Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison Chart of Gram +ve & - Ve
Comparison Chart of Gram +ve & - Ve
Uploaded by
سيفل إسلامCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Microbiology Notes 2Document69 pagesMicrobiology Notes 2Marie Llanes100% (1)
- Pre-Board Examination in Hematology (Part 1) : Polychromatophilic NormoblastDocument5 pagesPre-Board Examination in Hematology (Part 1) : Polychromatophilic NormoblastGodofredo HermosuraNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology Ch1Document38 pagesBurton's Microbiology Ch1Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano91% (11)
- Bi0 310 Bacteria Lab ReportDocument11 pagesBi0 310 Bacteria Lab ReportChiletso PhiriNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Quiz ResultsNicoleNo ratings yet
- Biochem AssignmentDocument7 pagesBiochem AssignmentSana eltafNo ratings yet
- Differences Between G+VE & G-VE BACTERIADocument3 pagesDifferences Between G+VE & G-VE BACTERIAADUGNA DEGEFENo ratings yet
- CorrectionDocument3 pagesCorrectionEtotoue ChristianNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Positive NotesDocument8 pagesGram Negative Positive NotesKusum Roy100% (1)
- Review of Medical Bacteriology: Prof. Yuwono, MD., PHD WWW - Yuwono.Gnc - Or.IdDocument24 pagesReview of Medical Bacteriology: Prof. Yuwono, MD., PHD WWW - Yuwono.Gnc - Or.IdLivia HanisamurtiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell and StainingDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cell and StainingKriziaoumo P. OrpiaNo ratings yet
- The Prokaryote: Bacteria: References and FiguresDocument21 pagesThe Prokaryote: Bacteria: References and Figureschan1080804No ratings yet
- Discuss The Various Theories On The Gram Stain.: Gram-Negative Bacteria Gram-Positive BacteriaDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Various Theories On The Gram Stain.: Gram-Negative Bacteria Gram-Positive BacteriaFiddo Waggay100% (3)
- Structure and Function of Prokaryotik (Eubacteria Dan Archaeobacteria)Document94 pagesStructure and Function of Prokaryotik (Eubacteria Dan Archaeobacteria)RositaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive and Gram NegativeDocument4 pagesGram Positive and Gram Negativememewala88No ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Microbiology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument731 pagesDAMS CRS - Microbiology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument11 pagesGram StainingSri Ram Prasath TNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining: Exercise 3Document4 pagesGram Staining: Exercise 3Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Part 10 ProkaryoticDocument54 pagesPart 10 ProkaryoticLê Thanh HằngNo ratings yet
- BakteriDocument8 pagesBakteriRhNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Morphology Growth Requirements 1Document7 pagesBacteria Morphology Growth Requirements 121-54405No ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment PDFaubrey yangzonNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL 4 MicrobDocument6 pagesPRACTICAL 4 Microbdomo- kunNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining Clinical ExerciseDocument10 pagesGram Staining Clinical ExerciseHimani Aggarwal100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Bacterial StructureDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Bacterial StructureAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BiodiversityDocument18 pagesChapter 11 Biodiversityvarshenn krishnanNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Model Project 2020Document6 pagesBacteria Model Project 2020api-484250989No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesLecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and Physiologyapi-370335280% (5)
- Study Guide3 Learning Acts Sci123 2023 For MergeDocument2 pagesStudy Guide3 Learning Acts Sci123 2023 For MergeRovic GasmenNo ratings yet
- Cell ProkaryotDocument107 pagesCell ProkaryotYani-dha CidHotNo ratings yet
- Bacteria & Protists Noted PDFDocument23 pagesBacteria & Protists Noted PDFXiaNo ratings yet
- Morphology & Gram StainingDocument10 pagesMorphology & Gram StainingFuad Hasan Pranto 1921147049No ratings yet
- Staining & Simple StainingDocument32 pagesStaining & Simple StainingHaji BhuttoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMicrobiology 1 PDFRaven CocjinNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesBacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNo ratings yet
- Transes-Micropara Lec PrelimsDocument25 pagesTranses-Micropara Lec Prelimsmikhyla.cardenoNo ratings yet
- Cyanobacteria Basic Characteristics Fo BacteriaDocument4 pagesCyanobacteria Basic Characteristics Fo BacteriaAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- 595-761 Microbial Culture 2-2564Document83 pages595-761 Microbial Culture 2-2564Muhammad Ali KhumainiNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeSK BuntunNo ratings yet
- 10 - Introduction To EnterobacteriaceaeDocument33 pages10 - Introduction To EnterobacteriaceaeМария М.No ratings yet
- Micro Part 1Document138 pagesMicro Part 1Perlie CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Kingdom Prokaryotea (Monera) : Presented by Dr. Maryam MukhtarDocument20 pagesChapter 6: Kingdom Prokaryotea (Monera) : Presented by Dr. Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Microbiology ThepharmapediaDocument20 pagesFundamental of Microbiology ThepharmapediaSwaroopSinghJakharNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument29 pagesProkaryotic CellSeshime Thyrone DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - ProkaryotesDocument64 pagesLecture 10 - Prokaryotesnm1006055No ratings yet
- The Bacterial CellDocument24 pagesThe Bacterial Celljose carlos jimenez huashuayoNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument30 pagesGram StainingSolomon Fallah Foa Sandy100% (1)
- in Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Document21 pagesin Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Mica-Ella CasasolaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Microbiology Session 7Document15 pagesIndustrial Microbiology Session 7Matthew GhaffariNo ratings yet
- Ruling The World: Microbial DiversityDocument47 pagesRuling The World: Microbial Diversityss2945No ratings yet
- Moyes 2009, Tinción de GramDocument8 pagesMoyes 2009, Tinción de GramVale rumazNo ratings yet
- Characterizing & Classifying ProkaryotesDocument4 pagesCharacterizing & Classifying ProkaryotesJennifer Davis CondimanNo ratings yet
- Sbs2013 Microbiology - Lecture 2 (Chapter 3 4)Document41 pagesSbs2013 Microbiology - Lecture 2 (Chapter 3 4)BakalJenazahNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFwilliam.collins296100% (31)
- Lab Sheet - Gram StainingDocument4 pagesLab Sheet - Gram Stainingbliss polleyNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining Technique Acid-Fast TechniqueDocument4 pagesGram Staining Technique Acid-Fast TechniqueNarcisa Romano AplodNo ratings yet
- Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17th Edition (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Document1,016 pagesReview of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17th Edition (Medicalstudyzone - Com)FaizNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ToxinsDocument21 pagesBacterial ToxinsMohan Prasad GuptaNo ratings yet
- Morfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDocument47 pagesMorfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDaffa YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Microbial Taxonomy and Phylogeny PATINGA CHRISTIAN V.Document2 pagesMicrobial Taxonomy and Phylogeny PATINGA CHRISTIAN V.Christian PatingaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument47 pagesBlood TransfusionVaishnavi BingumallaNo ratings yet
- Zone of InhibitionDocument3 pagesZone of InhibitionSubrata BhadraNo ratings yet
- Presentation GeneticsDocument18 pagesPresentation GeneticsAzhar Ud Din AzadNo ratings yet
- Gangaram Rate List PDFDocument315 pagesGangaram Rate List PDFAmit Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility TestDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility TestMATTHEW EARL MALUMAY100% (1)
- DCR 's-4 AprilDocument33 pagesDCR 's-4 AprilVidya BudihalNo ratings yet
- Mha PDFDocument2 pagesMha PDFrajeevmkNo ratings yet
- Physiology Assignment: Complete Blood CountDocument7 pagesPhysiology Assignment: Complete Blood CountMuhammad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Reference: Harmening, D.M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices. 6 Ed. Pg. 123. F.A. Davis CompanyDocument2 pagesReference: Harmening, D.M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices. 6 Ed. Pg. 123. F.A. Davis CompanyMARC AIVIN BEATONo ratings yet
- KUHS - MBBS - Chapter Wise Important Questions - Physiology - Hematology PhysiologyDocument2 pagesKUHS - MBBS - Chapter Wise Important Questions - Physiology - Hematology PhysiologyHARPREETNo ratings yet
- BACTERIOPHAGEDocument21 pagesBACTERIOPHAGERobin Oben100% (1)
- Infection and EpizootiologyDocument3 pagesInfection and EpizootiologyAdrian Mausig100% (1)
- StaphylococosisDocument11 pagesStaphylococosisvasanthi balanNo ratings yet
- Pricelist MonotestDocument3 pagesPricelist MonotestMimi AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups & Blood BankingDocument36 pagesBlood Groups & Blood BankingGodfrey Pizaroh Mujuzi100% (2)
- Gram Positive Cocci Differentiation: Catalase TestDocument2 pagesGram Positive Cocci Differentiation: Catalase TestQueancy Joy HilarioNo ratings yet
- 15) Dr. Firdaus, Ph. D - Penjelasan Praktikum REPRODUKSI PALUDocument35 pages15) Dr. Firdaus, Ph. D - Penjelasan Praktikum REPRODUKSI PALUcimyNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soalan 14Document4 pagesContoh Soalan 14Rozaiya RamliNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank and Blood TransfusionDocument11 pagesBlood Bank and Blood TransfusionMostafa Adel Ahmd100% (1)
- Cico Biweekly Vol 3 No 15Document2 pagesCico Biweekly Vol 3 No 15mactopiaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria&YeastDocument13 pagesBacteria&YeastGuy SoreqNo ratings yet
- IMPAACT 2034 - LPC - v1.1 - 12jul23Document13 pagesIMPAACT 2034 - LPC - v1.1 - 12jul23Lucas Masiêro AraujoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Transfer Associated With Blowing Out Candles On A Birthday CakeDocument5 pagesBacterial Transfer Associated With Blowing Out Candles On A Birthday CakeWSETNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Q&ADocument3 pagesBlood Transfusion Q&APratheebaNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping 12thDocument17 pagesBlood Grouping 12thPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- PAT T 2 V 5 Blood Transfusion Policy FinalDocument64 pagesPAT T 2 V 5 Blood Transfusion Policy FinalAyman MehassebNo ratings yet
Comparison Chart of Gram +ve & - Ve
Comparison Chart of Gram +ve & - Ve
Uploaded by
سيفل إسلامOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparison Chart of Gram +ve & - Ve
Comparison Chart of Gram +ve & - Ve
Uploaded by
سيفل إسلامCopyright:
Available Formats
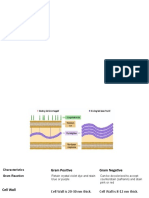
Comparison chart
Gram-negative Bacteria versus Gram-positive Bacteria comparison chart
Gram-negative Gram-positive
Bacteria Bacteria
Gram reaction Can be decolorized to accept Retain crystal violet dye and
counterstain (safranin) and stain stain blue or purple
pink or red
Cell Wall They have a wavy and double- Their cell wall is smooth and
layered cell-wall single-layered
Cell Wall thickness The thickness of the cell wall is 8 to The thickness of the cell wall
10 nanometres is 20 to 80 nanometres
Peptidoglycan Thin (single-layered) Thick (multilayered)
layer
Lipid and 20 to 30% Very low
lipoprotein content
Lipopolysaccharid High Virtually none
e (LPS) content
Teichoic acids Absent Present in many
Periplasmic space present Absent
Outer membrane Present Absent
Mesosome Mesosome is less prominent. Mesosome is more
prominent.
Porins Occurs in Outer Membrane Absent
Flagellar structure 4 rings in basal body 2 rings in basal body
Morphology Non-spore forming rods Cocci or spore-forming rods
Gram-negative Bacteria versus Gram-positive Bacteria comparison chart
Gram-negative Gram-positive
Bacteria Bacteria
Toxins produced Primarily Endotoxins Primarily Exotoxins
Resistance to Low High
physical disruption
Inhibition by basic Low High
dyes
Susceptibility to Low High
anionic detergents
Resistance to Low High
sodium azide
Resistance to Low High
drying
Cell Wall Low (requires pretreatment to High
Disruption by destabilize outer membrane)
Lysozyme
Antibiotic More resistant More susceptible
Resistance
Examples Escherichia, Salmonella, etc. Staphylococcus,
Streptococcus, etc.
You might also like
- Microbiology Notes 2Document69 pagesMicrobiology Notes 2Marie Llanes100% (1)
- Pre-Board Examination in Hematology (Part 1) : Polychromatophilic NormoblastDocument5 pagesPre-Board Examination in Hematology (Part 1) : Polychromatophilic NormoblastGodofredo HermosuraNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology Ch1Document38 pagesBurton's Microbiology Ch1Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano91% (11)
- Bi0 310 Bacteria Lab ReportDocument11 pagesBi0 310 Bacteria Lab ReportChiletso PhiriNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Quiz ResultsNicoleNo ratings yet
- Biochem AssignmentDocument7 pagesBiochem AssignmentSana eltafNo ratings yet
- Differences Between G+VE & G-VE BACTERIADocument3 pagesDifferences Between G+VE & G-VE BACTERIAADUGNA DEGEFENo ratings yet
- CorrectionDocument3 pagesCorrectionEtotoue ChristianNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Positive NotesDocument8 pagesGram Negative Positive NotesKusum Roy100% (1)
- Review of Medical Bacteriology: Prof. Yuwono, MD., PHD WWW - Yuwono.Gnc - Or.IdDocument24 pagesReview of Medical Bacteriology: Prof. Yuwono, MD., PHD WWW - Yuwono.Gnc - Or.IdLivia HanisamurtiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell and StainingDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cell and StainingKriziaoumo P. OrpiaNo ratings yet
- The Prokaryote: Bacteria: References and FiguresDocument21 pagesThe Prokaryote: Bacteria: References and Figureschan1080804No ratings yet
- Discuss The Various Theories On The Gram Stain.: Gram-Negative Bacteria Gram-Positive BacteriaDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Various Theories On The Gram Stain.: Gram-Negative Bacteria Gram-Positive BacteriaFiddo Waggay100% (3)
- Structure and Function of Prokaryotik (Eubacteria Dan Archaeobacteria)Document94 pagesStructure and Function of Prokaryotik (Eubacteria Dan Archaeobacteria)RositaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive and Gram NegativeDocument4 pagesGram Positive and Gram Negativememewala88No ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Microbiology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument731 pagesDAMS CRS - Microbiology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument11 pagesGram StainingSri Ram Prasath TNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining: Exercise 3Document4 pagesGram Staining: Exercise 3Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Part 10 ProkaryoticDocument54 pagesPart 10 ProkaryoticLê Thanh HằngNo ratings yet
- BakteriDocument8 pagesBakteriRhNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Morphology Growth Requirements 1Document7 pagesBacteria Morphology Growth Requirements 121-54405No ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment PDFaubrey yangzonNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL 4 MicrobDocument6 pagesPRACTICAL 4 Microbdomo- kunNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining Clinical ExerciseDocument10 pagesGram Staining Clinical ExerciseHimani Aggarwal100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Bacterial StructureDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Bacterial StructureAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BiodiversityDocument18 pagesChapter 11 Biodiversityvarshenn krishnanNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Model Project 2020Document6 pagesBacteria Model Project 2020api-484250989No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesLecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and Physiologyapi-370335280% (5)
- Study Guide3 Learning Acts Sci123 2023 For MergeDocument2 pagesStudy Guide3 Learning Acts Sci123 2023 For MergeRovic GasmenNo ratings yet
- Cell ProkaryotDocument107 pagesCell ProkaryotYani-dha CidHotNo ratings yet
- Bacteria & Protists Noted PDFDocument23 pagesBacteria & Protists Noted PDFXiaNo ratings yet
- Morphology & Gram StainingDocument10 pagesMorphology & Gram StainingFuad Hasan Pranto 1921147049No ratings yet
- Staining & Simple StainingDocument32 pagesStaining & Simple StainingHaji BhuttoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMicrobiology 1 PDFRaven CocjinNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesBacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNo ratings yet
- Transes-Micropara Lec PrelimsDocument25 pagesTranses-Micropara Lec Prelimsmikhyla.cardenoNo ratings yet
- Cyanobacteria Basic Characteristics Fo BacteriaDocument4 pagesCyanobacteria Basic Characteristics Fo BacteriaAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- 595-761 Microbial Culture 2-2564Document83 pages595-761 Microbial Culture 2-2564Muhammad Ali KhumainiNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeSK BuntunNo ratings yet
- 10 - Introduction To EnterobacteriaceaeDocument33 pages10 - Introduction To EnterobacteriaceaeМария М.No ratings yet
- Micro Part 1Document138 pagesMicro Part 1Perlie CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Kingdom Prokaryotea (Monera) : Presented by Dr. Maryam MukhtarDocument20 pagesChapter 6: Kingdom Prokaryotea (Monera) : Presented by Dr. Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Microbiology ThepharmapediaDocument20 pagesFundamental of Microbiology ThepharmapediaSwaroopSinghJakharNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument29 pagesProkaryotic CellSeshime Thyrone DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - ProkaryotesDocument64 pagesLecture 10 - Prokaryotesnm1006055No ratings yet
- The Bacterial CellDocument24 pagesThe Bacterial Celljose carlos jimenez huashuayoNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument30 pagesGram StainingSolomon Fallah Foa Sandy100% (1)
- in Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Document21 pagesin Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Mica-Ella CasasolaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Microbiology Session 7Document15 pagesIndustrial Microbiology Session 7Matthew GhaffariNo ratings yet
- Ruling The World: Microbial DiversityDocument47 pagesRuling The World: Microbial Diversityss2945No ratings yet
- Moyes 2009, Tinción de GramDocument8 pagesMoyes 2009, Tinción de GramVale rumazNo ratings yet
- Characterizing & Classifying ProkaryotesDocument4 pagesCharacterizing & Classifying ProkaryotesJennifer Davis CondimanNo ratings yet
- Sbs2013 Microbiology - Lecture 2 (Chapter 3 4)Document41 pagesSbs2013 Microbiology - Lecture 2 (Chapter 3 4)BakalJenazahNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFwilliam.collins296100% (31)
- Lab Sheet - Gram StainingDocument4 pagesLab Sheet - Gram Stainingbliss polleyNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining Technique Acid-Fast TechniqueDocument4 pagesGram Staining Technique Acid-Fast TechniqueNarcisa Romano AplodNo ratings yet
- Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17th Edition (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Document1,016 pagesReview of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17th Edition (Medicalstudyzone - Com)FaizNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ToxinsDocument21 pagesBacterial ToxinsMohan Prasad GuptaNo ratings yet
- Morfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDocument47 pagesMorfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDaffa YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Microbial Taxonomy and Phylogeny PATINGA CHRISTIAN V.Document2 pagesMicrobial Taxonomy and Phylogeny PATINGA CHRISTIAN V.Christian PatingaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument47 pagesBlood TransfusionVaishnavi BingumallaNo ratings yet
- Zone of InhibitionDocument3 pagesZone of InhibitionSubrata BhadraNo ratings yet
- Presentation GeneticsDocument18 pagesPresentation GeneticsAzhar Ud Din AzadNo ratings yet
- Gangaram Rate List PDFDocument315 pagesGangaram Rate List PDFAmit Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility TestDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility TestMATTHEW EARL MALUMAY100% (1)
- DCR 's-4 AprilDocument33 pagesDCR 's-4 AprilVidya BudihalNo ratings yet
- Mha PDFDocument2 pagesMha PDFrajeevmkNo ratings yet
- Physiology Assignment: Complete Blood CountDocument7 pagesPhysiology Assignment: Complete Blood CountMuhammad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Reference: Harmening, D.M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices. 6 Ed. Pg. 123. F.A. Davis CompanyDocument2 pagesReference: Harmening, D.M. (2012) - Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices. 6 Ed. Pg. 123. F.A. Davis CompanyMARC AIVIN BEATONo ratings yet
- KUHS - MBBS - Chapter Wise Important Questions - Physiology - Hematology PhysiologyDocument2 pagesKUHS - MBBS - Chapter Wise Important Questions - Physiology - Hematology PhysiologyHARPREETNo ratings yet
- BACTERIOPHAGEDocument21 pagesBACTERIOPHAGERobin Oben100% (1)
- Infection and EpizootiologyDocument3 pagesInfection and EpizootiologyAdrian Mausig100% (1)
- StaphylococosisDocument11 pagesStaphylococosisvasanthi balanNo ratings yet
- Pricelist MonotestDocument3 pagesPricelist MonotestMimi AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups & Blood BankingDocument36 pagesBlood Groups & Blood BankingGodfrey Pizaroh Mujuzi100% (2)
- Gram Positive Cocci Differentiation: Catalase TestDocument2 pagesGram Positive Cocci Differentiation: Catalase TestQueancy Joy HilarioNo ratings yet
- 15) Dr. Firdaus, Ph. D - Penjelasan Praktikum REPRODUKSI PALUDocument35 pages15) Dr. Firdaus, Ph. D - Penjelasan Praktikum REPRODUKSI PALUcimyNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soalan 14Document4 pagesContoh Soalan 14Rozaiya RamliNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank and Blood TransfusionDocument11 pagesBlood Bank and Blood TransfusionMostafa Adel Ahmd100% (1)
- Cico Biweekly Vol 3 No 15Document2 pagesCico Biweekly Vol 3 No 15mactopiaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria&YeastDocument13 pagesBacteria&YeastGuy SoreqNo ratings yet
- IMPAACT 2034 - LPC - v1.1 - 12jul23Document13 pagesIMPAACT 2034 - LPC - v1.1 - 12jul23Lucas Masiêro AraujoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Transfer Associated With Blowing Out Candles On A Birthday CakeDocument5 pagesBacterial Transfer Associated With Blowing Out Candles On A Birthday CakeWSETNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Q&ADocument3 pagesBlood Transfusion Q&APratheebaNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping 12thDocument17 pagesBlood Grouping 12thPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- PAT T 2 V 5 Blood Transfusion Policy FinalDocument64 pagesPAT T 2 V 5 Blood Transfusion Policy FinalAyman MehassebNo ratings yet