Professional Documents
Culture Documents
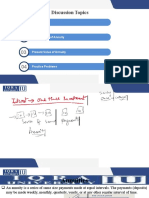
Simple Annuity
Simple Annuity
Uploaded by
Arden AnagapCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple Annuities PDFDocument12 pages2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple Annuities PDFKim Cinderell PestijoNo ratings yet
- Simple and General AnnuitiesDocument25 pagesSimple and General AnnuitiesJohn Mar CeaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 AnnuitiesDocument6 pages3.2 AnnuitiesAngela 18 PhotosNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - AnnuityDocument5 pagesUnit 4 - AnnuityShashank HundiaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Topics: AnnuitiesDocument15 pagesDiscussion Topics: AnnuitiesM. Amin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Annuities and MortgagesDocument15 pagesLecture 13 - Annuities and MortgagesM. Amin QureshiNo ratings yet
- gm11 Businessmath Annuity Part1withpetaDocument38 pagesgm11 Businessmath Annuity Part1withpetaEmer John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Annuity - Introduction Ordinary AnnuityDocument24 pagesAnnuity - Introduction Ordinary AnnuityThomasaquinos msigala JrNo ratings yet
- Annuities and Amortization: Classifications Formula Sample ProblemsDocument27 pagesAnnuities and Amortization: Classifications Formula Sample ProblemsMr.Clown 107No ratings yet
- Hand Out PPT For INSET DemoDocument14 pagesHand Out PPT For INSET DemoJeseryl VillosoNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Simple AnnuityDocument41 pagesModule 12 - Simple AnnuityColleen Mae San DiegoNo ratings yet
- Simple AnnuityDocument22 pagesSimple AnnuityAshley AniganNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledNgân Võ Trần TuyếtNo ratings yet
- Simple and General AnnuitiesDocument18 pagesSimple and General Annuitiesfrancistabotabo99No ratings yet
- AnnuitiesDocument12 pagesAnnuitiesNapoleon ChiongNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Math Mod 7Document18 pagesGrade 11 Math Mod 7John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- GENMATH - Simple and General AnnuitiesDocument2 pagesGENMATH - Simple and General AnnuitiesBern Balingit-Arnaiz100% (5)
- Module 7-8-AnnuityDocument19 pagesModule 7-8-AnnuityI am AngelllNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Investment SemisDocument2 pagesMathematics of Investment SemisLhance Angelo Magsino AbarraNo ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Simple-Annuity EDITEDDocument66 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Simple-Annuity EDITEDkcereban2021No ratings yet
- Simple AnnuityDocument12 pagesSimple Annuityprincessnylighte13No ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesTime Value of MoneyLatasha AdhiakriNo ratings yet
- Bond Market AnnuityDocument21 pagesBond Market Annuitytgtk8xgdx9No ratings yet
- FIN 438 Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesFIN 438 Practice ProblemstayyabNo ratings yet
- 05 03 04 Ann Sinkfund AmortDocument7 pages05 03 04 Ann Sinkfund AmortLöshini Priscilla EgbunikeNo ratings yet
- Module 7. Annuities: 1. Simple AnnuityDocument19 pagesModule 7. Annuities: 1. Simple AnnuityMori OugaiNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesDocument39 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesGeraldine Gementiza Poliquit85% (27)
- Genmath Q2 W3 4.1Document21 pagesGenmath Q2 W3 4.1Halloween NightNo ratings yet
- Moi L05 AnnuityDocument2 pagesMoi L05 AnnuityNyctos From MHMNo ratings yet
- 2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple AnnuitiesDocument12 pages2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple AnnuitiesKim Cinderell PestijoNo ratings yet
- AnnuitiesDocument20 pagesAnnuitiesGideon CayogNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesDocument40 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesBreanna CIel E. Cabahit100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - AnnuityDocument20 pagesLecture 3 - AnnuityReu Emmanuel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow OADocument11 pagesCash Flow OAadil khanNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Part IIDocument3 pagesTime Value of Money Part IINailiah MacakilingNo ratings yet
- Trabajo en Ingles 2Document4 pagesTrabajo en Ingles 2Claudia Velez GomezNo ratings yet
- ORDINARY ANNUITY - Future and Present ValueDocument33 pagesORDINARY ANNUITY - Future and Present ValueSALIM SHARIFUNo ratings yet
- Annuity, Sinking Fund, AmortizationDocument6 pagesAnnuity, Sinking Fund, AmortizationClydeLisboaNo ratings yet
- 15 AnnuitiesDocument28 pages15 AnnuitiesMahendra AvinashNo ratings yet
- Concept Check Quiz: First SessionDocument27 pagesConcept Check Quiz: First SessionMichael MillerNo ratings yet
- AnnuityDocument8 pagesAnnuityDiego Silvano J. BarrosNo ratings yet
- Discount, Denoted by D Which Is A Measure of Interest Where The Interest IsDocument3 pagesDiscount, Denoted by D Which Is A Measure of Interest Where The Interest IsNguyễn Quang TrườngNo ratings yet
- Simple Ordinary AnnuityDocument9 pagesSimple Ordinary AnnuityAngelo DonatoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Time Value and MoneyDocument2 pagesAssignment Time Value and MoneySaqib Mirza0% (1)
- Annuity Cash Flow Diagram Economic EquivalenceDocument76 pagesAnnuity Cash Flow Diagram Economic EquivalenceDarkie DrakieNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Marios MavridesDocument35 pagesTime Value of Money: Marios Mavridesandreas panayiotouNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 - Chapter 3Document8 pagesCalculus 2 - Chapter 3Silverwolf CerberusNo ratings yet
- AnnuityDocument40 pagesAnnuityREYNAN OMONGAYONNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Topic 4 - 3Document22 pagesGen Math Topic 4 - 3Jian Christian FerminNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics 2nd Quarter Week 3 TERESA A. TACIS NHC HS NewDocument11 pagesGeneral Mathematics 2nd Quarter Week 3 TERESA A. TACIS NHC HS NewjohnNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument34 pagesUntitledXoan DươngNo ratings yet
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument43 pagesSimple and Compound InterestAnne BergoniaNo ratings yet
- Gen-Math General Annuity ReportDocument17 pagesGen-Math General Annuity Reportayenjayalmonte7No ratings yet
- Lesson - 2 COMPOUND INTERESTDocument39 pagesLesson - 2 COMPOUND INTERESTMark LesterNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Future Value of AnnuitiesDocument3 pagesLesson 11 Future Value of AnnuitiesTheChallenge BoyNo ratings yet
- Simple Annuities (Revised)Document6 pagesSimple Annuities (Revised)Juliana CanonigoNo ratings yet
- Module in General Mathematics Grade 11 Second Quarter, Week 3 To Week 4Document39 pagesModule in General Mathematics Grade 11 Second Quarter, Week 3 To Week 4Hanseuuu100% (1)
- 2nd GR AnnuityDocument23 pages2nd GR AnnuityJAVELOSA, YUAN ALDRICH M.No ratings yet
- PL 1 - 6Document2 pagesPL 1 - 6Yaya Training DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Accounting Group Case IndofoodDocument15 pagesAccounting Group Case IndofoodNaufal FirdanNo ratings yet
- BOP Category Guide PDFDocument29 pagesBOP Category Guide PDFsimbamikeNo ratings yet
- BCM 2303 FM Unit 2 Chapter 1Document23 pagesBCM 2303 FM Unit 2 Chapter 1Priynah ValechhaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument7 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalancesknagarNo ratings yet
- BUSANA1 Chapter 3 (1) : Annuities With Simple DataDocument51 pagesBUSANA1 Chapter 3 (1) : Annuities With Simple Data7 bit100% (1)
- Account Statement From 1 Sep 2017 To 15 Jan 2018: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDocument7 pagesAccount Statement From 1 Sep 2017 To 15 Jan 2018: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit Balancevandv printsNo ratings yet
- QuestionaireDocument4 pagesQuestionaireanindya_kunduNo ratings yet
- SQE - Basic AccoDocument111 pagesSQE - Basic AccoCristinaNo ratings yet
- CE On Receivables T2 AY2021Document4 pagesCE On Receivables T2 AY2021Gian Carlo RamonesNo ratings yet
- Career Camp May22 Training AgreementDocument15 pagesCareer Camp May22 Training AgreementSudhanshu Shekhar SinglaNo ratings yet
- CIMA BA3 Study Text Fundamentals of Financial AccountingDocument19 pagesCIMA BA3 Study Text Fundamentals of Financial AccountingSwaraNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument10 pagesConstitutionapi-234193160No ratings yet
- Sources of Finance DefinitionDocument6 pagesSources of Finance Definitionpallavi4846100% (1)
- Solution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition MishkinDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition Mishkinmaitlandmohammedfx100% (13)
- Tokyo, Japan (April 11, 2014) - As Announced in A Release Dated April 7, 2014, Pursuant To ADocument9 pagesTokyo, Japan (April 11, 2014) - As Announced in A Release Dated April 7, 2014, Pursuant To AnarayanasamNo ratings yet
- School Finance and Business Administration SYLLABUSDocument9 pagesSchool Finance and Business Administration SYLLABUSnoreen fuentesNo ratings yet
- 1231 ISV ListDocument2 pages1231 ISV Listtest123No ratings yet
- 11.11.2017 Audit of PPEDocument9 pages11.11.2017 Audit of PPEPatOcampoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs in BusinessDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs in BusinessamitiansrcksNo ratings yet
- Shareholder Value Creation: An OverviewDocument5 pagesShareholder Value Creation: An OverviewggeettNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: Law of Investment.: Chanakya National Law University, PatnaDocument30 pagesSUBJECT: Law of Investment.: Chanakya National Law University, PatnaPammi ShergillNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer CAP II June 2018Document128 pagesSuggested Answer CAP II June 2018Pradeep Bhattarai67% (3)
- Assignment 1.1 International Monetary SystemDocument2 pagesAssignment 1.1 International Monetary SystemAnfernee Yu JecoNo ratings yet
- Fin ZC415 Ec-3r First Sem 2019-2020Document5 pagesFin ZC415 Ec-3r First Sem 2019-2020srideviNo ratings yet
- Asu 2019-04Document131 pagesAsu 2019-04janineNo ratings yet
- Competency Exam - Eeco2011Document1 pageCompetency Exam - Eeco2011WinsletJoyDauagNo ratings yet
- Fundcard: ICICI Prudential Value Discovery Fund - Direct PlanDocument4 pagesFundcard: ICICI Prudential Value Discovery Fund - Direct PlanHemant DujariNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting: Prepared by University of California, Santa BarbaraDocument69 pagesIntermediate Accounting: Prepared by University of California, Santa BarbaraHenry BarlowNo ratings yet
Simple Annuity
Simple Annuity
Uploaded by
Arden AnagapOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Annuity
Simple Annuity
Uploaded by
Arden AnagapCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Annuity
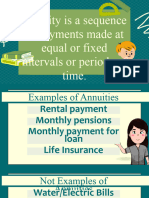
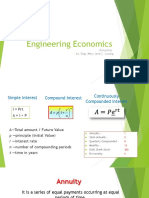
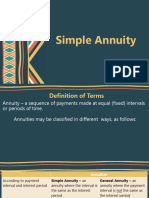
Annuity is a sequence of payments made at equal (fixed) intervals or periods of time. Annuities may be
classified in different ways, as follows:
Annuities
General Annuity is an annuity
Simple Annuity is an annuity
According to payment interval where the payment interval is the where the payment interval is
and interest period NOT the same as the interest
same as the interest period. period.
Ordinary Annuity (or Annuity Annuity Due is an annuity in which
Immediate) is an annuity in which the payments are made at the
According to time of payment the payments are made at the beginning of each payment
end of each payment interval. interval.
Contingent Annuity is an annuity
Annuity Certain is an annuity in in which the payments extend
According to duration which payments begin and end at over an indefinite (or
definite times. indeterminate) length of time.
Term of an annuity (t) is the time between the first payment interval and last payment interval.
Regular or Periodic payment (R) is the amount of each payment.
Amount (Future Value) of an annuity (F) is the sum of future values of all the payments to be made during
the entire term of the annuity.
Present value of an annuity (P) is the sum of present values of all the payments to be made during the entire
term of the annuity.
Sinking fund is any account that is established for accumulating funds to meet future obligations or debts.
Amortizing (mort means “death” you have “killed” the loan) a debt means that the debt is retired in a given
length of time by equal periodic payments that include compound interest.
Future Value of an Annuity
1. Suppose Joanna would like to save 3,000 pesos every month in a fund that gives 9% compounded monthly.
How much is the amount or future value of her savings after 6 months?
2. In order to save for her high school graduation, Missy decided to save 200 pesos at the end of each
month. If the bank pays 0.25% compounded monthly, how much will her money be at the end of 6 years?
3. Marie started to deposit 2,000 pesos quarterly in a fund that pays 5.5% compounded quarterly. How
much will be in the fund after 6 years?
4. Abigail would like to save 500,000 pesos for his son’s college education. How much should he deposit in a
savings account every 6 months for 12 years if interest is at 1% compounded semi-annually?
5. Find the future value F of the following ordinary annuities:
a. Monthly payments of 3,000 for 4 years with interest rate of 3% compounded monthly
b. Quarterly payment of 5,000 pesos for 10 years with interest rate of 2% compounded quarterly
c. Semi-annual payments of 12,500 pesos with interest rate of 10.5% compounded semi-annually for 6
years
d. Annual payments of 105,000 pesos with interest rate of 12% compounded annually for 5 years
e. Daily payments of 20 pesos for 30 days with interest rate of 20% compounded daily for 1 month
6. Suppose the parents of a newborn child decide that on each of the child’s birthdays up to the 17th year,
they will deposit in an account that pays 6% compounded annually. The money is to be used for college
expenses. What should the annual deposit be in order for the amount in the account to be 80,000 pesos
after the 17th deposit?
7. A company estimates that it will have to replace a piece of equipment at a cost of 800,000 pesos in 5
years. To have this money available in 5 years, a sinking fund is established by making equal monthly
payments into an account paying 6.6% compounded monthly. (a) How much should each payment be? (b)
How much interest is earned during the last year?
8. Amaia deposits 2,000 pesos annually into a retirement fund that earns 6.85% compounded annually. (The
interest earned by the retirement fund is tax free.) Due to a change in employment, these deposits stop
after 10 years, but the account continues to earn interest until Euler retires 25 years after the last
deposit was made. How much is in the account when Euler retires?
9. A person makes monthly deposits of 100 pesos into an ordinary annuity. After 30 years, the annuity is
worth 160,000 pesos. What annual rate compounded monthly has this annuity earned during this 30-year
period? Express the answer as a percentage, correct to two decimal places.
10. Alfonso started to deposit 18,000 pesos semi-annually in a fund that pays 5% compounded semi-annually.
How much will be in the fund after 10 years?
Present Value of an Annuity
1. How much should you deposit in an account paying 6% compounded semiannually in order to be able to
withdraw 1,000 pesos every 6 months for the next 3 years? (After the last payment is made, no money is
to be left in the account.)
2. What is the present value of an annuity that pays 200 pesos per month for 5 years if money is worth 6%
compounded monthly?
3. Solar Life offered an ordinary annuity that earned 6.5% compounded annually. A person plans to make
equal annual deposits into this account for 25 years and then make 20 equal annual withdrawals of
25,000 pesos, reducing the balance in the account to zero. How much must be deposited annually to
accumulate sufficient funds to provide for these payments? How much total interest is earned during
this entire 45-year process?
4. Assume that you buy a TV for 80,000 pesos and agree to pay for it in 18 equal monthly payments at 1.5%
interest per month on the unpaid balance. (a) How much are your payments? (b) How much interest will
you pay?
5. If you borrow 5,000 pesos that you agree to repay in six equal monthly payments at 1% interest per
month on the unpaid balance, how much of each monthly payment is used for interest and how much is
used to reduce the unpaid balance? (Amortization schedule)
6. A family purchased a home 10 years ago for 80,000 dollars. The home was financed by paying 20% down
and signing a 30-year mortgage at 9% on the unpaid balance. The net market value of the house (amount
received after subtracting all costs involved in selling the house) is now 120,000 dollars, and the family
wishes to sell the house. How much equity (to the nearest dollar) does the family have in the house now
after making 120 monthly payments? [Equity = (current net market value) – (unpaid balance).]
7. You have negotiated a price of 25,200 dollars for a new Tesla Model 3. Now you must choose between 0%
financing for 48 months or a 3,000-dollar rebate. If you choose the rebate, you can obtain a credit
union loan for the balance at 4.5% compounded monthly for 48 months. Which option should you choose?
8. Euler paid 200,000 pesos as down payment for a second hand Tesla Model S. The remaining amount is to
be settled by paying 16,200 pesos at the end of each month for 5 years. If interest is 10.5% compounded
monthly, what is the cash price of his car?
9. Gauss borrowed 100,000 pesos. He agrees to pay the principal plus interest by paying an equal amount of
money each year for 3 years. What should be his annual payment if interest is 8% compounded annually?
10. The buyer of a house and lot pays 200,000 pesos cash and 10,000 pesos every month for 20 years. If
money is 9% compounded monthly, how much is the cash value of the lot?
You might also like
- 2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple Annuities PDFDocument12 pages2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple Annuities PDFKim Cinderell PestijoNo ratings yet
- Simple and General AnnuitiesDocument25 pagesSimple and General AnnuitiesJohn Mar CeaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 AnnuitiesDocument6 pages3.2 AnnuitiesAngela 18 PhotosNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - AnnuityDocument5 pagesUnit 4 - AnnuityShashank HundiaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Topics: AnnuitiesDocument15 pagesDiscussion Topics: AnnuitiesM. Amin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Annuities and MortgagesDocument15 pagesLecture 13 - Annuities and MortgagesM. Amin QureshiNo ratings yet
- gm11 Businessmath Annuity Part1withpetaDocument38 pagesgm11 Businessmath Annuity Part1withpetaEmer John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Annuity - Introduction Ordinary AnnuityDocument24 pagesAnnuity - Introduction Ordinary AnnuityThomasaquinos msigala JrNo ratings yet
- Annuities and Amortization: Classifications Formula Sample ProblemsDocument27 pagesAnnuities and Amortization: Classifications Formula Sample ProblemsMr.Clown 107No ratings yet
- Hand Out PPT For INSET DemoDocument14 pagesHand Out PPT For INSET DemoJeseryl VillosoNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Simple AnnuityDocument41 pagesModule 12 - Simple AnnuityColleen Mae San DiegoNo ratings yet
- Simple AnnuityDocument22 pagesSimple AnnuityAshley AniganNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledNgân Võ Trần TuyếtNo ratings yet
- Simple and General AnnuitiesDocument18 pagesSimple and General Annuitiesfrancistabotabo99No ratings yet
- AnnuitiesDocument12 pagesAnnuitiesNapoleon ChiongNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Math Mod 7Document18 pagesGrade 11 Math Mod 7John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- GENMATH - Simple and General AnnuitiesDocument2 pagesGENMATH - Simple and General AnnuitiesBern Balingit-Arnaiz100% (5)
- Module 7-8-AnnuityDocument19 pagesModule 7-8-AnnuityI am AngelllNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Investment SemisDocument2 pagesMathematics of Investment SemisLhance Angelo Magsino AbarraNo ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Simple-Annuity EDITEDDocument66 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Simple-Annuity EDITEDkcereban2021No ratings yet
- Simple AnnuityDocument12 pagesSimple Annuityprincessnylighte13No ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesTime Value of MoneyLatasha AdhiakriNo ratings yet
- Bond Market AnnuityDocument21 pagesBond Market Annuitytgtk8xgdx9No ratings yet
- FIN 438 Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesFIN 438 Practice ProblemstayyabNo ratings yet
- 05 03 04 Ann Sinkfund AmortDocument7 pages05 03 04 Ann Sinkfund AmortLöshini Priscilla EgbunikeNo ratings yet
- Module 7. Annuities: 1. Simple AnnuityDocument19 pagesModule 7. Annuities: 1. Simple AnnuityMori OugaiNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesDocument39 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesGeraldine Gementiza Poliquit85% (27)
- Genmath Q2 W3 4.1Document21 pagesGenmath Q2 W3 4.1Halloween NightNo ratings yet
- Moi L05 AnnuityDocument2 pagesMoi L05 AnnuityNyctos From MHMNo ratings yet
- 2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple AnnuitiesDocument12 pages2Q - STEM - GenMath - LEC 07 - Simple AnnuitiesKim Cinderell PestijoNo ratings yet
- AnnuitiesDocument20 pagesAnnuitiesGideon CayogNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesDocument40 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 AnnuitiesBreanna CIel E. Cabahit100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - AnnuityDocument20 pagesLecture 3 - AnnuityReu Emmanuel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow OADocument11 pagesCash Flow OAadil khanNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Part IIDocument3 pagesTime Value of Money Part IINailiah MacakilingNo ratings yet
- Trabajo en Ingles 2Document4 pagesTrabajo en Ingles 2Claudia Velez GomezNo ratings yet
- ORDINARY ANNUITY - Future and Present ValueDocument33 pagesORDINARY ANNUITY - Future and Present ValueSALIM SHARIFUNo ratings yet
- Annuity, Sinking Fund, AmortizationDocument6 pagesAnnuity, Sinking Fund, AmortizationClydeLisboaNo ratings yet
- 15 AnnuitiesDocument28 pages15 AnnuitiesMahendra AvinashNo ratings yet
- Concept Check Quiz: First SessionDocument27 pagesConcept Check Quiz: First SessionMichael MillerNo ratings yet
- AnnuityDocument8 pagesAnnuityDiego Silvano J. BarrosNo ratings yet
- Discount, Denoted by D Which Is A Measure of Interest Where The Interest IsDocument3 pagesDiscount, Denoted by D Which Is A Measure of Interest Where The Interest IsNguyễn Quang TrườngNo ratings yet
- Simple Ordinary AnnuityDocument9 pagesSimple Ordinary AnnuityAngelo DonatoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Time Value and MoneyDocument2 pagesAssignment Time Value and MoneySaqib Mirza0% (1)
- Annuity Cash Flow Diagram Economic EquivalenceDocument76 pagesAnnuity Cash Flow Diagram Economic EquivalenceDarkie DrakieNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Marios MavridesDocument35 pagesTime Value of Money: Marios Mavridesandreas panayiotouNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 - Chapter 3Document8 pagesCalculus 2 - Chapter 3Silverwolf CerberusNo ratings yet
- AnnuityDocument40 pagesAnnuityREYNAN OMONGAYONNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Topic 4 - 3Document22 pagesGen Math Topic 4 - 3Jian Christian FerminNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics 2nd Quarter Week 3 TERESA A. TACIS NHC HS NewDocument11 pagesGeneral Mathematics 2nd Quarter Week 3 TERESA A. TACIS NHC HS NewjohnNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument34 pagesUntitledXoan DươngNo ratings yet
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument43 pagesSimple and Compound InterestAnne BergoniaNo ratings yet
- Gen-Math General Annuity ReportDocument17 pagesGen-Math General Annuity Reportayenjayalmonte7No ratings yet
- Lesson - 2 COMPOUND INTERESTDocument39 pagesLesson - 2 COMPOUND INTERESTMark LesterNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Future Value of AnnuitiesDocument3 pagesLesson 11 Future Value of AnnuitiesTheChallenge BoyNo ratings yet
- Simple Annuities (Revised)Document6 pagesSimple Annuities (Revised)Juliana CanonigoNo ratings yet
- Module in General Mathematics Grade 11 Second Quarter, Week 3 To Week 4Document39 pagesModule in General Mathematics Grade 11 Second Quarter, Week 3 To Week 4Hanseuuu100% (1)
- 2nd GR AnnuityDocument23 pages2nd GR AnnuityJAVELOSA, YUAN ALDRICH M.No ratings yet
- PL 1 - 6Document2 pagesPL 1 - 6Yaya Training DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Accounting Group Case IndofoodDocument15 pagesAccounting Group Case IndofoodNaufal FirdanNo ratings yet
- BOP Category Guide PDFDocument29 pagesBOP Category Guide PDFsimbamikeNo ratings yet
- BCM 2303 FM Unit 2 Chapter 1Document23 pagesBCM 2303 FM Unit 2 Chapter 1Priynah ValechhaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument7 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalancesknagarNo ratings yet
- BUSANA1 Chapter 3 (1) : Annuities With Simple DataDocument51 pagesBUSANA1 Chapter 3 (1) : Annuities With Simple Data7 bit100% (1)
- Account Statement From 1 Sep 2017 To 15 Jan 2018: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDocument7 pagesAccount Statement From 1 Sep 2017 To 15 Jan 2018: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit Balancevandv printsNo ratings yet
- QuestionaireDocument4 pagesQuestionaireanindya_kunduNo ratings yet
- SQE - Basic AccoDocument111 pagesSQE - Basic AccoCristinaNo ratings yet
- CE On Receivables T2 AY2021Document4 pagesCE On Receivables T2 AY2021Gian Carlo RamonesNo ratings yet
- Career Camp May22 Training AgreementDocument15 pagesCareer Camp May22 Training AgreementSudhanshu Shekhar SinglaNo ratings yet
- CIMA BA3 Study Text Fundamentals of Financial AccountingDocument19 pagesCIMA BA3 Study Text Fundamentals of Financial AccountingSwaraNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument10 pagesConstitutionapi-234193160No ratings yet
- Sources of Finance DefinitionDocument6 pagesSources of Finance Definitionpallavi4846100% (1)
- Solution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition MishkinDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition Mishkinmaitlandmohammedfx100% (13)
- Tokyo, Japan (April 11, 2014) - As Announced in A Release Dated April 7, 2014, Pursuant To ADocument9 pagesTokyo, Japan (April 11, 2014) - As Announced in A Release Dated April 7, 2014, Pursuant To AnarayanasamNo ratings yet
- School Finance and Business Administration SYLLABUSDocument9 pagesSchool Finance and Business Administration SYLLABUSnoreen fuentesNo ratings yet
- 1231 ISV ListDocument2 pages1231 ISV Listtest123No ratings yet
- 11.11.2017 Audit of PPEDocument9 pages11.11.2017 Audit of PPEPatOcampoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs in BusinessDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs in BusinessamitiansrcksNo ratings yet
- Shareholder Value Creation: An OverviewDocument5 pagesShareholder Value Creation: An OverviewggeettNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: Law of Investment.: Chanakya National Law University, PatnaDocument30 pagesSUBJECT: Law of Investment.: Chanakya National Law University, PatnaPammi ShergillNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer CAP II June 2018Document128 pagesSuggested Answer CAP II June 2018Pradeep Bhattarai67% (3)
- Assignment 1.1 International Monetary SystemDocument2 pagesAssignment 1.1 International Monetary SystemAnfernee Yu JecoNo ratings yet
- Fin ZC415 Ec-3r First Sem 2019-2020Document5 pagesFin ZC415 Ec-3r First Sem 2019-2020srideviNo ratings yet
- Asu 2019-04Document131 pagesAsu 2019-04janineNo ratings yet
- Competency Exam - Eeco2011Document1 pageCompetency Exam - Eeco2011WinsletJoyDauagNo ratings yet
- Fundcard: ICICI Prudential Value Discovery Fund - Direct PlanDocument4 pagesFundcard: ICICI Prudential Value Discovery Fund - Direct PlanHemant DujariNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting: Prepared by University of California, Santa BarbaraDocument69 pagesIntermediate Accounting: Prepared by University of California, Santa BarbaraHenry BarlowNo ratings yet