Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsTYPES OF CONDITIONALS Explanation
TYPES OF CONDITIONALS Explanation
Uploaded by
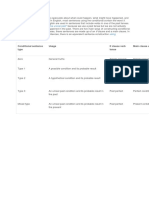
Ester TedjoThere are 3 main types of conditional sentences:
1. Type 1 uses the present tense to talk about possible future events.
2. Type 2 uses the past tense to talk about present events that are contrary to fact.
3. Type 3 uses the past perfect tense to talk about past events that are contrary to fact.
There is also a type 0 conditional that refers to general truths or habits using the present tense in both clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- GIA Pre TestDocument24 pagesGIA Pre TestAng Jin Wei77% (13)
- Classroom Management Theorists and TheoriesDocument5 pagesClassroom Management Theorists and TheoriesAzmi ZainalNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument6 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument5 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument7 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Makalah B InggrisDocument12 pagesTugas Makalah B InggrisLuthfiana KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- GE B1 - Conditional TensesDocument10 pagesGE B1 - Conditional TensesSadhvi SitaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Lesson 10 V2 - Converse, Inverse, Contra Positive and BiconditionalDocument11 pagesGeometry Lesson 10 V2 - Converse, Inverse, Contra Positive and Biconditionalezmoreldo100% (2)
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceBunnarin ChrunNo ratings yet
- Group6 Conditional SenteceDocument12 pagesGroup6 Conditional SenteceHarni Mei LastinahNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument4 pagesThe Zero ConditionalKim SeorinNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence TypeDocument6 pagesConditional Sentence TypeHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Conditional 2pagesDocument2 pagesConditional 2pagesTechArea GamingNo ratings yet
- Situation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFDocument1 pageSituation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFKenia AquinoNo ratings yet
- Conditional If PDF To Be SharedDocument21 pagesConditional If PDF To Be SharedMiandy CelestinnNo ratings yet
- Materi 4Document4 pagesMateri 4Ciitraa AggrrNo ratings yet
- 2.godina IF Clauses 0, 1, 2 TabelaDocument2 pages2.godina IF Clauses 0, 1, 2 TabelaMarijam SafargalijevaNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument5 pagesThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Câu Điều Kiện (Clauses Of Condition) : 1. FORMDocument3 pagesBài Tập Câu Điều Kiện (Clauses Of Condition) : 1. FORMLe Huyen TramNo ratings yet
- Conditional EF GlobalDocument1 pageConditional EF GlobalMARINA SARAHY HERNANDEZ OROZCONo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Notes Forall XDocument1 pageChapter 3 - Notes Forall XjadynisaraNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument7 pagesConditionalserdakovaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: If You Will LearnDocument28 pagesConditionals: If You Will LearnAkhmad FauziNo ratings yet
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoNo ratings yet
- Conditional - English Grammar - EFDocument2 pagesConditional - English Grammar - EFNameless 00No ratings yet
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocument4 pagesAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangNo ratings yet
- English For Computer Use: Web PageDocument10 pagesEnglish For Computer Use: Web PageSally LuNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesRekaman IstiNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument7 pagesConditional SentenceAbhieey Choi Soo Hyun100% (1)
- Transition WordsDocument5 pagesTransition WordsGökberk TaluNo ratings yet
- MERTOWv 1Document33 pagesMERTOWv 1Cafezinho NoturnoNo ratings yet
- Mapa Mental-Pablo Cesar 2.2Document1 pageMapa Mental-Pablo Cesar 2.2Pablo César Zuñiga HernandezNo ratings yet
- Grammar - QuantifiersDocument3 pagesGrammar - QuantifiersCherrie Mae NietesNo ratings yet
- Tugas Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument15 pagesTugas Makalah Bahasa InggrisMysteri OusNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris PtsDocument2 pagesBahasa Inggris PtsZahra SabilaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2, Week 8 - Module 14Document9 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2, Week 8 - Module 14samantha buban100% (2)
- Conditional SentencesDocument1 pageConditional Sentencescampus.headNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences TableDocument1 pageConditional Sentences TableaswerffNo ratings yet
- Kel. 11 Conditonal SentenceDocument15 pagesKel. 11 Conditonal SentenceNu FaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Methods of Proofs and DisproofsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Methods of Proofs and DisproofsJawayria D. DitucalanNo ratings yet
- Cliff's (Module 3) PDFDocument43 pagesCliff's (Module 3) PDFMario AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Sentence Syntax Curs 7Document7 pagesSentence Syntax Curs 7Andreea DianaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleDocument13 pagesConditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleAurelia Mihaela SoleaNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument1 page"The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseGheorghe DianaNo ratings yet
- ConditionDocument1 pageConditionGheorghe DianaNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument1 page"The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseGheorghe DianaNo ratings yet
- Revised Biconditional Inverse Converse and Contrapositive StatementsDocument14 pagesRevised Biconditional Inverse Converse and Contrapositive StatementsNathalieNo ratings yet
- PEL 130 Lecture 2Document19 pagesPEL 130 Lecture 2soumyosishpal.108No ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument25 pagesCONDITIONALShiella Mae Vispo100% (1)
- CONDITIONAL Sentences All TypesDocument9 pagesCONDITIONAL Sentences All TypesMaríaEstelaVinellaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument2 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseMagmag MagmagNo ratings yet
- 0 Conditional 1 Conditional 2 Conditional 3 ConditionalDocument3 pages0 Conditional 1 Conditional 2 Conditional 3 ConditionalAnda AdaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- Songs and Emotions: Are Lyrics and Melodies Equal Partners?Document25 pagesSongs and Emotions: Are Lyrics and Melodies Equal Partners?Luiz Cesar MagalhaesNo ratings yet
- Budget of Lesson Grade 10Document5 pagesBudget of Lesson Grade 10Charlito PlasabasNo ratings yet
- Handling Thoughts and Emotions: Swami Bhoomananda TirthaDocument2 pagesHandling Thoughts and Emotions: Swami Bhoomananda TirthaDeepuNo ratings yet
- Cooperative-Learning: Essential 5Document5 pagesCooperative-Learning: Essential 5liliana_oana3400No ratings yet
- ThinkingDocument807 pagesThinkingArjun NarangNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument18 pagesInglesclaudia Marcela RamirezNo ratings yet
- Elt 6 Pre-Finals ExamDocument4 pagesElt 6 Pre-Finals ExamDeory May NodaloNo ratings yet
- Empathy and Aeonic Perspective in The Esoteric Tradition of The Order of Nine AnglesDocument7 pagesEmpathy and Aeonic Perspective in The Esoteric Tradition of The Order of Nine AnglesDark Japer100% (2)
- Chapter 1 5Document29 pagesChapter 1 5April ManabatNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan U 7Document31 pagesLesson Plan U 7Duong Huong ThuyNo ratings yet
- Creativity in Education PDFDocument37 pagesCreativity in Education PDFHatem HadiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form of The Verb To Be or Personal Pronouns. Use Contractions Where PossibleDocument4 pages1 Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form of The Verb To Be or Personal Pronouns. Use Contractions Where PossibleLes RagNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Music (COT 2)Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Music (COT 2)flor galinganNo ratings yet
- Assignment HBET4703 English For Specific Purposes January 2022 Semester - Specific InstructionDocument10 pagesAssignment HBET4703 English For Specific Purposes January 2022 Semester - Specific InstructionaliaazmanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Prtyaksha PramanaDocument5 pagesConcept of Prtyaksha PramanaAshwini Parkanthe100% (1)
- Seminar On Language TeachingDocument27 pagesSeminar On Language TeachingElsa BastienNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative PracticeDocument1 pageAffirmative Negative PracticeFrancisco AlasiaNo ratings yet
- Rubric SDocument3 pagesRubric SNelson50% (2)
- ABCDocument8 pagesABCZhank Creex YusranNo ratings yet
- Personal Case Study: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For GE1: Understanding The SelfDocument6 pagesPersonal Case Study: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For GE1: Understanding The SelfPaulo RicardoNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN For Peer DemoDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN For Peer DemoAngelito MendozaNo ratings yet
- إنج302 Unit 10 Psychology - Lesson 1 Group Psychology (Part 1)Document16 pagesإنج302 Unit 10 Psychology - Lesson 1 Group Psychology (Part 1)AlaaNo ratings yet
- TeamDocument22 pagesTeamManny De MesaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychosocial SupportDocument39 pagesMental Health and Psychosocial Supportarlene pagarNo ratings yet
- Approaches in Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocument6 pagesApproaches in Teaching Listening and SpeakingNur AzamNo ratings yet
- ARABIC (Code: 116) : CLASS - XI (2019-20)Document2 pagesARABIC (Code: 116) : CLASS - XI (2019-20)chin chanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Grade Colonial Maryland Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFourth Grade Colonial Maryland Lesson Planapi-281284426No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Simple Present - How Often Do You - USDocument22 pagesWorksheet - Simple Present - How Often Do You - USBianca SantosNo ratings yet
TYPES OF CONDITIONALS Explanation
TYPES OF CONDITIONALS Explanation
Uploaded by
Ester Tedjo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThere are 3 main types of conditional sentences:
1. Type 1 uses the present tense to talk about possible future events.
2. Type 2 uses the past tense to talk about present events that are contrary to fact.
3. Type 3 uses the past perfect tense to talk about past events that are contrary to fact.
There is also a type 0 conditional that refers to general truths or habits using the present tense in both clauses.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are 3 main types of conditional sentences:
1. Type 1 uses the present tense to talk about possible future events.
2. Type 2 uses the past tense to talk about present events that are contrary to fact.
3. Type 3 uses the past perfect tense to talk about past events that are contrary to fact.
There is also a type 0 conditional that refers to general truths or habits using the present tense in both clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageTYPES OF CONDITIONALS Explanation
TYPES OF CONDITIONALS Explanation
Uploaded by
Ester TedjoThere are 3 main types of conditional sentences:
1. Type 1 uses the present tense to talk about possible future events.
2. Type 2 uses the past tense to talk about present events that are contrary to fact.
3. Type 3 uses the past perfect tense to talk about past events that are contrary to fact.
There is also a type 0 conditional that refers to general truths or habits using the present tense in both clauses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
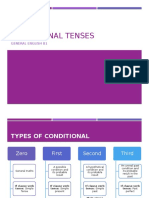
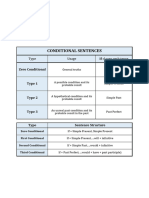
TYPES OF CONDITIONAL SENTENCES
In general, there are 3 types of conditionals:
TYPE VERB PATTERN MEANING EXPLANATION
The time is FUTURE. Conditional type 1 is
1 If __Present (V1)_____ , __Present FUTURE (will + V-inf.)_ Future possible used to express something that is possible
to happen in the future.
The time is PRESENT. Conditional type 2 is
Present untrue (contrary to
2 If __Past (V2)________ , __Past FUTURE (would + V-inf.)_ used to express something that is contrary
the fact in the present)
to the fact in the present time.
The time is PAST. Conditional type 3 is used
If _Past Perfect (had + V3) , _Past FUTURE Perfect (would have + Past untrue (contrary to the
3 to express something that is contrary to the
V3)_ fact in the past)
fact in the past time.
For examples of each type, see handout page 32.
Note on Verb Pattern: The clause with ‘IF’ is without ‘FUTURE’, and the clause without ‘IF’ is with ‘FUTURE’.
There is another type of conditional called type zero:
TYPE VERB PATTERN MEANING
habits, scientific facts, general
Ø If __Present (V1)_____ , ___Present (V1)______________
truths
In conditional type Ø, we can replace ‘if’ with ‘when’ or ‘whenever’.
Examples:
1. If/Whenever I have a headache, I take Panadol. (=habit)
2. If/When you mix yellow and blue, you get green. (=scientific fact)
3. If/When you heat ice, it melts. (=scientific fact)
4. It gets dark if/when the sun goes down. (=general truth)
You might also like
- GIA Pre TestDocument24 pagesGIA Pre TestAng Jin Wei77% (13)
- Classroom Management Theorists and TheoriesDocument5 pagesClassroom Management Theorists and TheoriesAzmi ZainalNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument6 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument5 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument7 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Makalah B InggrisDocument12 pagesTugas Makalah B InggrisLuthfiana KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- GE B1 - Conditional TensesDocument10 pagesGE B1 - Conditional TensesSadhvi SitaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Lesson 10 V2 - Converse, Inverse, Contra Positive and BiconditionalDocument11 pagesGeometry Lesson 10 V2 - Converse, Inverse, Contra Positive and Biconditionalezmoreldo100% (2)
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceBunnarin ChrunNo ratings yet
- Group6 Conditional SenteceDocument12 pagesGroup6 Conditional SenteceHarni Mei LastinahNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument4 pagesThe Zero ConditionalKim SeorinNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence TypeDocument6 pagesConditional Sentence TypeHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Conditional 2pagesDocument2 pagesConditional 2pagesTechArea GamingNo ratings yet
- Situation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFDocument1 pageSituation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFKenia AquinoNo ratings yet
- Conditional If PDF To Be SharedDocument21 pagesConditional If PDF To Be SharedMiandy CelestinnNo ratings yet
- Materi 4Document4 pagesMateri 4Ciitraa AggrrNo ratings yet
- 2.godina IF Clauses 0, 1, 2 TabelaDocument2 pages2.godina IF Clauses 0, 1, 2 TabelaMarijam SafargalijevaNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument5 pagesThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Câu Điều Kiện (Clauses Of Condition) : 1. FORMDocument3 pagesBài Tập Câu Điều Kiện (Clauses Of Condition) : 1. FORMLe Huyen TramNo ratings yet
- Conditional EF GlobalDocument1 pageConditional EF GlobalMARINA SARAHY HERNANDEZ OROZCONo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Notes Forall XDocument1 pageChapter 3 - Notes Forall XjadynisaraNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument7 pagesConditionalserdakovaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: If You Will LearnDocument28 pagesConditionals: If You Will LearnAkhmad FauziNo ratings yet
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoNo ratings yet
- Conditional - English Grammar - EFDocument2 pagesConditional - English Grammar - EFNameless 00No ratings yet
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocument4 pagesAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangNo ratings yet
- English For Computer Use: Web PageDocument10 pagesEnglish For Computer Use: Web PageSally LuNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesRekaman IstiNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument7 pagesConditional SentenceAbhieey Choi Soo Hyun100% (1)
- Transition WordsDocument5 pagesTransition WordsGökberk TaluNo ratings yet
- MERTOWv 1Document33 pagesMERTOWv 1Cafezinho NoturnoNo ratings yet
- Mapa Mental-Pablo Cesar 2.2Document1 pageMapa Mental-Pablo Cesar 2.2Pablo César Zuñiga HernandezNo ratings yet
- Grammar - QuantifiersDocument3 pagesGrammar - QuantifiersCherrie Mae NietesNo ratings yet
- Tugas Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument15 pagesTugas Makalah Bahasa InggrisMysteri OusNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris PtsDocument2 pagesBahasa Inggris PtsZahra SabilaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2, Week 8 - Module 14Document9 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2, Week 8 - Module 14samantha buban100% (2)
- Conditional SentencesDocument1 pageConditional Sentencescampus.headNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences TableDocument1 pageConditional Sentences TableaswerffNo ratings yet
- Kel. 11 Conditonal SentenceDocument15 pagesKel. 11 Conditonal SentenceNu FaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Methods of Proofs and DisproofsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Methods of Proofs and DisproofsJawayria D. DitucalanNo ratings yet
- Cliff's (Module 3) PDFDocument43 pagesCliff's (Module 3) PDFMario AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Sentence Syntax Curs 7Document7 pagesSentence Syntax Curs 7Andreea DianaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleDocument13 pagesConditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleAurelia Mihaela SoleaNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument1 page"The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseGheorghe DianaNo ratings yet
- ConditionDocument1 pageConditionGheorghe DianaNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument1 page"The Unreal Past": Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseGheorghe DianaNo ratings yet
- Revised Biconditional Inverse Converse and Contrapositive StatementsDocument14 pagesRevised Biconditional Inverse Converse and Contrapositive StatementsNathalieNo ratings yet
- PEL 130 Lecture 2Document19 pagesPEL 130 Lecture 2soumyosishpal.108No ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument25 pagesCONDITIONALShiella Mae Vispo100% (1)
- CONDITIONAL Sentences All TypesDocument9 pagesCONDITIONAL Sentences All TypesMaríaEstelaVinellaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument2 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseMagmag MagmagNo ratings yet
- 0 Conditional 1 Conditional 2 Conditional 3 ConditionalDocument3 pages0 Conditional 1 Conditional 2 Conditional 3 ConditionalAnda AdaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- Songs and Emotions: Are Lyrics and Melodies Equal Partners?Document25 pagesSongs and Emotions: Are Lyrics and Melodies Equal Partners?Luiz Cesar MagalhaesNo ratings yet
- Budget of Lesson Grade 10Document5 pagesBudget of Lesson Grade 10Charlito PlasabasNo ratings yet
- Handling Thoughts and Emotions: Swami Bhoomananda TirthaDocument2 pagesHandling Thoughts and Emotions: Swami Bhoomananda TirthaDeepuNo ratings yet
- Cooperative-Learning: Essential 5Document5 pagesCooperative-Learning: Essential 5liliana_oana3400No ratings yet
- ThinkingDocument807 pagesThinkingArjun NarangNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument18 pagesInglesclaudia Marcela RamirezNo ratings yet
- Elt 6 Pre-Finals ExamDocument4 pagesElt 6 Pre-Finals ExamDeory May NodaloNo ratings yet
- Empathy and Aeonic Perspective in The Esoteric Tradition of The Order of Nine AnglesDocument7 pagesEmpathy and Aeonic Perspective in The Esoteric Tradition of The Order of Nine AnglesDark Japer100% (2)
- Chapter 1 5Document29 pagesChapter 1 5April ManabatNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan U 7Document31 pagesLesson Plan U 7Duong Huong ThuyNo ratings yet
- Creativity in Education PDFDocument37 pagesCreativity in Education PDFHatem HadiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form of The Verb To Be or Personal Pronouns. Use Contractions Where PossibleDocument4 pages1 Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form of The Verb To Be or Personal Pronouns. Use Contractions Where PossibleLes RagNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Music (COT 2)Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Music (COT 2)flor galinganNo ratings yet
- Assignment HBET4703 English For Specific Purposes January 2022 Semester - Specific InstructionDocument10 pagesAssignment HBET4703 English For Specific Purposes January 2022 Semester - Specific InstructionaliaazmanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Prtyaksha PramanaDocument5 pagesConcept of Prtyaksha PramanaAshwini Parkanthe100% (1)
- Seminar On Language TeachingDocument27 pagesSeminar On Language TeachingElsa BastienNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative PracticeDocument1 pageAffirmative Negative PracticeFrancisco AlasiaNo ratings yet
- Rubric SDocument3 pagesRubric SNelson50% (2)
- ABCDocument8 pagesABCZhank Creex YusranNo ratings yet
- Personal Case Study: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For GE1: Understanding The SelfDocument6 pagesPersonal Case Study: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For GE1: Understanding The SelfPaulo RicardoNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN For Peer DemoDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN For Peer DemoAngelito MendozaNo ratings yet
- إنج302 Unit 10 Psychology - Lesson 1 Group Psychology (Part 1)Document16 pagesإنج302 Unit 10 Psychology - Lesson 1 Group Psychology (Part 1)AlaaNo ratings yet
- TeamDocument22 pagesTeamManny De MesaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychosocial SupportDocument39 pagesMental Health and Psychosocial Supportarlene pagarNo ratings yet
- Approaches in Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocument6 pagesApproaches in Teaching Listening and SpeakingNur AzamNo ratings yet
- ARABIC (Code: 116) : CLASS - XI (2019-20)Document2 pagesARABIC (Code: 116) : CLASS - XI (2019-20)chin chanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Grade Colonial Maryland Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFourth Grade Colonial Maryland Lesson Planapi-281284426No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Simple Present - How Often Do You - USDocument22 pagesWorksheet - Simple Present - How Often Do You - USBianca SantosNo ratings yet