Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alternating and Direct Current: War of The Currents
Alternating and Direct Current: War of The Currents
Uploaded by
Amey KhawaleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alternating and Direct Current: War of The Currents
Alternating and Direct Current: War of The Currents
Uploaded by
Amey KhawaleCopyright:
Available Formats
Alternating and direct current
See also: War of the currents
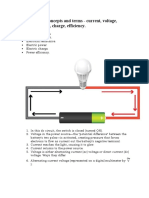
In alternating current (AC) systems, the movement of electric charge periodically reverses
direction. AC is the form of electric power most commonly delivered to businesses and
residences. The usual waveform of an AC power circuit is a sine wave. Certain applications use
different waveforms, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on
electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. An important goal in these applications
is recovery of information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal.
In contrast, direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge, or a system in which
the movement of electric charge is in one direction only. Direct current is produced by sources
such as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of
the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow
through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams.
An old name for direct current was galvanic current.[15]
Occurrences
Natural observable examples of electrical current include lightning, static electric discharge, and
the solar wind, the source of the polar auroras.
Man-made occurrences of electric current include the flow of conduction electrons in metal wires
such as the overhead power lines that deliver electrical energy across long distances and the
smaller wires within electrical and electronic equipment. Eddy currents are electric currents that
occur in conductors exposed to changing magnetic fields. Similarly, electric currents occur,
particularly in the surface, of conductors exposed to electromagnetic waves. When oscillating
electric currents flow at the correct voltages within radio antennas, radio waves are generated.
In electronics, other forms of electric current include the flow of electrons through resistors or
through the vacuum in a vacuum tube, the flow of ions inside a battery or a neuron, and the flow
of holes within metals and semiconductors.
You might also like
- Current.: ModulatedDocument1 pageCurrent.: ModulatedmmgcourrielNo ratings yet
- Direction. An Electric Charge Would For Instance Move Forward, Then Backward, Then Forward, ThenDocument2 pagesDirection. An Electric Charge Would For Instance Move Forward, Then Backward, Then Forward, ThenjovitawayawayNo ratings yet
- Direct Current (DC) Is The Unidirectional Flow ofDocument1 pageDirect Current (DC) Is The Unidirectional Flow ofMohd Nasir Md BakhirNo ratings yet
- Soldering IronDocument12 pagesSoldering IronfjsabNo ratings yet
- Electric Current: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument46 pagesElectric Current: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBerny ManalangNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicoleDocument8 pagesActivity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicolenicsNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesPrinciple of ElectricSyahmi FadziNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- Electric CCC PDFDocument9 pagesElectric CCC PDFbasswardNo ratings yet
- L3-Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesL3-Principle of ElectricIzzah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesKib-anne Miguel PasikanNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Beee Ac-I NewDocument19 pagesUnit-II Beee Ac-I NewParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Voltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDocument8 pagesVoltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDuck520No ratings yet
- Brany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Document8 pagesBrany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Brany Alejandro Gomez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- What and How To Acquire Voltage Power Resistor CurrentDocument8 pagesWhat and How To Acquire Voltage Power Resistor CurrentNie TofuNo ratings yet
- (Basics) : 1. What Are Electrical Currents?Document7 pages(Basics) : 1. What Are Electrical Currents?Raedler MarcaidaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics ProjectthaswikaamaraNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument11 pagesElectronicsChris Benedict LatosaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Concepts and TermsDocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Concepts and TermsMark Jerwin SacapañoNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thDocument11 pagesCurrent Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bu LectureDocument64 pagesBu LecturePark JeongseongNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Group 1Document20 pagesAlternating Current: Group 1nichinichi_14No ratings yet
- Eeuti130 Lec1Document22 pagesEeuti130 Lec1frankorola0207No ratings yet
- Physics Ac DC ProDocument6 pagesPhysics Ac DC Prohi_scribdNo ratings yet
- Unit I Electrical AND Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systems 10Document38 pagesUnit I Electrical AND Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systems 10NithinNo ratings yet
- Hello This Is It: Direct Current (DC) Is The Unidirectional Flow of AnDocument6 pagesHello This Is It: Direct Current (DC) Is The Unidirectional Flow of AnSiddiqui.Mazhar Btech2017No ratings yet
- What Is AC CurrentDocument1 pageWhat Is AC CurrentMaha BalaNo ratings yet
- Electric Power - WikipediaDocument10 pagesElectric Power - WikipediaRana SufyanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ac Vs DC Power PointDocument4 pagesAssignment Ac Vs DC Power Pointapi-295212665No ratings yet
- Grade 9 IctDocument18 pagesGrade 9 IctJohn Carl ToledoNo ratings yet
- Yla May Villareal ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMDocument12 pagesYla May Villareal ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMJohn Ry-Mhel GatacilloNo ratings yet
- BEEEDocument145 pagesBEEERohith GajawadaNo ratings yet
- BE3251 BEEE - 02 - by WWW - Notesfree.inDocument221 pagesBE3251 BEEE - 02 - by WWW - Notesfree.inmathuammu6805No ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument9 pagesElectric CurrentDraganJordanovNo ratings yet
- Boi Quiz 1Document4 pagesBoi Quiz 1JoNo ratings yet
- UNIT I NotesDocument34 pagesUNIT I NotesKarthikeyan VNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalJohn Florenz VasquezNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-EeeDocument112 pagesUNIT 1-EeeRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- BaliwDocument3 pagesBaliwZeref SprigganNo ratings yet
- Illut Ee Lab Research 1Document15 pagesIllut Ee Lab Research 1carlverano0428No ratings yet
- Physics: AssignmentDocument27 pagesPhysics: AssignmentElakkiya Elakkiya0% (1)
- Physics: AssignmentDocument27 pagesPhysics: AssignmentElakkiya ElakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity ParametersDocument90 pagesBasic Electricity Parameterssubbaiah54100% (1)
- Alternating Current - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesAlternating Current - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Jose RizalDocument11 pagesJose RizalBaet RayanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Is The Set ofDocument2 pagesElectricity Is The Set ofSam Axel BenedictoNo ratings yet
- Electron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDocument1 pageElectron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDean ParconNo ratings yet
- 276 - BE8251 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS and MEASUREMENTS NotesDocument42 pages276 - BE8251 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS and MEASUREMENTS NotesBalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document61 pagesLecture 1jackdrejeNo ratings yet
- Simple DC Circuits ElectromagnetismDocument26 pagesSimple DC Circuits ElectromagnetismBlessel MatosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Venkat TakkellaNo ratings yet
- EIT Lecture01Document16 pagesEIT Lecture01Kevon BvunzaNo ratings yet
- Electric Power - WikipediaDocument26 pagesElectric Power - Wikipediaapple munda crruzNo ratings yet
- Guía 1Document8 pagesGuía 1AlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- Areola, ELECTRODocument7 pagesAreola, ELECTROsimeon tayawaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Portfolio 3Document5 pagesElectricity Portfolio 3Ashish KumarNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thDocument40 pagesCurrent Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Fuseless Selection Type 2, Iq 50ka, IS/IEC:60947-4-1: IE1 IE2Document4 pagesFuseless Selection Type 2, Iq 50ka, IS/IEC:60947-4-1: IE1 IE2Amey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Switching & Controlling - Pricelist - WEF Jun 1, 2021Document84 pagesSwitching & Controlling - Pricelist - WEF Jun 1, 2021Amey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Batteries: Performance Comparison of Rechargeable Batteries For Stationary Applications (Ni/MH vs. Ni-Cd and VRLA)Document7 pagesBatteries: Performance Comparison of Rechargeable Batteries For Stationary Applications (Ni/MH vs. Ni-Cd and VRLA)Amey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- History: Nitrous OxideDocument2 pagesHistory: Nitrous OxideAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Production: Electromagnetic FieldsDocument1 pageProduction: Electromagnetic FieldsAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Resistive Circuits: Resistive Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesResistive Circuits: Resistive Ohm's LawAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Treatment in Circuit Theory: Circuit Analysis Electrical Engineering Lumped Element ModelDocument1 pageTreatment in Circuit Theory: Circuit Analysis Electrical Engineering Lumped Element ModelAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument1 pagePowerAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Resistive Heating: ElectromagnetDocument2 pagesResistive Heating: ElectromagnetAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Passive Devices (Loads) : Q Is Electric Charge in Tistimein I Is Electric Current in V Is Electric Potential or Voltage inDocument2 pagesPassive Devices (Loads) : Q Is Electric Charge in Tistimein I Is Electric Current in V Is Electric Potential or Voltage inAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Definition As Potential of Electric FieldDocument2 pagesDefinition As Potential of Electric FieldAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet