Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostics CVD
Diagnostics CVD
Uploaded by
ZmiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diagnostics CVD
Diagnostics CVD
Uploaded by
ZmiaCopyright:
Available Formats
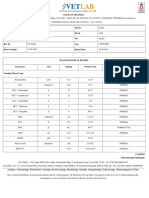
TEST NAME OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
CBC PC
Hemoglobin 15.6 14-18 g/dL Normal
Hematocrit 0.49 0.40-0.54 Normal
WBC count 9.4 4-11 x109/L Normal
RBC count 5.7 5-6.4 X1012/L Normal
Platelet count 237 150-450 x109/L Normal
Mean Cell Volume
85.8 80-95 fL Normal
(MCV)
Mean Cell
27.4 27-31 pg Normal
Hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean Cell Hgb. Conc,
32.0 32-36 g/L Normal
(MCHC)
Mean Platelet Volume
9.5 6.5-12 fL Normal
(MPV)
Red Cell Distribution
14.2 11.6-14.6 % Normal
Width (RDW)
Segmenter 69 50-70 % Normal
Lymphocyte 21 20-40 % Normal
Increase number of
monocytes indicate
presence of chronic
infection, and
Monocyte 7 2-5 % autoimmune or blood
disorder, cancer, or
other medical
conditions.
(Falck, 2018)
Date: February 11, 2019
Eosinophil 3 2-4 % Normal
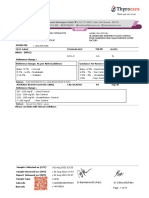
TEST NAME OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
PARTIAL THROMBOPLASTIN TIME (PTT)
Activated PTT 38.2 30.4-41.2 seconds Normal
PROTHROMBIN TIME
INR 0.96 0.88-1.21 Normal
Prothrombin Time 11.3 10.4-14.0 seconds Normal
% activity 117.1 73-127 % Normal
Date: February 11, 2019
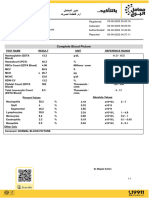
TEST NAME OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
UREL/BUN 4.30 3.0-9.3 mmol/L Normal
Slight decrease or
normal creatinine with
BUN within normal
Creatinine 63 64-104 umol/L range suggest
dehydration
(Kee, 2006)
Potassium 4.6 3.5-5.1 mmol/L Normal
Sodium 138 136-145 mmol/L Normal
Date: February 12, 2019
TEST NAME OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
Albumin 37 3.0-9.3 g/L Normal
Chloride
HISTORY: Left sided body weakness 109 64-104 mmol/L Normal
Magnesium
COMPARISONS: 1.00 0.66-1.07 mmol/L Normal
Phosphorus 1.06 0.74-1.52 mmol/L Normal
TECHNIQUE: Multiple axial images of the head were obtained without intravenous contrast.
Date: February 12, 2019
FINDINGS:
Ill-defined hypodensities are noted in the inferior aspect of the pons.
Date: February 13, 2019
Encephalomalacic
Test Type: CT changes are present in the right parieto-temporal lobes. Well defined
Examination: NECT of theinBrain
hypodensities are seen the left thalamus and left corona radiata. There are faint patchy areas
decrease in density in the fronto-parietal periventricular white matter. No evidence of intracranial
hemorrhage
Midline structures are in place.
Ventricles are not dilated.
Impression:
Infarct of indeterminate age, inferior aspect of the pons
Encephalomalacic changes, right parieto-temporal lobes
Chronic lacunar infarct, left thalamus and left-corona radiata
Microvascular ischemic changes, fronto-parietal periventricular white matter
Mild age-related cerebrocerebellar volume loss
Atherosclerotic vessel disease
Date: February 13, 2019
TEST NAME OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
LIPID PROFILE
HDL 0.88 Up to 1.04 mmol/L Normal
VLDL 0.32 mmol/L Normal
Triglyceride 0.70 Up to 1.70 mmol/L Normal
LDL 3.72 Up to 2.59 mmol/L High LDL can
be due to
unhealthy diet,
inactivity, or
obesity.
(Mayo Clinic,
2017)
Cholesterol 4.70 Up to 5.18 mmol/L Normal
HbA1c 5.70 4.5-6.5 % Normal
Date: February 13, 2019
TEST NAME OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
FBS 5.07 3.89-5.49 mmol/L Normal
REFERENCES:
Kee, J.L. (2006). A Look At Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests With Nursing Implications. Singapore:
Pearson Education South Asia Pte. Ltd. Pp. 142
Mayo Clinic. (2017). Cholesterol. Retrieved from www.mayoclinic.com last February 19, 2019.
Falck, S. (2018). What to know about high white blood cell count. Retrieved from www.
medicalnewstoday.com last February 19, 2019.
You might also like
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmlodipineDhanNie Cenita100% (6)
- Client Name - : Axelia Solutions PVT LTD - PP0564Document6 pagesClient Name - : Axelia Solutions PVT LTD - PP0564Ashutosh PandaNo ratings yet
- 353 Med Terminology PDFDocument5 pages353 Med Terminology PDFNicole NicholsonNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PT KEIDocument6 pagesCompany Profile PT KEIMochammad IrchamNo ratings yet
- LabDocument3 pagesLabryanster21No ratings yet
- Revil Lab Fem WardDocument2 pagesRevil Lab Fem WardJohn Emmanuel RevilNo ratings yet
- Labs Finals Case PreDocument4 pagesLabs Finals Case Prereized02No ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument6 pagesDiagnostic and Laboratory Proceduresmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Study: Complete Blood CountDocument5 pagesLaboratory Study: Complete Blood CountNicole Angeli ManuelNo ratings yet
- References: Treatment, Page 227-229Document6 pagesReferences: Treatment, Page 227-229Nur AzzahanaNo ratings yet
- Group F DXDocument2 pagesGroup F DXmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- WBW/ Reena:, UttarDocument2 pagesWBW/ Reena:, UttarRana Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Case 444Document20 pagesCase 444jovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Case Study LaboratoryDocument4 pagesCase Study LaboratoryKJay SolijonNo ratings yet
- LabTest 06jun2023Document1 pageLabTest 06jun2023abhishekmenonNo ratings yet
- LabsDocument7 pagesLabsshaztamendozaNo ratings yet
- Rajesh R D - 2312316Document2 pagesRajesh R D - 2312316dr.menganeNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- WBC Differential Count Clinical Chemistry Section: Hematology Result Reduce RBC Production Reduce RBC ProductionDocument10 pagesWBC Differential Count Clinical Chemistry Section: Hematology Result Reduce RBC Production Reduce RBC ProductionknicknucksNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test W/ Normal Values Result Interpretat ION Significance Nursing Responsibility RE MA RKSDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test W/ Normal Values Result Interpretat ION Significance Nursing Responsibility RE MA RKSjanna mae patriarcaNo ratings yet
- LAB & DIAGNOSTIC TEST (TAHBSO) - Garcia, Jimlord A.Document7 pagesLAB & DIAGNOSTIC TEST (TAHBSO) - Garcia, Jimlord A.Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sample Hematology ResultDocument3 pagesSample Hematology ResultRaul ArranguezNo ratings yet
- Case Study 10Document8 pagesCase Study 10Cathleen Nasis ForrosueloNo ratings yet
- LabReport L12 Mrs - REKHA25YRS F 06 04 202420240406 2 Zte6iuDocument3 pagesLabReport L12 Mrs - REKHA25YRS F 06 04 202420240406 2 Zte6iuAnkit GairolaNo ratings yet
- Uterine Atony-Case-AnalysisDocument25 pagesUterine Atony-Case-AnalysisAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Ah4379200077182260 RLSDocument10 pagesAh4379200077182260 RLSAnusha NNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Hematology ReportDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Hematology ReportMartin T ManuelNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document7 pagesJurnal 1faisalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory FindingsDocument1 pageLaboratory FindingsJade ParkNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Findings Nursing InterventionsDocument29 pagesLaboratory Findings Nursing InterventionstflorenzNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Findings Complete Blood Count (April 10, 2008) Results Normal Values Remarks HemoglobinDocument29 pagesLaboratory Findings Complete Blood Count (April 10, 2008) Results Normal Values Remarks HemoglobintflorenzNo ratings yet
- Arogyam1 3Document12 pagesArogyam1 3Sashikanta NayakNo ratings yet
- Final Lab ValDocument10 pagesFinal Lab ValJoseph Emmanuel CandaNo ratings yet
- Speedtest by Ookla - The Global Broadband Speed TestDocument10 pagesSpeedtest by Ookla - The Global Broadband Speed TestBibhu Prasanna SinghNo ratings yet
- LabReport L19 Mrs - REKHA53YRS F 23 01 202420240123 2 Ekgo1fDocument2 pagesLabReport L19 Mrs - REKHA53YRS F 23 01 202420240123 2 Ekgo1fAnkit GairolaNo ratings yet
- MAHAAM3Document2 pagesMAHAAM3vlande897No ratings yet
- Case Study 3Document11 pagesCase Study 3Mary Grace TirolNo ratings yet
- Case #3 (Macazo, Manueke, Purba) : CBC ResultsDocument2 pagesCase #3 (Macazo, Manueke, Purba) : CBC ResultsironNo ratings yet
- Haematology, Biochemistry, Serology and Immunology, Microbiology, Cytology, Histopathology, Endocrinology, Ultrasonography & X-RayDocument2 pagesHaematology, Biochemistry, Serology and Immunology, Microbiology, Cytology, Histopathology, Endocrinology, Ultrasonography & X-RayPankaj BeniwalNo ratings yet
- February 28,2011Document3 pagesFebruary 28,2011Beth PascuaNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Test Result Unit Normal Range Differentia LDocument3 pagesHematology: Test Result Unit Normal Range Differentia Lshnoesam2004No ratings yet
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument10 pagesCase Study PneumoniaGrace Ann67% (3)
- A58677300074696275 RLSDocument20 pagesA58677300074696275 RLSvirupakshudu kodiyalaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: DIOSANA, Janine V. - 2018 - 10241 - Group CDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: DIOSANA, Janine V. - 2018 - 10241 - Group CJanine DiosanaNo ratings yet
- Kgmu Trauma 22092200943 7355326825Document2 pagesKgmu Trauma 22092200943 7355326825Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Invest and Medication 1Document9 pagesInvest and Medication 1RajaNo ratings yet
- Masto 4 PDFDocument6 pagesMasto 4 PDFezzat anasNo ratings yet
- Self Amalendu Bikash Nath (66Y/M) 3B Amardham Apartment South Station Road Agarpara Near Aqua Diamond Water FactoryDocument19 pagesSelf Amalendu Bikash Nath (66Y/M) 3B Amardham Apartment South Station Road Agarpara Near Aqua Diamond Water FactoryOritra BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Af69016900076120179 RLSDocument9 pagesAf69016900076120179 RLSLoke RajpavanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam SampleDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Exam SampledawnNo ratings yet
- Jan 2024Document10 pagesJan 2024shubhy.saffroninteractiveNo ratings yet
- Barcenas, Alejandro - Resumen de Salud 4Document9 pagesBarcenas, Alejandro - Resumen de Salud 4alejandro BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Mlybi3T9WERlsEB6bd3 - Report - 2021-10-14 17 - 15 - 12Document5 pagesMlybi3T9WERlsEB6bd3 - Report - 2021-10-14 17 - 15 - 12vaibhavnikhil06No ratings yet
- Laboratory Results & InterpretationDocument11 pagesLaboratory Results & InterpretationLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Case Pre 2Document11 pagesCase Pre 2Juviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Medicine: Haematology Test Result Unit Biological Reference Interval Complete Blood Count (CBC)Document3 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Medicine: Haematology Test Result Unit Biological Reference Interval Complete Blood Count (CBC)abhilash eNo ratings yet
- Danesh Pathobiology Lab ﺶﻧاد يژﻮﻟﻮﻴﺑﻮﺗﺎﭘ هﺎﮕﺸﻳﺎﻣزآ: BIOCHEMISTRY - Random UrineDocument3 pagesDanesh Pathobiology Lab ﺶﻧاد يژﻮﻟﻮﻴﺑﻮﺗﺎﭘ هﺎﮕﺸﻳﺎﻣزآ: BIOCHEMISTRY - Random Urinesoheil farahbakhshianNo ratings yet
- Case Draft BPHDocument20 pagesCase Draft BPHKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- ATTAR49Document10 pagesATTAR49vlande897No ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture: DR - Magda SultanDocument3 pagesComplete Blood Picture: DR - Magda SultanNada MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of The NewbornDocument47 pagesHemolytic Disease of The NewbornJanine CabreraNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Conference CaseDocument4 pagesClinicopathological Conference CasePraneeth PaletiNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetic Abnormalities: Chromosomal, FISH, and Microarray-Based Clinical Reporting and Interpretation of ResultFrom EverandCytogenetic Abnormalities: Chromosomal, FISH, and Microarray-Based Clinical Reporting and Interpretation of ResultNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy Bipolar Disorder: Interpersonal TherapyDocument3 pagesPsychotherapy Bipolar Disorder: Interpersonal TherapyZmiaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPZmiaNo ratings yet
- Ncp. Oral MucosaDocument1 pageNcp. Oral MucosaZmiaNo ratings yet
- I. Review of Systems System/ Organ Subjective Cues AnalysisDocument1 pageI. Review of Systems System/ Organ Subjective Cues AnalysisZmiaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZmiaNo ratings yet
- Ncp. HyperDocument2 pagesNcp. HyperZmiaNo ratings yet
- DRUGDocument2 pagesDRUGZmiaNo ratings yet
- Iv. Gordon'S Functional Health Pattern Table 1: Gordon's Functional Health Pattern in Patient WithDocument6 pagesIv. Gordon'S Functional Health Pattern Table 1: Gordon's Functional Health Pattern in Patient WithZmiaNo ratings yet
- Rift Valley Water Supply and Sanitation ProjectDocument59 pagesRift Valley Water Supply and Sanitation ProjectcherogonyaNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesQuestionnaireIan AtienzaNo ratings yet
- BS BuzzDocument8 pagesBS BuzzBS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"No ratings yet
- Artikel 3Document23 pagesArtikel 3Hadian UwuoNo ratings yet
- Perceived Stress and Coping Levels of College Students During PandemicDocument10 pagesPerceived Stress and Coping Levels of College Students During PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Endodontic TopicsDocument16 pagesEndodontic TopicsSandra RamirezNo ratings yet
- 158611132743426Document19 pages158611132743426akel aliNo ratings yet
- Thip - Media-Create Your Ayushman Bharat Health Account ABHA Health IDDocument8 pagesThip - Media-Create Your Ayushman Bharat Health Account ABHA Health IDshivanithip.mediaNo ratings yet
- Out Of: Corvinus Language Examination Centre English Language Test Language Competence Level B2 - PróbavizsgaDocument2 pagesOut Of: Corvinus Language Examination Centre English Language Test Language Competence Level B2 - PróbavizsgaEbbes LiangNo ratings yet
- Worksheets - Isbar Week 4 x2Document3 pagesWorksheets - Isbar Week 4 x2api-631170779No ratings yet
- National Security Threats in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageNational Security Threats in The PhilippinesJonahweine BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Petrofac: Job Safety Analysis / Risk AssessmentDocument7 pagesPetrofac: Job Safety Analysis / Risk AssessmentazerNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Colorectal CancerDocument4 pagesCase Analysis Colorectal CancerKhie-An Ocampo0% (1)
- 108下牙周期末Document10 pages108下牙周期末新手冒險家No ratings yet
- Where The Sun Never SetsDocument151 pagesWhere The Sun Never SetsBumpadikaNo ratings yet
- Essay 2 Gabi A Girl in Pieces 1Document7 pagesEssay 2 Gabi A Girl in Pieces 1api-709176884No ratings yet
- Society For Maternal-Fetal Medicine Consult Series #52: Diagnosis and Management of Fetal Growth RestrictionDocument16 pagesSociety For Maternal-Fetal Medicine Consult Series #52: Diagnosis and Management of Fetal Growth RestrictionRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- Icu Journal ClubDocument4 pagesIcu Journal Clubapi-610938913No ratings yet
- Pro6 Infotext: Hotline Numbers: Smart 0949 883 3741 0921 939 3004 Globe 0917 594 3753Document2 pagesPro6 Infotext: Hotline Numbers: Smart 0949 883 3741 0921 939 3004 Globe 0917 594 3753Deo Quimpo QuinicioNo ratings yet
- Review Paper: The Concept of Self-Esteem in Nursing Education and Its Impact On Professional BehaviourDocument6 pagesReview Paper: The Concept of Self-Esteem in Nursing Education and Its Impact On Professional BehaviourDewiNo ratings yet
- Section 84Document5 pagesSection 84Mahi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Penyimpanan Obat - Anjar Putri W - 24185650aDocument49 pagesPenyimpanan Obat - Anjar Putri W - 24185650aGista Andita100% (2)
- Waste Not Want Not (Tests & Exams)Document15 pagesWaste Not Want Not (Tests & Exams)sara wilson100% (3)
- Gmail - FWD - ORDER CONFIRMED - Dental Plaster Algin..Document3 pagesGmail - FWD - ORDER CONFIRMED - Dental Plaster Algin..Yander Luis Hernández ArmasNo ratings yet
- Conservative Technique For Restoration of Anterior Teeth: Clinical Case ReportDocument6 pagesConservative Technique For Restoration of Anterior Teeth: Clinical Case ReportNonoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2. Protocol and Amenities in The Uniformed Service - 104604Document2 pagesTOPIC 2. Protocol and Amenities in The Uniformed Service - 104604Khalvinclyde BernabeNo ratings yet
- CP05-03-MMC-MST-ELE-0027 REV.00 Testing & Commissioning For Emergency Lighting SystemDocument35 pagesCP05-03-MMC-MST-ELE-0027 REV.00 Testing & Commissioning For Emergency Lighting SystemMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet