Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compositional or Structural Changes of The Extracellular Matrix
Compositional or Structural Changes of The Extracellular Matrix
Uploaded by
CT Johara MusorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compositional or Structural Changes of The Extracellular Matrix
Compositional or Structural Changes of The Extracellular Matrix
Uploaded by
CT Johara MusorCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
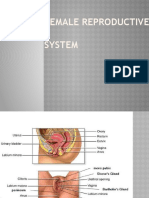
Labia Minora- lack of hair follicles, eccrine glands and apocrine glands
2. Clitoris- principal female erogenous organ
3. Sampson Artery- a branch of the uterine ligament- runs along the round ligament
4. Suspensory ligament/ infundibulopelvic ligament- peritoneum that extends beneath the fimbriated end of the fallopian tube
toward the pelvic wall
5. Parametrium- used to describe the connective tissues adjacent and lateral to the uterus within the broad ligament
6. The nulligravid uterus measure 6-8 cm in length compared with 9-10 cm in multiparas
7. Interstitial> isthmus>ampulla>infundibulum
8. Obstetrical conjugate
9. Gonadotropin releasing hormone- Hypothalamus
10. Progesterone- promote secretory changes in the uterine endometrium
11. Decidua basalis: maternal part of the placenta
12. Misoprostol- stomach ulcers
13. Stromal breakdown- menstrual phase
14. Oxytocin- highly dependent on estrogen
15. Misoprostol: prostaglandin E1
16. Cervical softening results from increased vascularity, stromal hypertrophy, glandular hypertrophy and slow, progressive
compositional or structural changes of the extracellular matrix
17. Maternal CRH levels are low in the first trimester and rise from midgestation to term
18. Strict definition of labor; uterine contractions that bring about demonstrable effacement and dilatation of the cervix
1. Vestibule- functionally mature female structure derived from the embryonic urogenital membrane
2. Broad Ligament- the anterior and posterior layers of pelvic
3. Average 20-45 days, may be short or long
4. Subnuclear vacuoles- secretory
5. During pregnancy, the levator ani usually undergoes hypertrophy, forming a thick band that extends backward from the pubis
and encircles the vagina about 2 cm above the plane of the hymen
6. Chorion Laeve is primarily protective and provides immunological acceptance
You might also like
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer-CompleteDocument66 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer-Completeposh003892% (39)
- Obstetric Nursing Review (NLE)Document48 pagesObstetric Nursing Review (NLE)'jmark Francia100% (4)
- Maternity Nursing EditedDocument54 pagesMaternity Nursing EditedAngelica Fontanilla Bajo RN75% (4)
- Obstetrics - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesObstetrics - Anatomy & PhysiologyDexter Lendio0% (1)
- Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument6 pagesOperative Vaginal DeliveryCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- OB NormalsDocument14 pagesOB NormalsLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- Review of The Reproductive System 4Document44 pagesReview of The Reproductive System 4Shermaigne Ananayo BuyaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer CompleteDocument40 pages2013 Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer CompleteHarley Justiniani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Reproductive AnatomyDocument10 pagesReproductive AnatomyjuhlynNo ratings yet
- Female GenitaliavDocument39 pagesFemale GenitaliavKathlyn PactorananNo ratings yet
- Maternity NursingDocument43 pagesMaternity NursingLyka Milo AvilaNo ratings yet
- MCN 03 Reproductive System-Menstrual CycleDocument37 pagesMCN 03 Reproductive System-Menstrual CycleBardiaga JmayNo ratings yet
- Maternity NursingDocument10 pagesMaternity NursingJustine Jake L. Ella100% (7)
- Maternal Ob NotesDocument37 pagesMaternal Ob NotesO.r. CadzNo ratings yet
- 1c ReproductiveOrgansDocument4 pages1c ReproductiveOrgansKenjie Palaganas CentenoNo ratings yet
- Maternal Ob NotesDocument103 pagesMaternal Ob NotesBoris OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ObstetricsDocument16 pagesReviewer in ObstetricsRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction.Document81 pagesHuman Reproduction.akulroy130507No ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing Lecture PresentationDocument69 pagesMaternity Nursing Lecture Presentationapi-3764215100% (8)
- Pretender PubisDocument28 pagesPretender Pubiskhaye_35100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1yunjung0518100% (7)
- I. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingDocument3 pagesI. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoNo ratings yet
- Maternal/Ob NotesDocument45 pagesMaternal/Ob NotesJoanne Christina Buenafe100% (1)
- Anaesthesia and Analgesia in Labour: Brett Johnson Vadewattie Ramnarine Anna Singh Gabrielle de Nobrega Bhavanie SinghDocument188 pagesAnaesthesia and Analgesia in Labour: Brett Johnson Vadewattie Ramnarine Anna Singh Gabrielle de Nobrega Bhavanie SinghRochelle BaileyNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System PDFDocument48 pagesFemale Reproductive System PDFTeppy the GreatNo ratings yet
- Ob Review To The MaxDocument40 pagesOb Review To The MaxMox SwanNo ratings yet
- Notes Maternal Health NursingdsdsDocument21 pagesNotes Maternal Health NursingdsdsL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Child Print 1-10Document11 pagesMaternity and Child Print 1-10ZYRHIL ANANONo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument36 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemcarolreynnNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesThe Male Reproductive Systemcoletealexis26No ratings yet
- 1-2 Female ReproductiveDocument9 pages1-2 Female ReproductivePauline SebastianNo ratings yet
- OB ReviewDocument257 pagesOB ReviewRosemaryCastro100% (1)
- Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: BY DR: AhmedDocument82 pagesReproductive Anatomy and Physiology: BY DR: AhmedAhmed ElryahNo ratings yet
- Quiz Histo LabDocument1 pageQuiz Histo Labhed-ajespirituNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF FEMALE InternalDocument49 pagesANATOMY OF FEMALE InternalJohaifha CompaniaNo ratings yet
- Female ReproductiveDocument55 pagesFemale ReproductiveDenise RegalaNo ratings yet
- Maternal NursingDocument37 pagesMaternal NursingCai Velasco DecenaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology FinalDocument20 pagesAnatomy and Physiology FinalShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument46 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing 2Document133 pagesMaternity Nursing 2Rick100% (1)
- Maternal Health Nursing Part 1Document193 pagesMaternal Health Nursing Part 1Nacel CelesteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemkukadiyaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument39 pagesGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- Bio NotesDocument180 pagesBio NotesjyotibhalaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Reproductive overvew.pptxDocument21 pages6 - Reproductive overvew.pptxjananithangaraj6624No ratings yet
- 23 - Development of Genital SystemDocument67 pages23 - Development of Genital SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Notes Maternal Health NursingDocument21 pagesNotes Maternal Health Nursingadrian ricañaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing: A.The Reproductive System 1. Male External Reproductive System A. PenisDocument36 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing: A.The Reproductive System 1. Male External Reproductive System A. PenisPachieNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemjonaNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing!Document138 pagesMaternity Nursing!cheenapberber100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- 50 Fun Facts About Sydney Opera HouseDocument3 pages50 Fun Facts About Sydney Opera HouseCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Organs and TissuesDocument3 pagesLymphatic Organs and TissuesCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa: DefinitionDocument4 pagesPlacenta Previa: DefinitionCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive DisordersDocument8 pagesHypertensive DisordersCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Antepartum Assessment of Fetal Well-Being: General Profile of Maternal HealthDocument7 pagesNon-Invasive Antepartum Assessment of Fetal Well-Being: General Profile of Maternal HealthCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Breech Delivery: Classification of Breech PresentationDocument1 pageBreech Delivery: Classification of Breech PresentationCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Dystocia Due To Abnormalities To Powers: Uterine DysfunctionDocument6 pagesDystocia Due To Abnormalities To Powers: Uterine DysfunctionCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet