Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15bt210e 3 Sem
15bt210e 3 Sem
Uploaded by
biovijay101Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
15bt210e 3 Sem
15bt210e 3 Sem
Uploaded by
biovijay101Copyright:
Available Formats
Reg. No.
b. Lactase, also known as p-galactosidase, catalyses the hydrolysis of lactose to produce
glucose and galactose from milk and whey. Experiments are carried out to determine the
Kinetic parameters for the enzyme. From the given data, evaluate Vr* and Km B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER 2016
Third Semester
Lactose concentration 2.50 2.27 1.84 1.35 t.25 0.730 0.460 0.204
(mol.1-1 x 102 I5BT2 lOE _ ENZYME ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
Reaction Velocity t.94 1.91 1.85 1.80 1.78 1.46 t.t7 0.779 (For the candidates admitted during the academic year 2015 - 2016 onwards)
(mol.l-rmin-r x 103) Note:
(D Part - A should be answered in OMR sheet within first 45 minutes and OMR sheet should be handed
over to hall invigilator at the end of 456 minute.
30. a. Analyze the internal mass tansfer effects in enzymes immobilized with porous support
(ii) Part - B and Part - C should be answered in answer booklet.
materials.
Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100
(oR)
b. Discuss the reactor configuration for immobilized enzymes and its applications. PART-A(20x 1:20Marks)
Answer ALL Questions
31. a. Elaborate the techniques available for determining the molecular weight of an enqFme- 1. Which of the following are coenzrymes?
(A) NAD, NADP, FAD, FMN (B) Vitamin, Fe, Cu
(oR) (C) NADPH2, Fe, CO (D) NAD, K CoA
b. Explain the following.
i. Nature of the extraction medium ii. Extraction of membrane bound en-rymes 2. Enzyme X requires Z* n order to caralyze the conversion of substrate Y. The Zn2* is best
identifred as.
32. a. Mention the applications of en-rymes in various industries. (A) Coen-zyme (B) Activator
(C) Substrate (D) Product
(oR)
b. Explain the applications of en-rymes in pharmaceutical and medicine. 3. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(A) Enzymes hasten the completion of a @) The two terms 'substrate' and 'product'
****,t
reaction signify the starting and ending materials of
a reacti on
(C) Enqymes are effected by the (D) Enzyme exhibit specif,rcity for the reactions
reactions they catalyze they catalyze
4. An example of a substrate specific enq,rne is
(A) Hexokinase @) Thiokinase
(C) Lactase (D) Aminopeptidase
5. Uncompetitive inhibition process is described by
(A) Ko, increases, V-o decreases (B) Kn-, increases, V.* increases
(C) K- decreases, V-* decreases (D) K. remains unchanged V** remains
unchanged
6. An allosteric enryme has
(A) One active site (B) One active site and one allosteric site
(C) Active site and two types of (D) Two types of active sites
allosteric sites
7. The enzyme hexokinase which catalyzes glucose to Glucose - t - phosphate in glycolysis is
inhibited by Glucose - t - phosphate. This is an example of
(A) Feedback allosteric inhibition (B) Positive feedback
(C) Competitiveinhibition (D) Non - competitive inhibition
Page 4 of4 l7NF315BT210E Page 1 of4 r7NF315BT2r0E
8. If K- : 30mM and V,o : 60mM min-t. What is the initial velocity at a substrate
concentration of 0. lmM? 19. The reaction catalyzed by glucose oxidase is used for
(A) 0.23 (B) 0.1e (A) Analysis of ATP (B) Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
(c) 0.27 (D) 0.13 (C) Diagnosis of tumor (D) Aralysis of blood clots
9. Which one of the following reaction is used for the purpose of recycling enzymes in 20. The enryme used in confectionary to produce "Soft Corner" is
bioprocess? (A) Amylase (B) Cellulase
(A) Isomerization (B) Immobilization (C) Protease (D) Invertase
(C) Phosphorylation (D) Polymerization
10. The immobilization technique involving physical method is PART -B (5 x 4=20 Marks)
(A) Covalent bond formation dependent (B) Non - covalent bond formation dependent Answer ANY FM Questions
(C) Both A and B (D) Ionic bond formation dependent
21. Explore the effect of enryme and substrate concentration on en-ryme activity.
11. The most commonly employed cross - linked polymer is the
(A) Polyacrylamide gel (B) Collagen 22. An enzyme has a K. of 6.7 x 10-5M. If the V,,o of the preparation is 26 pmoles. lirr.min-r,
(C) Celluloses (D) Cation exchange resin what velocity would be observed in the presence of 6 x I 0a M substrate and 7 x 104 M of
Non - competitive inhibitors with Kr: 5 x 10-a M.
t2. An immobilized enzyme used in CSTR exhibits an effectiveness factor (r1) of 1.5. This
indicates. 23. Describe allosteric enzrymes and explain their characteristics,
(A) The enzymes follows substrate (B) The erlryrne experiences extemal frtm
inhibited Kinetics diffusion limitation 24. Explain the various methods of enzymes immobilization
(C) The en-q/me follows competitive (D) The immobilized enryme is operationally
inhibited Kinetics unstable 25. Illustrate the comprehensive process flow sheet for enryme purification.
13. Which of the following is not considered as the physical method for the cells rupturing? 26. How the molecular weight of an enzyme can be analyzed by Ultracentrifugation?
(A) Milling (B) Homogenization
(C) Ultrasonication (D) Alkali Treatment 27. Highlight the applications of en-zymes in IIFCS production.
14. Diethioteritol is added in extraction media to prevent
(A) Oxidation of sulphahydral PART-C(5x 12=60 Marks)
groups (B) Loss of enryme activity Answer ALL Questions
(C) Stabilization of solubilized enzyme (D) A, B and C
28. a. With illustrations, describe the mode of action of enzrymes, their structural of enzymes, their
15. The molec.ular weight of en4,mes can be determined by using
structural components and characteristics.
(A) SEC (B) rEC
(c) rEF (D) UV - Spectrophotometer (oR)
16. Enzyme TPA or Tissue plasminogen activator is used for
b. Derive the Michaelts-Menten kinetics equation for enryme substrate reactions.
(A) Dissolving blood clots (B) Maintaining plasma contents 29. a. i. Write short notes on the following.
(C) Clearing Eurbidity ofjuices (D) Stimulating thromboplastin production i. Feedback inhibiton
17. Enrymes are often used as Diagnostic tools, because
ii. Turn over number of an en-q.rne
(A) Damaged cells release en-4/mes into (B) The liver releases enzymes that accumulate ii. A marine microorganism contains an enryme that hydrolyzes. 6 - sulfate(s).
the blood so that plasma levels of the in the urine
Glucose -
The assay is based on the rate of glucose formation the en4rme in a cell - free extract has
enrymes are noticeably elevated
(c)
Enzymes destroy damaged cells, so (D) Enzymes destroy pathogenic bacteria so
KineticconstantsofKm:6.lx70aMandV,ou*:3OOpmoleslit'r.minlGalactose-6-
sulfate is acompetitive inhibitor(I). At 10-5 Mgalactose-t-sulfate and 2 x l0-5.glucose
X-rays reveals smaller body organs blood levels of bacteria deuline
- 6- sulfate, V was 1.5 pmol lit-t.min-r. Calculate K1 for galactose - 6- sulfate.
18. Size Exclusion chromatography, separates molecules on the basis of
(A) Size (B) Electricalcharge (oR)
(C) Molecular weight (D) AffiniU
Page 2 of4 rTNI'3158T210E Page 3 ol4 l7NF315BT2l0E
You might also like
- Chemical Reaction Engineering IDocument42 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering IMuthu UmayalNo ratings yet
- OBGYN and Infertility Handbook For CliniciansDocument237 pagesOBGYN and Infertility Handbook For CliniciansAmal Farah100% (2)
- Handle Large Messages in Apache KafkaDocument59 pagesHandle Large Messages in Apache KafkaBùi Văn KiênNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem End B.sc. Bio, MicroDocument12 pages1st Sem End B.sc. Bio, MicroayushNo ratings yet
- (Sem. Iv) Theory Examination 2013-14: PAPER ID: 151407Document2 pages(Sem. Iv) Theory Examination 2013-14: PAPER ID: 151407Sarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Printed Pages-4 OR: (Sem. Vii) Odd Semester Theory EXAMINATION 2013-14Document2 pagesPrinted Pages-4 OR: (Sem. Vii) Odd Semester Theory EXAMINATION 2013-14Raja RamNo ratings yet
- Optimal Catalyst Pellet Activity Distributions Fixed-Bed Reactor With Catalyst DeactivationDocument6 pagesOptimal Catalyst Pellet Activity Distributions Fixed-Bed Reactor With Catalyst Deactivationfdt11No ratings yet
- 1ST SEM 2019 InternalDocument82 pages1ST SEM 2019 InternalUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- CRE-2 Semester PapersDocument12 pagesCRE-2 Semester PapersSarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument2 pagesEngineering Chemistryalex mcraeNo ratings yet
- AKTU Previous Years Que - Paper 2019-23Document4 pagesAKTU Previous Years Que - Paper 2019-23nitin kumarNo ratings yet
- XII Sem - CHEMISTRY.Chemical Kinetics - Old CBCS - MSC Ed May 2019Document3 pagesXII Sem - CHEMISTRY.Chemical Kinetics - Old CBCS - MSC Ed May 2019Raghavendra BNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2: 2012-DSE-CHEM 2 IDocument8 pagesChemistry Paper 2: 2012-DSE-CHEM 2 I5E26 YEUNG KA HEI 楊嘉禧No ratings yet
- Uec401 2017Document2 pagesUec401 2017g SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Mid Term PYQs 2018&2019Document20 pages1st Sem Mid Term PYQs 2018&2019Sujeet RaiNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document2 pagesPaper 1subhaNo ratings yet
- Sem 6 Dse 3 Physical ChemistryDocument4 pagesSem 6 Dse 3 Physical ChemistryGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- ICH 501-May 2022Document3 pagesICH 501-May 2022Jagadeesh YNo ratings yet
- (Id (I) (Id O: May - B. LVDRDocument2 pages(Id (I) (Id O: May - B. LVDRSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 4 Sem Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry 3 bp401t 2020Document1 pageBpharm 4 Sem Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry 3 bp401t 2020soni royNo ratings yet
- ECH3707 Worksheets Multiple ReactionDocument5 pagesECH3707 Worksheets Multiple ReactionNyanNo ratings yet
- ICH503-May 2022Document3 pagesICH503-May 2022Jagadeesh YNo ratings yet
- Unit IV 8.: B. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2018Document2 pagesUnit IV 8.: B. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2018Rahul Garg100% (1)
- CH101C PYQsDocument14 pagesCH101C PYQsBhavya VermaNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Questions 2023Document7 pagesSem 2 Questions 2023Atashi MandalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry - Ii-2004-15 PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Chemistry - Ii-2004-15 PDFAnonymous tKvEmleNo ratings yet
- Solid State MSC PYQ 2022Document12 pagesSolid State MSC PYQ 2022Rudranarayan NayakNo ratings yet
- Ctre Q Paper 1Document2 pagesCtre Q Paper 1VAISHNAV VINODNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Simulated Moving Bed Reactors-Cristino MiglioriniDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Simulated Moving Bed Reactors-Cristino MiglioriniShaikh RazzakNo ratings yet
- X Sem - CHEMISTRY.Quantum, Nuclear & Radiation Chem - Old CBCS - MSC Ed May 2019Document3 pagesX Sem - CHEMISTRY.Quantum, Nuclear & Radiation Chem - Old CBCS - MSC Ed May 2019Raghavendra BNo ratings yet
- Btech 1 Sem Chemistry Kas 102 2018 19Document2 pagesBtech 1 Sem Chemistry Kas 102 2018 19Viraj RuhelaNo ratings yet
- Btech 1 Sem Engineering Chemistry Ras102 2020Document2 pagesBtech 1 Sem Engineering Chemistry Ras102 2020Hariom SinghNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem 2022Document3 pagesMid Sem 2022AshishNo ratings yet
- 408 ChemistryDocument4 pages408 ChemistrybholuNo ratings yet
- FLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationDocument2 pagesFLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationJerry SinghNo ratings yet
- Btech Ee 4 Sem Sensor and Instrumentation Nee405 2019Document1 pageBtech Ee 4 Sem Sensor and Instrumentation Nee405 2019shruti51015No ratings yet
- 6sem Mid Sem PyqDocument7 pages6sem Mid Sem PyqSahil KhanNo ratings yet
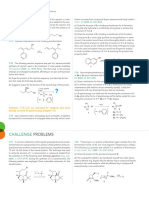
- Challenge Problems in David Klein Chap 7-17Document32 pagesChallenge Problems in David Klein Chap 7-17Ling LingNo ratings yet
- P Electrons Using Briet's Scheme.: Dual Degree B. Sc. (Hons.) Physics-M.Sc. Physics EXAMINATION, May 2019Document3 pagesP Electrons Using Briet's Scheme.: Dual Degree B. Sc. (Hons.) Physics-M.Sc. Physics EXAMINATION, May 2019Vishal TanwarNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 2 Sem Biochemistry bp203t 2023Document1 pageBpharm 2 Sem Biochemistry bp203t 2023aaryasharmamrtNo ratings yet
- CDB2043 - Reaction EngineeringDocument6 pagesCDB2043 - Reaction EngineeringXin-YiWoonNo ratings yet
- Chemicalreactionengineering-I Jntu Model ComDocument8 pagesChemicalreactionengineering-I Jntu Model ComsapabapliveNo ratings yet
- K.C.S.E BIOLOGY 1995 BIOLOGY 231/1 Questions Section A (20 MKS)Document4 pagesK.C.S.E BIOLOGY 1995 BIOLOGY 231/1 Questions Section A (20 MKS)Bob TheLowlyNo ratings yet
- Office Hours CH 15 and CH 14Document2 pagesOffice Hours CH 15 and CH 14DAMIAN WADOLOWSKINo ratings yet
- CHEM18CYB101J 1 SemDocument2 pagesCHEM18CYB101J 1 SemHrishikesh VasanthamNo ratings yet
- Eec-301 Fundamentals of Electronics Devices 2010-11Document2 pagesEec-301 Fundamentals of Electronics Devices 2010-11Pankaj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Process Modeling and SimulationDocument8 pagesProcess Modeling and SimulationRakesh KanjilalNo ratings yet
- 15EE207 3 SemDocument2 pages15EE207 3 SemSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 7 Study Material English MediumDocument18 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 7 Study Material English MediumAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Classnote 50ea6df90af1bDocument31 pagesClassnote 50ea6df90af1bFATHIMANo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Question PaperDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics Question Paperlustmord688No ratings yet
- 408 Organic ChemistryDocument4 pages408 Organic ChemistrybholuNo ratings yet
- Chems 7Document1 pageChems 7Mohsin Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Minutes: First Biotechnology Examination, CellDocument2 pagesMinutes: First Biotechnology Examination, CellAshish BharadwajNo ratings yet
- PG, 1 Sem, Apc, CC-2, Question Paper - Jan 23Document5 pagesPG, 1 Sem, Apc, CC-2, Question Paper - Jan 23Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Laminar-Flow Reactors: From Experimentation To CFD SimulationDocument9 pagesTeaching Laminar-Flow Reactors: From Experimentation To CFD Simulationsiddharth ranaNo ratings yet
- BCHCT 135 June 2022 PaperDocument10 pagesBCHCT 135 June 2022 PaperAdityaNo ratings yet
- Chem (1st&2nd) May2018Document2 pagesChem (1st&2nd) May2018damansahota2902No ratings yet
- 15PY101 2 SemDocument2 pages15PY101 2 Semraghul kannanNo ratings yet
- (2nd Sem) - Engineering-Physics-2-As-202-E-2012-13Document2 pages(2nd Sem) - Engineering-Physics-2-As-202-E-2012-13Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 4 Sem Physical Pharmaceutics 2 bp403t 2019Document1 pageBpharm 4 Sem Physical Pharmaceutics 2 bp403t 2019I DNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Membranes Used in Fuel Cells: Degradation and StabilizationFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Membranes Used in Fuel Cells: Degradation and StabilizationShulamith SchlickNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms 09 02284 v2Document10 pagesMicroorganisms 09 02284 v2biovijay101No ratings yet
- Cell Disruption by Chemical or Enzymatic MethodDocument9 pagesCell Disruption by Chemical or Enzymatic Methodbiovijay101100% (1)
- Whole Genome Sequencing of HumanDocument17 pagesWhole Genome Sequencing of Humanbiovijay101No ratings yet
- Bio Instrumentation - John D. EnderleDocument220 pagesBio Instrumentation - John D. EnderleRoberto Armenta100% (3)
- Bioinstrumentation To Understanding The LifeDocument339 pagesBioinstrumentation To Understanding The Lifebiovijay101No ratings yet
- Metland Menteng e Brochure SDocument22 pagesMetland Menteng e Brochure Selha2727No ratings yet
- Draft Minutes Apr 5, 2023Document5 pagesDraft Minutes Apr 5, 2023PPSMU PAMPANGA PPONo ratings yet
- Mycoplasma ContaminationDocument4 pagesMycoplasma ContaminationashueinNo ratings yet
- Bio L 2281 Experiment 6Document8 pagesBio L 2281 Experiment 6karyanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Year 3 LNS Pets WorldDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Year 3 LNS Pets WorldtgDeanNo ratings yet
- First Aid InstructionDocument2 pagesFirst Aid Instructionmiraç burak navruzNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development 2Document58 pagesChild and Adolescent Development 2Princess Mae CuayzonNo ratings yet
- 0510 w09 Ms 3 PDFDocument13 pages0510 w09 Ms 3 PDFmastermido524No ratings yet
- 201806290521342834814ReadyReckonerJune2018web PDFDocument94 pages201806290521342834814ReadyReckonerJune2018web PDFahabasiNo ratings yet
- Annual General Report On The Audit of Information Systems FY 2021-22Document69 pagesAnnual General Report On The Audit of Information Systems FY 2021-22ABINo ratings yet
- Stanford - Discrete Time Markov Chains PDFDocument23 pagesStanford - Discrete Time Markov Chains PDFSofoklisNo ratings yet
- Hearst Demystifying Media Fireside Chat - The Bloomberg Way With Matthew WinklerDocument16 pagesHearst Demystifying Media Fireside Chat - The Bloomberg Way With Matthew WinklerDemystifying MediaNo ratings yet
- Workbook Cookbook in SAP SourcingDocument23 pagesWorkbook Cookbook in SAP SourcingShanker_Kaura_3256100% (1)
- Manuals 299h Series Pressure Reducing Regulators Fisher en en 6106242 PDFDocument20 pagesManuals 299h Series Pressure Reducing Regulators Fisher en en 6106242 PDFMushfiqur Rahman0% (1)
- Childrens Health First McKinsey Report 2006Document64 pagesChildrens Health First McKinsey Report 2006Rachel LavinNo ratings yet
- CSC 218 Notes 3Document8 pagesCSC 218 Notes 3Musa JubrilNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: A. Background Information For Learners B. Most Essential Learning CompetencyDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: A. Background Information For Learners B. Most Essential Learning CompetencyCamille CaigaNo ratings yet
- Kargil Diwas Script - 230712 - 224828Document4 pagesKargil Diwas Script - 230712 - 224828kashyapakarshanaNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm DetectorDocument4 pagesFire Alarm DetectorNEERAJ0% (1)
- Nikon Ti2-E Price PDFDocument8 pagesNikon Ti2-E Price PDFBrandon LEeNo ratings yet
- Bank ReconciliationDocument3 pagesBank ReconciliationjinyangsuelNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Interpersonal Violence Against Athletes in The Sport Context (2017)Document5 pagesPrevalence of Interpersonal Violence Against Athletes in The Sport Context (2017)Juan Kmilo Martinez FernandezNo ratings yet
- AaDocument4 pagesAaCheck OndesNo ratings yet
- 1 - Norovirus Care Home Poster 2018Document1 page1 - Norovirus Care Home Poster 2018GarryNo ratings yet
- HCS301Document20 pagesHCS301Anonymous iNxLvwNo ratings yet
- True or False (8 PTS.) : Bio 11 2 Lecture LE Mock Exam October 2015Document8 pagesTrue or False (8 PTS.) : Bio 11 2 Lecture LE Mock Exam October 2015Alexander Miguel SyNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning - 9: BITS PilaniDocument13 pagesMachine Learning - 9: BITS PilaniSimran sandhuNo ratings yet
- ME PED-Scheme & Syllabus 2018Document21 pagesME PED-Scheme & Syllabus 2018Angamuthu AnanthNo ratings yet