Professional Documents
Culture Documents
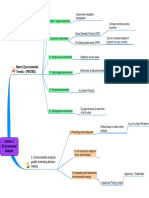
Strategic Planning 6b
Strategic Planning 6b
Uploaded by
Baher WilliamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Strategic Planning 6b
Strategic Planning 6b
Uploaded by
Baher WilliamCopyright:
Available Formats
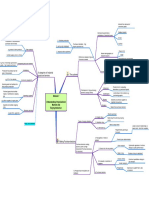
Similar to ETOP
Research
Never permanent
Development
Continously eroded by competitors based upon internal factors -
Competitive advantage SAP - Strategic Advantage Profile rankedOpportunities and Threaths for each production
Temporary advantage
technology & IT Module 6 B marketing
erodes faster & faster
finance
Avoid conflict
constant % of sales / cost? value chain connection
Misallocation of resources
How much to spend
High R cost Low D cost economies of scale
Spill-over effect sunk cost
Big joint production in R & D
problem of resource allocation barries to entry
Research and Innovation Result is prototype Strategic assets legislation
Which criteria for id pot product experience effects
Ideas come sporadic & unpredictable market position
Must consider opp.cost of R&I expenditure Sustainable?
reputation
Definition of Competitive architecture
measure Research expend.
advantage Distinctive capabilities Internal strength
Past R expend Core competence
Innovation
% of sales / cost expend Indicative factors of Research expend
Spill over effects
architecture
power base causal ambiguity
core competence
Awareness of R & I critical for success Protection
will imitation work?
uncertain imitability
CTO - max quality
CFO. - limit budget
employees
Internal
CMO - get product to market
CEO - Alt use of resources Strategic architecture Unique
suppliers/customer
group objetives differ relational contracts with: External
last $ on dev < last on profit
marginal analysis
can marginal benefit be estimated? related activities
networks
Communicate & compromise
ID factors
Sensitivity analysis
NPV, Risk & uncertainity etc. Potential access to markets
Screening ID core through test contribution to perceived customer benefit
Incentives
1. Invention Development Short time when difficult to imitate
product from prototype rare max 5/6 per compay
potential 2. Prototype core competence lead to core products
Core competence goals, culture, org design
priority Competence systems
protection
3. Patent
good routines
Innovation process 3 levels Distinctive capabilities
expense Internal analysis R & I & D
4. Development
Mngt & comp advantage Core output
resources
competitor reaction
market share
Positioning pool of experience, knowledge & systems
5. Launch
Each stage managed effective Link
between stage must be effective ID likely benefits
Where is synergy effect
Questions
Must produce at competitive cost Little emperical evidence Wishful thinking What evidence exist
One period ahead
Hiring / firing cost Corp mngt.
Reactive Synergy
learning lost Economies of scale
vertical integration
PLC Resource management Components
2 approaches Capacity utilisation
prod launch periods
Joint production
select planning horizon Proactive
Innovative stimulus
dev resource plan
implications for marketing strategy
lack of positive evidence
mngt risk?
Power culture minimize risk
Role culture Diversification value destruction?
Incentives economies of scope
task culture HRM
personal culture add value through parenting
Culture problem - principal/ agent problem? synergy
economies of scale in-bound logistics
benefits
merket dicipline operations
primary activities out-bound logistics
different priorities Buy?
marketing & sales
Information leakages Costs
service
transaction cost
procurement
avoid paying the cost Vertical integration
Value chain analysis tech. development
avoid paying profit margin Incorrect arguments! support activities
HRM
avoid high prices - peak demand
make? mngt. systems
more powerful structure
value to the ultimate user
balance competitive & cooperative Correct arguments
Incentive to get things right unique to company
formidable principal/agent problem maybe in the linkage
ID comp advantage sustainable comp advantage
Strength / Weakness in comp setting
Mod 6b.mmap - 30/11/2011 - - - prepared by Carl Olav Staff / Rune Fjellvang
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- SAP Functional SpecificationDocument33 pagesSAP Functional SpecificationShams Tabrez40% (5)
- Defense Acquisition Life Cycle Wall Chart v1.3Document2 pagesDefense Acquisition Life Cycle Wall Chart v1.3joe TNo ratings yet
- Segregation of Duties Matrix SampleDocument3 pagesSegregation of Duties Matrix SampleNijith p.nNo ratings yet
- Using BPM For Agility in A Globalized WorldDocument6 pagesUsing BPM For Agility in A Globalized WorldWonderware Skelta BPM100% (1)
- Mindmap High Tech Supply Chain 4.0Document1 pageMindmap High Tech Supply Chain 4.0Juliana Castañeda Jimenez67% (3)
- Cost Control Techniques in Construction ProjectsDocument14 pagesCost Control Techniques in Construction ProjectsannisaedrianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 8 Testing of HypothesisDocument51 pagesLecture Notes 8 Testing of HypothesisFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- SWOT-Analyse ISO /TS 16949:2009Document1 pageSWOT-Analyse ISO /TS 16949:2009Nedra DebbechNo ratings yet
- 20.COBIT5 For Assurance LaminateDocument2 pages20.COBIT5 For Assurance LaminateLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Design of Goods and Services OpmDocument1 pageChapter 5 Design of Goods and Services Opmnurfarhana6789No ratings yet
- Value-Map TM DeloitteDocument1 pageValue-Map TM DeloitteHugo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Data 11052022Document1 pageData 11052022aljarrahcs2431No ratings yet
- Lean Management: Business ExcellenceDocument68 pagesLean Management: Business Excellencesharma301100% (4)
- Defense Acquisition Life Cycle Compliance Baseline (Pre-Tailoring)Document2 pagesDefense Acquisition Life Cycle Compliance Baseline (Pre-Tailoring)Chit Win MaungNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 The Firm and Its Customers - The EconomyDocument1 pageUnit 7 The Firm and Its Customers - The EconomyOğuzhan IzgiNo ratings yet
- All FrameworksDocument1 pageAll FrameworksArnav RoyNo ratings yet
- Project Concept / Business Proposal / Business Case Fund Authorization Letter Project Definition and PlanningDocument1 pageProject Concept / Business Proposal / Business Case Fund Authorization Letter Project Definition and Planningvivekcp87No ratings yet
- Lecture-15 Enterprise ArchitectureDocument14 pagesLecture-15 Enterprise ArchitectureAdnan aslamNo ratings yet
- Delloite Operator Value MapDocument1 pageDelloite Operator Value MapDiogo Pimenta Barreiros0% (1)
- Mindmap For Pharma Supply ChainsDocument1 pageMindmap For Pharma Supply ChainsNgoc PhamNo ratings yet
- The Voice of The Manufacturing Manager 2023Document41 pagesThe Voice of The Manufacturing Manager 2023gabriela alejandra leon blancoNo ratings yet
- JPM Earnings Momentum 2016-05-08Document32 pagesJPM Earnings Momentum 2016-05-08kmacculloughNo ratings yet
- Chaitra ResumeDocument1 pageChaitra ResumechaitrareddyNo ratings yet
- Wholesale Retail - Main PanelDocument1 pageWholesale Retail - Main PanelMuhammad Amri IdrisNo ratings yet
- Asset Disposal Form2Document2 pagesAsset Disposal Form2Evans MugaNo ratings yet
- No Place Left To SqueezeDocument8 pagesNo Place Left To SqueezedesikanNo ratings yet
- SID9Document1 pageSID9vermvivNo ratings yet
- SessionsDocument260 pagesSessionsAhmed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Tool Selector V2Document1 pageTool Selector V2Mohammed MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- FCJ Competency MapDocument2 pagesFCJ Competency MapNyoNo ratings yet
- Your Industry Challenges and How A Modern Can Help: Manufacturing Execution System (MES)Document1 pageYour Industry Challenges and How A Modern Can Help: Manufacturing Execution System (MES)ÆdzitØn EstradaNo ratings yet
- Mindmap For An Ethical Supply ChainDocument1 pageMindmap For An Ethical Supply ChainNgoc PhamNo ratings yet
- Dmaic 12873122766122 Phpapp01Document1 pageDmaic 12873122766122 Phpapp01quycoctuNo ratings yet
- General Budget Support: Policy Questions and Answers: Q10. What Is Good Practice in GBS Design and Implementation?Document6 pagesGeneral Budget Support: Policy Questions and Answers: Q10. What Is Good Practice in GBS Design and Implementation?ChremataNo ratings yet
- Huawei Technology Campus Network Solution BrochureDocument16 pagesHuawei Technology Campus Network Solution BrochureHailay WeldegebrielNo ratings yet
- LeanIX Poster EA Vs SA Vs TA ENDocument1 pageLeanIX Poster EA Vs SA Vs TA ENchetan2309No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Competency PDFDocument12 pagesEntrepreneurial Competency PDFShiela OchoaNo ratings yet
- Vishnu Dutt PMDocument2 pagesVishnu Dutt PMvishnu choudharyNo ratings yet
- Agiba Safety Workshop June 2019Document5 pagesAgiba Safety Workshop June 2019QHSE Manager100% (1)
- Classified 20240317 1Document3 pagesClassified 20240317 1makeencvNo ratings yet
- Value Stream Improvement Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesValue Stream Improvement Plan TemplatemilandivacNo ratings yet
- Micro businessDocument3 pagesMicro businessRehman Gaming FFNo ratings yet
- Estrategy EngDocument3 pagesEstrategy EngJoseph GaonaNo ratings yet
- QFD TesisDocument1 pageQFD TesisGabriel VazquezNo ratings yet
- Competence Format ExampleDocument10 pagesCompetence Format ExampleAbraham GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Embedded Project WorksheetDocument4 pagesEmbedded Project WorksheetcammanderNo ratings yet
- Offre de Places Mobilité 4A 2022-23Document1 pageOffre de Places Mobilité 4A 2022-23Valérie PaulusNo ratings yet
- Translating Customer Needs (QFD)Document33 pagesTranslating Customer Needs (QFD)PrashantNo ratings yet
- Investor Day: 13 October 2009Document134 pagesInvestor Day: 13 October 2009tilak52No ratings yet
- Auto Mechanic Assessment Package in UrduDocument29 pagesAuto Mechanic Assessment Package in UrduInfinity School of Engineering LahoreNo ratings yet
- Autos PoolDocument8 pagesAutos PoolPARASCADD Private LimitedNo ratings yet
- Organizational Analysis TemplateDocument8 pagesOrganizational Analysis TemplateLict ImranNo ratings yet
- S-Quot PT Koka Indonesia TBKDocument1 pageS-Quot PT Koka Indonesia TBKHans HendryanNo ratings yet
- Dmaic 12873122766122 Phpapp01Document1 pageDmaic 12873122766122 Phpapp01quycoctuNo ratings yet
- LIFE CYCLE INSTITUTE-Criticality AnalysisDocument1 pageLIFE CYCLE INSTITUTE-Criticality AnalysisJonathan Ferney CastroNo ratings yet
- Base Enterprise Value Map PDFDocument1 pageBase Enterprise Value Map PDFjvr001100% (1)
- List of C.P.D Programs Attended 2016 - 21 Category: Professional Engineer (P.e)Document63 pagesList of C.P.D Programs Attended 2016 - 21 Category: Professional Engineer (P.e)rohitNo ratings yet
- Ref JOUNAL SkilliZeeDocument12 pagesRef JOUNAL SkilliZeeRashi SharmaNo ratings yet
- (PREVIEW - ONLY) SH SCCCI Flyer - 20160815 - 4Document2 pages(PREVIEW - ONLY) SH SCCCI Flyer - 20160815 - 4me2 monkNo ratings yet
- Theranos Exercise OPSDocument1 pageTheranos Exercise OPSGummadi Banu PrakashNo ratings yet
- My Strategic Plan: Name of Film: Impact VisionDocument3 pagesMy Strategic Plan: Name of Film: Impact VisionRoyalNavNo ratings yet
- GMAT First Reading and SolutionDocument6 pagesGMAT First Reading and SolutionBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Jean-Baptiste de La Salle: Background StoryDocument3 pagesJean-Baptiste de La Salle: Background StoryBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Math Tests Part 2 Math Tests Part 1Document1 pageMath Tests Part 2 Math Tests Part 1Baher WilliamNo ratings yet
- CV TemplateDocument2 pagesCV TemplateBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Technology and ScienceDocument4 pagesTechnology and ScienceBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Function S 1 .1: (Math Level 1)Document5 pagesFunction S 1 .1: (Math Level 1)Baher WilliamNo ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument1 pageScheduleBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Module 2k PDFDocument1 pageModule 2k PDFBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Module 12k PDFDocument1 pageModule 12k PDFBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Macro Environmental Trends - (PESTED) : 2. Environmental Analyisis Guides Marketing Decison MakingDocument1 pageMacro Environmental Trends - (PESTED) : 2. Environmental Analyisis Guides Marketing Decison MakingBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- The Customer 6 Categories of Industrial Goods and Services: Understanding Organisational Markets and Buying BehaviourDocument1 pageThe Customer 6 Categories of Industrial Goods and Services: Understanding Organisational Markets and Buying BehaviourBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PDFDocument1 pageModule 4 PDFBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise 2 - Int Rates + Capl Budgeting - SolutionsDocument25 pagesRevision Exercise 2 - Int Rates + Capl Budgeting - SolutionsBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Option Pricing - Binomial - Black Scholes - How To Do It - UPDATEDDocument20 pagesModule 12 - Option Pricing - Binomial - Black Scholes - How To Do It - UPDATEDBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - 6 - Capital Budgeting - CF From Acs - APV - Leasing - EAC - International ProjectsDocument15 pagesModule 3 - 6 - Capital Budgeting - CF From Acs - APV - Leasing - EAC - International ProjectsBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Theories in Cyberloafing Studies: Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience September 2017Document4 pagesA Review of The Theories in Cyberloafing Studies: Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience September 2017Seh LahNo ratings yet
- Constant Selection Bi ReportingDocument10 pagesConstant Selection Bi ReportinggiacurbanoNo ratings yet
- The Little DeathDocument1 pageThe Little DeathkukutxiNo ratings yet
- A and H (Film Analysis)Document5 pagesA and H (Film Analysis)Jelly ManuelNo ratings yet
- Recommended New Books: The BeautyDocument1 pageRecommended New Books: The Beautymª josé pérezNo ratings yet
- Behind The File FestivalsDocument7 pagesBehind The File FestivalsSaruba BaienNo ratings yet
- BeckettDocument16 pagesBeckettVincenzo Di GioiaNo ratings yet
- The Reasons Why Family Is So Much Important in Our LifeDocument4 pagesThe Reasons Why Family Is So Much Important in Our LifeLara Jane DogoyNo ratings yet
- Meetings With Remarkable Men: Commentary by Terry Winter OwensDocument7 pagesMeetings With Remarkable Men: Commentary by Terry Winter OwensManjushree777No ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument19 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiNata NayottamaNo ratings yet
- English Grammer 19Document62 pagesEnglish Grammer 19Chandra Shekhar ChaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Post Tensioned SlabsDocument44 pagesPost Tensioned SlabsMaad Ahmed Al-Maroof100% (2)
- Top International Design 2011 PDFDocument4 pagesTop International Design 2011 PDFcesperon39No ratings yet
- AGINGDocument113 pagesAGINGmalathi kotaNo ratings yet
- Hamilton Howard "Albert" Fish: Early LifeDocument6 pagesHamilton Howard "Albert" Fish: Early LifeAngela DguezNo ratings yet
- Monday To Friday Except Wednesday For INNA (No Class) : Before SchoolDocument3 pagesMonday To Friday Except Wednesday For INNA (No Class) : Before SchoolJhullian Frederick Val VergaraNo ratings yet
- English Language and Linguistics Notes: RatingDocument1 pageEnglish Language and Linguistics Notes: RatingPrince Digital ComputersNo ratings yet
- Buying Behavior of Consumer For Sanitary ProductsDocument65 pagesBuying Behavior of Consumer For Sanitary ProductsfxvsfvNo ratings yet
- CMOSIC For Current-Mode PWM Power Supply: Hiroshi MaruyamaDocument6 pagesCMOSIC For Current-Mode PWM Power Supply: Hiroshi MaruyamaMalfo10No ratings yet
- CODY Et Al v. TYLER PLACE, INC. - Document No. 19Document2 pagesCODY Et Al v. TYLER PLACE, INC. - Document No. 19Justia.comNo ratings yet
- URBN288 Module 8Document4 pagesURBN288 Module 8Kemal AkbugaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Pop Culture and New Media: Memeology 101: Group 2Document7 pagesPhilippine Pop Culture and New Media: Memeology 101: Group 2Jacob HurstNo ratings yet
- n360 - WK 2 - Mini Care PlanDocument1 pagen360 - WK 2 - Mini Care Planapi-245887979No ratings yet
- Epictetus' Encheiridion and Epicurus's WritingsDocument5 pagesEpictetus' Encheiridion and Epicurus's WritingsAganooru VenkateswaruluNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StructureDocument47 pagesNuclear StructureJohnNo ratings yet
- SOALDocument7 pagesSOALMahar Catur FernizaNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis - Ako, Tipik Lamang Sa KagahaponDocument1 pageCritical Analysis - Ako, Tipik Lamang Sa KagahaponAq C YoyongNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 7.v1Document44 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 7.v1Sue Adames de VelascoNo ratings yet