Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vacuum Distillation PDF
Vacuum Distillation PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamed Ouichaoui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
599 views9 pagesVacuum distillation uses reduced pressure and larger diameter towers to further separate high boiling point materials like heavy crude oil fractions. It works similarly to atmospheric distillation but uses packing and demisters instead of trays in the towers. Steam ejectors provide a simple, reliable means of producing the vacuum needed for the process and have low costs due to using available steam. They are commonly used for vacuum systems in petroleum refining, urea production, and other industrial processes.
Original Description:
Original Title
vacuum-distillation.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVacuum distillation uses reduced pressure and larger diameter towers to further separate high boiling point materials like heavy crude oil fractions. It works similarly to atmospheric distillation but uses packing and demisters instead of trays in the towers. Steam ejectors provide a simple, reliable means of producing the vacuum needed for the process and have low costs due to using available steam. They are commonly used for vacuum systems in petroleum refining, urea production, and other industrial processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
599 views9 pagesVacuum Distillation PDF
Vacuum Distillation PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamed OuichaouiVacuum distillation uses reduced pressure and larger diameter towers to further separate high boiling point materials like heavy crude oil fractions. It works similarly to atmospheric distillation but uses packing and demisters instead of trays in the towers. Steam ejectors provide a simple, reliable means of producing the vacuum needed for the process and have low costs due to using available steam. They are commonly used for vacuum systems in petroleum refining, urea production, and other industrial processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
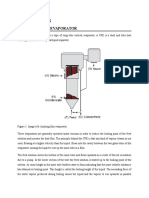
Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum Distillation Tower
• to further distill high
boiling point
materials, reduced
pressure is required
to prevent thermal
cracking
• The process takes
place in one or more
vacuum distillation
towers.
Atmospheric vs. Vacuum
• The principles of vacuum distillation
resemble those of fractional distillation,
except that:
• larger-diameter columns are used to maintain
comparable vapor velocities at the reduced
pressures, the equipment is also similar
• The internal designs of some vacuum towers are
different in that random packing and demister pads
are used instead of trays.
In Petroleum Industry
• Vacuum distillation involves taking the residue produced
in the crude distillation unit and further separating this
fraction into lighter fractions:
• inerts/gas
• vacuum gas oil (light, medium and heavy)
• residue
Steam Ejectors
• simple, reliable means of producing
vacuum
• They have low installed cost as well
• They are commonly found in process
plants having available steam
• They provide many years of trouble-free
operation
Ejector basics
• a three-stage ejector system with two surface-
contact inter-condensers. motive force is provided
by steam jets, which draw vapor from a vessel and
through the system. The condensers act to reduce
the load on the next ejector.
Examples (1)
• Triple element first-
stage ejectors for
crude vacuum
distillation
Examples (2)
• A first-stage ejector
for a urea plant
vacuum system.
The ejector
includes heat
tracing and flushing
nozzles to remove
solid deposits from
ejector internals
Examples (3)
• Three large
booster
ejectors ready
for shipment
to a steel mill
You might also like
- 4.3. Consider The Flowsheet For The Manufacture of Vinyl Chloride in Figure 4.8Document2 pages4.3. Consider The Flowsheet For The Manufacture of Vinyl Chloride in Figure 4.8Anonymous QwUTQlAO100% (1)
- Liquid Liquid Extraction in A Packed BedDocument26 pagesLiquid Liquid Extraction in A Packed BedAr SaidNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - 4: ChloromethaneDocument4 pagesLECTURE - 4: Chloromethaneمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Simulink Development of Single Effect Evaporator Using MatlabDocument12 pagesSimulink Development of Single Effect Evaporator Using MatlabRhea MambaNo ratings yet
- Lab With Index1Document35 pagesLab With Index1Labdhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Cascade Control BasicsDocument2 pagesCascade Control Basicsjsrplc7952100% (2)
- Distillation ColumnDocument6 pagesDistillation ColumnArif HanafiNo ratings yet
- Henrys Law Solved ProblemsDocument3 pagesHenrys Law Solved ProblemsayushNo ratings yet
- Hysys Class 5Document5 pagesHysys Class 5Salim ChohanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Vapor-Liquid Separation (Multicomponent Distillation)Document19 pagesWeek 4 - Vapor-Liquid Separation (Multicomponent Distillation)psychopassNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Gas AbsorptionDocument18 pagesExp 4 Gas AbsorptionakuNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption LabDocument8 pagesGas Absorption Labsolehah misni100% (1)
- Process Calculations Sample ChaptersDocument21 pagesProcess Calculations Sample ChaptersGurunath Epili50% (2)
- Metodos de Analisis de OleumDocument3 pagesMetodos de Analisis de OleumArmando PerezNo ratings yet
- Compressor Api617 LMC BMC 311f Maintenance ManualDocument6 pagesCompressor Api617 LMC BMC 311f Maintenance ManualAvishek HazraNo ratings yet
- 2 Phase Seperator PDFDocument66 pages2 Phase Seperator PDFKanthan DevanNo ratings yet
- Lect FractionizationDocument57 pagesLect Fractionizationraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating CompressorDocument24 pagesReciprocating CompressorSANTHOSH NAGARAJA0% (1)
- Climbing Film Evaporation Data (2016) - All GroupsDocument12 pagesClimbing Film Evaporation Data (2016) - All GroupsJuwon Jeremiah MakuNo ratings yet
- BY Tamil Selvam 2282ADocument11 pagesBY Tamil Selvam 2282AKarthickNo ratings yet
- HP Fuel Gas SystemDocument8 pagesHP Fuel Gas SystemAnonymous QSfDsVxjZNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship At: Haldia Petrochemicals LTDDocument11 pagesSummer Internship At: Haldia Petrochemicals LTDJyoti PrakashNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column 1-2-3 - SizingDocument35 pagesDistillation Column 1-2-3 - SizingKirstie ImeldaNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Lecture 3-1Document20 pagesMass Transfer Lecture 3-1EDWIN SIMBARASHE MASUNUNGURENo ratings yet
- GAS ABSORPTION - ReportDocument6 pagesGAS ABSORPTION - Reportgzairene8762No ratings yet
- Process Design: Vessel Sizing (Liquid & Vapour Separators)Document36 pagesProcess Design: Vessel Sizing (Liquid & Vapour Separators)Krishanu SahaNo ratings yet
- Oil Characterization: Process Simulation Using HYSYS V8Document18 pagesOil Characterization: Process Simulation Using HYSYS V8Jagan BoseNo ratings yet
- Azeotropic Mass BalanceDocument25 pagesAzeotropic Mass BalancesowjanyaavkNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Plates Calculation by McCabe-Thiele MethodDocument4 pagesTheoretical Plates Calculation by McCabe-Thiele Methodmohammad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Cab2054 L1 Absorption and StrippingDocument61 pagesCab2054 L1 Absorption and StrippingAzmi Musa100% (1)
- Absorption (Part 1)Document38 pagesAbsorption (Part 1)Syazwan WanNo ratings yet
- 02 ChE421 - Flash DistillationDocument4 pages02 ChE421 - Flash DistillationAllyana Marie Tiemsim0% (1)
- Heat Transfer Equipment EvaporatorDocument57 pagesHeat Transfer Equipment EvaporatorAsadulhaq Ali HamidiNo ratings yet
- Ch8551 Mass Transfer-I Unit I - (Diffusion) C303.1: Department of Chemical Engineering, VSBECDocument12 pagesCh8551 Mass Transfer-I Unit I - (Diffusion) C303.1: Department of Chemical Engineering, VSBECSaravanan SundaramNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Air CompressorsDocument20 pagesReciprocating Air CompressorsAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- ChE 132 Report (FUG Method)Document35 pagesChE 132 Report (FUG Method)Rio Cañal100% (1)
- Design of Absorber: 5.1 AbsorptionsDocument6 pagesDesign of Absorber: 5.1 AbsorptionssuganthNo ratings yet
- Combustion StoichiometryDocument29 pagesCombustion StoichiometryFatima MasoodNo ratings yet
- 05 Introduction To Multi-Component DistillationDocument30 pages05 Introduction To Multi-Component Distillationchemical08112009100% (1)
- Efflux Time For A Pipe With Different ExitDocument17 pagesEfflux Time For A Pipe With Different ExitChelley Sharleene PecajasNo ratings yet
- Absorption Tray TowersDocument28 pagesAbsorption Tray Towerstalhawasim100% (1)
- Separator 3 FasaDocument14 pagesSeparator 3 FasaAndhy Arya EkaputraNo ratings yet
- Gas AbsorptionDocument34 pagesGas Absorptionlickaa200100% (1)
- DistillationDocument17 pagesDistillationRenu SekaranNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Propane Refrigeration Loop - 4Document24 pages1.1.2 Propane Refrigeration Loop - 4JohnNo ratings yet
- Two-Phase Flow - Condensate Drain Lines Design GuideDocument2 pagesTwo-Phase Flow - Condensate Drain Lines Design Guidec_nghiaNo ratings yet
- Economic Aspects of Setting Up Purge Gas Recovery Unit (PGRU) With Ammonia Production ProcessDocument7 pagesEconomic Aspects of Setting Up Purge Gas Recovery Unit (PGRU) With Ammonia Production ProcessWilly ChandraNo ratings yet
- Evaporation NewDocument64 pagesEvaporation NewshashwatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Source ModelDocument69 pagesChapter 4-Source ModelSatvik SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Kaduna Refining and Petrochemical Company (KRPC) Crude Distillation Unit (CDU I) Using HysysDocument7 pagesSimulation of Kaduna Refining and Petrochemical Company (KRPC) Crude Distillation Unit (CDU I) Using HysysAdhityaEkoBagusNo ratings yet
- Stripping and Distillation Are Both Methods of Separation of Components That Have Differences in Their Relative VolatilityDocument1 pageStripping and Distillation Are Both Methods of Separation of Components That Have Differences in Their Relative VolatilityNthabiseng Mo MalukeNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Document26 pages6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Neybil100% (1)
- Imtp High-Performance Random Packing: Norton Chemical Process Products CorporationDocument16 pagesImtp High-Performance Random Packing: Norton Chemical Process Products Corporationchemkumar16100% (1)
- Adu & VduDocument19 pagesAdu & Vduvijetakumari.201ch059No ratings yet
- What Is Vacuum: Vacuum Refers To The Degree of Emptiness of A Process SystemDocument38 pagesWhat Is Vacuum: Vacuum Refers To The Degree of Emptiness of A Process Systemrnsasikumar100% (1)
- Air Pollution Control DevicesDocument48 pagesAir Pollution Control DevicesPratyush Vaibhav75% (4)
- Lecture 5Document17 pagesLecture 5MuhammadFarooq44No ratings yet
- Aircraft PowerplantDocument93 pagesAircraft PowerplantPranavNo ratings yet
- DehumidificationDocument31 pagesDehumidificationmohammed hussienNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة السابعةDocument5 pagesالمحاضرة السابعةMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- الكيمياء العضوية نظري البعثDocument42 pagesالكيمياء العضوية نظري البعثMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- خواص الغازاتDocument25 pagesخواص الغازاتMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Crude Production PlantDocument16 pagesCrude Production PlantMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Skikda Training CDU (Basis - Process.EQ Modi. Interlock)Document48 pagesSkikda Training CDU (Basis - Process.EQ Modi. Interlock)Mohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- 6648 0500 5 PS Pi 0001 - F PDFDocument65 pages6648 0500 5 PS Pi 0001 - F PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- 6648 0200 5 PS Pi 0001 4 PDFDocument46 pages6648 0200 5 PS Pi 0001 4 PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- 6648 0400 5 PS Pi 0001 - F PDFDocument97 pages6648 0400 5 PS Pi 0001 - F PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Skikda Training CDU (Goal Content)Document26 pagesSkikda Training CDU (Goal Content)Mohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Technip - Petroleum Refining III Conversion Processes PDFDocument364 pagesTechnip - Petroleum Refining III Conversion Processes PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- (6648-0200-5-PS-DS-0026) 200-C-51 - Rev.FDocument15 pages(6648-0200-5-PS-DS-0026) 200-C-51 - Rev.FMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- (6648-0200-5-PS-MB-0001-F) Heat and Material Balance (200 Unit)Document34 pages(6648-0200-5-PS-MB-0001-F) Heat and Material Balance (200 Unit)Mohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram FOR Aromatics Recovery Unit (UNIT NO: 200)Document13 pagesProcess Flow Diagram FOR Aromatics Recovery Unit (UNIT NO: 200)Mohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram FOR Aromatics Recovery Unit (UNIT NO: 200)Document13 pagesProcess Flow Diagram FOR Aromatics Recovery Unit (UNIT NO: 200)Mohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Overview From AONG Website PDFDocument22 pagesNatural Gas Overview From AONG Website PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- (6648-0200-5-PS-DS-0026) 200-C-51 - Rev.FDocument15 pages(6648-0200-5-PS-DS-0026) 200-C-51 - Rev.FMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Unit9 LightNaphthaIsomerization LectureDocument13 pagesUnit9 LightNaphthaIsomerization LectureAyman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Technip - Petroleum Refining III Conversion Processes PDFDocument364 pagesTechnip - Petroleum Refining III Conversion Processes PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram FOR Magnaforming Unit (UNIT NO: 100) : Skikda Refinery Rehabilitation & Adaptation ProjectDocument14 pagesProcess Flow Diagram FOR Magnaforming Unit (UNIT NO: 100) : Skikda Refinery Rehabilitation & Adaptation ProjectMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet