Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questions From DHA Exam
Questions From DHA Exam
Uploaded by
Mohsen Saeed OzaibiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Atlas of Orthodontics - ViazisDocument320 pagesAtlas of Orthodontics - ViazisAdil Houem100% (20)
- Viva MFD Book - Sample With Link To Full VersionDocument20 pagesViva MFD Book - Sample With Link To Full Versiongarima100% (1)
- All April 2018Document32 pagesAll April 2018ravi guptaNo ratings yet
- Open Bite MalocclusionDocument71 pagesOpen Bite MalocclusionMohsen Saeed Ozaibi100% (2)
- EAGLE LSAR Product GuideDocument26 pagesEAGLE LSAR Product Guidejaved iqbal0% (1)
- BBA1201 Principles of Marketing Open Book ExamDocument3 pagesBBA1201 Principles of Marketing Open Book Examraj chauhanNo ratings yet
- Questions From DHA ExamDocument3 pagesQuestions From DHA ExamMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- An Interview With Chris ChangDocument5 pagesAn Interview With Chris ChangDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- April 2011 Sydney Dental Hospital Theory RadiologyDocument8 pagesApril 2011 Sydney Dental Hospital Theory RadiologyMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Approaches in Endodontic PracticeFrom EverandMinimally Invasive Approaches in Endodontic PracticeGianluca PlotinoNo ratings yet
- Westmead July 2013 Viva Q SDocument5 pagesWestmead July 2013 Viva Q Ssoomro76134No ratings yet
- Day 2 Unicorn 1 1Document48 pagesDay 2 Unicorn 1 1Nancy NaeimNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument19 pagesFinal RevisionFree PizzaNo ratings yet
- Implant Supported Prosthetic Therapy of An Edentolous Patient Clinical and Technical Aspects-DikonversiDocument15 pagesImplant Supported Prosthetic Therapy of An Edentolous Patient Clinical and Technical Aspects-DikonversiLouis HutahaeanNo ratings yet
- Mds Oral Pathology Thesis TopicsDocument7 pagesMds Oral Pathology Thesis Topicsafkodkedr100% (2)
- Clubfoot 2004Document48 pagesClubfoot 2004Shah AazadNo ratings yet
- Sdle 19 PDFDocument11 pagesSdle 19 PDFQq qNo ratings yet
- Part 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesPart 2 Questionsaagam0% (1)
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning For Partially Edentulous PatientsDocument40 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment Planning For Partially Edentulous PatientsSankar Madhavan100% (1)
- Comparison of One Versus Multi Visit Tic TreatmentDocument47 pagesComparison of One Versus Multi Visit Tic TreatmentamitdrsNo ratings yet
- MFD OSCE Sample Papers With Link To Full VersionDocument14 pagesMFD OSCE Sample Papers With Link To Full VersiongarimaNo ratings yet
- Jced 12 E327Document8 pagesJced 12 E327Ezza RezzaNo ratings yet
- Experience With Inbde Corona RQDocument10 pagesExperience With Inbde Corona RQHajira AmjidNo ratings yet
- Moh Exam 2022 - DR KumkumaDocument5 pagesMoh Exam 2022 - DR KumkumaDarwin Nunez100% (1)
- Arroz Con Mango-My RQDocument84 pagesArroz Con Mango-My RQallyson100% (1)
- DentHypotheses7267-3698345 101623Document4 pagesDentHypotheses7267-3698345 101623Aliyah SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Original Article: AbstractDocument3 pagesOriginal Article: AbstractMarco Antonio MiraveteNo ratings yet
- Nbde IiDocument5 pagesNbde IisoyrubeNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Plastic Surgery To Improve AestheticsDocument7 pagesPeriodontal Plastic Surgery To Improve AestheticsElizabet KalmykovaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Office Report GutierrezDocument5 pagesPeriodontal Office Report Gutierrezapi-673363347No ratings yet
- MJDF John NabilDocument50 pagesMJDF John NabilAyesha Awan67% (3)
- Educate The Patient Then Go With The Patient To A Safe PlaceDocument30 pagesEducate The Patient Then Go With The Patient To A Safe PlaceghanimNo ratings yet
- MFD Part 2 Exam Held in JUST, Jordan On 12-2013Document2 pagesMFD Part 2 Exam Held in JUST, Jordan On 12-2013sohaib197No ratings yet
- Dental Education Department Comprehensive Clinical Dentistry - DDE620 Comprehensive Clinical DentistryDocument23 pagesDental Education Department Comprehensive Clinical Dentistry - DDE620 Comprehensive Clinical DentistrySnap18No ratings yet
- Otraas RQ MaovDocument34 pagesOtraas RQ MaovNancy NaeimNo ratings yet
- Turner P. Clinical Guide To Oral Implantology... 3ed 2018Document226 pagesTurner P. Clinical Guide To Oral Implantology... 3ed 2018Daniel EmilevNo ratings yet
- September 17-18 ?Document20 pagesSeptember 17-18 ?Qq q100% (1)
- A Case Report On Orthodontic Management of An Adolescent Cleft PatientDocument4 pagesA Case Report On Orthodontic Management of An Adolescent Cleft PatientMichelle WibiantoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis in EndodoticsDocument10 pagesDiagnosis in EndodoticsAhmed AbozaidNo ratings yet
- Hygiene Town ArticleDocument5 pagesHygiene Town Articlejatt_mu_phattNo ratings yet
- Iatrogenic Fracture of The Maxillary Tuberosity - A Case ReportDocument14 pagesIatrogenic Fracture of The Maxillary Tuberosity - A Case Reportplenilunio29No ratings yet
- Endodontology 4: RootsDocument44 pagesEndodontology 4: RootsCarlos San Martin100% (1)
- Evaluation Among Health Care Professionals and General Public On The Scope of Maxillofacial Surgery: Cross Sectional StudyDocument7 pagesEvaluation Among Health Care Professionals and General Public On The Scope of Maxillofacial Surgery: Cross Sectional StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ijoi Vol 33Document132 pagesIjoi Vol 33Chin-lungHsiehNo ratings yet
- Israeli State Exam For DentistryDocument75 pagesIsraeli State Exam For Dentistryشبيبةالروم الملكيين الكاثوليكNo ratings yet
- Lec01.clinical ExaminationDocument4 pagesLec01.clinical ExaminationLateef K Al-RubaeiNo ratings yet
- The Journey From The Past To The FutureDocument2 pagesThe Journey From The Past To The FutureplsssssNo ratings yet
- Westmead+2012+Nov DecemberDocument3 pagesWestmead+2012+Nov Decembersoomro76134No ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cutaneous Sinus Tract Associated With A Mandibular Second Molar Having A Rare Distolingual Root: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesOdontogenic Cutaneous Sinus Tract Associated With A Mandibular Second Molar Having A Rare Distolingual Root: A Case ReportMa NelNo ratings yet
- Esthetic DentistryDocument346 pagesEsthetic Dentistryreered100% (3)
- Gorucu Coskuner2017Document8 pagesGorucu Coskuner2017MairenNo ratings yet
- Revised 2017 RCT GuideDocument12 pagesRevised 2017 RCT GuideJubileelovekundalNo ratings yet
- Operative Cba 2Document3 pagesOperative Cba 2AsmaNo ratings yet
- Single Visit Vs Multiple Visit EndodonticsDocument47 pagesSingle Visit Vs Multiple Visit Endodonticspiece_of_mindzz1969No ratings yet
- BIODENTINEDocument5 pagesBIODENTINERiyoandaNo ratings yet
- Ortho Patient ContractDocument2 pagesOrtho Patient Contractaxle29No ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of The Maxillary Defect Secondary To Mucormycosis: A Case ReportDocument9 pagesProsthodontic Management of The Maxillary Defect Secondary To Mucormycosis: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- QatarDocument10 pagesQatarmidhunNo ratings yet
- Qatar PDFDocument10 pagesQatar PDFmidhun100% (1)
- 01 03 Endodontics - enDocument3 pages01 03 Endodontics - enamirmahdi82.s.fNo ratings yet
- Class NoteDocument25 pagesClass NoteHAMIDNo ratings yet
- Cystic Mass of The Floor of The MouthDocument4 pagesCystic Mass of The Floor of The MouthMARIA KARINA HERNANDEZ PEREZNo ratings yet
- 2015 Revision: Dubai Health Authority Exam For G. DentistsDocument99 pages2015 Revision: Dubai Health Authority Exam For G. DentistsMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shazzly - 2015 PDFDocument8 pagesDr. Shazzly - 2015 PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Prometric Exam Collection 2018: AuthorsDocument11 pagesPrometric Exam Collection 2018: AuthorsMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- 2014 Revision Questions - OziDent PDFDocument297 pages2014 Revision Questions - OziDent PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- April 2019: Dubai Health Authority (DHA) Questions ForDocument3 pagesApril 2019: Dubai Health Authority (DHA) Questions ForMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Questions From DHA ExamDocument3 pagesQuestions From DHA ExamMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Updated Prometic Dental Exam 2018: Important NoticesDocument51 pagesUpdated Prometic Dental Exam 2018: Important NoticesMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- 2014 Revision Answers - OziDent PDFDocument16 pages2014 Revision Answers - OziDent PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- 2000+ Prometric Questions PDFDocument254 pages2000+ Prometric Questions PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Tooling CatalogDocument20 pagesTooling CatalogAlisNo ratings yet
- Reform of Retirement Benefits in Sindh, PakistanDocument19 pagesReform of Retirement Benefits in Sindh, PakistanAsian Development BankNo ratings yet
- Vlookup Index Match - StudentsDocument17 pagesVlookup Index Match - StudentsRahul DudejaNo ratings yet
- Climographs 2Document11 pagesClimographs 2Thomas BookerNo ratings yet
- Esok RPHDocument1 pageEsok RPHAzira RoshanNo ratings yet
- Compliance RegisterDocument2 pagesCompliance RegisterDipjyoti SenNo ratings yet
- Ricoh MP2550 Parts CatalogDocument135 pagesRicoh MP2550 Parts Catalogmorganco1100% (1)
- Surveying Lab 2.0Document41 pagesSurveying Lab 2.0omay12No ratings yet
- Independent Contractor Agreement For Construction ContractorDocument8 pagesIndependent Contractor Agreement For Construction ContractorSheeraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Owners Manual Cayman PCNADocument284 pagesOwners Manual Cayman PCNASzigyarto Alex-MihaiNo ratings yet
- 2023-08-12Document5 pages2023-08-12nurull.samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Iota PDFDocument6 pagesIota PDFariniNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing TOS With ExamDocument2 pagesReading and Writing TOS With Examjoy grace jaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document16 pagesChapter 13Mussadaq JavedNo ratings yet
- Onals Oilfield - Official Offer Letter, Viacheslav OzerovDocument5 pagesOnals Oilfield - Official Offer Letter, Viacheslav OzerovВячеслав ОзеровNo ratings yet
- Welcome Unit - Basic - Aula 2 e Aula 3 e 4grammarDocument167 pagesWelcome Unit - Basic - Aula 2 e Aula 3 e 4grammarRayane VenceslauNo ratings yet
- Annotated Assigment 1 ECON1194B - Huynh Tuan Khai - s3926685 1Document5 pagesAnnotated Assigment 1 ECON1194B - Huynh Tuan Khai - s3926685 1Tue NgoNo ratings yet
- Getting To Grips With FDADocument84 pagesGetting To Grips With FDATanishq VashisthNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Attenuation DesignDocument3 pagesStormwater Attenuation DesignOscar vega guevaraNo ratings yet
- 7 - Serving Through FriendshipDocument12 pages7 - Serving Through FriendshipCarmen FielNo ratings yet
- Oem Ap471 - en PDocument2 pagesOem Ap471 - en PAnonymous iDJw3bDEW2No ratings yet
- OSCP Personal Cheatsheet: September 18Th, 2020 o o o oDocument76 pagesOSCP Personal Cheatsheet: September 18Th, 2020 o o o omahesh yadavNo ratings yet
- UA Fall 2017Document236 pagesUA Fall 2017Charles CearleyNo ratings yet
- A Commentary On The KulbhushanDocument53 pagesA Commentary On The KulbhushanVinayak GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0959652610001368 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0959652610001368 Mainducduy55No ratings yet
- Problems Based On Units and DimensionsDocument6 pagesProblems Based On Units and DimensionsApoorvNo ratings yet
- Li ReportDocument47 pagesLi ReportRizal RizalmanNo ratings yet
- How To Install MDMDocument9 pagesHow To Install MDMDomingo GarcíaNo ratings yet
Questions From DHA Exam
Questions From DHA Exam
Uploaded by
Mohsen Saeed OzaibiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Questions From DHA Exam
Questions From DHA Exam
Uploaded by
Mohsen Saeed OzaibiCopyright:
Available Formats
Follow us at instagram: @ozidents | Facebook: www.FB.
com/ozident | Twitter: @ozident
Questions from DHA Exam
23rd May 2017
Important Notice
It is important to understand that this list of questions are from Dr. Rasha, she took the exam and
had the courtesy and goodness to share the questions she remembered at the exam. These
questions are a reference to give a basic idea of how the exam questions are in nature.
The OziDent team took their time to orginse these questions in a way to show the question
nature and basic idea of the question.
Anything marked as yellow is a question that can’t be easily identified, we try our best but we are
still human in nature. We can’t guarantee success but we try to be the best possible choice to
help achieve success.
Special thanks to
Written Dr. Rasha
Edited by Dr. Mohsen
Please contact us for any correction or information at our email at
Mail@ozident.com or visit our website at www.ozident.com
The Questions
Impression: Reason Why Alginate impression Appears Chalky?
RCT: Reason that my lead to extrusion of Gutta Percha beyond the apex?
Lesions: Which White lesions when wiped off leave blood?
Pedo: When must a Child start brushing?
Restoration: Which metal restoration is most ductile and malleable?
Case: An old male patient with teeth mobility and shiny hands?
Case: An old female want to make new denture but had drooping of corners Of mouth and lip. How to
resolve this?
Minimal incisal liability to prevent crowdning
Radiology: Which kind of radiographic view shows TMJ morphology?
Histology: When trauma occurs at angle of mandible and cause numbness of lower lip ,which nerve is
injured?
Fluoride: Healthy and acceptable amount fluoride in water?
Visit us at www.ozident.com |Contact us at mail@ozident.com | All rights reserved 2017
Follow us at instagram: @ozidents | Facebook: www.FB.com/ozident | Twitter: @ozident
Fluoride: causes of fluorosis in children, amount of fluoride consumed by child.
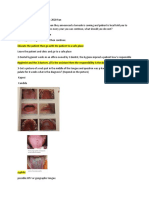
Lesions: Picture with white lesion on palate, patient has kidney transplant.
Restoration: Reverse bevel in class II amalgam restoration is what form convenient / retention/ ….
after injection of diazepam (iv) patient feels burning ,cause: large vein injection/ methyl in diazepam/
propylene glycol
Lesions: tumour with peri-neural invasion in parotid gland
Lesion: most common tumour in salivary glands?
Surgery: what are the flap designs during extraction of upper third molar to tearing of tissue.
Histology: Component does not exist in saliva is: ( potassium / proteolytic enzymes/ antibodies/ ……)
Prostho: which kind of ridge will resist lateral forces of the denture but not vertical?
Ortho: 1st and most important plane studied by orthodontist? (sagittal / anterio-posterior/ transverse).
RCT: vasoconstrictor in apicectomy is used fro?
Restoration : chisel is used to : ( carve enamel/ carve dentin/ smooth cavity walls)
Restoration given : 10-85-8 … , length of instrument is
RCT: Cutting 1mm of gutta cone size 31 , exact apex size is :
Lesion difference between chronic and acute abscess
maxillary growth
Hygiene: removal of sub-gingival calculus is by? (hoe/ curette/ sickle )
Ortho: easiest move in orthodontic? (tipping / intrusion/ bodily movement/..)
Restoration: matrix in class ii cavity extends in occlusal by
Restorations: best treatment with newly erupted second molar with discoloured dentin : ( sealant /
restoration/ no treatment..)
Restorations: old patient has smooth caries on proximal surface next to edentulous area , on xray
translucent confined to enamel , treatment :
Pedo: best management technique used with children?
RCT: Why is MTA best? Used?
Prostho : Old patient has lower edentulous area except for teeth 28/29, what kennedy classification?
Surgery: instruments used to grasp epulis: (addison / allis)
Hygiene: Uses of floss.
Medicine: diabetic patients we can find : (neutrophil / macrophages)
Lesion : a picture of large cyst around upper central and lateral, teeth with deep caries and pulp is
affected?
Lesion: a child has gingiva lesion over the tooth that appears white and surrounding tissue red?
RCT: fibre-optic transillumination in endo will show canal orifice in what color
RCT: reasons of failure after root canal treatment?
RCT: what kind obturation of canal we use for children.
Surgery: elevators parts : handle-shank-blade
single dose gic advantage over classic gic
Restorations: GIC as a restoration reduces caries?
RCT: root canal access cavity in lower molar is what form?
Restorations : For prevention we use with sealant? ( flowable composite)
RCT: patient feels pain with cold , what test we use?
RCT :if dentist fails to make diagnosis with all the test ( cold, hot..)he uses :
RCT: intrapuplpal anesthesia injection success
RCT: gutta percha constitution
luxation plus displacement of teeth and mobility and not aligned
Perio: acute pericoronitis management
Visit us at www.ozident.com |Contact us at mail@ozident.com | All rights reserved 2017
Follow us at instagram: @ozidents | Facebook: www.FB.com/ozident | Twitter: @ozident
Pedo: eruption pattern of crown and root
Prostho: maryland bridge is used with
Pedo: 5 year old patient lost his upper permanent central. What is treatment? managment?
Restorations: moderately deep caries with healthy gingiva : two visits restoration / one visit restoration
Prostho :wax used in dental clinic
Restorations: type of varnish applied only by dentist is ?
question about dentist finish procedure and removes gloves the write in patient file, he wants to
sterilize the instrument first thing to do : wears double gloves , put in ultrasonic, clean instruments…
question about draining abcess , where u put the debris of pus and blood
Case: Doctor had a pin point injury during treatment of a patient who is HBV positive. What is the
procedure that the doctor must do? ( if or if not taken the vaccine)
Restorations: which bur used for class V cavity preparation?
Pedo: child with avulsed permanent incisor before 45 minutes ,
Hygiene: most potent anesthetic is : cocaine- tetracaine…
Ortho: space between laterals and canines :
Surgery: mucoperiosteal flap disadvantage
Hygiene: material stays in oral cavity as antibacterial agent for long : chlohexidine/fluoride …
Restorations: about permanent deformation after stress on material: (ductility / malleability/ …..)
Hygiene: blade angle used in scaling
Prostho: old female with resorbed ridge and lingual projections what impression
Perio: periodontal involvement in furcation area.
Prostho: dental lab should correct mounting
Medicine: factor to predict the outcome of disease
Surgery: a picture with closed mouth and point in back what anaesthesia technique?
Surgery: tooth is pushed in maxillary sinus , what to do
Prostho: milling system in prostho is called
Restorations: when should composite filling be placed after bleaching?
Prostho : most retentive type of crown preparation : 3/4 – full metal – veneer
Implants: percentage of success of implant in new studies is
Perio: what are the fibres in coronal or cervical part of PDL? ( know the name of all PDL Fibers!)
RCT: pain in pulp is caused by what mechanism :free end nerve fibers
organic occlusion
Restorions: which approved instrument are used in detecting pit and fissure caries: (sharp probe – non
sharp probe - ….)
Medicine: most common congenital : cleft lip and palate
RCT: why when placing rubber dam for child , clamp makes gingiva red and swallowen , why
Pedo: incidence of fracture of centrals in children is found correlated with : weak enamel – weak dentin
protrusion of these teeth
Medicine: question about something affected by fracture of illiac bone
Restorations: caries are affected mostly by: (frequency-time-…)
RCT: lateral canals are found in what part of the tooth?
Prostho : patient with three units Fixed Partial Denture, you put air spray there is bubbles because is
Restoration: uses of temporary cement?
Surgery: what type of graft is used from same person?
Medicine: questions related hyperapnea.
Ortho: which type of orthodontic force should be used with PDL disease.
Visit us at www.ozident.com |Contact us at mail@ozident.com | All rights reserved 2017
You might also like
- Atlas of Orthodontics - ViazisDocument320 pagesAtlas of Orthodontics - ViazisAdil Houem100% (20)
- Viva MFD Book - Sample With Link To Full VersionDocument20 pagesViva MFD Book - Sample With Link To Full Versiongarima100% (1)
- All April 2018Document32 pagesAll April 2018ravi guptaNo ratings yet
- Open Bite MalocclusionDocument71 pagesOpen Bite MalocclusionMohsen Saeed Ozaibi100% (2)
- EAGLE LSAR Product GuideDocument26 pagesEAGLE LSAR Product Guidejaved iqbal0% (1)
- BBA1201 Principles of Marketing Open Book ExamDocument3 pagesBBA1201 Principles of Marketing Open Book Examraj chauhanNo ratings yet
- Questions From DHA ExamDocument3 pagesQuestions From DHA ExamMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- An Interview With Chris ChangDocument5 pagesAn Interview With Chris ChangDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- April 2011 Sydney Dental Hospital Theory RadiologyDocument8 pagesApril 2011 Sydney Dental Hospital Theory RadiologyMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Approaches in Endodontic PracticeFrom EverandMinimally Invasive Approaches in Endodontic PracticeGianluca PlotinoNo ratings yet
- Westmead July 2013 Viva Q SDocument5 pagesWestmead July 2013 Viva Q Ssoomro76134No ratings yet
- Day 2 Unicorn 1 1Document48 pagesDay 2 Unicorn 1 1Nancy NaeimNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument19 pagesFinal RevisionFree PizzaNo ratings yet
- Implant Supported Prosthetic Therapy of An Edentolous Patient Clinical and Technical Aspects-DikonversiDocument15 pagesImplant Supported Prosthetic Therapy of An Edentolous Patient Clinical and Technical Aspects-DikonversiLouis HutahaeanNo ratings yet
- Mds Oral Pathology Thesis TopicsDocument7 pagesMds Oral Pathology Thesis Topicsafkodkedr100% (2)
- Clubfoot 2004Document48 pagesClubfoot 2004Shah AazadNo ratings yet
- Sdle 19 PDFDocument11 pagesSdle 19 PDFQq qNo ratings yet
- Part 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesPart 2 Questionsaagam0% (1)
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning For Partially Edentulous PatientsDocument40 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment Planning For Partially Edentulous PatientsSankar Madhavan100% (1)
- Comparison of One Versus Multi Visit Tic TreatmentDocument47 pagesComparison of One Versus Multi Visit Tic TreatmentamitdrsNo ratings yet
- MFD OSCE Sample Papers With Link To Full VersionDocument14 pagesMFD OSCE Sample Papers With Link To Full VersiongarimaNo ratings yet
- Jced 12 E327Document8 pagesJced 12 E327Ezza RezzaNo ratings yet
- Experience With Inbde Corona RQDocument10 pagesExperience With Inbde Corona RQHajira AmjidNo ratings yet
- Moh Exam 2022 - DR KumkumaDocument5 pagesMoh Exam 2022 - DR KumkumaDarwin Nunez100% (1)
- Arroz Con Mango-My RQDocument84 pagesArroz Con Mango-My RQallyson100% (1)
- DentHypotheses7267-3698345 101623Document4 pagesDentHypotheses7267-3698345 101623Aliyah SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Original Article: AbstractDocument3 pagesOriginal Article: AbstractMarco Antonio MiraveteNo ratings yet
- Nbde IiDocument5 pagesNbde IisoyrubeNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Plastic Surgery To Improve AestheticsDocument7 pagesPeriodontal Plastic Surgery To Improve AestheticsElizabet KalmykovaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Office Report GutierrezDocument5 pagesPeriodontal Office Report Gutierrezapi-673363347No ratings yet
- MJDF John NabilDocument50 pagesMJDF John NabilAyesha Awan67% (3)
- Educate The Patient Then Go With The Patient To A Safe PlaceDocument30 pagesEducate The Patient Then Go With The Patient To A Safe PlaceghanimNo ratings yet
- MFD Part 2 Exam Held in JUST, Jordan On 12-2013Document2 pagesMFD Part 2 Exam Held in JUST, Jordan On 12-2013sohaib197No ratings yet
- Dental Education Department Comprehensive Clinical Dentistry - DDE620 Comprehensive Clinical DentistryDocument23 pagesDental Education Department Comprehensive Clinical Dentistry - DDE620 Comprehensive Clinical DentistrySnap18No ratings yet
- Otraas RQ MaovDocument34 pagesOtraas RQ MaovNancy NaeimNo ratings yet
- Turner P. Clinical Guide To Oral Implantology... 3ed 2018Document226 pagesTurner P. Clinical Guide To Oral Implantology... 3ed 2018Daniel EmilevNo ratings yet
- September 17-18 ?Document20 pagesSeptember 17-18 ?Qq q100% (1)
- A Case Report On Orthodontic Management of An Adolescent Cleft PatientDocument4 pagesA Case Report On Orthodontic Management of An Adolescent Cleft PatientMichelle WibiantoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis in EndodoticsDocument10 pagesDiagnosis in EndodoticsAhmed AbozaidNo ratings yet
- Hygiene Town ArticleDocument5 pagesHygiene Town Articlejatt_mu_phattNo ratings yet
- Iatrogenic Fracture of The Maxillary Tuberosity - A Case ReportDocument14 pagesIatrogenic Fracture of The Maxillary Tuberosity - A Case Reportplenilunio29No ratings yet
- Endodontology 4: RootsDocument44 pagesEndodontology 4: RootsCarlos San Martin100% (1)
- Evaluation Among Health Care Professionals and General Public On The Scope of Maxillofacial Surgery: Cross Sectional StudyDocument7 pagesEvaluation Among Health Care Professionals and General Public On The Scope of Maxillofacial Surgery: Cross Sectional StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ijoi Vol 33Document132 pagesIjoi Vol 33Chin-lungHsiehNo ratings yet
- Israeli State Exam For DentistryDocument75 pagesIsraeli State Exam For Dentistryشبيبةالروم الملكيين الكاثوليكNo ratings yet
- Lec01.clinical ExaminationDocument4 pagesLec01.clinical ExaminationLateef K Al-RubaeiNo ratings yet
- The Journey From The Past To The FutureDocument2 pagesThe Journey From The Past To The FutureplsssssNo ratings yet
- Westmead+2012+Nov DecemberDocument3 pagesWestmead+2012+Nov Decembersoomro76134No ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cutaneous Sinus Tract Associated With A Mandibular Second Molar Having A Rare Distolingual Root: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesOdontogenic Cutaneous Sinus Tract Associated With A Mandibular Second Molar Having A Rare Distolingual Root: A Case ReportMa NelNo ratings yet
- Esthetic DentistryDocument346 pagesEsthetic Dentistryreered100% (3)
- Gorucu Coskuner2017Document8 pagesGorucu Coskuner2017MairenNo ratings yet
- Revised 2017 RCT GuideDocument12 pagesRevised 2017 RCT GuideJubileelovekundalNo ratings yet
- Operative Cba 2Document3 pagesOperative Cba 2AsmaNo ratings yet
- Single Visit Vs Multiple Visit EndodonticsDocument47 pagesSingle Visit Vs Multiple Visit Endodonticspiece_of_mindzz1969No ratings yet
- BIODENTINEDocument5 pagesBIODENTINERiyoandaNo ratings yet
- Ortho Patient ContractDocument2 pagesOrtho Patient Contractaxle29No ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of The Maxillary Defect Secondary To Mucormycosis: A Case ReportDocument9 pagesProsthodontic Management of The Maxillary Defect Secondary To Mucormycosis: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- QatarDocument10 pagesQatarmidhunNo ratings yet
- Qatar PDFDocument10 pagesQatar PDFmidhun100% (1)
- 01 03 Endodontics - enDocument3 pages01 03 Endodontics - enamirmahdi82.s.fNo ratings yet
- Class NoteDocument25 pagesClass NoteHAMIDNo ratings yet
- Cystic Mass of The Floor of The MouthDocument4 pagesCystic Mass of The Floor of The MouthMARIA KARINA HERNANDEZ PEREZNo ratings yet
- 2015 Revision: Dubai Health Authority Exam For G. DentistsDocument99 pages2015 Revision: Dubai Health Authority Exam For G. DentistsMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shazzly - 2015 PDFDocument8 pagesDr. Shazzly - 2015 PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Prometric Exam Collection 2018: AuthorsDocument11 pagesPrometric Exam Collection 2018: AuthorsMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- 2014 Revision Questions - OziDent PDFDocument297 pages2014 Revision Questions - OziDent PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- April 2019: Dubai Health Authority (DHA) Questions ForDocument3 pagesApril 2019: Dubai Health Authority (DHA) Questions ForMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Questions From DHA ExamDocument3 pagesQuestions From DHA ExamMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Updated Prometic Dental Exam 2018: Important NoticesDocument51 pagesUpdated Prometic Dental Exam 2018: Important NoticesMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- 2014 Revision Answers - OziDent PDFDocument16 pages2014 Revision Answers - OziDent PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- 2000+ Prometric Questions PDFDocument254 pages2000+ Prometric Questions PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Tooling CatalogDocument20 pagesTooling CatalogAlisNo ratings yet
- Reform of Retirement Benefits in Sindh, PakistanDocument19 pagesReform of Retirement Benefits in Sindh, PakistanAsian Development BankNo ratings yet
- Vlookup Index Match - StudentsDocument17 pagesVlookup Index Match - StudentsRahul DudejaNo ratings yet
- Climographs 2Document11 pagesClimographs 2Thomas BookerNo ratings yet
- Esok RPHDocument1 pageEsok RPHAzira RoshanNo ratings yet
- Compliance RegisterDocument2 pagesCompliance RegisterDipjyoti SenNo ratings yet
- Ricoh MP2550 Parts CatalogDocument135 pagesRicoh MP2550 Parts Catalogmorganco1100% (1)
- Surveying Lab 2.0Document41 pagesSurveying Lab 2.0omay12No ratings yet
- Independent Contractor Agreement For Construction ContractorDocument8 pagesIndependent Contractor Agreement For Construction ContractorSheeraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Owners Manual Cayman PCNADocument284 pagesOwners Manual Cayman PCNASzigyarto Alex-MihaiNo ratings yet
- 2023-08-12Document5 pages2023-08-12nurull.samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Iota PDFDocument6 pagesIota PDFariniNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing TOS With ExamDocument2 pagesReading and Writing TOS With Examjoy grace jaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document16 pagesChapter 13Mussadaq JavedNo ratings yet
- Onals Oilfield - Official Offer Letter, Viacheslav OzerovDocument5 pagesOnals Oilfield - Official Offer Letter, Viacheslav OzerovВячеслав ОзеровNo ratings yet
- Welcome Unit - Basic - Aula 2 e Aula 3 e 4grammarDocument167 pagesWelcome Unit - Basic - Aula 2 e Aula 3 e 4grammarRayane VenceslauNo ratings yet
- Annotated Assigment 1 ECON1194B - Huynh Tuan Khai - s3926685 1Document5 pagesAnnotated Assigment 1 ECON1194B - Huynh Tuan Khai - s3926685 1Tue NgoNo ratings yet
- Getting To Grips With FDADocument84 pagesGetting To Grips With FDATanishq VashisthNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Attenuation DesignDocument3 pagesStormwater Attenuation DesignOscar vega guevaraNo ratings yet
- 7 - Serving Through FriendshipDocument12 pages7 - Serving Through FriendshipCarmen FielNo ratings yet
- Oem Ap471 - en PDocument2 pagesOem Ap471 - en PAnonymous iDJw3bDEW2No ratings yet
- OSCP Personal Cheatsheet: September 18Th, 2020 o o o oDocument76 pagesOSCP Personal Cheatsheet: September 18Th, 2020 o o o omahesh yadavNo ratings yet
- UA Fall 2017Document236 pagesUA Fall 2017Charles CearleyNo ratings yet
- A Commentary On The KulbhushanDocument53 pagesA Commentary On The KulbhushanVinayak GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0959652610001368 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0959652610001368 Mainducduy55No ratings yet
- Problems Based On Units and DimensionsDocument6 pagesProblems Based On Units and DimensionsApoorvNo ratings yet
- Li ReportDocument47 pagesLi ReportRizal RizalmanNo ratings yet
- How To Install MDMDocument9 pagesHow To Install MDMDomingo GarcíaNo ratings yet