Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculation: Emissivity Radiating Area
Calculation: Emissivity Radiating Area
Uploaded by
Alexander MugabeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Massey Ferguson 50e Industrial Tractor Service ManualDocument38 pagesMassey Ferguson 50e Industrial Tractor Service ManualAlexander Mugabe0% (2)
- Dipoles, Unintentional Antennas and EMC: Berend DankerDocument8 pagesDipoles, Unintentional Antennas and EMC: Berend DankerZorana StojanovicNo ratings yet
- ASTR112 4light2 6ppDocument4 pagesASTR112 4light2 6ppSpira DeltsNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation LawDocument20 pagesBlackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation Lawpauljkt1No ratings yet
- Chapter1blackbodyradiation 131023012246 Phpapp02 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter1blackbodyradiation 131023012246 Phpapp02 PDFShakir KhattakNo ratings yet
- Phy502repDocument10 pagesPhy502repRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Phy502repDocument10 pagesPhy502repSarveshNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 INtro Mitods TioriDocument2 pagesExperiment 7 INtro Mitods Tiorikashawna fujiwaraNo ratings yet
- Thermography PDFDocument12 pagesThermography PDFAnthonio MJNo ratings yet
- Phy502repDocument17 pagesPhy502repSarveshNo ratings yet
- 14 RadiationDocument27 pages14 RadiationZhu Chen ChuanNo ratings yet
- .. Writable Uploads Resources Files Notes - Thermodynamics Page 3Document1 page.. Writable Uploads Resources Files Notes - Thermodynamics Page 3Jayson Ca-ongNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument61 pagesIlovepdf MergedArth LubayNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Quantum MechanicsDocument31 pagesThe Origin of Quantum Mechanicshassantech.ngNo ratings yet
- 02MP L04 C2.2 0312 Blackbody p19 40mDocument19 pages02MP L04 C2.2 0312 Blackbody p19 40m林宸No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermometry - Part 8Document15 pagesFundamentals of Thermometry - Part 8AntmavrNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat TransferDocument31 pagesRadiation Heat TransferMark Anthony Salazar ArcayanNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 5 Lec 2 03 Nov 2023Document10 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 5 Lec 2 03 Nov 2023Rasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- Therm - Lum 2Document6 pagesTherm - Lum 2SophiaNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Quantum MechanicsDocument28 pagesThe Origin of Quantum Mechanicshassantech.ngNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation PresentationDocument42 pagesThermal Radiation PresentationRajan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - Thermal - Application - v3 (Topic 4)Document13 pagesLecture 04 - Thermal - Application - v3 (Topic 4)Aisyah KiswantohNo ratings yet
- RWatermarkDocument36 pagesRWatermarkJakkula LavanyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Quantum PhysicsDocument45 pages3 Quantum Physicsnitdhakar04No ratings yet
- Radiation - 230303 - 161222Document28 pagesRadiation - 230303 - 161222manu patankarNo ratings yet
- 4 QuantumPhysicsDocument45 pages4 QuantumPhysicsChop DownNo ratings yet
- BlackbodyDocument34 pagesBlackbodyvilen143853No ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Experiment 7Document4 pagesBlackbody Radiation Experiment 7kashawna fujiwaraNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument45 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Spectrum NotesDocument10 pagesBlackbody Radiation Spectrum NotesKarthick JyothieshwarNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Planck's Constant Using A Light BulbDocument9 pagesMeasurement of Planck's Constant Using A Light BulbTop SecretNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document6 pagesLecture 2ranganadh yadlapalliNo ratings yet
- CHE34 LabReport Group5 Activity1Document4 pagesCHE34 LabReport Group5 Activity1Ian LuyaoNo ratings yet
- Prob9 Final PDFDocument13 pagesProb9 Final PDFJuan ElricNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Basic PrincipleDocument20 pagesQuantum Mechanics Basic PrincipleDinda BazliahNo ratings yet
- Radiation 22021Document84 pagesRadiation 22021Manas ChuriNo ratings yet
- An Approximate Realization of A Black Body As A Tiny Hole in An Insulated EnclosureDocument11 pagesAn Approximate Realization of A Black Body As A Tiny Hole in An Insulated EnclosureamanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation - Properties & ProcessesDocument32 pagesThermal Radiation - Properties & Processesraghu.entrepreneurNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument14 pagesReportVipul KumarNo ratings yet
- BASIC PRINCIPLES Non Contact Temperature MeasurementDocument40 pagesBASIC PRINCIPLES Non Contact Temperature MeasurementAkul BrigacNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles: of Non-Contact Temperature MeasurementDocument32 pagesBasic Principles: of Non-Contact Temperature Measurementchitturi jagadishNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Radiation Heat TransferDocument65 pagesUnit 6 - Radiation Heat TransferVerify Ki ShopNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Radiation Heat Transfer PDFDocument52 pagesChapter 4 - Radiation Heat Transfer PDFSuraya Johari0% (1)
- Bose-Einstein Condensation: A PreludeDocument8 pagesBose-Einstein Condensation: A PreludeSk. Golam Ali0% (1)
- Technical SupportDocument2 pagesTechnical SupportprabhakarNo ratings yet
- Plank The Exiting TheoryDocument5 pagesPlank The Exiting TheorySumit khanathiaNo ratings yet
- Topics: 1 Be-Physics-Introduction To Quantum Physics-2018-19 04/03/2020 MUJDocument70 pagesTopics: 1 Be-Physics-Introduction To Quantum Physics-2018-19 04/03/2020 MUJTomesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory of Light: Introduction To Modern PhysicsDocument10 pagesQuantum Theory of Light: Introduction To Modern PhysicsSoma KhanraNo ratings yet
- Quantum NotesDocument29 pagesQuantum NotesJayant JoshiNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat TransferDocument11 pagesRadiation Heat Transferfarshan296015No ratings yet
- Chem 1Document35 pagesChem 1f20212592No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: 1 Some DefinitionsDocument20 pagesQuantum Physics: 1 Some DefinitionsDr. Shobhit SachanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12&13Document40 pagesChapter 12&13alinader20022No ratings yet
- Optics: Stefan-Boltzmann LawDocument4 pagesOptics: Stefan-Boltzmann LawSergio Duque MejíaNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation and Atomic Emission - Unit - 07Document70 pagesBlackbody Radiation and Atomic Emission - Unit - 07TEBATSONo ratings yet
- 1 Blackbody RadiationDocument23 pages1 Blackbody RadiationFariz AbdiNo ratings yet
- A White - Hot Cube Only Seconds After Removed From Hot Furnace Material Silica Fiber InsulationDocument46 pagesA White - Hot Cube Only Seconds After Removed From Hot Furnace Material Silica Fiber InsulationAbinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Thermal Radiationverify nameNo ratings yet
- Kuantum. Ra. I-1 Intro. Upload 7 Sept 2021.Document32 pagesKuantum. Ra. I-1 Intro. Upload 7 Sept 2021.Bella Lestari 004No ratings yet
- Black Body PDFDocument6 pagesBlack Body PDFAnonymous dJtVwACcNo ratings yet
- Career Engineering UnisaDocument41 pagesCareer Engineering Unisaabubakr fingerNo ratings yet
- Membership Rules BookletDocument8 pagesMembership Rules BookletAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Blocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsDocument2 pagesBlocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III Steam TurbineDocument51 pagesUNIT-III Steam TurbineAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- GEC 117 Module 9-10 Lecture Note (Repaired)Document19 pagesGEC 117 Module 9-10 Lecture Note (Repaired)Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Blocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsDocument2 pagesBlocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Timing and Injection Pump Setting & Locking SetDocument1 pageDiesel Engine Timing and Injection Pump Setting & Locking SetAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- AdhesionDocument10 pagesAdhesionAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Requirements For The May 2021 Students 1. Automotive Department 2. Information Technology DepartmentDocument21 pagesRequirements For The May 2021 Students 1. Automotive Department 2. Information Technology DepartmentAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electrical Control ComponentsDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Electrical Control ComponentsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Island Job InterviewDocument2 pagesIsland Job InterviewAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Reverse Modulated Wet Disc Brake System: SectionDocument7 pagesReverse Modulated Wet Disc Brake System: SectionAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Question PaperDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Question PaperAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Machine Design P2-1Document1 pageMachine Design P2-1Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Fluid MechanicsDocument29 pagesChapter One Fluid MechanicsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- SOM - Fieldwork 02Document1 pageSOM - Fieldwork 02Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Brake Schematic.: N.R.Z. DRAWING No. D - 9722A Drawer No. L - 3 D.E. 10A & 11A Class LocomotivesDocument1 pageBrake Schematic.: N.R.Z. DRAWING No. D - 9722A Drawer No. L - 3 D.E. 10A & 11A Class LocomotivesAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- EXPLODEDDocument1 pageEXPLODEDAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- High and Low Strain Dynamic Pile Testing - Independent Geoscience Pty LTDDocument5 pagesHigh and Low Strain Dynamic Pile Testing - Independent Geoscience Pty LTDindependentgeoscienceNo ratings yet
- A New Ultrasound Method For Determining The AcousticDocument10 pagesA New Ultrasound Method For Determining The AcousticMale RamìrezNo ratings yet
- Flight Performance-Part 1 (Steady Level Flight) Min and Max SpeedDocument5 pagesFlight Performance-Part 1 (Steady Level Flight) Min and Max SpeedGCVishnuKumarNo ratings yet
- FEA CEP Report: ANSYS SoftwareDocument10 pagesFEA CEP Report: ANSYS SoftwareAli Raza100% (1)
- Entropy I PDFDocument19 pagesEntropy I PDFsNo ratings yet
- David Taylor Research Center: Turbo-MachineryDocument66 pagesDavid Taylor Research Center: Turbo-MachineryArakis Barath RajNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter Research PaperDocument7 pagesDark Matter Research Paperapi-242018443100% (1)
- Duct Size Calculator (Si) Duct Size Calculator (Ip) : W H Galvanised 0.15Document4 pagesDuct Size Calculator (Si) Duct Size Calculator (Ip) : W H Galvanised 0.15Mohd Izham Idris100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Document26 pagesFundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Venu Gopal AnneNo ratings yet
- Conduction IVDocument52 pagesConduction IVAhmad FikriNo ratings yet
- Baldor BasicsDocument6 pagesBaldor Basicsmaryam javedNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Porosity-1Document37 pagesSurface Area and Porosity-1Ghana Cintai DiaNo ratings yet
- 03MC0132 Rev. 00Document11 pages03MC0132 Rev. 0089deveshNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment ReportDocument7 pagesHeat Treatment ReportEric Fitterling0% (1)
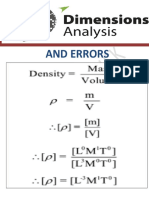
- Dimensional Analysis and ErrorsDocument17 pagesDimensional Analysis and ErrorsLastschoolkingZNo ratings yet
- Week 2.apsychrometry-Air ConditioningdocxDocument20 pagesWeek 2.apsychrometry-Air ConditioningdocxMariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- Gravitation MCQsDocument1 pageGravitation MCQsKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- Module-2A Reactance Variation and Electromagnetic Sensors: StructureDocument21 pagesModule-2A Reactance Variation and Electromagnetic Sensors: StructureN R Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Word Problems - Projectile MotionDocument4 pagesQuadratic Word Problems - Projectile Motionyaw197No ratings yet
- L1 - Nuclear Physics - 22nd NovDocument43 pagesL1 - Nuclear Physics - 22nd NovAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- Technical Report: Subject / Title: Reference Place Date Author(s) Period of Time: Content Approved ReleasedDocument28 pagesTechnical Report: Subject / Title: Reference Place Date Author(s) Period of Time: Content Approved ReleasedMayurNo ratings yet
- Flexure Strength of MC6x15.1Document2 pagesFlexure Strength of MC6x15.1G.DhanabalNo ratings yet
- Daily Learning Plan - Science and Technology: First QuarterDocument2 pagesDaily Learning Plan - Science and Technology: First Quarterkristine martinezNo ratings yet
- AP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusDocument17 pagesAP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusbbbbbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Bracing Requirements To Improve System Buckling of Narrow Girder SystemsDocument13 pagesBracing Requirements To Improve System Buckling of Narrow Girder Systemsjackcan501No ratings yet
- ESQ 04 Mechanics G Value, ProjectilesDocument8 pagesESQ 04 Mechanics G Value, ProjectilesJack BornNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis: N N N N A A A ADocument15 pagesChapter 3 - Methods of Analysis: N N N N A A A AvampakkNo ratings yet
- 12 Mole-Mole Ratios NewDocument3 pages12 Mole-Mole Ratios NewscirugbyNo ratings yet
- Yarmouk University Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Laboratory CE 354Document9 pagesYarmouk University Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Laboratory CE 354Mohammed MigdadyNo ratings yet
Calculation: Emissivity Radiating Area
Calculation: Emissivity Radiating Area
Uploaded by
Alexander MugabeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation: Emissivity Radiating Area
Calculation: Emissivity Radiating Area
Uploaded by
Alexander MugabeCopyright:
Available Formats
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
The thermal energy radiated by a blackbody radiator per second per unit area is proportional
to the fourth power of the absolute temperature and is given by
For hot objects other than ideal radiators, the law is expressed in the form: Index
Blackbody
radiation
concepts
Heat
transfer
where e is the emissivity of the object (e = 1 for ideal radiator). If the hot object is radiating
concepts
energy to its cooler surroundings at temperature Tc, the net radiation loss rate takes the form
The Stefan-Boltzmann relationship is also related to the energy density in the radiation in a
given volume of space.
Calculation Development of the relationship
HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics ***** Quantum Go Back
R Nave
Physics
Heat Radiation
Thermal radiation is energy transfer by the emission of electromagnetic waves which carry
energy away from the emitting object. For ordinary temperatures (less than red hot"), the
radiation is in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The relationship
governing the net radiation from hot objects is called the Stefan-Boltzmann law:
Index
Calculation
Blackbody
radiation
concepts
Heat
transfer
concepts
While the typical situation envisioned here is the radiation from a hot object to its cooler
surroundings, the Stefan-Boltzmann law is not limited to that case. If the surroundings are
at a higher temperature (TC > T) then you will obtain a negative answer, implying net
radiative transfer to the object.
Why is a good absorber of radiation also a good emitter?
Go Back
HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics R Nave
Radiation Calculation
The Sun at 5800K and a hot campfire at
perhaps 800 K give off radiation at a rate
proportional to the 4th power of the
temperature.
Discussion
Index
= Blackbody
radiation
concepts
Emissivity = (e = 1 for ideal radiator)
Heat
transfer
Radiating area = concepts
= x 10^ m2
= m2 = cm2 = ft2
Radiation rate = x 10^ watts
= watts
= calories/s = BTU/hr
After entering data, a calculation may be made by clicking on the highlighted symbol for
the quantity you wish to calculate. A value for emissivity between 0 and 1 must be entered,
with 1 representing a perfect radiator. The units for a given quantity will be reconciled
when you enter data, but the relationship will not be forced to be consistent until you click
on the quantity you desire to calculate.
Modeling of cooling time
Fraction of power in a wavelength range.
Go Back
HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics R Nave
You might also like
- Massey Ferguson 50e Industrial Tractor Service ManualDocument38 pagesMassey Ferguson 50e Industrial Tractor Service ManualAlexander Mugabe0% (2)
- Dipoles, Unintentional Antennas and EMC: Berend DankerDocument8 pagesDipoles, Unintentional Antennas and EMC: Berend DankerZorana StojanovicNo ratings yet
- ASTR112 4light2 6ppDocument4 pagesASTR112 4light2 6ppSpira DeltsNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation LawDocument20 pagesBlackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation Lawpauljkt1No ratings yet
- Chapter1blackbodyradiation 131023012246 Phpapp02 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter1blackbodyradiation 131023012246 Phpapp02 PDFShakir KhattakNo ratings yet
- Phy502repDocument10 pagesPhy502repRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Phy502repDocument10 pagesPhy502repSarveshNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 INtro Mitods TioriDocument2 pagesExperiment 7 INtro Mitods Tiorikashawna fujiwaraNo ratings yet
- Thermography PDFDocument12 pagesThermography PDFAnthonio MJNo ratings yet
- Phy502repDocument17 pagesPhy502repSarveshNo ratings yet
- 14 RadiationDocument27 pages14 RadiationZhu Chen ChuanNo ratings yet
- .. Writable Uploads Resources Files Notes - Thermodynamics Page 3Document1 page.. Writable Uploads Resources Files Notes - Thermodynamics Page 3Jayson Ca-ongNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument61 pagesIlovepdf MergedArth LubayNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Quantum MechanicsDocument31 pagesThe Origin of Quantum Mechanicshassantech.ngNo ratings yet
- 02MP L04 C2.2 0312 Blackbody p19 40mDocument19 pages02MP L04 C2.2 0312 Blackbody p19 40m林宸No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermometry - Part 8Document15 pagesFundamentals of Thermometry - Part 8AntmavrNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat TransferDocument31 pagesRadiation Heat TransferMark Anthony Salazar ArcayanNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 5 Lec 2 03 Nov 2023Document10 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 5 Lec 2 03 Nov 2023Rasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- Therm - Lum 2Document6 pagesTherm - Lum 2SophiaNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Quantum MechanicsDocument28 pagesThe Origin of Quantum Mechanicshassantech.ngNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation PresentationDocument42 pagesThermal Radiation PresentationRajan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - Thermal - Application - v3 (Topic 4)Document13 pagesLecture 04 - Thermal - Application - v3 (Topic 4)Aisyah KiswantohNo ratings yet
- RWatermarkDocument36 pagesRWatermarkJakkula LavanyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Quantum PhysicsDocument45 pages3 Quantum Physicsnitdhakar04No ratings yet
- Radiation - 230303 - 161222Document28 pagesRadiation - 230303 - 161222manu patankarNo ratings yet
- 4 QuantumPhysicsDocument45 pages4 QuantumPhysicsChop DownNo ratings yet
- BlackbodyDocument34 pagesBlackbodyvilen143853No ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Experiment 7Document4 pagesBlackbody Radiation Experiment 7kashawna fujiwaraNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument45 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Spectrum NotesDocument10 pagesBlackbody Radiation Spectrum NotesKarthick JyothieshwarNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Planck's Constant Using A Light BulbDocument9 pagesMeasurement of Planck's Constant Using A Light BulbTop SecretNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document6 pagesLecture 2ranganadh yadlapalliNo ratings yet
- CHE34 LabReport Group5 Activity1Document4 pagesCHE34 LabReport Group5 Activity1Ian LuyaoNo ratings yet
- Prob9 Final PDFDocument13 pagesProb9 Final PDFJuan ElricNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Basic PrincipleDocument20 pagesQuantum Mechanics Basic PrincipleDinda BazliahNo ratings yet
- Radiation 22021Document84 pagesRadiation 22021Manas ChuriNo ratings yet
- An Approximate Realization of A Black Body As A Tiny Hole in An Insulated EnclosureDocument11 pagesAn Approximate Realization of A Black Body As A Tiny Hole in An Insulated EnclosureamanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation - Properties & ProcessesDocument32 pagesThermal Radiation - Properties & Processesraghu.entrepreneurNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument14 pagesReportVipul KumarNo ratings yet
- BASIC PRINCIPLES Non Contact Temperature MeasurementDocument40 pagesBASIC PRINCIPLES Non Contact Temperature MeasurementAkul BrigacNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles: of Non-Contact Temperature MeasurementDocument32 pagesBasic Principles: of Non-Contact Temperature Measurementchitturi jagadishNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Radiation Heat TransferDocument65 pagesUnit 6 - Radiation Heat TransferVerify Ki ShopNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Radiation Heat Transfer PDFDocument52 pagesChapter 4 - Radiation Heat Transfer PDFSuraya Johari0% (1)
- Bose-Einstein Condensation: A PreludeDocument8 pagesBose-Einstein Condensation: A PreludeSk. Golam Ali0% (1)
- Technical SupportDocument2 pagesTechnical SupportprabhakarNo ratings yet
- Plank The Exiting TheoryDocument5 pagesPlank The Exiting TheorySumit khanathiaNo ratings yet
- Topics: 1 Be-Physics-Introduction To Quantum Physics-2018-19 04/03/2020 MUJDocument70 pagesTopics: 1 Be-Physics-Introduction To Quantum Physics-2018-19 04/03/2020 MUJTomesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory of Light: Introduction To Modern PhysicsDocument10 pagesQuantum Theory of Light: Introduction To Modern PhysicsSoma KhanraNo ratings yet
- Quantum NotesDocument29 pagesQuantum NotesJayant JoshiNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat TransferDocument11 pagesRadiation Heat Transferfarshan296015No ratings yet
- Chem 1Document35 pagesChem 1f20212592No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: 1 Some DefinitionsDocument20 pagesQuantum Physics: 1 Some DefinitionsDr. Shobhit SachanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12&13Document40 pagesChapter 12&13alinader20022No ratings yet
- Optics: Stefan-Boltzmann LawDocument4 pagesOptics: Stefan-Boltzmann LawSergio Duque MejíaNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation and Atomic Emission - Unit - 07Document70 pagesBlackbody Radiation and Atomic Emission - Unit - 07TEBATSONo ratings yet
- 1 Blackbody RadiationDocument23 pages1 Blackbody RadiationFariz AbdiNo ratings yet
- A White - Hot Cube Only Seconds After Removed From Hot Furnace Material Silica Fiber InsulationDocument46 pagesA White - Hot Cube Only Seconds After Removed From Hot Furnace Material Silica Fiber InsulationAbinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Thermal Radiationverify nameNo ratings yet
- Kuantum. Ra. I-1 Intro. Upload 7 Sept 2021.Document32 pagesKuantum. Ra. I-1 Intro. Upload 7 Sept 2021.Bella Lestari 004No ratings yet
- Black Body PDFDocument6 pagesBlack Body PDFAnonymous dJtVwACcNo ratings yet
- Career Engineering UnisaDocument41 pagesCareer Engineering Unisaabubakr fingerNo ratings yet
- Membership Rules BookletDocument8 pagesMembership Rules BookletAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Blocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsDocument2 pagesBlocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III Steam TurbineDocument51 pagesUNIT-III Steam TurbineAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- GEC 117 Module 9-10 Lecture Note (Repaired)Document19 pagesGEC 117 Module 9-10 Lecture Note (Repaired)Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Blocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsDocument2 pagesBlocked Ears Wax Self Guidelines For PatientsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Timing and Injection Pump Setting & Locking SetDocument1 pageDiesel Engine Timing and Injection Pump Setting & Locking SetAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- AdhesionDocument10 pagesAdhesionAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Requirements For The May 2021 Students 1. Automotive Department 2. Information Technology DepartmentDocument21 pagesRequirements For The May 2021 Students 1. Automotive Department 2. Information Technology DepartmentAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electrical Control ComponentsDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Electrical Control ComponentsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Island Job InterviewDocument2 pagesIsland Job InterviewAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Reverse Modulated Wet Disc Brake System: SectionDocument7 pagesReverse Modulated Wet Disc Brake System: SectionAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Question PaperDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Question PaperAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Machine Design P2-1Document1 pageMachine Design P2-1Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Fluid MechanicsDocument29 pagesChapter One Fluid MechanicsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- SOM - Fieldwork 02Document1 pageSOM - Fieldwork 02Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Brake Schematic.: N.R.Z. DRAWING No. D - 9722A Drawer No. L - 3 D.E. 10A & 11A Class LocomotivesDocument1 pageBrake Schematic.: N.R.Z. DRAWING No. D - 9722A Drawer No. L - 3 D.E. 10A & 11A Class LocomotivesAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- EXPLODEDDocument1 pageEXPLODEDAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- High and Low Strain Dynamic Pile Testing - Independent Geoscience Pty LTDDocument5 pagesHigh and Low Strain Dynamic Pile Testing - Independent Geoscience Pty LTDindependentgeoscienceNo ratings yet
- A New Ultrasound Method For Determining The AcousticDocument10 pagesA New Ultrasound Method For Determining The AcousticMale RamìrezNo ratings yet
- Flight Performance-Part 1 (Steady Level Flight) Min and Max SpeedDocument5 pagesFlight Performance-Part 1 (Steady Level Flight) Min and Max SpeedGCVishnuKumarNo ratings yet
- FEA CEP Report: ANSYS SoftwareDocument10 pagesFEA CEP Report: ANSYS SoftwareAli Raza100% (1)
- Entropy I PDFDocument19 pagesEntropy I PDFsNo ratings yet
- David Taylor Research Center: Turbo-MachineryDocument66 pagesDavid Taylor Research Center: Turbo-MachineryArakis Barath RajNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter Research PaperDocument7 pagesDark Matter Research Paperapi-242018443100% (1)
- Duct Size Calculator (Si) Duct Size Calculator (Ip) : W H Galvanised 0.15Document4 pagesDuct Size Calculator (Si) Duct Size Calculator (Ip) : W H Galvanised 0.15Mohd Izham Idris100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Document26 pagesFundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Venu Gopal AnneNo ratings yet
- Conduction IVDocument52 pagesConduction IVAhmad FikriNo ratings yet
- Baldor BasicsDocument6 pagesBaldor Basicsmaryam javedNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Porosity-1Document37 pagesSurface Area and Porosity-1Ghana Cintai DiaNo ratings yet
- 03MC0132 Rev. 00Document11 pages03MC0132 Rev. 0089deveshNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment ReportDocument7 pagesHeat Treatment ReportEric Fitterling0% (1)
- Dimensional Analysis and ErrorsDocument17 pagesDimensional Analysis and ErrorsLastschoolkingZNo ratings yet
- Week 2.apsychrometry-Air ConditioningdocxDocument20 pagesWeek 2.apsychrometry-Air ConditioningdocxMariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- Gravitation MCQsDocument1 pageGravitation MCQsKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- Module-2A Reactance Variation and Electromagnetic Sensors: StructureDocument21 pagesModule-2A Reactance Variation and Electromagnetic Sensors: StructureN R Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Word Problems - Projectile MotionDocument4 pagesQuadratic Word Problems - Projectile Motionyaw197No ratings yet
- L1 - Nuclear Physics - 22nd NovDocument43 pagesL1 - Nuclear Physics - 22nd NovAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- Technical Report: Subject / Title: Reference Place Date Author(s) Period of Time: Content Approved ReleasedDocument28 pagesTechnical Report: Subject / Title: Reference Place Date Author(s) Period of Time: Content Approved ReleasedMayurNo ratings yet
- Flexure Strength of MC6x15.1Document2 pagesFlexure Strength of MC6x15.1G.DhanabalNo ratings yet
- Daily Learning Plan - Science and Technology: First QuarterDocument2 pagesDaily Learning Plan - Science and Technology: First Quarterkristine martinezNo ratings yet
- AP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusDocument17 pagesAP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusbbbbbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Bracing Requirements To Improve System Buckling of Narrow Girder SystemsDocument13 pagesBracing Requirements To Improve System Buckling of Narrow Girder Systemsjackcan501No ratings yet
- ESQ 04 Mechanics G Value, ProjectilesDocument8 pagesESQ 04 Mechanics G Value, ProjectilesJack BornNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis: N N N N A A A ADocument15 pagesChapter 3 - Methods of Analysis: N N N N A A A AvampakkNo ratings yet
- 12 Mole-Mole Ratios NewDocument3 pages12 Mole-Mole Ratios NewscirugbyNo ratings yet
- Yarmouk University Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Laboratory CE 354Document9 pagesYarmouk University Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Laboratory CE 354Mohammed MigdadyNo ratings yet