoglobin to
methemoglobinemia. Ifosamide- hemoglobin.
induced encephalopathy.
nalmefene or naloxone Opioid analgesics Prevents or reverses the
effects of opioids including
respiratory depression,
sedation and hypotension.
naloxone (Narcan) Narcotics Naloxone is believed to
antagonize opioid effects by
competing for the µ, ? and ?
opiate receptor sites in the
CNS, with the greatest
affinity for the µ receptor.
Neostigmine Anticholinergics Anticholinesterase which
causes accumulation of
acetylcholine at cholinergic
receptor sites.
Nitrite, sodium and Cyanide Oxidizes hemoglobin to
glycerytrinitrate methemoglobin which binds
the free cyanide and can
enhance endothelial cyanide
detoxification by producing
vasodilation.
Penicillamine Copper, gold, lead, mercury, Chelation of metal ions.
zinc, arsenic
phentolamine (Regitine) Dopamine Regitine produces an alpha-
adrenergic block of relatively
short duration. It also has
direct, but less marked,
positive inotropic and
chronotropic effects on
cardiac muscle and
vasodilator effects on
vascular smooth muscle.
phyostigmine or NaHCO3 Tricyclic antidepressants A reversible
anticholinesterase which
effectively increases the
concentration of
acetylcholine at the sites of
cholinergic transmission.
Phytomenadione (Vitamin Coumadin/Warfarin Bypasses inhibition of
K.) Vitamin K epoxide reductase
enzyme.
protamine sulfate Heparin Protamine that is strongly
basic combines with acidic
heparin forming a stable
complex and neutralizes the
anticoagulant activity of both
drugs.
Pyridoxine Isoniazid, theophylline, Reverses acute pyridoxine
monomethyl hydrazine. deficiency by promoting
Adjunctive therapy in ethylene GABA synthesis. Promotes
Pioneer Pharma AcademySagar (M.P.)(5) 7000409969, 6264805074
NOTES ON DRUG POISONING AND ANTIDOTE @2018PPASagar [Copyright protected]
glycol poisoning. the conversion of toxic
metabolite glycolic acid to
glycine.
Snake anti-venin Cobra bite Neutralizes venom by
binding with circulating
venom components and with
locally deposited venom by
accumulating at the bite site.
Sodium Bicarbonate Iron Prevents convertion of
ferrous to ferric.
Cardiotoxic drug affecting fast Decreases affinity of
sodium channel (TCA, cocaine) cardiotoxic drugs to the fast
sodium channel.
Weak acids Promotes ionization of weak
acids.
Chlorine gas inhalational Neutralization of
poisoning hydrochloric acid formed
when chlorine gas reacts
with water in the airways.
Sodium thiosulphate Cyanide Replenishes depleted
thiosulphate stores by acting
as sulfur donor necessary for
the conversion of CN-O to
thiocyanate through the
action of sulfur transferase
enzyme rhodanese.
Thiamine Alcohol, Wernicke-Korsakoff Reverses acute thiamine
Syndrome deficiency
Adjunctive in ethylene glycol Enhances detoxification of
glyoxylic acid.
Vitamin C Chemicals causing Reduces methemoglobin to
methemoglobinemia in patients hemoglobin.
with G6PD deficiency
Pioneer Pharma AcademySagar (M.P.)(6) 7000409969, 6264805074
You might also like
- Drugs Affecting Calcium BalanceDocument63 pagesDrugs Affecting Calcium BalanceRd Chandane100% (1)
- Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument5 pagesAntidote Indication Mode of ActionRegalado AguhayonNo ratings yet
- CVS MCQS 06 QDocument2 pagesCVS MCQS 06 Qharshad patelNo ratings yet
- Drug Design: Functional Groups / Pharmacological ActivityDocument24 pagesDrug Design: Functional Groups / Pharmacological ActivityIoana Mirela VasincuNo ratings yet
- Aclf NejmDocument9 pagesAclf NejmandreeaNo ratings yet
- Rug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaDocument40 pagesRug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaNiteesh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Case PresentationDocument58 pagesDiabetic Foot Case PresentationZH. omg sarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology PDFDocument109 pagesPharmacology PDFRanjit TharuNo ratings yet
- Cvs PharmacologyDocument75 pagesCvs PharmacologyTamratKelelegn100% (1)
- 1a..antimicrobials IntroductionDocument84 pages1a..antimicrobials IntroductionAnonymous RlDDdTAsKJNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesIschaemic Heart DiseaseEB100% (1)
- Electrolyte Replacement Guide - ICU CliniciansDocument8 pagesElectrolyte Replacement Guide - ICU Cliniciansnolan4266No ratings yet
- Vancomycin ReviewDocument26 pagesVancomycin Reviewkhangsiean89No ratings yet
- Bpac Inr Poem 2006 WVDocument26 pagesBpac Inr Poem 2006 WVmrezasyahliNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument69 pagesCardiovascular NotesAnnissaLarnardNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Document40 pagesDrug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Kamal SikandarNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument17 pagesMCQpradeephdNo ratings yet
- Pharmacist HasifDocument66 pagesPharmacist HasifJoy AndresNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Analgesics DR H AboshoushaDocument7 pagesAutacoids Analgesics DR H AboshoushaMoustafa HazzaaNo ratings yet
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocument26 pagesA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- 1 Bullets Pain & orDocument7 pages1 Bullets Pain & orAnne Mae PaculaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Receptor ChartDocument1 pageAdrenergic Receptor Chartsas345sas345No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: Ana Sharmaine S. Uera, MD DR PJGMRMC Anesthesiology Department 1st Year ResidentDocument68 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology: Ana Sharmaine S. Uera, MD DR PJGMRMC Anesthesiology Department 1st Year ResidentLalay CabanagNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document40 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)HiwaNo ratings yet
- COPD ExacerbationDocument2 pagesCOPD ExacerbationjusthoangNo ratings yet
- Drug Recommendation GuideDocument6 pagesDrug Recommendation GuideGenNo ratings yet
- 8B - Antianginal DrugsDocument70 pages8B - Antianginal Drugslalitrajindolia100% (1)
- College of Medicine and Health Sciences: For Public Health C-I StudentsDocument29 pagesCollege of Medicine and Health Sciences: For Public Health C-I StudentsWĩž BŕëãžÿNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GitDocument35 pagesDrugs Acting On GitPridho GaziansyahNo ratings yet
- Drug Succinylcholine Atracurium Cis-Atracurium Rocuronium Vecuronium Pancuronium ED95 Intubating Dose Onset Duration MetabolismDocument1 pageDrug Succinylcholine Atracurium Cis-Atracurium Rocuronium Vecuronium Pancuronium ED95 Intubating Dose Onset Duration MetabolismMarshallMcGoughNo ratings yet
- How To Practice O.T.CDocument106 pagesHow To Practice O.T.Chazar mkNo ratings yet
- ACE 2007 4A QuestionsDocument29 pagesACE 2007 4A QuestionsRachana GudipudiNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry-III MCQsDocument11 pagesMedicinal Chemistry-III MCQsShahrukh SindhiNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Document4 pagesDrug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Leyla MajundaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocument146 pagesMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Pre Assessment Diabetes Nursing CareDocument4 pagesPre Assessment Diabetes Nursing CareHabib UllahNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument16 pagesAntiemeticswalt65No ratings yet
- Athma, COPD and Cough AgentsDocument71 pagesAthma, COPD and Cough AgentsBriana NdayisabaNo ratings yet
- Classification of DrugsDocument10 pagesClassification of DrugsSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-2-QuestionsDocument7 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-2-QuestionsDrishya BioplannetNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- lec2 المعدلةDocument120 pageslec2 المعدلةAhmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Drugs PharmacologyDocument33 pagesAnesthetic Drugs PharmacologynasyariesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs For AnemiaDocument49 pagesPharmacology of Drugs For AnemiaTeus Fatamorgana100% (2)
- Pharmacology Notes: By: Khurram AbbasDocument48 pagesPharmacology Notes: By: Khurram AbbasAsma AnjumNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Alcohol/ Ethanol/ Ethyl Alcohol IndicationDocument19 pagesDrug Name Alcohol/ Ethanol/ Ethyl Alcohol IndicationFauzi Ramadhani muhNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of HTNDocument57 pagesPharmacotherapy of HTNAbera JamboNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic and NonadrenergicDocument49 pagesAdrenergic and Nonadrenergicsweta sumanNo ratings yet
- (Pha) Le 5Document19 pages(Pha) Le 5Gabby TanNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument62 pagesVitaminKrunal Patel100% (1)
- Mark M Calban MD MPM-HSDDocument58 pagesMark M Calban MD MPM-HSDZllison Mae Teodoro Mangabat100% (1)
- Drugs Used in Heart Failure: Pharmacology (2) PHAR 342Document19 pagesDrugs Used in Heart Failure: Pharmacology (2) PHAR 342Dana HamarshehNo ratings yet
- 2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument58 pages2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDKishan SethNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders LectureDocument132 pagesCardiovascular Disorders LectureHarper Epps100% (1)
- Mishba +pharmacology + Tapan ShahDocument232 pagesMishba +pharmacology + Tapan ShahRaushan BlakeNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument10 pagesAntiemeticsnk999999100% (1)
- 783 Q - 650 Answered 07.04.2019Document96 pages783 Q - 650 Answered 07.04.2019Syed Ibrahim100% (1)
- Introduction To Pharmacology AntibioticDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology AntibioticZaira Reine SantosNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationFrom EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument11 pagesPharmaceutical ChemistryVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument24 pagesPathophysiologyVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- CologyDocument31 pagesCologyVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Biopharm NotesDocument16 pagesBiopharm NotesVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Med 5th Sem PDFDocument28 pagesMed 5th Sem PDFVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Chandni VermaDocument29 pagesChandni VermaVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Gpat A Companion PDFDocument1 pageGpat A Companion PDFVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- PharmaceuticsDocument38 pagesPharmaceuticsVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Chalcone DerivativeDocument25 pagesChalcone DerivativeVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 12 Lecture 4-Seismic Waves AFTER MidDocument80 pages12 Lecture 4-Seismic Waves AFTER MidusamaNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions Mechanical Temperature Switches ML1H, MT1H, L2H, T2H, L1X/L1X-EX, T1X/T1X-EX, T2X/T2X-EXDocument8 pagesOperating Instructions Mechanical Temperature Switches ML1H, MT1H, L2H, T2H, L1X/L1X-EX, T1X/T1X-EX, T2X/T2X-EXمحمد فرحاتNo ratings yet
- More On Shrivinayaka AstrologyDocument11 pagesMore On Shrivinayaka AstrologysubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Data Sht. K Type ThermocoupleDocument4 pagesData Sht. K Type ThermocoupleMahek PatelNo ratings yet
- Design and Estimation of Rain Water Harvesting Scheme in VIVA Institute of TechnologyDocument4 pagesDesign and Estimation of Rain Water Harvesting Scheme in VIVA Institute of TechnologyVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- 1-MEPs-ELECT-LTG-B4&7-0001 (SH 1-1) - R-2 (FND Reviewed) - LTG-B4-0001Document1 page1-MEPs-ELECT-LTG-B4&7-0001 (SH 1-1) - R-2 (FND Reviewed) - LTG-B4-0001muzeek306No ratings yet
- Reservation List As of June 27Document104 pagesReservation List As of June 27Francis DedumoNo ratings yet
- XII BIOLOGY Practical 2023-24 NewDocument28 pagesXII BIOLOGY Practical 2023-24 Newpranjal.goswami1830No ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Pygmy Current Meter Model Oss-Pc1: Hyquest Solutions Pty LTDDocument17 pagesInstruction Manual Pygmy Current Meter Model Oss-Pc1: Hyquest Solutions Pty LTDTomás Londoño GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Department of Technical EducationDocument24 pagesDepartment of Technical EducationGagan SNo ratings yet
- Fracture CrurisDocument44 pagesFracture CrurisAnonymous turPUJtErNo ratings yet
- T Rec G.984.7 201007 I!!pdf eDocument14 pagesT Rec G.984.7 201007 I!!pdf eEduardo LanchiNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Characteristics: Table 7.1.5 Table 7.1.6Document4 pagesWastewater Characteristics: Table 7.1.5 Table 7.1.6Amin EnviroNo ratings yet
- Plumbing 2008 Includes FU Calculation Fire Fighting..Document203 pagesPlumbing 2008 Includes FU Calculation Fire Fighting..michelghanem100% (2)
- How To Clean and JerkDocument3 pagesHow To Clean and JerkTim Donahey100% (4)
- TPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3Document88 pagesTPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3DeniMestiWidiantoNo ratings yet
- Effects Temp On PropsDocument5 pagesEffects Temp On Propsdina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Inverted Nipple PaperDocument7 pagesInverted Nipple PaperFarisah Dewi Batari EmsilNo ratings yet
- E700 CatalogDocument77 pagesE700 CatalogAnonymous T0KltPNo ratings yet
- Maths Crossword Puzzle 1c8bb 61632ad7Document1 pageMaths Crossword Puzzle 1c8bb 61632ad7Yash VermaNo ratings yet
- kh7 CVPDocument50 pageskh7 CVPأبوأحمد الحكيمNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Cast Resin Transformer 01Document80 pagesCatalogue Cast Resin Transformer 01Bayu PutraNo ratings yet
- Engine Valve DesignsDocument6 pagesEngine Valve DesignsGhanvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Water Recticulation (16.12.04)Document8 pagesMethod Statement For Water Recticulation (16.12.04)mochacino6867% (6)
- AmraDocument6 pagesAmraShantu ShirurmathNo ratings yet
- Meth QuPPe PO V11 PDFDocument86 pagesMeth QuPPe PO V11 PDFDasharath OulkarNo ratings yet
- Owner's Manual: Main FeaturesDocument56 pagesOwner's Manual: Main FeaturesTie PereiraNo ratings yet
- Civil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Document1 pageCivil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Joel AganNo ratings yet
- Pradeep Kumar Singh: Mob - No.+91-9350532171Document2 pagesPradeep Kumar Singh: Mob - No.+91-9350532171Puspendra Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Infectious Mononucleosis in Adults and Adolescents - UpToDateDocument26 pagesInfectious Mononucleosis in Adults and Adolescents - UpToDateEduardo Romero StéfaniNo ratings yet