Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Class 6 HOTs - Living Orgasims and Sorroundings PDF
CBSE Class 6 HOTs - Living Orgasims and Sorroundings PDF
Uploaded by
Kiss 002Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Class 6 HOTs - Living Orgasims and Sorroundings PDF
CBSE Class 6 HOTs - Living Orgasims and Sorroundings PDF
Uploaded by
Kiss 002Copyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.
com
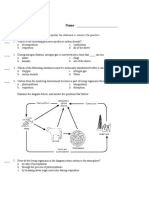
8. LIVING ORANISMS & THEIR SURROUNDINGS
1. The place where living beings live is called their ______________
(a) Adaptation (b) Habitat (c) Habit (d) Movement
2. In Cactus plant, _____________ are reduced to spines
(a) Leaves (b) Flowers (c) roots (d) Stem
3. Singhara is an example of _______________
(a) Xerophyte (b) Hydrophyte (c) Mesophyte (d) None of the above
m
4. Global warming increases the concentration of ___________ in the atmosphere
co
(a) Oxygen (b) Nitrogen (c) Carbon dioxide (d) Hydrogen
y.
5. Science of study of living things is called ___________
(a) Botany (b) Biology
da
(c) Zoology (d) None of these
6. Bacteria and fungus are examples for ____________
to
(a) Producers (b) Consumers (c) Decomposers (d) None of these
es
7. A microscopic plant which can move in water is _____________
di
(a) Sea-nemone (b) Sponge (c) Celotropis (d) Chlamybomonas
tu
8. Plant waste given out in the form of thick fluid is called as ___________________
.s
(a) Gum (b) Urine (c) Latex (d) Sweat
w
9. Growth in living things is ____________
w
(a) Temporary & reversible (b) Permanent and irreversible
w
(c) Both (a) & (b) (d) None of the above
10. The process of producing energy by the break down of food is called ______________
(a) photosynthesis (b) transpiration (c) respiration (d) reproduction
11. Minute pores present in the leaves which help in exchange of gases are called
_____________
(a) Style (b) Stamen (c) Stomata (d) Stigma
12. The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms are called as
_______________
(a) Cells (b) tissue (c) Organ (d) Organ - System
20
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
13. Hydrilla is an example for ____________
(a) Submerged Hydrophyte (b) Floating Hydrophyte (c) Semi-floating Hydrophyte
(d) None of the above
14. Living component of a habitat is called as ____________
(a) Abiotic (b) Aquatic (c) Biotic (d) Amphibious
15. ____________ are organisms which cannot prepare their food.
(a) Autotrophs (b) Phototrophs (c) Heterotrophs (d) None of the above
16. Anything which produce and response in an organism is called as ____________
(a) Life Cycle (b) Adaptation (c) Stimulus (d) Growth
m
17. An example for unicellular organism is ___________
(a) Yeast (b) Mango Plant (c) Dog (d) Men
co
18. Life cycle of a living organism begins with _____________
y.
(a) Birth (b) Growth (c) Death (d) Reproduction
19. Wind dispersed seeds have ____________________
da
(a) wings & hair (b) Hooks (c) fibrous outercoat (d) None of the above
to
20. Adaptation found in palm and coconut trees is ________________
(a) Leaves are reduced (b) Leaves become needle shape
es
(c) Leaves become deeply incised / Seveted (d) Trees grow tall without branches
di
21. Buffaloes are often found near ponds because
(a) They breath only in the pond (b) They cool themselves in the pond
tu
(c) They like to play in water (d) None of the above
.s
22. A potted plant is kept in a card board box with a small slit of sun light exhibits
w
___________
(a) Photographic movement (b) Geo-movement (c) Both a & b (d) None of the above
w
w
23. If we blow through lime water it turns milky. This proves that _________
(a) lime water has milk in it (b) lime water has oxygen in it
(c) Exhaled air contains carbon dioxide (d) None of the above
24. We move our hand immediately, if we touch the hot object. In this which is stimulus.
(a) hand (b) brain (c) hot object (d) spinal cord
25. Dolphins and whales breathe through _____________
(a) Gills (b) Skin (c) Lungs (d) Blowholes
21
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
ANSWER KEY FOR : LIVING ORGANISMS &THEIR SURROUNDINGS
1.The place where living beings live is called their Habitat
2. In Cactus plant, Leaves are reduced to spines
3. Singhara is an example of _______________
4. Global warming increases the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
5. Science of study of living things is called Biology
6. Bacteria and fungus are examples for Decomposers
7. A microscopic plant which can move in water is Chlamydomonas
8. Plant waste given out in the form of thick fluid is called as Latex
9. Growth in living things is permanent & irreversible
10. The process of producing energy by the break down of food is called Respiration
m
11. Minute pores present in the leaves which help in exchange of gases are called Stomata
12. The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms are called as Cells
co
13. Hydrilla is an example for Submerged Hydrophyte
14. Living component of a habitat is called as Biotic
y.
15. Heterotrophs are organisms which cannot prepare their food.
da
16. Anything which produce and response in an organism is called as Stimulus
17. An example for unicellular organism is Yeast
to
18. Life cycle of a living organism begins with Birth
19. Wind dispersed seeds have wings & hair
es
20. Adaptation found in palm and coconut trees is Leaves become needle shape
di
21. Buffaloes are often found near ponds because they cool themselves in the pond
22. A potted plant is kept in a card board box with a small slit of sun light exhibits
tu
Phototraphic movement
.s
23. If we blow through lime water it turns milky. This proves that exhaled air contains
carbon dioxide
w
24. We move our hand immediately, if we touch the hot object. In this which is stimulus hand
w
w
25. Dolphins and whales breathe through Blowholes
22
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
You might also like
- Biotechnology: Quarter 4 - Module 3: Biotechnology in Industry and EnvironmentDocument24 pagesBiotechnology: Quarter 4 - Module 3: Biotechnology in Industry and EnvironmentJaeda Baltazar100% (9)
- BASIC SCIENCE PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Grade 7)Document10 pagesBASIC SCIENCE PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Grade 7)Richard100% (3)
- Photosynthesis TestDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis TestLester Eslava OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Systlab 2Document4 pagesSystlab 2Art Julius HallazgoNo ratings yet
- Cell Model Project RubricDocument2 pagesCell Model Project Rubricapi-273429922No ratings yet
- Basic ScienceDocument3 pagesBasic Sciencechi noraNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 General Science 2024Document6 pagesGrade 3 General Science 2024Ashley AimableNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (2) UI - RemovedDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY (2) UI - Removedbalikisyakubu64No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Subject FileDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY Subject Filegreatoduah72No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SS2 Second Term ExamDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY SS2 Second Term ExamchrizyboyziNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDocument7 pagesWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Test (Cell+biodiversity+microorgnismDocument8 pagesTest (Cell+biodiversity+microorgnismSUMANTA KUMAR MasantaNo ratings yet
- Oss MS00050025Document19 pagesOss MS00050025milapdhruvcomputerworkNo ratings yet
- UI POST UTME-University of Ibadan Biology POST UTME Past Question and Answer-2019Document6 pagesUI POST UTME-University of Ibadan Biology POST UTME Past Question and Answer-2019Daniel PadillaNo ratings yet
- STD 7 Sample Question PaperDocument8 pagesSTD 7 Sample Question PaperAayushree BorgeNo ratings yet
- Full Syllabus 11th - Test 2Document92 pagesFull Syllabus 11th - Test 2amodsingh472No ratings yet
- Physics MatDocument5 pagesPhysics MatNitin MittalNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY by AgbaDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY by AgbaKoladeNo ratings yet
- Botany M.C.Q.SDocument86 pagesBotany M.C.Q.SMalik TAHIR100% (2)
- 6 TH C V Raman-Englis Notes1Document39 pages6 TH C V Raman-Englis Notes1shivitpc2No ratings yet
- Biology Questio-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesBiology Questio-WPS OfficeogunfunminiyiestherNo ratings yet
- Sellf Assessment Test: To Purchase Hard Book of From Amazon Click HereDocument5 pagesSellf Assessment Test: To Purchase Hard Book of From Amazon Click HereosumNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceAyah LorraineNo ratings yet
- Biology Class X: Assignment No. 2 Chapter 11: HOMEOSTASISDocument1 pageBiology Class X: Assignment No. 2 Chapter 11: HOMEOSTASISAbdullah ButtNo ratings yet
- biolOGY TESTDocument2 pagesbiolOGY TESTAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessDocument32 pagesLife Processsiya bhatiNo ratings yet
- SSC General Studies - Cracker (WWW - Qmaths.in)Document135 pagesSSC General Studies - Cracker (WWW - Qmaths.in)Shubhra MathurNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Solutions For Class 6 Science CH 9Document9 pagesNcert Exemplar Solutions For Class 6 Science CH 9Vyan Anand (Admn. No : 7366)No ratings yet
- 3rd Science ExamDocument2 pages3rd Science ExamFahad HADJI USOPHNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology V 2020Document2 pagesScience and Technology V 2020Daines MtonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter No - 01 Chapter Name - Bio-Nutrition in Plant: Worksheet Class 7 ScienceDocument5 pagesChapter No - 01 Chapter Name - Bio-Nutrition in Plant: Worksheet Class 7 ScienceshvmkrthakurNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Work Sheet 1Document3 pagesNutrition in Plants Work Sheet 1AakritiNo ratings yet
- B8 Super MockDocument5 pagesB8 Super MockRebecca AduNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS - CBSEDocument3 pagesAssignment - 1 - ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS - CBSEIIT ASHRAM DAHODNo ratings yet
- Cycles in Nature Pretest A NameDocument10 pagesCycles in Nature Pretest A NameClay JensenNo ratings yet
- Algae TestDocument3 pagesAlgae TestSeika SaliNo ratings yet
- SSC General Studies - Cracker (WWW - Mission-Success - In)Document135 pagesSSC General Studies - Cracker (WWW - Mission-Success - In)kaustav royNo ratings yet
- PDF 1697458932862Document11 pagesPDF 1697458932862harshalgajananwaghmodeNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 CH 8 9 Assignment 1 NewDocument7 pagesGrade 6 CH 8 9 Assignment 1 NewnitinNo ratings yet
- Online Test - 1 - (25!7!2016) - Zoology - Animal Kingdom (Upto Ctenophora) - Prof SCZ - FinalDocument5 pagesOnline Test - 1 - (25!7!2016) - Zoology - Animal Kingdom (Upto Ctenophora) - Prof SCZ - FinalRiteshNo ratings yet
- Modern XI Biology Page 51 - 100 Editable and SearchableDocument50 pagesModern XI Biology Page 51 - 100 Editable and Searchablelotus25369No ratings yet
- 10-Bg-Module IDocument4 pages10-Bg-Module IPixcasso 21No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Diagnostic ExamDocument3 pagesEarth and Life Science Diagnostic ExamJohn Mark JarencioNo ratings yet
- Final McqsDocument119 pagesFinal McqsSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Post Test For Science 4Document4 pagesPost Test For Science 4Gerry EstillerNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 BiologyDocument6 pagesGrade 9 BiologyMelecia SeniorNo ratings yet
- SS 3 2ND Mock Nov 2022Document6 pagesSS 3 2ND Mock Nov 2022Akachinedum NwaoguNo ratings yet
- Quiz QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuiz QuestionsbittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS - GSEBDocument4 pagesAssignment - 1 - ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS - GSEBChetanNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet HA Class XIDocument6 pagesWork Sheet HA Class XIAditya MundeNo ratings yet
- Biology PaperDocument3 pagesBiology PaperUsama ZafarNo ratings yet
- Class XII ZOOLOGY Warm Up Test Sir Salman HussainDocument2 pagesClass XII ZOOLOGY Warm Up Test Sir Salman HussainFarid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Science 9Document7 pagesClass 6 Science 9Bhavna DixitNo ratings yet
- Notefile 1 1696505481Document3 pagesNotefile 1 1696505481deore.nitin1699No ratings yet
- Assessment of LearningDocument5 pagesAssessment of LearningJan Lloyd OdruniaNo ratings yet
- KOOOLDocument5 pagesKOOOLAkachinedum NwaoguNo ratings yet
- Nearpeer MDCAT Biology 2018Document733 pagesNearpeer MDCAT Biology 2018ayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Botany 2Document48 pagesBotany 2Abhishek shukla100% (1)
- I. Choose The Correct Answer: Do at ClassDocument9 pagesI. Choose The Correct Answer: Do at ClassNishali SamNo ratings yet
- Biology: Life On Earth 7e Student Self Test Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesBiology: Life On Earth 7e Student Self Test Questions and AnswersRO OMNo ratings yet
- GenEd Science PART 1Document5 pagesGenEd Science PART 1Ralph Tama Mangacop BenitoNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNo ratings yet
- Ssor 2023-24Document1 pageSsor 2023-24sirkali1973No ratings yet
- Tabulation For Suitable Component of Shuttering ArrangementsDocument1 pageTabulation For Suitable Component of Shuttering Arrangementssirkali1973No ratings yet
- Problem No .1: Chart TitleDocument11 pagesProblem No .1: Chart Titlesirkali1973100% (1)
- Problem No.1: Sensitivity: LNT Construction Internal UseDocument9 pagesProblem No.1: Sensitivity: LNT Construction Internal Usesirkali1973No ratings yet
- HR FormDocument2 pagesHR Formsirkali1973No ratings yet
- Incremental Benefit With The ProjectDocument1 pageIncremental Benefit With The Projectsirkali1973No ratings yet
- Discharge Through BridgeDocument2 pagesDischarge Through Bridgesirkali1973No ratings yet
- Pollination - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasDocument10 pagesPollination - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasSwaraj KhedekarNo ratings yet
- G8 Q4M4 BiodiversityDocument14 pagesG8 Q4M4 BiodiversityronnieNo ratings yet
- w3 Critical ThinkingDocument6 pagesw3 Critical ThinkingGiang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Surgery Trans 1 - Systemic Response To InjuryDocument29 pagesSurgery Trans 1 - Systemic Response To InjuryJoan Caacbay De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Immunoinformatics Notes2019Document20 pagesImmunoinformatics Notes2019Anamitra SenNo ratings yet
- Interferon-Stimulated Genes: A Complex Web of Host Defenses: FurtherDocument36 pagesInterferon-Stimulated Genes: A Complex Web of Host Defenses: FurtherStephani LopezNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Ecology Notes Week 4-5Document23 pagesYear 7 Ecology Notes Week 4-5avaneesh.nirmalNo ratings yet
- Pahang Trial STPM 2008Document40 pagesPahang Trial STPM 2008david ngNo ratings yet
- Maria Immaculata Iwo: Sekolah Farmasi ItbDocument55 pagesMaria Immaculata Iwo: Sekolah Farmasi ItbEkwan Prasetyo AzlinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Methodologies Chapter 4 9-1.2012 PDFDocument26 pagesEndocrine Methodologies Chapter 4 9-1.2012 PDFLeora LiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism in PlantsDocument40 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism in Plantsguswinda alvaniNo ratings yet
- Session III Ichq6b SpecificationsDocument84 pagesSession III Ichq6b Specificationsamandbhaskar100% (1)
- An Ordinance Promoting Organic Farming and Providing Tax Incentives ThereofDocument3 pagesAn Ordinance Promoting Organic Farming and Providing Tax Incentives ThereofNuepe Manuel Jr.No ratings yet
- APS Abstracts Hawaii, USA 2011Document206 pagesAPS Abstracts Hawaii, USA 2011ggajendranNo ratings yet
- Complement-System Complement - SystemDocument6 pagesComplement-System Complement - Systemrenato renatoNo ratings yet
- Biology ChallengeDocument7 pagesBiology Challengemartynapet50% (2)
- Coconut Genetic ResourcesDocument797 pagesCoconut Genetic ResourcesJohnDavidNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Evaluation of Probiotics in FoodDocument11 pagesGuidelines For The Evaluation of Probiotics in Foodkadec100% (1)
- 2012 Training Manual Malaria EntomologyDocument85 pages2012 Training Manual Malaria EntomologyAntony RajNo ratings yet
- Enumeration of Bacteria by Different MethodDocument4 pagesEnumeration of Bacteria by Different MethodFarooq KhattakNo ratings yet
- Section 1.3 & 1.6 - Cell Structures and Functions QuizDocument1 pageSection 1.3 & 1.6 - Cell Structures and Functions QuizMay MontanoNo ratings yet
- Uji SensitivitasDocument33 pagesUji SensitivitasDein RenskaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument35 pagesBiochemistryGølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ExamDocument3 pagesDigestive System ExamRouse Leanne NicolasNo ratings yet
- Neuronal Damage Pathology MkuDocument8 pagesNeuronal Damage Pathology MkuElvisNo ratings yet
- Berry Full of DNADocument15 pagesBerry Full of DNA3leniNo ratings yet
- What Is Development?Document36 pagesWhat Is Development?jebojorkezNo ratings yet